Professional Documents
Culture Documents
555 Timer
555 Timer
Uploaded by
Nandhini G0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views19 pages555 timer
Original Title
555 TIMER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document555 timer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views19 pages555 Timer
555 Timer
Uploaded by
Nandhini G555 timer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
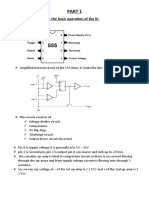
555 TIMER IC
BLOCK DIAGRAM, PIN DIAGRAM, OPERATIONS IN
ASTABLE AND MONOSTABLE MODE, APPLICATIONS
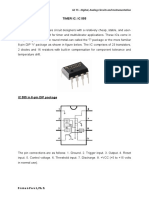
555 TIMER IC PIN DIAGRAM
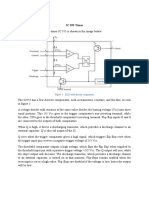
555 TIMER IC BLOCK DIAGRAM
BLOCKS
Voltage divider block
Comparator block
Flip flop block
Discharge block
Output block
BLOCKS
The block diagram of 555 timer IC showcases
number of blocks carrying of various
operations. The Voltage divider circuit plays a
crucial role in setting the reference voltage for
the comparators. The three resistors in the
voltage divider circuit are always equal.
Consider the comparator op-amp is ideal thus
no current flows through it. The reference
voltage of the two comparators can be
calculated as;
PINS
Depending upon the threshold and trigger pulse the comparators will provide either ‘0’ or ‘1’ as
the outputs. They are the inputs S and R to the SR flip flop. Thus depending upon the comparator
output the output of the IC is determined.
The reset pin in the flip flop block resets the flip flop when it is applied a logic ‘0’. So usually the
reset pin is connected to the supply voltage Vcc.
The control pin is connected to the inverting terminal of the first comparator which is useful to
change the timing of the output when voltage is applied.
The discharge pin consists of a transistor which helps in discharging the capacitor when the IC
output is low.
OPERATION
When the threshold voltage is greater than
the reference voltage(Vr1= 2/3Vcc), the
comparator 1 gives a +ve output whose logic
is 1.
Likely when the trigger is less than 1/3Vcc ,
the second comparator gives an output 1.
Depending upon the comparators’ output,
the system provides an output which is either
‘0’ or ‘1’
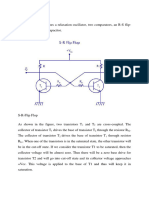
555 TIMER IN ASTABLE MODE
BLOCK DIAGRAM
GRAPH
DUTY CYCLE
Consider charging time as t1 and discharging time as t2. Hence,
t1 = 0.693(R1+R2)C;
t2 = 0.693(R2)C;
Hence the duty cycle is given by,
Duty cycle = t1/(t1+t2);
= (R1+R2)/(R1+2R2);
From the above equation, one can say that the duty cycle for astable mode is always >50%.
To get a 50% duty cycle we could simply eliminate the resistor R1. But by doing this the internal
transistor is directly exposed to the supply Vcc which may lead to damage. Another method is to
connect a diode D parallel to the resistor R2.
50% DUTY CYCLE
555 TIMER IN MONOSTABLE
MODE
BLOCK DIAGAM
GRAPH
APPLICATIONS
GENERATING TIME DELAY
FREQUENCY DIVISION
PULSE WIDTH MODULATION
You might also like
- Burglar Alarm ProjectDocument4 pagesBurglar Alarm ProjectAvik PathakNo ratings yet
- A Brief Description About The Basic Operation of The IC:: NE555 PinoutsDocument12 pagesA Brief Description About The Basic Operation of The IC:: NE555 PinoutsTanishq VarshneyNo ratings yet
- 3.1555 TIMER:: Schematic SymbolDocument10 pages3.1555 TIMER:: Schematic SymbolnagpradasNo ratings yet
- Astable Multivibrator Using 555 TimerDocument22 pagesAstable Multivibrator Using 555 TimerMaryam AsadNo ratings yet
- IC 555 Multivibrator CircuitsDocument11 pagesIC 555 Multivibrator CircuitsKaran YadavNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 ReportDocument12 pagesLab 3 ReportTanishq VarshneyNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer: by D.V.Kamat, Faculty Department of E&C Engg., MITDocument21 pages555 Timer: by D.V.Kamat, Faculty Department of E&C Engg., MITRupsa SahaNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer IC-Block Diagram-Working-Pin Out Configuration-Data SheetDocument13 pages555 Timer IC-Block Diagram-Working-Pin Out Configuration-Data SheetΔημητριος ΣταθηςNo ratings yet
- LIC Mod 2Document15 pagesLIC Mod 2Sona PrakashNo ratings yet
- Astable Multivibrator Using 555 TimerDocument12 pagesAstable Multivibrator Using 555 TimerΔημητριος ΣταθηςNo ratings yet
- The Important Features of The 555 Timer AreDocument7 pagesThe Important Features of The 555 Timer ArePathella SudhakarNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer Operation With Internal CircuitDocument9 pages555 Timer Operation With Internal Circuitjanakiram473No ratings yet
- SE/NE 555 Timer. It Is Basically A Monolithic Timing Circuit That Produces Accurate and Highly Stable Time Delays orDocument12 pagesSE/NE 555 Timer. It Is Basically A Monolithic Timing Circuit That Produces Accurate and Highly Stable Time Delays orEFraim Manzano FranciscoNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Special Ics The 555 Timer IcDocument10 pagesUNIT-4 Special Ics The 555 Timer IcVerloves LoveNo ratings yet
- Timer Ic: Ic 555: GE T5 - Digital, Analog Circuits and InstrumentationDocument5 pagesTimer Ic: Ic 555: GE T5 - Digital, Analog Circuits and InstrumentationFavourite MoviesNo ratings yet
- Lab#10: Design and Study of IC 555 Multivibrator Circuits (2 Turns)Document11 pagesLab#10: Design and Study of IC 555 Multivibrator Circuits (2 Turns)Ayushman ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Operational AmplifierDocument10 pagesOperational AmplifierSalman AliNo ratings yet
- Integratedelectronics (Unit2) 555 TIMER ASTABLE MONOSTABLE MVDocument5 pagesIntegratedelectronics (Unit2) 555 TIMER ASTABLE MONOSTABLE MVYogeshwaranNo ratings yet
- Multivibrator CircuitsDocument11 pagesMultivibrator CircuitsSatyaki ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 555 Timers Modi12Document21 pages555 Timers Modi12jewixe8466No ratings yet
- Tutorial Timmer 555Document9 pagesTutorial Timmer 555gabrielamedeletNo ratings yet
- Lab 10555 TimerDocument10 pagesLab 10555 Timermanaj_mohapatra2041No ratings yet
- ECEN4618: Experiment #1 Timing Circuits With The 555 TimerDocument9 pagesECEN4618: Experiment #1 Timing Circuits With The 555 TimerMashgol KarimNo ratings yet
- UtbsDocument41 pagesUtbsGaurav ChauhaanNo ratings yet
- 555 TimerDocument76 pages555 TimerSai Krishna KodaliNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer ExplainedDocument27 pages555 Timer ExplainedThe Lost WolfNo ratings yet
- IC 555 TimerDocument32 pagesIC 555 TimerAmaradi KondababuNo ratings yet
- ElectronicIII - L3Document14 pagesElectronicIII - L3Aya MazinNo ratings yet
- Multivibrador Com Ci 555Document11 pagesMultivibrador Com Ci 555joselito1juniorNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer PDFDocument76 pages555 Timer PDFronaldo19940% (1)
- Laboratory Experiment # 4 "An Introduction To The 555 Integrated Circuit Timer"Document26 pagesLaboratory Experiment # 4 "An Introduction To The 555 Integrated Circuit Timer"Moris MascariñasNo ratings yet
- Timer 555 - ManualDocument20 pagesTimer 555 - ManualXen XeonNo ratings yet
- List The Features of 555 TimersDocument3 pagesList The Features of 555 TimersDivyesh DivakarNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer Integrated CircuitDocument8 pages555 Timer Integrated CircuitTalha WaqarNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer TutorialDocument12 pages555 Timer Tutorialrowell ramosNo ratings yet
- Ae Exp 9 To Design Monostable Multivibrators Using 555 IcDocument6 pagesAe Exp 9 To Design Monostable Multivibrators Using 555 IcPriyanshu KumawatNo ratings yet
- LIC Unit IVDocument32 pagesLIC Unit IVDINESH KUMAR DRAVIDAMANINo ratings yet
- N555e Intergrated CircuitDocument6 pagesN555e Intergrated CircuitGeorge Boman SethNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer DesignDocument8 pages555 Timer DesignManuel BalasbasNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer IC: The Important Features of The 555 Timer AreDocument5 pages555 Timer IC: The Important Features of The 555 Timer AreChara GalaNo ratings yet
- Designing A Boost-Switching Regulator With The MCP1650Document0 pagesDesigning A Boost-Switching Regulator With The MCP1650Asad MalikNo ratings yet
- The 555 Timer: Monostable Bistable AstableDocument10 pagesThe 555 Timer: Monostable Bistable AstableSrikanth ThulluriNo ratings yet
- Practical Application of Timer ICDocument5 pagesPractical Application of Timer ICManojkumarNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer ICDocument20 pages555 Timer ICZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- 1 Ic 555Document6 pages1 Ic 555Harish PatilNo ratings yet
- 555 Integrated Circuit (Timer Operation)Document5 pages555 Integrated Circuit (Timer Operation)Geet SehgalNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer As MultivibratorDocument25 pages555 Timer As MultivibratorShrutJainNo ratings yet
- Lic Eec-501 Notes Unit5 Iftm UniversityDocument14 pagesLic Eec-501 Notes Unit5 Iftm UniversitySougata GhoshNo ratings yet
- Piano ReportDocument9 pagesPiano ReportMaryam TariqNo ratings yet
- Creation of A Piano Using A 555 Timer ICDocument9 pagesCreation of A Piano Using A 555 Timer ICPruthvi Trinath100% (1)
- Fire Leakage Indicator: Pin Name PurposeDocument7 pagesFire Leakage Indicator: Pin Name Purposethasarathanr1993_939No ratings yet
- IC 555 TimerDocument6 pagesIC 555 Timeraditya pandeyNo ratings yet
- Erii5 555 Timer Astable OperationDocument16 pagesErii5 555 Timer Astable OperationAnonymous VASS3z0wTHNo ratings yet
- 6.1 IC555 TIMER: Circuit ComponentsDocument8 pages6.1 IC555 TIMER: Circuit ComponentsManish PradhanNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer As Mono Stable Multi VibratorDocument29 pages555 Timer As Mono Stable Multi VibratorsrvdharNo ratings yet
- 555 IcDocument5 pages555 IcNabeel MuqarrabNo ratings yet
- 555 Oscillator TutorialDocument19 pages555 Oscillator TutorialHùng ĐoànNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer Monostable OperationDocument13 pages555 Timer Monostable OperationGrigore ManNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)