Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanical Engineering Cams and Followers
Mechanical Engineering Cams and Followers
Uploaded by
Valentina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views22 pagesOriginal Title
New Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views22 pagesMechanical Engineering Cams and Followers
Mechanical Engineering Cams and Followers
Uploaded by
ValentinaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 22
Mechanical Engineering Cams and
Followers
University of Guyana
FET- MEC
Theory of Machines IV
MEC 3207
Lecturer: Mr. Vishal Persaud
GROUP MEMBERS
TROY ALFRED - 1037753
MOHAMMED BAKSH -1036007
LERON DAWSON- 1037478
NATHAN GANGADEEN - 1037895
SARAH GARRIDO- 1037080
ALEEM KHAN - 1040281
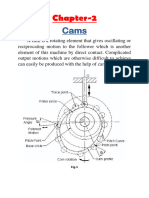
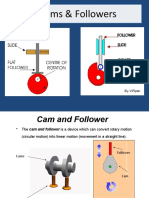
CAM & FOLLOWER
What is a CAM?
A cam is a notch- equipped tool used to convert
rotational motion into linear motion. They come in a
variety of sizes, styles, and materials. All of them are
made to transform rotational motion into linear
motion. The rotary motion of a part will press against
the cam, thus generating linear motion.
CAM & FOLLOWER
TYPES OF CAMS
1. Radial CAM
2. Cylindrical CAM
3. Wedge CAM
4. Conjugate CAM
5. Spherical CAM
Radial CAM
A flat plate or disc is carved and
is used as a cam to obtain the
required motion of the follower.
In this type, the motion of the
follower is perpendicular to the
axis of rotation of the cam.
CAM & FOLLOWER
Applications
Radial cams: These are commonly used in the IC engine to
control the opening and closing of the inlet and outlet valves.
Where the follower track (groove) on the radial cam causes
the follower to move linearly in and out as the cam rotates.
This linear motion can be used to rotate another object,
control the flow of materials, or trigger on-off mechanisms.
Cylindrical CAM
This cam is cylindrical in
shape, and there is a groove cut
on its surface. The follower
moves along the path of the
groove. In this type, the motion
of the follower is parallel to the axis of rotation of the
cam.
CAM & FOLLOWER
Applications
Cylindrical cams: A common application is in web
handling and tensioning systems, where a
cylindrical cam can be used to maintain constant
tension on a web of material as it feeds through a
machine, i.e. in sewing machines to guide thread,
packaging machines, pick and place machines, and
musical instruments.
Wedge CAM
The cam is in the shape of a
wedge and has a sliding
motion. The follower moves
up and down as the cam
moves to and from. Here the motion of the cam and
follower are perpendicular to each other.
CAM & FOLLOWER
Applications
Wedge cams: These are used for generating
quick on-off or switching actions. Wedge cams
are often used in machinery such as punch
presses and bottling machines, where they
control the actuation of valves or levers.
Conjugate CAM
Two rollers are connected to
the follower in this cam.
Both rollers restrict the motion
of each other, and this type
of cam is used primarily for noiseless operation.
CAM & FOLLOWER
Applications
Conjugate cams: Conjugate cams are used in
applications such as textile weaving looms and
robotics, where precise control over the
follower's motion is essential
Spherical CAM
The spherical cam are similar to
the cylindrical cam as it has a
groove cut in it, except here, the
cam is in the shape of a sphere.
CAM & FOLLOWER
Applications
Spherical cams: These are used to generate three-
dimensional motions for the follower. The spherical
shape of the cam allows the follower to move in any
direction relative to the cam center. Spherical cams
are less common than other types but can be found
in applications such as machine tool positioning
systems and gimbals
CAM & FOLLOWER
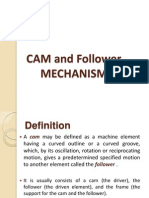
What is a Follower?
A cam follower, also called a track follower, roller
follower, or oscillating component of an assembly
follows the translating cam's motion by means of
direct contact and moves with respect to the cam's
axis to convert the reciprocating motions of the
cam into a linear motion.
CAM & FOLLOWER
TYPES OF FOLLOWERS
1. Knife Edge Follower
2. Roller Follower
3. Flat Faced Follower
4. Spherical Faced Follower
Knife Edge Follower
This follower has a pointed tip in
contact with the cam. The pointed
tip causes wear and tear in the
cam.
Roller Follower
To overcome the defect of knife-edge
followers, roller followers are used.
In this, a roller is attached to the tip of
the follower to make contact with the
cam. It reduces the friction as well as
wear and tear of the cam.
Flat- Faced Follower
This follower has a flat surface to
make contact with the cam. This
is used when a quick motion is
needed, but it develops a high
surface tension during
misalignment and deflection.
Spherical- Faced Follower
Spherical followers are used to
overcome the difficulty of
flat-faced followers. Here, the
contact area is spherical,
resulting in lesser wear and
tension.
Design Considerations
1. Follower Motion 4. CAM Speed
2. Follower Force 5. Manufacturing Cost
3. Friction and Wear 6. Accuracy and Repeatability
7. Safety
Thank You For Listening !
You might also like
- Sample Scoping ReportDocument92 pagesSample Scoping ReportEm Mar0% (1)
- 557-Assign 2-Action Plan For Culturally-Diverse School ClimateDocument10 pages557-Assign 2-Action Plan For Culturally-Diverse School Climateapi-566276833No ratings yet
- Cam and Follower: Definition, Types, Working Principle, and ApplicationsDocument17 pagesCam and Follower: Definition, Types, Working Principle, and Applicationsniaz kilamNo ratings yet
- Resource Related Billing 01Document10 pagesResource Related Billing 01Suresh Nayak100% (2)
- Cam and FollowerDocument38 pagesCam and Follower1blank100% (4)
- Introduction To CAMS:: Definition of CamDocument11 pagesIntroduction To CAMS:: Definition of CamSultan FuryNo ratings yet
- Binay-An ReportDocument4 pagesBinay-An Reportjohn.tubolNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowersDocument18 pagesCam and Followersnandkishore_singh100% (1)
- Mechanics of Machine Lab ReportDocument22 pagesMechanics of Machine Lab ReportFaisal MehrbanNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower PDFDocument17 pagesCam and Follower PDFKlucifer XinNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument17 pagesCam and Followerniaz kilamNo ratings yet
- Cam Gate Notes 761686837008983Document8 pagesCam Gate Notes 761686837008983Somu SinghNo ratings yet
- ME 7 - Activity 5Document5 pagesME 7 - Activity 5Rygen Faye Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower MechanismDocument44 pagesCam and Follower MechanismAkshay100% (1)
- Assignment 2 Eot .Document19 pagesAssignment 2 Eot .Nitin KumarNo ratings yet
- Cams & Followers: ME 323 / 321 D Machine Elements 2 Prepared By: A. RecachoDocument49 pagesCams & Followers: ME 323 / 321 D Machine Elements 2 Prepared By: A. RecachoMark Angelo Uy0% (1)
- Written Sa DymacDocument16 pagesWritten Sa DymacTrisha FernandezNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument6 pagesCam and FollowerMUHAMMAD UMAR KAMRANNo ratings yet
- Cam 1Document20 pagesCam 1rajroshansatapathyNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument13 pagesCam and FollowerJOHN LENNARD DATUINNo ratings yet
- Dom - CamDocument27 pagesDom - Camroshanbond001No ratings yet
- CamsDocument60 pagesCamsmaryamkhosroshahiNo ratings yet
- End Term EotDocument22 pagesEnd Term Eotishika SHANDILYANo ratings yet
- Classification of CAMS 1.uniform Velocity 2.simple Harmonic Motion 3.uniform Acceleration and RetardationDocument19 pagesClassification of CAMS 1.uniform Velocity 2.simple Harmonic Motion 3.uniform Acceleration and RetardationGuru MaheshNo ratings yet
- CAM and FollowerDocument13 pagesCAM and Followerpratik thakareNo ratings yet
- 16 CamsDocument26 pages16 CamsVinayak AryanNo ratings yet
- BY Daniel .HDocument49 pagesBY Daniel .Hdaniel hambissaNo ratings yet
- Cam MechanismDocument37 pagesCam MechanismZia Muhammad HaiderNo ratings yet
- Cam Jump Phenomenon-1Document10 pagesCam Jump Phenomenon-1Dhairyasheel Bhutkar100% (1)
- CamsDocument17 pagesCamsMohamed Abd ElmohsenNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Prof K N Wakchaure: A Frame Which Supports The Cam and Guides The FollowerDocument11 pagesPrepared By: Prof K N Wakchaure: A Frame Which Supports The Cam and Guides The Followerkiran_wakchaureNo ratings yet
- 02P - Group 3 - Lab 3 PDFDocument18 pages02P - Group 3 - Lab 3 PDFadidas tempoNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower - MET 261-3 Mechanics of MachinesDocument19 pagesCam and Follower - MET 261-3 Mechanics of MachinesAmazing ClipsNo ratings yet
- Cams Knitting TechnologyDocument19 pagesCams Knitting Technologyadeka199133% (3)
- Week 7 Lecture 3 SlidesDocument28 pagesWeek 7 Lecture 3 SlidesChander Prakash KamraNo ratings yet
- Cams in AutomationDocument18 pagesCams in AutomationSamridh VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter:-3 Cam and Cam ProfileDocument19 pagesChapter:-3 Cam and Cam ProfileParesh BhuvaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual ME 2409Document135 pagesLab Manual ME 2409Mohit lilhoreNo ratings yet
- Cams and FollowerDocument63 pagesCams and FollowerPawanNagdaNo ratings yet
- Cams and Followers Lecture - 2Document13 pagesCams and Followers Lecture - 2niaz kilamNo ratings yet
- CamshaftDocument5 pagesCamshaftPrabha KaranNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument12 pagesCam and FollowermalikNo ratings yet
- Unit No.4-Cam: Presented By-Jitendra BhatDocument12 pagesUnit No.4-Cam: Presented By-Jitendra BhatRohit GhulanavarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Cams: Cams With Different Follower MotionDocument76 pagesKinematics of Cams: Cams With Different Follower MotionMPee Finance SumerpurNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower: Presented By: Zain Ali Sami Ullah Majeed Samama Ijaz KhanDocument14 pagesCam and Follower: Presented By: Zain Ali Sami Ullah Majeed Samama Ijaz Khansamama khanNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower - pptx-1Document24 pagesCam and Follower - pptx-1Syam Raju50% (2)
- Cam Based Sand FilterDocument56 pagesCam Based Sand FilterANAND KRISHNAN100% (1)
- Cam and FollowerDocument16 pagesCam and FollowerDaniaNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Cylindrical Cam Shaper MachineDocument11 pagesFabrication of Cylindrical Cam Shaper MachineretechNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four MechanismDocument42 pagesChapter Four Mechanismmekete mulualemNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower Final NotesDocument18 pagesCam and Follower Final NotesSexy IdolNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower: Omar Ahmad Ali Ayman Mohammad Alkhwiter Eid Sunhat AlharbiDocument17 pagesCam and Follower: Omar Ahmad Ali Ayman Mohammad Alkhwiter Eid Sunhat AlharbiOmar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines-II: Course Instructor:Engr Ambreen TajammalDocument20 pagesMechanics of Machines-II: Course Instructor:Engr Ambreen TajammalSyed Saad GardaziNo ratings yet
- file:///C/Users/Lucas/Desktop/cam - TXT (5/7/2024 4:56:40 PM)Document1 pagefile:///C/Users/Lucas/Desktop/cam - TXT (5/7/2024 4:56:40 PM)kinglobstersignalsNo ratings yet
- CAMS TheoryDocument16 pagesCAMS TheorySurya RSNo ratings yet
- CAMSDocument35 pagesCAMSAnurag JenaNo ratings yet
- CamDocument30 pagesCamShangarab BeraNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Lab Procedure TheoryDocument10 pagesMachine Design Lab Procedure TheoryMuhammad Taufiq YusofNo ratings yet
- 1.1 A Simple Experiment: What Is A Cam?Document14 pages1.1 A Simple Experiment: What Is A Cam?Mohamed AwadNo ratings yet
- Dual Direction Gera MechanisumDocument61 pagesDual Direction Gera Mechanisumpaul_jaikumarm2753No ratings yet
- CamesDocument22 pagesCamesعبدالله عمرNo ratings yet
- How to Run a Lathe - Volume I (Edition 43) The Care and Operation of a Screw-Cutting LatheFrom EverandHow to Run a Lathe - Volume I (Edition 43) The Care and Operation of a Screw-Cutting LatheRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Sunken SlabDocument2 pagesSunken SlabAlexLionNo ratings yet
- Portarlington Parish NewsletterDocument2 pagesPortarlington Parish NewsletterJohn HayesNo ratings yet
- FSM 2000Document52 pagesFSM 2000aram_hNo ratings yet
- Final Trust ListDocument19 pagesFinal Trust Listnamdev bkNo ratings yet
- Data Collection MethodsDocument18 pagesData Collection MethodsachsurajNo ratings yet
- Experiments in Art and Technology A Brief History and Summary of Major Projects 1966 - 1998Document12 pagesExperiments in Art and Technology A Brief History and Summary of Major Projects 1966 - 1998mate maricNo ratings yet
- Envisci Revised FloodingDocument5 pagesEnvisci Revised Floodingrjosephine529No ratings yet
- Kci Fi001261149Document9 pagesKci Fi001261149minjokcsy99No ratings yet
- Primus Overview Catalogue ANGDocument8 pagesPrimus Overview Catalogue ANGpesumasinad0% (1)
- Game Sense ApproachDocument7 pagesGame Sense Approachapi-408626896No ratings yet
- Structural Analysis of Complex Networks 2011Document501 pagesStructural Analysis of Complex Networks 2011kemalihsan_17959No ratings yet
- Enhanced Employees Financial Assistance (Eefa) Form For JGSPC and JGSOC EmployeesDocument1 pageEnhanced Employees Financial Assistance (Eefa) Form For JGSPC and JGSOC EmployeesJ LaraNo ratings yet
- Present Etac Dep Psis PDFDocument96 pagesPresent Etac Dep Psis PDFRobiahZakariaNo ratings yet
- Community Forest 1Document20 pagesCommunity Forest 1Ananta ChaliseNo ratings yet
- 2003 Nissan Maxima NaviDocument167 pages2003 Nissan Maxima NaviMarco OchoaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals Sentence TransformationDocument3 pagesConditionals Sentence Transformationroxana kwiekNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth 4.2 SpecificationDocument2,772 pagesBluetooth 4.2 SpecificationScott PooleNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Single-Phase Diode RectifiersDocument32 pages7.2 Single-Phase Diode RectifiersTrương Anh DuyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 - 2020 PDFLusambo SimpasaNo ratings yet
- CT CalculationDocument2 pagesCT CalculationTheresia AndinaNo ratings yet
- Maranlig NHS Grade 11 Student's Enhanced Knowledge Skills Through Modular Learning2Document41 pagesMaranlig NHS Grade 11 Student's Enhanced Knowledge Skills Through Modular Learning2Uzziel Joy PondividaNo ratings yet
- Thin Film Composite Reverse Osmosis MembranesDocument42 pagesThin Film Composite Reverse Osmosis MembranesGunay Tekkale100% (1)
- Complete Guide For Growing Plants Hydroponically by J Benton Jones JR B00hznqitmDocument5 pagesComplete Guide For Growing Plants Hydroponically by J Benton Jones JR B00hznqitmnagesh dolasNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Design CHE 311 Final Project MSUDocument15 pagesHeat Exchanger Design CHE 311 Final Project MSUnefoussiNo ratings yet
- BVM L230Document156 pagesBVM L230JFrink333No ratings yet
- Kiosk Design & Construction CriteriaDocument33 pagesKiosk Design & Construction CriteriaAdson AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- 3.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST, PortFast, and BPDU GuardDocument9 pages3.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST, PortFast, and BPDU Guardsebastian ruiz100% (1)