Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Food
Food
Uploaded by
rungarunchanyoung0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views32 pagesOriginal Title
1. FOOD
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views32 pagesFood
Food
Uploaded by
rungarunchanyoungCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 32
Classes of Food
☻Food is any substance that can be eaten or
drunk by human or animal for nutrition and
pleasure.
♣ Food is important for the following reasons:
It supplies energy.
It provides raw materials for growth and
repair of damaged tissues.
It keeps the organism healthy.
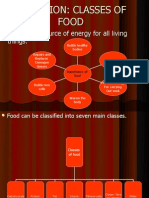
Classes of food
The 7 main classes of food are:
(1)Carbohydrates
(2) Proteins
(3) fats
(4) Vitamins
(5) Minerals
(6) Water
(7) Fiber
Classes of food
Carbohyd Fats and
protein oils Vitamin Mineral Water Fiber
-rate
Nutrients
Nutrients are substances in food that the body uses
uses :
- To provide energy
- For growth and repair
Diet is the food that you eat everyday.
A diet which provides all the different kinds of
nutrients in their correct amount is called a balance
diet.
If a person does not eat enough of a particular
nutrient, they may have a deficiency disease.
1. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrate is the most important source of energy.
Rice Corn Cassava Sweat potato
Carbohydrates can be sugar or starch.
They are made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Sugar provides quick energy. For example:
Grape sugar(glucose) Milk sugar(lactose) Cane sugar(sucrose) Malt sugar (maltose)
Carbohydrates : Sugar
Carbohydrates can be sugar or starch
1.1) Sugar gives the body quick energy . Some
examples are white sugar, brown sugar, honey,
candy and fruits.
Glucose is a simple molecule (monosaccharide).
Starch
1.2) Starch gives the body long lasting energy. Some
examples are potatoes, rice, noodles, bread, sweat
potatoes, barley and pasta.
Starch is a polysaccharide. It’s made up of many
glucose units.
2. Proteins
The main function of proteins is for growth and the repair of
damaged cells and tissues.
Protein is also used to make enzymes and antibodies in the
body.
Proteins contain amino acids which are made up of carbon,
hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.
Examples of protein foods are meat, poultry, seafood, beans
and peas, eggs, processed soy products etc
Excess protein is converted into glycogen and stored in the
liver.
3. Fats and Oils
Liquid fat is called oil. For example palm oil.
Fat provides energy.
It provides insulation when stored underneath the
skin.
It helps to make new cell membrane.
Palm oil pork butter
Energy
The energy value in food is measured in
kilojoules (kJ) or kilocalories (kcal).
Fats provide 9 calories per gram but
carbohydrates and protein each provide 4
calories per gram.
-Generally too much fat causes obesity.
Minerals
• Minerals help the body to grow and work well.
• Our body only needs small amounts of minerals
each day.
• Examples of minerals are calcium, chloride, iron,
iodine, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, sodium and
magnesium.
Minerals
Mineral Example of Function Deficiency disease
food
Calcium Diary products -formation of strong Rickets
bones and teeth.
Ca
Chloride Table salt -Produces HCl in the -Digestive
Cl- stomach. problems.
Iron Red meat - Formation of Anemia
Fe haemoglobion which
carries oxygen in the
blood
Extra Minerals
Example of food Function Deficiency disease
Mineral
Iodine Iodized salt -Controls body Goiter
I growth
Potassium Mushroom and normal functioning -Paralysis
K banana of the nerves
Sodium Table salt and sea normal functioning Nervous problems
Na fish. of the nerves.
Vitamins
• Vitamins help the body to stay healthy. There are
two main groups namely:
• Fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K)
• Water soluble vitamins (B-complex and vitamin C).
Vitamins
Vitamin Example of food Function Deficiency disease
A -Carrot For night vision Night blindness
B1 - Whole grains Healthy brain and Paralysis
nerves
-Fresh fruits Keeps skin, gums Scurvy (internal
C and bones healthy bleeding)
-Liver Formation of healthy Rickets
D -Formed in skin by teeth and bones
sunlight
Fiber
Fiber helps the body to remove wastes. Some
examples are vegetables, fruits, whole
grains(brown rice and wheat meal).
Fibers are cellulose which can not be digested.
Their function is to prevent hunger and control sugar
level in the body.
Food Tests (Aim: Test for starch)
1. Procedure:
-In test tube 1, grind the starchy food and cook it.
Add 2cm into a test tube and add some water.
In test tube 2, don’t add any food sample.
-Add a few drops of iodine solution to both test tubes
and observe.
2. Observation and interpretation: test tube 1 will
change to blue -black because of the presence of
starch.
Test tube 2 (control) will not change( have the colour
of iodine).
Extra Food Tests (Aim: Test for vitamins)
• Procedure: cook and grind starchy food. Put 2cm 3 of
food sample in test tube 1 and add some water. Pour
the vitamin food sample into test tube one. In test
tube 2, don’t add any food sample. Continually add
drops of iodine and observe for any color change.
• Observation and interpretation: The solution will
become almost colorless.
Food Tests (Aim: Test for Glucose)
1. Procedure: pour 2cm of glucose solution into a test
tube. Add 10 drops of benedicts solution, place the
test tube in a boiling bath and observe the color
change after about 10 minutes.
2. Observation and interpretation: the solution will
change from blue to either green(trace),
yellow(low) or brick red (orange).
Food Tests (Aim: Test for proteins)
1. Procedure: Pour 2cm of protein solution into a test
tube. Add 5 drops of biuret solution (Biuret
solution is made up of CuSO4 and NaOH) and
observe.
2. Observation and interpretation: the biuret
solution will cause the protein food to change to
pink (low) or purple(more).
Food Tests (Aim: Test for lipids)
1. Procedure: Add 2cm of fat or oil into a test tube,
add 2cm of ethanol and shake well.
2. Observation and interpretation: A layer of cloudy
suspension forms at the top of the solution. This is
an emulsion.
Or
Procedure: Put 2-3 drops of oil onto one side of a
paper. On the other side put 2-3 drops of water.
Observation and interpretation: the area with oil is
translucent while that with water is transparent.
Energy values of food
• Food provides energy.
we can also use kilocalories (Kcal) or kilojoules
(KJ) to measure food energy.
• The need for energy each day depend on the
following: Age, gender and activity.
Pregnant women need about 300 extra kcal a
day and also much Calcium rich foods.
Breast feeding mothers also need 400-500 extra
kcal a day. Males need more energy than
females because heat loss is faster in males.
Extra- Becoming a Wise Consumer
1. Eat different kinds of food:
Carbohydrates with starch and fiber. Different
color foods.
Becoming a Wise Consumer
2. Eat less sugar and salt:
Sugar causes people to gain weight.
Salt causes high blood pressure and heart
problems.
Becoming a Wise Consumer
3. Eat less fats: Eat less saturated fat.
Fats can block the blood vessels or lead to stroke.
Eat low fat yoghurt or milk.
Becoming a Wise Consumer
4. Eat lots of fiber, vegetables and fruits:
Eat vegetables or fruits from different color groups.
Eat fiber such as brown or whole wheat bread,
corn and brown rice.
Becoming a Wise Consumer
5. Eat the right amount of calories:
This will keep your body at a healthy weight.
Becoming a Wise Consumer
6. Avoid smoked foods or chemicals:
Nitrate chemicals such as borax and
preservatives are harmful.
Becoming a Wise Consumer
7. Do not drink alcohol:
Alcohol has no nutrients. It instead has high
calories. It damages the body.
Choosing the Right Food
• Food labels tell us about the ingredients, nutrients,
calories and servings.
Ingredients are listed in order of weight from the
most to the least.
Food labels can help us choose healthy foods.
Activities
1. Testing foods for carbohydrates: activity 2.1 apge
19
2. Advice requiring answers- activity on page 21
1. Experiment on absorption. Activity 2.3 page 23.
2. Digestion by enzyme . Activity 2.6 page 29.
3. End of unit activities page 30 -31.
You might also like
- Nutrition: iGCSE BiologyDocument76 pagesNutrition: iGCSE Biologyviolet paul100% (1)
- Microgravity NASA Hunch (Uy & Brown)Document10 pagesMicrogravity NASA Hunch (Uy & Brown)JeremyMarrNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in The Formulation of Gluten-FreeDocument10 pagesRecent Advances in The Formulation of Gluten-FreeBeni HidayatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NuritionDocument54 pagesChapter 2 NuritionteacherYatie82No ratings yet
- Green White Illustration Vegetables Healthy Balanced Diet PresentationDocument31 pagesGreen White Illustration Vegetables Healthy Balanced Diet PresentationEvangeline De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Digestion Revision NotesDocument4 pagesDigestion Revision NotesManisha SamantNo ratings yet
- Unit 8A Food and Digestion: Name: .Document14 pagesUnit 8A Food and Digestion: Name: .rickyNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Diet and GrowthDocument173 pagesUnit 7 Diet and GrowthBlop100% (2)
- Chapter 5 Grade-12Document5 pagesChapter 5 Grade-12umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Nutrition: Classes of Food: Food Is The Source of Energy For All Living ThingsDocument36 pagesNutrition: Classes of Food: Food Is The Source of Energy For All Living ThingsSuria SawalNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument4 pagesScienceSylvia SanlyNo ratings yet
- Module 6 NutritionsDocument35 pagesModule 6 Nutritionsleonardwatch12No ratings yet
- Stage I. Health ProblemsDocument24 pagesStage I. Health ProblemsBalajinagarajan AlagappanNo ratings yet
- Stage I. Health ProblemsDocument24 pagesStage I. Health ProblemsBalajinagarajan AlagappanNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument13 pagesBIOLOGYRahaf MohammedNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Class 12 (1) PDFDocument48 pagesCH-2 Class 12 (1) PDFAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 GEST1007 2022 ClassDocument30 pagesLecture9 GEST1007 2022 Classa28437938No ratings yet
- ABRERA, Lucky Lynn R. - Laboratory - Activity - CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesABRERA, Lucky Lynn R. - Laboratory - Activity - CarbohydratesLucky Lynn AbreraNo ratings yet
- InfoDocument7 pagesInfoAndre EaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Concepts Explained Simply: CarbohydrateDocument3 pagesNutrition Concepts Explained Simply: CarbohydrateNavneetNo ratings yet
- Balance Diet 321Document5 pagesBalance Diet 321Aroob YaseenNo ratings yet
- Components of Food - Class 6, Components of FoodDocument10 pagesComponents of Food - Class 6, Components of FoodPriyaNo ratings yet
- Diet and Growth (Part 1)Document8 pagesDiet and Growth (Part 1)Kenzy HassanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.balance Food Major Food GroupsDocument30 pagesLecture 1.balance Food Major Food Groupsshani9976614No ratings yet
- Food and NutritionDocument113 pagesFood and NutritionSUNNY YADAVNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Document5 pagesUnit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Mr : NADe?RNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Document5 pagesUnit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Mr : NADe?RNo ratings yet
- مادة التغذيهDocument119 pagesمادة التغذيهNoor NonaNo ratings yet
- Folio Form 2 Nutrition IIDocument11 pagesFolio Form 2 Nutrition IIEncik Amir Kamal100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Section 1 (Nutrients)Document26 pagesChapter 7 Section 1 (Nutrients)lolyvwuNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2A Nutritional Elements:: Carbohydrate, Protein, Fats and MineralsDocument34 pagesUnit - 2A Nutritional Elements:: Carbohydrate, Protein, Fats and MineralsEvet VaxbmNo ratings yet
- Nutrition BasicsDocument49 pagesNutrition Basicstoty-berryNo ratings yet
- Nutrient DictionaryDocument22 pagesNutrient DictionaryBlossom PlayzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2Abhinaba PaulNo ratings yet
- Food and DigestionDocument51 pagesFood and Digestionshahbaz saahilNo ratings yet
- Diet & Nutrition Advanced Ver 1Document52 pagesDiet & Nutrition Advanced Ver 1Ina100% (1)
- Food and Health Unit 1Document59 pagesFood and Health Unit 1Tsz Yan LeungNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument8 pagesNutritionhy1606537No ratings yet
- NUT201 - Chapter 2 Nutrients Spring 2023Document119 pagesNUT201 - Chapter 2 Nutrients Spring 2023Ghina RedaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-HUMAN NUTRITIONDocument31 pagesUnit 7-HUMAN NUTRITIONfreefortnie75No ratings yet
- Concept of Nutrition & Dietary (Document46 pagesConcept of Nutrition & Dietary (Hina AslamNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in FoodDocument39 pagesNutrition in FoodLeafrast GamingNo ratings yet
- 26 July 2018: Geology 101 Report Page ! of ! 1 2Document6 pages26 July 2018: Geology 101 Report Page ! of ! 1 2Anshu MovvaNo ratings yet
- L-7 Public Health Nutrition (PHN)Document50 pagesL-7 Public Health Nutrition (PHN)Asta BlackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Components of FoodDocument12 pagesChapter 2 Components of FoodHarsha BhamreNo ratings yet
- Health Program Nutrition & HygieneDocument36 pagesHealth Program Nutrition & HygieneMaster Harold100% (2)
- Exp SC 6 - Chapter 02Document15 pagesExp SC 6 - Chapter 02megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Health2ndgradinglecture 221110063621 d58f92ddDocument88 pagesHealth2ndgradinglecture 221110063621 d58f92ddnorthernsamar.jbbinamera01No ratings yet
- The 7 Components of A Healthy DietDocument3 pagesThe 7 Components of A Healthy DietChibale Mchere BandaNo ratings yet
- NutrientsDocument40 pagesNutrientsOmar FaourNo ratings yet
- Hygenic Needs-Nutritional NeedsDocument120 pagesHygenic Needs-Nutritional Needssamitha madurangaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 101 Presentation PDFDocument20 pagesNutrition 101 Presentation PDFViktória MolnárNo ratings yet
- Macronutrien TS: Alexander John Apuang Allessandria Daphne Bagacina Alyssa Kristine RealuyoDocument49 pagesMacronutrien TS: Alexander John Apuang Allessandria Daphne Bagacina Alyssa Kristine RealuyoAllessandria Daphne Sac BagacinaNo ratings yet
- KP 8 - Diet and Nutrition A 2019Document39 pagesKP 8 - Diet and Nutrition A 2019Luthi PratiwiNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument53 pagesNutritionanesahmedtofik932No ratings yet
- Food Nutrition Hygiene Preservation NotesDocument18 pagesFood Nutrition Hygiene Preservation NotesJasmina SanganiNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients PPT - Sept. 2023Document72 pagesMacronutrients PPT - Sept. 2023Jedelyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 101: Brought To You by The University of HoustonDocument20 pagesNutrition 101: Brought To You by The University of HoustonRaquel AgasaNo ratings yet
- Public Health Nutrition: Its Importance For Health Promotion & Health PreservationDocument36 pagesPublic Health Nutrition: Its Importance For Health Promotion & Health PreservationSumaia Rahman100% (1)
- BIT Healty MealDocument7 pagesBIT Healty MealAnna Ruby SofianaNo ratings yet
- Healthy EatingDocument7 pagesHealthy EatingmertNo ratings yet
- Fats and OilsDocument10 pagesFats and Oilsaishi94No ratings yet
- Vegetarian Diets: Quick FactsDocument5 pagesVegetarian Diets: Quick Facts001srvnNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition MCQ CarboDocument6 pagesFood and Nutrition MCQ CarboShivangi Singh50% (4)
- Health - Food To Clean ArteriesDocument21 pagesHealth - Food To Clean ArteriesRoh MihNo ratings yet
- Production of Economically Important Products by The Use of Pullulanase EnzymeDocument8 pagesProduction of Economically Important Products by The Use of Pullulanase EnzymeijsidonlineinfoNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Stasis: Review and Current TherapyDocument14 pagesGastrointestinal Stasis: Review and Current TherapyCati SofiNo ratings yet
- Valorization of Apple Pomace Powder in Development of Functional CookieDocument6 pagesValorization of Apple Pomace Powder in Development of Functional CookieSujata GhodkeNo ratings yet
- Diry FarmingDocument48 pagesDiry FarmingRaj KamalNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 12114 F19 PDFDocument4 pagesSyllabus 12114 F19 PDFDaniel SongerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - CARBOHYDRATESDocument47 pagesChapter 4 - CARBOHYDRATESKinjal100% (1)
- Wafers PresenationDocument12 pagesWafers Presenationsadbad6No ratings yet
- Crude FiberDocument5 pagesCrude FiberKhairul AnwarNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Nestlé Professional Nutrition MagazineDocument24 pagesCarbohydrates: Nestlé Professional Nutrition MagazinedenisseNo ratings yet
- Basic IELTS Reading 5-10Document48 pagesBasic IELTS Reading 5-10Giang HươngNo ratings yet
- EballaststoffeDocument12 pagesEballaststoffePhan VanduNo ratings yet
- The Top 16 Health Benefits of Grapes: Health Conditions Discover Plan ConnectDocument26 pagesThe Top 16 Health Benefits of Grapes: Health Conditions Discover Plan Connectkarina chaswinNo ratings yet
- Ajpt v11 Id1172Document4 pagesAjpt v11 Id1172haftamu GebreHiwotNo ratings yet
- BittersHandbook 110419 PDFDocument12 pagesBittersHandbook 110419 PDFdavidmargiotta100% (1)
- Notes in Normal and Therapeutic DietsDocument17 pagesNotes in Normal and Therapeutic DietsJojebelle Kate Iyog-cabanlet100% (1)
- Banana Peel As Dietary FiberDocument7 pagesBanana Peel As Dietary FiberBagas Aryo SasongkoNo ratings yet
- Eat For HealthDocument67 pagesEat For HealthVladimir VladNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Black Wheat A ReviewDocument5 pagesHealth Benefits of Black Wheat A ReviewIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Muñoz PDFDocument40 pagesMuñoz PDFNutricionista Cleide SalustinoNo ratings yet
- VIP List Exclusive - Nutrition 101 GuideDocument34 pagesVIP List Exclusive - Nutrition 101 GuideVictor SoaresNo ratings yet
- 1976 Changes in Fecal Composition and Colonic Function Due To Cereal FiberDocument6 pages1976 Changes in Fecal Composition and Colonic Function Due To Cereal FiberMyriam CardenasNo ratings yet
- Global Nutrition Philosophy Presentation NoVideo U.S.English PDFDocument187 pagesGlobal Nutrition Philosophy Presentation NoVideo U.S.English PDFMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Brochure - Whole Grains and Oats in The Asian DietDocument11 pagesBrochure - Whole Grains and Oats in The Asian DietkaraNo ratings yet