Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views19ehs 302-Unit 4-Part Ii
19ehs 302-Unit 4-Part Ii
Uploaded by
Chamarthy SribharathicharanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Financial Markets and Institutions 7th Edition by SaundersDocument24 pagesSolution Manual For Financial Markets and Institutions 7th Edition by SaundersRobertGonzalesyijx100% (37)
- BBT Tradebook Strategies Cheatsheet PDFDocument13 pagesBBT Tradebook Strategies Cheatsheet PDFRaghavendra Rao TNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal Heavy BombersDocument12 pagesJose Rizal Heavy BombersKYN KIETH PAMA100% (3)
- 50 Important Questions and Answers Business StudiesDocument10 pages50 Important Questions and Answers Business Studiescchendrimada100% (2)
- Delegation of AuthorityDocument8 pagesDelegation of Authoritysangeetha0% (1)
- PMF Unit 3Document21 pagesPMF Unit 3dummy manNo ratings yet
- Organisation Structure: UNIT:2Document28 pagesOrganisation Structure: UNIT:2S. B.No ratings yet
- Delegation As A Management MethodDocument7 pagesDelegation As A Management MethodnasareenauNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4-OrganizingDocument36 pagesCHAPTER 4-OrganizingNur IzzahNo ratings yet
- Delegation Benefits Limitations and WhyDocument13 pagesDelegation Benefits Limitations and WhyYogesh Gharpure100% (1)
- Unit 2.2 - Organizational Structure - Business IB HLDocument23 pagesUnit 2.2 - Organizational Structure - Business IB HLAmbar DunskiNo ratings yet
- Leading & Managing Project Teams: Session-2Document18 pagesLeading & Managing Project Teams: Session-2Choudhary HammadNo ratings yet
- of McobDocument12 pagesof McobAnkita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mas Chapter-3 DraftDocument36 pagesMas Chapter-3 DraftRuiz, CherryjaneNo ratings yet
- Site Manage I I BookDocument60 pagesSite Manage I I BookEnebinelsonNo ratings yet
- Imst 2Document18 pagesImst 2satyaNo ratings yet
- Report QTHDocument16 pagesReport QTHk61.2212250053No ratings yet
- UNIT 4 ORGANIZATION (Questions and Answers) 1Document41 pagesUNIT 4 ORGANIZATION (Questions and Answers) 1ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Principles of Administration-Amita SenDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Administration-Amita SenAaradhika MehtaNo ratings yet
- Delegation FinalDocument30 pagesDelegation Finalreal history and series real history and seriesNo ratings yet
- Organising 08.07.20Document12 pagesOrganising 08.07.20Mahima 1No ratings yet
- .Chapter One Cont'd: Organization StructureDocument61 pages.Chapter One Cont'd: Organization StructureGood JasperNo ratings yet
- Delegation of Authority and Decenralisation: Presented By: Kamlesh Rautela PGT (Commerce) KV Masimpur Silchar RegionDocument15 pagesDelegation of Authority and Decenralisation: Presented By: Kamlesh Rautela PGT (Commerce) KV Masimpur Silchar Regiond-fbuser-65596417No ratings yet
- Delegation of AuthorityDocument10 pagesDelegation of AuthorityrivalrydeadNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document8 pagesUnit 3mkarjun mkarjunNo ratings yet
- Developing Work Integration Positions: Engineering Division With Liaison Department (The Expeditor)Document5 pagesDeveloping Work Integration Positions: Engineering Division With Liaison Department (The Expeditor)Sergio Olvera GNo ratings yet
- Span of ControlDocument3 pagesSpan of ControlThe LegendaryNo ratings yet
- Organizing Function of Management - May 2023Document8 pagesOrganizing Function of Management - May 2023Fatma HusseinNo ratings yet
- Unit Code Unit Name Assessment Code Due Date Student Name Student IDDocument14 pagesUnit Code Unit Name Assessment Code Due Date Student Name Student IDLiliana PuentesNo ratings yet
- Organization ProcessDocument4 pagesOrganization ProcessssNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 ManagementDocument8 pagesChapter1 Managementnacereddine.kingNo ratings yet
- Principle and PracticesDocument15 pagesPrinciple and Practicespooja shindeNo ratings yet
- PPM Lesson 9Document60 pagesPPM Lesson 9annstine makenaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Delegation and DecentralizationDocument4 pagesDifference Between Delegation and Decentralizationjatinder99No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document41 pagesChapter 2Renad ObaidNo ratings yet
- DelegationDocument34 pagesDelegationanon_784834955No ratings yet
- BM Midterm Chapter 7Document10 pagesBM Midterm Chapter 7James MontesNo ratings yet
- IM Business Management AccountingDocument59 pagesIM Business Management AccountingMarianel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Delegating Authority and Empowering Employees WrittenDocument5 pagesDelegating Authority and Empowering Employees WrittenHarold MaribojocNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document7 pagesLesson 3Nishani wickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- MODULE V Mescenotes - inDocument15 pagesMODULE V Mescenotes - inSuppu SamudNo ratings yet
- DelegationDocument3 pagesDelegationkhushi jaisinghNo ratings yet
- Skip To Main ContentDocument3 pagesSkip To Main Contentfaith olaNo ratings yet
- ANISING by SRCCDocument26 pagesANISING by SRCCRonakNo ratings yet
- Module 20Document10 pagesModule 20sidharth psNo ratings yet
- E Chapter 10Document19 pagesE Chapter 10aerosmethpagapulanNo ratings yet
- Span of Management Also Known As Span of Control Means How Many Subordinates Are Handled by A Superior. It Is One of The Basic Functions of OrganizationDocument1 pageSpan of Management Also Known As Span of Control Means How Many Subordinates Are Handled by A Superior. It Is One of The Basic Functions of OrganizationAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Organization Structures: Dr. Ramzi AdrimanDocument49 pagesChapter 3. Organization Structures: Dr. Ramzi AdrimanAry DasmaraNo ratings yet
- Management Theory and Practice: Organizing FunctionDocument59 pagesManagement Theory and Practice: Organizing FunctionBontu H AmeyaNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 Designing Adaptive OrganizationsDocument45 pagesChap 6 Designing Adaptive Organizationslaibaahmedkhan7860No ratings yet
- Chandighar University CMT117 Principal of Management: Name - Muskan Yadav Uid - 19bcm1072 Submitted To - Dr. JaspreetDocument6 pagesChandighar University CMT117 Principal of Management: Name - Muskan Yadav Uid - 19bcm1072 Submitted To - Dr. Jaspreetmuskan yadavNo ratings yet
- Situational Theory:: Leadership & Management TheoriesDocument2 pagesSituational Theory:: Leadership & Management Theoriesshazeb aliNo ratings yet
- DelegationDocument18 pagesDelegationdoesnotexistuNo ratings yet
- Assignment No - 1 ON "Principle & Practices of Management" (PGCM - 11)Document14 pagesAssignment No - 1 ON "Principle & Practices of Management" (PGCM - 11)JaiyanthNo ratings yet
- MGT 162 Fundamentals of ManagementDocument36 pagesMGT 162 Fundamentals of ManagementAqil Anwar100% (2)
- Determining, Grouping and Structuring The Activities. Creating Rules For Effective Performance at WorkDocument8 pagesDetermining, Grouping and Structuring The Activities. Creating Rules For Effective Performance at WorkPhani Kumar MallelaNo ratings yet
- MGMT CH 5Document59 pagesMGMT CH 5molalign tekalignNo ratings yet
- Design of Ion StructureDocument7 pagesDesign of Ion StructureAdityaNo ratings yet
- MGT 4, 5 and 6Document109 pagesMGT 4, 5 and 6tewodros bayisaNo ratings yet
- Organizing NewDocument6 pagesOrganizing Newnajaffathimak96No ratings yet
- 8-Dimensions of Organization StructureDocument31 pages8-Dimensions of Organization StructureShilpa N. LendeNo ratings yet
- Principals of Organizing: Basics of Management Group Assignment No-2Document3 pagesPrincipals of Organizing: Basics of Management Group Assignment No-2simranNo ratings yet
- Semester II (2021) - Soft Skills Course OutlineDocument3 pagesSemester II (2021) - Soft Skills Course OutlineChamarthy SribharathicharanNo ratings yet
- PSP UNIT (1-5) v2Document74 pagesPSP UNIT (1-5) v2Chamarthy SribharathicharanNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Computational Thinking and Visual Programming ConceptsDocument4 pagesUnit I: Computational Thinking and Visual Programming ConceptsChamarthy SribharathicharanNo ratings yet
- Venture Discovery AssignmentDocument15 pagesVenture Discovery AssignmentChamarthy SribharathicharanNo ratings yet
- Q PX Py+9 PZ+ MDocument5 pagesQ PX Py+9 PZ+ MDane Matthew PilapilNo ratings yet
- Mechanical - Piping Works For The Fl3b Project Paket 1 (Woodyard) - Rev.03Document2 pagesMechanical - Piping Works For The Fl3b Project Paket 1 (Woodyard) - Rev.03sudarsonoNo ratings yet
- Addressing Youth Unemployment in Uganda : The Inevitable Advice of The 21 CenturyDocument9 pagesAddressing Youth Unemployment in Uganda : The Inevitable Advice of The 21 CenturyLillian KobusingyeNo ratings yet
- Annex 51 Inventory and Inspection Report of Unserviceable PropertyDocument1 pageAnnex 51 Inventory and Inspection Report of Unserviceable PropertyFreddie TabamoNo ratings yet
- International Accounting: A User PerspectiveDocument38 pagesInternational Accounting: A User PerspectiveMarietzaNo ratings yet
- GST Council To Discuss Tax On Covid Essentials: Applied Materials Explores Setting Up Plant in IndiaDocument22 pagesGST Council To Discuss Tax On Covid Essentials: Applied Materials Explores Setting Up Plant in IndiaManikNo ratings yet
- Bite Type FittingsDocument42 pagesBite Type FittingsWilson JustinoNo ratings yet
- Soal Uts Akuntansi Kelas Pagi Semester 2Document2 pagesSoal Uts Akuntansi Kelas Pagi Semester 2Ajikk T7No ratings yet
- 07 - Chapter 4Document78 pages07 - Chapter 4pooja shandilyaNo ratings yet
- CMA I - Chapter 4, Process CostingDocument68 pagesCMA I - Chapter 4, Process CostingLakachew GetasewNo ratings yet
- MT Everest Disaster Case StudyDocument3 pagesMT Everest Disaster Case StudyCea Jay100% (1)
- Pilot Valve Boxes SG110ADocument2 pagesPilot Valve Boxes SG110AVictor Ruiz FuentesNo ratings yet
- Russia - A Wounded EconomyDocument8 pagesRussia - A Wounded EconomyPham Thi Diem PhuongNo ratings yet
- Session: 2014 - 2015 (Spring)Document2 pagesSession: 2014 - 2015 (Spring)Bharat Chandra SahuNo ratings yet
- HVAC - List of ManufacturersDocument2 pagesHVAC - List of ManufacturersAdnan Ahmed KidwaiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledprasannaNo ratings yet
- CARICOM PresentationDocument10 pagesCARICOM Presentationjahlina fridayNo ratings yet
- Dimensions of InformationDocument12 pagesDimensions of Informationرفاه مهند كاظمNo ratings yet
- Company Profile: Pt. Bali Dana SejahteraDocument54 pagesCompany Profile: Pt. Bali Dana SejahteraRSS347No ratings yet
- Fme6 Activity2 PDFDocument7 pagesFme6 Activity2 PDFFred BorjaNo ratings yet
- AMAT TestDocument102 pagesAMAT Testhossam.morsy1984No ratings yet
- BASF, CD&R Sell Solenis To Platinum Equity For $5.25 BillionDocument4 pagesBASF, CD&R Sell Solenis To Platinum Equity For $5.25 BillionCDI Global IndiaNo ratings yet
- Indo Danish Tool Room: Industrial TrainingDocument28 pagesIndo Danish Tool Room: Industrial TrainingPriyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Tugas MLTIDocument16 pagesTugas MLTIArinisa PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Ait Handling Unit 1 - PreviewDocument24 pagesAit Handling Unit 1 - PreviewRiskia FatiaaNo ratings yet
- Special Power of Attorney Citi Fire NewDocument2 pagesSpecial Power of Attorney Citi Fire NewRobert marollanoNo ratings yet
- 2-Daily Concrete Gradation RegisterDocument1 page2-Daily Concrete Gradation Registershinde rushiNo ratings yet
19ehs 302-Unit 4-Part Ii
19ehs 302-Unit 4-Part Ii
Uploaded by
Chamarthy Sribharathicharan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views28 pagesOriginal Title
19EHS 302-UNIT 4-PART II
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views28 pages19ehs 302-Unit 4-Part Ii
19ehs 302-Unit 4-Part Ii
Uploaded by
Chamarthy SribharathicharanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 28
ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
UNIT 4
Department of CSE, GIT
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
SPAN OF MANAGEMENT
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Department of CSE, GIT
The Span of Management refers to the number of
subordinates who can be managed efficiently by a
superior. Simply, the manager having the group of
subordinates who report him directly is called as the
span of management.
The Span of Management has two implications:
Influences the complexities of the individual manager’s
job
Determine the shape or configuration of the Organization
SPAN OF MANAGEMENT
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
The span of management is related to the horizontal
levels of the organization structure.
There is a wide and a narrow span of management.
Department of CSE, GIT
With the wider span, there will be less hierarchical
levels, and thus, the organizational structure would be
flatter.
Whereas, with the narrow span, the hierarchical levels
increases, hence the organizational structure would be
tall.
SPAN OF MANAGEMENT
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Department of CSE, GIT
Both these organizational structures have their advantages and the disadvantages.
But however the tall organizational structure imposes more challenges
NARROW SPAN OF MANAGEMENT
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Since the span is narrow, which means less number of
subordinates under one superior, requires more managers
to be employed in the organization. Thus, it would be very
expensive in terms of the salaries to be paid to each
Department of CSE, GIT
senior.
With more levels in the hierarchy, the communication
suffers drastically. It takes a lot of time to reach the
appropriate points, and hence the actions get delayed.
Lack of coordination and control because the operating
staff is far away from the top management.
NARROW SPAN OF MANAGEMENT
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
The major advantage of using this structure is that the
cross communication gets facilitated,
i.e., operative staff communicating with the top
management. Also, the chance of promotion increases
Department of CSE, GIT
with the availability of several job positions.
WIDE SPAN OF MANAGEMENT
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
In the case of a flatter organizational structure, where the
span is wide leads to a more complex supervisory
relationship between the manager and the subordinate.
It will be very difficult for a superior to manage a large
Department of CSE, GIT
number of subordinates at a time and also may not listen
to all efficiently.
However, the benefit of using the wider span of
management is that the number of managers gets reduced
in the hierarchy, and thus, the expense in terms of
remuneration is saved.
Also, the subordinates feel relaxed and develop their
independent spirits in a free work environment, where the
strict supervision is absent.
DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
The Delegation of Authority is an organizational process
wherein, the manager divides his work among the
subordinates and give them the responsibility to
accomplish the respective tasks. Along with the
Department of CSE, GIT
responsibility, he also shares the authority,
i.e. the power to take decisions with the subordinates,
such that responsibilities can be completed efficiently
DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
In other words, a delegation of authority involves the sharing
of authority downwards to the subordinates and checking
their efficiency by making them accountable for their doings.
In an organization, the manager has several responsibilities
Department of CSE, GIT
and work to do.
So, in order to reduce his burden, certain responsibility and
authority are delegated to the lower level,
i.e. to the subordinates, to get the work done on the
manager’s behalf.
Under the delegation of authority, the manager does not
surrender his authority completely, but only shares certain
responsibility with the subordinate and delegates that much
authority which is necessary to complete that responsibility.
Department of CSE, GIT
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY
FEATURES OF DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Delegation means giving power to the subordinate to act
independently but within the limits prescribed by the superior. Also,
he must comply with the provisions of the organizational policy,
rules, and regulations.
Department of CSE, GIT
Delegation does not mean that manager give up his authority, but
certainly he shares some authority with the subordinate essential to
complete the responsibility entrusted to him.
Authority once delegated can be further expanded, or withdrawn by
the superior depending on the situation.
The manager cannot delegate the authority which he himself does not
possess. Also, he can not delegate his full authority to a subordinate.
The delegation of authority may be oral or written, and may be
specific or general.
The delegation is an art and must comply with all the fundamental
rules of an organization.
Department of CSE, GIT
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
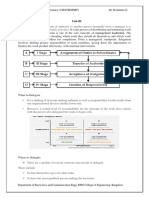
PROCESS OF DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Assignment of Duties to Subordinates: Before the actual
delegation of authority, the delegator must decide on the
duties which he wants the subordinate or the group of
subordinates to perform. Here, the manager lists the
Department of CSE, GIT
activities to be performed along with the targets to be
achieved, and the same is spelled out to the subordinates.
Thus, in the first stage, the duties are assigned to the
subordinates as per their job roles.
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Transfer of Authority to perform the duty: At this stage,
an adequate authority is delegated to the subordinate
which is essential to perform the duty assigned to him. A
manager must make sure; that authority is strictly
Department of CSE, GIT
delegated just to perform the responsibility, as more
authority may lead to its misuse by the subordinate.
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Acceptance of the Assignment: At this stage, the
subordinate either accepts or rejects the tasks assigned to
him by his superior. If the subordinate or the delegate,
refuses to accept the duty and the authority to perform it,
Department of CSE, GIT
then the manager looks for the other person who is
capable of and is willing to undertake the assignment.
Once the assignment gets accepted by the subordinate, the
delegation process reaches its last stage.
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Accountability: The process of delegation of authority ends
at the creation of an obligation on the part of the
subordinate to perform his responsibility within the
powers assigned to him. Once the assignment is accepted
Department of CSE, GIT
by the subordinate, then he becomes responsible for the
completion of the duty and is accountable to the superior
for his performance.
Thus, the process of delegation of authority begins with the
duties assigned to the subordinates and ends when the
subordinate is obliged to carry out the operations as
intended.
WHAT IS POWER ??
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Power is a personal trait that affects people at every social
level of their lives. Power can be gained through
experience and lost through mistakes and bad behavior,
but people tend to continue becoming more powerful and
Department of CSE, GIT
influential the longer they work and live. Power is not
hierarchical, and can flow in any direction of a
relationship.
WHAT IS AUTHORITY?
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Authority is a formal title or position that gives someone the
tools to influence other people within their organization. A
person in authority is often powerful, but power is not
necessary for authority. Authority is important for many
Department of CSE, GIT
hierarchical systems and organizations to operate
smoothly and quickly.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN POWER AND AUTHORITY
Power is defined as the ability or potential of an individual to
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
influence others and control their actions. Authority is the legal and
formal right to give orders and commands, and take decisions.
Power is a personal trait, i.e. an acquired ability, whereas authority
is a formal right, that vest in the hands of high officials or
management personnel.
Department of CSE, GIT
The major source of power is knowledge and expertise. On the
other hand, position and office determine the authority of a person.
Power flows in any direction, i.e. it can be upward, downward,
crosswise or diagonal, lateral. As opposed to authority, that flows
only in one direction, i.e. downward (from superior to
subordinate).
The power lies in person, in essence, a person acquires it, but
authority lies in the designation, i.e. whoever get the designation,
get the authority attached to it.
Authority is legitimate whereas the power is not.
DEFINITION OF LINE ORGANIZATION
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Line organization, as the name suggests, is an
organization wherein a direct vertical relationship
between the superior and subordinate exists.
It relies on the scalar principle, which encompasses that
Department of CSE, GIT
authority flows downward, i.e. the person at the top,
delegates authority to the person at the middle, who in
turn delegates the authority to the bottom level.
LINE ORGANISATION
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Department of CSE, GIT
When it comes to the quantum of authority, it is highest at the foremost
level, which tends to decrease at each following level.
LINE ORGANISATION
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
This type of organization is characterized by a direct chain
of command, which is like a thread that passes through all
the members of the organization.
So, who is responsible for what and who is accountable to
Department of CSE, GIT
whom is defined, that is to say, subordinates work under
the supervision of the superior.
DEFINITION OF LINE AND STAFF ORGANIZATION
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Line and staff organization is the organization that
combines the merits of line and functional organization,
by adding the functional specialist to the line organization.
Here, line authority stays same, as in the case of line
Department of CSE, GIT
organization and it flows downward.
The functional experts, give advise to the front line
managers, in the matters relevant to the object of the
organization.
The specialist works as staff and serves the line officials,
by supporting and guiding them, whenever necessary.
Department of CSE, GIT
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
LINE AND STAFF ORGANIZATION
LINE AND STAFF ORGANIZATION
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
There are a number of benefits of line and staff
organization, in the sense that it gives relief to the line
managers and they can concentrate on the implementation
of policies and plans.
Department of CSE, GIT
Moreover, there is a benefit of specialization, as in work is
divided between the line and staff executives, and they
focus on their respective area.
In this type of organization, the decision making is quick
and easy, as the expert advice can help in making better
decisions.
KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN LINE AND LINE & STAFF
ORGANIZATION
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
Line organization can be understood as a vertical organization, wherein the
superior can give orders to a subordinate, through a direct chain of command.
Line and staff organization is the organization structure, in which there is a
normal departmentation of the regular business operations, and there is the
Department of CSE, GIT
functional specialist to perform specialised activities.
While line authority relies on command, line and staff authority is based on
command and advise.
As we talk about discipline, line organization, is strict, whereas line and staff
organization is loose.
In a line organization, the line executives are the generalist, who is directly
responsible for accomplishing the objectives of the organization.
On the other hand, in line and staff organization, the staff executives are
specialist who supports and advice the line managers in the accomplishment
of organization’s objectives.
KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN LINE AND LINE
& STAFF ORGANIZATION
19EHS302 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT
There is centralization of authority in a line organization,
and so all the decisions of the organization are taken by
the top authority only. Conversely, in line and staff
organization, there is a combination of centralisation and
Department of CSE, GIT
decentralisation, in essence, some of the decisions are
centrally taken while some are diffused.
Line organization, is good for small corporations, as, in
such a structure, the authority is concentrated at the top,
which makes it difficult to manage if the number of
employees are large. On the contrary, Line and staff
organization, is best suited for large corporations due to
the presence of staff specialist, who use their knowledge
to advice line managers on complex issues.
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Financial Markets and Institutions 7th Edition by SaundersDocument24 pagesSolution Manual For Financial Markets and Institutions 7th Edition by SaundersRobertGonzalesyijx100% (37)
- BBT Tradebook Strategies Cheatsheet PDFDocument13 pagesBBT Tradebook Strategies Cheatsheet PDFRaghavendra Rao TNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal Heavy BombersDocument12 pagesJose Rizal Heavy BombersKYN KIETH PAMA100% (3)
- 50 Important Questions and Answers Business StudiesDocument10 pages50 Important Questions and Answers Business Studiescchendrimada100% (2)
- Delegation of AuthorityDocument8 pagesDelegation of Authoritysangeetha0% (1)
- PMF Unit 3Document21 pagesPMF Unit 3dummy manNo ratings yet
- Organisation Structure: UNIT:2Document28 pagesOrganisation Structure: UNIT:2S. B.No ratings yet
- Delegation As A Management MethodDocument7 pagesDelegation As A Management MethodnasareenauNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4-OrganizingDocument36 pagesCHAPTER 4-OrganizingNur IzzahNo ratings yet
- Delegation Benefits Limitations and WhyDocument13 pagesDelegation Benefits Limitations and WhyYogesh Gharpure100% (1)
- Unit 2.2 - Organizational Structure - Business IB HLDocument23 pagesUnit 2.2 - Organizational Structure - Business IB HLAmbar DunskiNo ratings yet
- Leading & Managing Project Teams: Session-2Document18 pagesLeading & Managing Project Teams: Session-2Choudhary HammadNo ratings yet
- of McobDocument12 pagesof McobAnkita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mas Chapter-3 DraftDocument36 pagesMas Chapter-3 DraftRuiz, CherryjaneNo ratings yet
- Site Manage I I BookDocument60 pagesSite Manage I I BookEnebinelsonNo ratings yet
- Imst 2Document18 pagesImst 2satyaNo ratings yet
- Report QTHDocument16 pagesReport QTHk61.2212250053No ratings yet
- UNIT 4 ORGANIZATION (Questions and Answers) 1Document41 pagesUNIT 4 ORGANIZATION (Questions and Answers) 1ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Principles of Administration-Amita SenDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Administration-Amita SenAaradhika MehtaNo ratings yet
- Delegation FinalDocument30 pagesDelegation Finalreal history and series real history and seriesNo ratings yet
- Organising 08.07.20Document12 pagesOrganising 08.07.20Mahima 1No ratings yet
- .Chapter One Cont'd: Organization StructureDocument61 pages.Chapter One Cont'd: Organization StructureGood JasperNo ratings yet
- Delegation of Authority and Decenralisation: Presented By: Kamlesh Rautela PGT (Commerce) KV Masimpur Silchar RegionDocument15 pagesDelegation of Authority and Decenralisation: Presented By: Kamlesh Rautela PGT (Commerce) KV Masimpur Silchar Regiond-fbuser-65596417No ratings yet
- Delegation of AuthorityDocument10 pagesDelegation of AuthorityrivalrydeadNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document8 pagesUnit 3mkarjun mkarjunNo ratings yet
- Developing Work Integration Positions: Engineering Division With Liaison Department (The Expeditor)Document5 pagesDeveloping Work Integration Positions: Engineering Division With Liaison Department (The Expeditor)Sergio Olvera GNo ratings yet
- Span of ControlDocument3 pagesSpan of ControlThe LegendaryNo ratings yet
- Organizing Function of Management - May 2023Document8 pagesOrganizing Function of Management - May 2023Fatma HusseinNo ratings yet
- Unit Code Unit Name Assessment Code Due Date Student Name Student IDDocument14 pagesUnit Code Unit Name Assessment Code Due Date Student Name Student IDLiliana PuentesNo ratings yet
- Organization ProcessDocument4 pagesOrganization ProcessssNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 ManagementDocument8 pagesChapter1 Managementnacereddine.kingNo ratings yet
- Principle and PracticesDocument15 pagesPrinciple and Practicespooja shindeNo ratings yet
- PPM Lesson 9Document60 pagesPPM Lesson 9annstine makenaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Delegation and DecentralizationDocument4 pagesDifference Between Delegation and Decentralizationjatinder99No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document41 pagesChapter 2Renad ObaidNo ratings yet
- DelegationDocument34 pagesDelegationanon_784834955No ratings yet
- BM Midterm Chapter 7Document10 pagesBM Midterm Chapter 7James MontesNo ratings yet
- IM Business Management AccountingDocument59 pagesIM Business Management AccountingMarianel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Delegating Authority and Empowering Employees WrittenDocument5 pagesDelegating Authority and Empowering Employees WrittenHarold MaribojocNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document7 pagesLesson 3Nishani wickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- MODULE V Mescenotes - inDocument15 pagesMODULE V Mescenotes - inSuppu SamudNo ratings yet
- DelegationDocument3 pagesDelegationkhushi jaisinghNo ratings yet
- Skip To Main ContentDocument3 pagesSkip To Main Contentfaith olaNo ratings yet
- ANISING by SRCCDocument26 pagesANISING by SRCCRonakNo ratings yet
- Module 20Document10 pagesModule 20sidharth psNo ratings yet
- E Chapter 10Document19 pagesE Chapter 10aerosmethpagapulanNo ratings yet
- Span of Management Also Known As Span of Control Means How Many Subordinates Are Handled by A Superior. It Is One of The Basic Functions of OrganizationDocument1 pageSpan of Management Also Known As Span of Control Means How Many Subordinates Are Handled by A Superior. It Is One of The Basic Functions of OrganizationAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Organization Structures: Dr. Ramzi AdrimanDocument49 pagesChapter 3. Organization Structures: Dr. Ramzi AdrimanAry DasmaraNo ratings yet
- Management Theory and Practice: Organizing FunctionDocument59 pagesManagement Theory and Practice: Organizing FunctionBontu H AmeyaNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 Designing Adaptive OrganizationsDocument45 pagesChap 6 Designing Adaptive Organizationslaibaahmedkhan7860No ratings yet
- Chandighar University CMT117 Principal of Management: Name - Muskan Yadav Uid - 19bcm1072 Submitted To - Dr. JaspreetDocument6 pagesChandighar University CMT117 Principal of Management: Name - Muskan Yadav Uid - 19bcm1072 Submitted To - Dr. Jaspreetmuskan yadavNo ratings yet
- Situational Theory:: Leadership & Management TheoriesDocument2 pagesSituational Theory:: Leadership & Management Theoriesshazeb aliNo ratings yet
- DelegationDocument18 pagesDelegationdoesnotexistuNo ratings yet
- Assignment No - 1 ON "Principle & Practices of Management" (PGCM - 11)Document14 pagesAssignment No - 1 ON "Principle & Practices of Management" (PGCM - 11)JaiyanthNo ratings yet
- MGT 162 Fundamentals of ManagementDocument36 pagesMGT 162 Fundamentals of ManagementAqil Anwar100% (2)
- Determining, Grouping and Structuring The Activities. Creating Rules For Effective Performance at WorkDocument8 pagesDetermining, Grouping and Structuring The Activities. Creating Rules For Effective Performance at WorkPhani Kumar MallelaNo ratings yet
- MGMT CH 5Document59 pagesMGMT CH 5molalign tekalignNo ratings yet
- Design of Ion StructureDocument7 pagesDesign of Ion StructureAdityaNo ratings yet
- MGT 4, 5 and 6Document109 pagesMGT 4, 5 and 6tewodros bayisaNo ratings yet
- Organizing NewDocument6 pagesOrganizing Newnajaffathimak96No ratings yet
- 8-Dimensions of Organization StructureDocument31 pages8-Dimensions of Organization StructureShilpa N. LendeNo ratings yet
- Principals of Organizing: Basics of Management Group Assignment No-2Document3 pagesPrincipals of Organizing: Basics of Management Group Assignment No-2simranNo ratings yet
- Semester II (2021) - Soft Skills Course OutlineDocument3 pagesSemester II (2021) - Soft Skills Course OutlineChamarthy SribharathicharanNo ratings yet
- PSP UNIT (1-5) v2Document74 pagesPSP UNIT (1-5) v2Chamarthy SribharathicharanNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Computational Thinking and Visual Programming ConceptsDocument4 pagesUnit I: Computational Thinking and Visual Programming ConceptsChamarthy SribharathicharanNo ratings yet
- Venture Discovery AssignmentDocument15 pagesVenture Discovery AssignmentChamarthy SribharathicharanNo ratings yet
- Q PX Py+9 PZ+ MDocument5 pagesQ PX Py+9 PZ+ MDane Matthew PilapilNo ratings yet
- Mechanical - Piping Works For The Fl3b Project Paket 1 (Woodyard) - Rev.03Document2 pagesMechanical - Piping Works For The Fl3b Project Paket 1 (Woodyard) - Rev.03sudarsonoNo ratings yet
- Addressing Youth Unemployment in Uganda : The Inevitable Advice of The 21 CenturyDocument9 pagesAddressing Youth Unemployment in Uganda : The Inevitable Advice of The 21 CenturyLillian KobusingyeNo ratings yet
- Annex 51 Inventory and Inspection Report of Unserviceable PropertyDocument1 pageAnnex 51 Inventory and Inspection Report of Unserviceable PropertyFreddie TabamoNo ratings yet
- International Accounting: A User PerspectiveDocument38 pagesInternational Accounting: A User PerspectiveMarietzaNo ratings yet
- GST Council To Discuss Tax On Covid Essentials: Applied Materials Explores Setting Up Plant in IndiaDocument22 pagesGST Council To Discuss Tax On Covid Essentials: Applied Materials Explores Setting Up Plant in IndiaManikNo ratings yet
- Bite Type FittingsDocument42 pagesBite Type FittingsWilson JustinoNo ratings yet
- Soal Uts Akuntansi Kelas Pagi Semester 2Document2 pagesSoal Uts Akuntansi Kelas Pagi Semester 2Ajikk T7No ratings yet
- 07 - Chapter 4Document78 pages07 - Chapter 4pooja shandilyaNo ratings yet
- CMA I - Chapter 4, Process CostingDocument68 pagesCMA I - Chapter 4, Process CostingLakachew GetasewNo ratings yet
- MT Everest Disaster Case StudyDocument3 pagesMT Everest Disaster Case StudyCea Jay100% (1)
- Pilot Valve Boxes SG110ADocument2 pagesPilot Valve Boxes SG110AVictor Ruiz FuentesNo ratings yet
- Russia - A Wounded EconomyDocument8 pagesRussia - A Wounded EconomyPham Thi Diem PhuongNo ratings yet
- Session: 2014 - 2015 (Spring)Document2 pagesSession: 2014 - 2015 (Spring)Bharat Chandra SahuNo ratings yet
- HVAC - List of ManufacturersDocument2 pagesHVAC - List of ManufacturersAdnan Ahmed KidwaiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledprasannaNo ratings yet
- CARICOM PresentationDocument10 pagesCARICOM Presentationjahlina fridayNo ratings yet
- Dimensions of InformationDocument12 pagesDimensions of Informationرفاه مهند كاظمNo ratings yet
- Company Profile: Pt. Bali Dana SejahteraDocument54 pagesCompany Profile: Pt. Bali Dana SejahteraRSS347No ratings yet
- Fme6 Activity2 PDFDocument7 pagesFme6 Activity2 PDFFred BorjaNo ratings yet
- AMAT TestDocument102 pagesAMAT Testhossam.morsy1984No ratings yet
- BASF, CD&R Sell Solenis To Platinum Equity For $5.25 BillionDocument4 pagesBASF, CD&R Sell Solenis To Platinum Equity For $5.25 BillionCDI Global IndiaNo ratings yet
- Indo Danish Tool Room: Industrial TrainingDocument28 pagesIndo Danish Tool Room: Industrial TrainingPriyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Tugas MLTIDocument16 pagesTugas MLTIArinisa PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Ait Handling Unit 1 - PreviewDocument24 pagesAit Handling Unit 1 - PreviewRiskia FatiaaNo ratings yet
- Special Power of Attorney Citi Fire NewDocument2 pagesSpecial Power of Attorney Citi Fire NewRobert marollanoNo ratings yet
- 2-Daily Concrete Gradation RegisterDocument1 page2-Daily Concrete Gradation Registershinde rushiNo ratings yet