Professional Documents
Culture Documents
عرض تقديمي من Microsoft PowerPoint جديد
عرض تقديمي من Microsoft PowerPoint جديد
Uploaded by
Hard Tube0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesعرض تقديمي من Microsoft PowerPoint جديد
عرض تقديمي من Microsoft PowerPoint جديد
Uploaded by
Hard TubeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
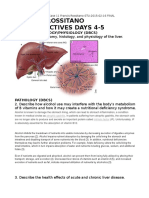
xerostomia
also known as dry mouth , is dryness in the mouth,
which may be associated with a change in the
composition of saliva, or reduced salivary flow,
.or have no identifiable cause
This symptom is very common and is often seen as
a side effect of many types of medication. It is more
common in older people,and in persons who breathe
through their
mouths Dehydration, radiotherapy involving
the salivary glands
chemotherapy and several diseases
can cause reduced salivation
(hyposalivation), or a change in saliva
consistency and hence a complaint of
xerostomia. Sometimes there is no
identifiable cause, and there may
sometimes be a psychogenic reason for
.the complain
Signs and symptoms
:Hyposalivation may give the following signs and symptoms
Dental caries (xerostomia related caries) – Without the buffering )1
effects of saliva, tooth decay becomes a common feature and may
progress much more aggressively than it would otherwise
.("rampant caries")
It may affect tooth surfaces that are normally spared, e.g., cervical
.caries and root surface caries
This is often seen in patients who have had radiotherapy involving
.the major salivary glands, termed radiation-induced caries
Therefore, it is important that any products used in managing dry
mouth symptoms are sugar-free, as the presence of sugars in the
mouth support the growth of oral bacteria, resulting in acid
production and development of dental caries
Acid erosion: Saliva acts as a buffer and )2
helps to prevent demineralization of
teeth.
3) Oral candidiasis – A loss of the
antimicrobial actions of saliva may also
lead to opportunistic
infection with Candida species
4) Burning mouth syndrome – a burning
or tingling sensation in the mouth
5) Saliva that appears thick or ropey
A lack of saliva pooling in the floor )7
of the mouth during examination.
8) Dysphagia – difficulty swallowing
and chewing, especially when eating
dry foods. Food may stick to the tissues
during eating.
9) Gloves or a dental mirror may stick
to the tissues.
10) Dry, sore, and cracked lips and
.angles of mouth
Causes
The differential of hyposalivation significantly overlaps with that
of xerostomia. A reduction in saliva production to about 50% of
the normal unstimulated level will usually result in the sensation
of dry mouth. Altered saliva composition may also be responsible
.for xerostomia
Physiologic: Salivary flow rate is decreased during sleep, which )1
may lead to a transient sensation of dry mouth upon waking. This
disappears with eating or drinking or with oral hygiene. When
associated with halitosis, this is sometimes termed "morning
breath". Dry mouth is also a common sensation during periods of
anxiety, probably owing to enhanced sympathetic drive. During
periods of stress, our body responds in a ‘fight or flight’ state that
will interfere with the saliva flow in the mouth Dehydration is
.known to cause hyposalivation
Drug induced: Aside from physiologic causes of )2
xerostomia, iatrogenic effects of medications are the most
common cause. A medication which is known to cause
xerostomia may be termed xerogenic. Over 400 medications
are associated with xerostomia. Although drug induced
xerostomia is commonly reversible, the conditions for which
these medications are prescribed are frequently chronic.[
The likelihood of xerostomia increases in relation to the total
number of medications taken, whether the individual
medications are xerogenic or not.
The sensation of dryness usually starts shortly after starting
the offending medication or after increasing the dose.
Anticholinergic, sympathomimetic, or diuretic drugs are
usually responsible
Celiac disease: Xerostomia may be the only )3
symptom of celiac disease, especially in adults, who
often have no obvious digestive symptoms.
4) Sjögren's syndrome: Xerostomia may be caused by
autoimmune conditions which damage saliva-
producing cells. Sjögren's syndrome is one such
disease, and it is associated with symptoms including
fatigue, myalgia and arthralgia.
The disease is characterised by inflammatory changes
in the moisture-producing glands throughout the
body, leading to reduced secretions from glands that
produce saliva, tears and other secretions throughout
the body
Other causes : Oral dryness may also be caused
by mouth breathing, usually caused by partial
obstruction of the upper respiratory tract.
Examples:
include hemorrhage, vomiting, diarrhea,
and fever.
Alcohol may be involved in the cause of salivary
gland disease, liver disease, or dehydration.
Smoking is another possible cause
Hormonal disorders, such as poorly controlled
diabetes
Treatment
The successful treatment of xerostomia is difficult to
achieve and often unsatisfactory. This involves finding
any correctable cause and removing it if possible, but in
many cases it is not possible to correct the xerostomia
itself, and treatment is symptomatic, and also focuses on
.preventing tooth decay through improving oral hygiene
Where the symptom is caused by hyposalivation
secondary to underlying chronic disease, xerostomia can
be considered permanent or even progressive. The
management of salivary gland dysfunction may involve
the use of saliva substitutes and/or saliva stimulants
You might also like
- Module 1-Ergonomics and Facilities PlanningDocument12 pagesModule 1-Ergonomics and Facilities Planninglei melendrez100% (6)
- Screenshot 2022-09-20 at 8.37.00 AMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2022-09-20 at 8.37.00 AMjvvistopptxNo ratings yet
- Xerostomia (Also Termed Dry Mouth: Xero-StomDocument6 pagesXerostomia (Also Termed Dry Mouth: Xero-Stomnazirrasheed123No ratings yet
- Dry Mouth EngDocument25 pagesDry Mouth EngJelena BlagojevicNo ratings yet
- Saliva DiseaseDocument8 pagesSaliva DiseaseJemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- A Patient With Dry Mouth PDFDocument6 pagesA Patient With Dry Mouth PDFWahdatNo ratings yet
- XerostomiaDocument6 pagesXerostomiaAmira Pradsnya ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner.: Dry Mouth and Disorders of SalivationDocument5 pagesOral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner.: Dry Mouth and Disorders of SalivationGowriNo ratings yet
- HalitosisDocument19 pagesHalitosisHhNo ratings yet
- Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)Document18 pagesDry Mouth (Xerostomia)dr_jamal1983No ratings yet
- Ibtisam Al-Hashimi, BDS, MS, PHD: Oral Aspects of Sjogren'S SyndromeDocument2 pagesIbtisam Al-Hashimi, BDS, MS, PHD: Oral Aspects of Sjogren'S SyndromeShree ElangovanNo ratings yet
- Xerostomia: Oedijani-Santoso Bagian/SMF Gigi Dan Mulut FK Undip/RSUP DR Kariadi SemarangDocument40 pagesXerostomia: Oedijani-Santoso Bagian/SMF Gigi Dan Mulut FK Undip/RSUP DR Kariadi SemarangRizal Saeful DrajatNo ratings yet
- Vanya FionaDocument3 pagesVanya FionaVanya FionaNo ratings yet
- Name: Nadia Yasmin NPM: 1810070110023 10 Questions and Answers Beside From Article Xerostomia (Dry Mouth) : Symtoms. Causes, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDocument4 pagesName: Nadia Yasmin NPM: 1810070110023 10 Questions and Answers Beside From Article Xerostomia (Dry Mouth) : Symtoms. Causes, Diagnosis, and TreatmentnadiaNo ratings yet
- Bad BreathDocument6 pagesBad BreathInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Oral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner.: Dry Mouth and Disorders of SalivationDocument5 pagesOral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner.: Dry Mouth and Disorders of SalivationMugiNo ratings yet
- Halitosis - An Overview: Part-I - Classification, Etiology, and Pathophysiology of HalitosisDocument9 pagesHalitosis - An Overview: Part-I - Classification, Etiology, and Pathophysiology of Halitosisdevi hambarwatiNo ratings yet
- Oral Complications of Cancer TreatmentDocument68 pagesOral Complications of Cancer TreatmentFarisha RasheedNo ratings yet
- Patology of LinguaDocument37 pagesPatology of LinguaVlad ScutelnicNo ratings yet
- Xerostomia Clinical Aspects and TreatmentDocument14 pagesXerostomia Clinical Aspects and TreatmentThanh Điền LưuNo ratings yet
- BMJ 10.1136/bmj.38954.631968.AE: Oral Malodour (Halitosis)Document9 pagesBMJ 10.1136/bmj.38954.631968.AE: Oral Malodour (Halitosis)Hansdika D'pabraNo ratings yet
- 53 Article XerosDocument5 pages53 Article XerosNivehthaa VisvamNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document11 pagesUntitled 1Rahul BalwanNo ratings yet
- Nasal-Paranasal Sinus Complex: Xerostomia: A Continuing Challenge For Oral Healthcare ProfessionalsDocument3 pagesNasal-Paranasal Sinus Complex: Xerostomia: A Continuing Challenge For Oral Healthcare ProfessionalsDuong LeNo ratings yet
- Article Diabetes and Dry MouthDocument2 pagesArticle Diabetes and Dry MouthKhamdaNo ratings yet
- Complications in Complete Denture: Prosthodontic 5th Class DR - Mithaq Radhi Lecture (7,8)Document4 pagesComplications in Complete Denture: Prosthodontic 5th Class DR - Mithaq Radhi Lecture (7,8)ابراهيم منعم حسينNo ratings yet
- Factors Which Complicate Impression Making PDFDocument18 pagesFactors Which Complicate Impression Making PDFMostafa FayadNo ratings yet
- StomatitisDocument17 pagesStomatitis4A - Hazel Ann G. EspinolNo ratings yet
- Dryness of Mouth, (Xerostomia) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDryness of Mouth, (Xerostomia) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine - Update For The Dental PractitionerDocument3 pagesOral Medicine - Update For The Dental PractitionerGowriNo ratings yet
- XEROSTOMIA and BIOXTRA - 2019 - ENDocument34 pagesXEROSTOMIA and BIOXTRA - 2019 - ENVu HuyenNo ratings yet
- Xerostomia Is The Medical Term For The Subjective Complaint of Dry Mouth Due To A Lack of SalivaDocument2 pagesXerostomia Is The Medical Term For The Subjective Complaint of Dry Mouth Due To A Lack of Salivaandy whiteNo ratings yet
- Salivary Gland DiseaseDocument63 pagesSalivary Gland DiseaseAnchal RainaNo ratings yet
- Mohammed 2014Document7 pagesMohammed 2014Larasati RamadianiNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Xerostomia in The Elderly PatientDocument59 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Xerostomia in The Elderly PatientDMnDLNo ratings yet
- What Is It?: HalitosisDocument6 pagesWhat Is It?: HalitosisRana SayedNo ratings yet
- EBL Case 4Document4 pagesEBL Case 4T LolaNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine - Update For The Dental PractitionerDocument3 pagesOral Medicine - Update For The Dental PractitionerMugiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Review: Oral Malodour (Halitosis)Document4 pagesClinical Review: Oral Malodour (Halitosis)Maghfira TiechaNo ratings yet
- Xerostomia in Geriatric Patients: A Burgeoning Global ConcernDocument8 pagesXerostomia in Geriatric Patients: A Burgeoning Global ConcernwhiezardNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Oral Manifestation of Sustemic DiseaseDocument43 pagesPediatric Oral Manifestation of Sustemic DiseaseMike SihombingNo ratings yet
- Oral, Git, Billiary ConditionsDocument107 pagesOral, Git, Billiary ConditionsNathaniel Mbiu TimNo ratings yet
- Xerostomia - Understanding The Diagnosis and The Treatment of Dry MouthDocument5 pagesXerostomia - Understanding The Diagnosis and The Treatment of Dry MouthferifhransNo ratings yet
- 1 Jihvaagat RogDocument13 pages1 Jihvaagat RogKnr GannuNo ratings yet
- Xerostomia & Periodontal Disease: Health Topics A-Z Healthy Living Fitness and NutritionDocument9 pagesXerostomia & Periodontal Disease: Health Topics A-Z Healthy Living Fitness and NutritionVinod S VinuNo ratings yet
- Oral Malodor: by - DR Monisha Kaushik 2Nd Yr MdsDocument55 pagesOral Malodor: by - DR Monisha Kaushik 2Nd Yr Mdsmonishakaus24No ratings yet
- Riaz Gul AHN Unit 1Document106 pagesRiaz Gul AHN Unit 1Riaz Gul RindNo ratings yet
- Oral Frictional HyperkeratosisDocument15 pagesOral Frictional HyperkeratosisFajarRahmantiyoNo ratings yet
- XEROSTOMIADocument9 pagesXEROSTOMIAsamys2ndemailNo ratings yet
- Disabilities Research PaperDocument6 pagesDisabilities Research Paperapi-742616973No ratings yet
- Halitosis: A Review of The Etiologic Factors and Association With Systemic Conditions and Its ManagementDocument6 pagesHalitosis: A Review of The Etiologic Factors and Association With Systemic Conditions and Its ManagementNadya PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Dental NursingDocument13 pagesDental NursingBéñtéñ BéñtéñNo ratings yet
- Felix2012 4Document6 pagesFelix2012 4rajesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Cara Perawatan Gigi Tiruan LepasanDocument3 pagesCara Perawatan Gigi Tiruan LepasanBayyin Bunayya CholidNo ratings yet
- Common Oral LesionsDocument13 pagesCommon Oral LesionsFaridaFoulyNo ratings yet
- Francis Rossitano Case Objectives Days 4-5: Anatomy/Histology/Physiology (DBCS)Document7 pagesFrancis Rossitano Case Objectives Days 4-5: Anatomy/Histology/Physiology (DBCS)Phil BobNo ratings yet
- Tongue Diseases NDocument46 pagesTongue Diseases NhazeemmegahedNo ratings yet
- Battling Bad Breath: Discovering An Effective Solution To An All-Too-Common Problem Profresh International CorpDocument3 pagesBattling Bad Breath: Discovering An Effective Solution To An All-Too-Common Problem Profresh International CorpGerardo MoraNo ratings yet
- Bad BreathDocument4 pagesBad BreathDaniel ParkerNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Bad Breath and Mouth DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Bad Breath and Mouth DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageRisk For InfectionRenz Carlo IllutNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Transfusi Darah 2Document11 pagesJurnal Transfusi Darah 2widiamNo ratings yet
- Ma 2021 Uveitis 101Document5 pagesMa 2021 Uveitis 101Jenny MaNo ratings yet
- English A Summary PracticeDocument2 pagesEnglish A Summary PracticeDanah SkinnerNo ratings yet
- Share 'Module - Safety and Sanitation 4-5.docx'Document24 pagesShare 'Module - Safety and Sanitation 4-5.docx'ana mejicoNo ratings yet
- Manual of Antimicrobial Stewardship (1st Edition)Document49 pagesManual of Antimicrobial Stewardship (1st Edition)Socrates AbroadNo ratings yet
- A Case of Severe Tuberculous Pericardial EffusionDocument2 pagesA Case of Severe Tuberculous Pericardial Effusionsweet hanaNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Check Your Understanding A. Use Your Notes. Answer The Questions Based On The LectureDocument2 pagesWeek 13 Check Your Understanding A. Use Your Notes. Answer The Questions Based On The LectureIrem YilmazNo ratings yet
- TBDocument5 pagesTBSuneel KumarNo ratings yet
- Philippine Handbook HIV Counseling Testing Handbook Section ThreeDocument59 pagesPhilippine Handbook HIV Counseling Testing Handbook Section Threeithran khoNo ratings yet
- DR Manish Soni: MD (Gold Medalist), IADVL Fellow (AIIMS, New Delhi) EDocument135 pagesDR Manish Soni: MD (Gold Medalist), IADVL Fellow (AIIMS, New Delhi) ESahib PathanNo ratings yet
- Treatment Guidelines For COVID-19 v6 - FINAL 14 JuneDocument36 pagesTreatment Guidelines For COVID-19 v6 - FINAL 14 JuneerikaNo ratings yet
- Yellow Card LetterDocument11 pagesYellow Card LetterJamie White100% (6)
- Pathophysiology - Chicken Pox Paper PDFDocument6 pagesPathophysiology - Chicken Pox Paper PDFRhiannon MartinNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Facts, Symptoms & TreatmentsDocument34 pagesReproductive System: Facts, Symptoms & TreatmentsJobelyn MalisaNo ratings yet
- 10.history Taking (DR - Hani)Document17 pages10.history Taking (DR - Hani)علي. احمدNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Conditions Didc ClassDocument14 pagesMetabolic Conditions Didc ClassSiddique SaandNo ratings yet
- Eczema HomeopathyDocument4 pagesEczema Homeopathyruhul72No ratings yet
- Lesson 9 & 10: A. Asking Family Sickness B. Expressions of PolitnessDocument13 pagesLesson 9 & 10: A. Asking Family Sickness B. Expressions of Politnessrani ameliaNo ratings yet
- Lyme DisorderLLDocument14 pagesLyme DisorderLLLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Philippine Pediatric Society in Cooperation With The Society of Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, PhilippinesDocument32 pagesPhilippine Pediatric Society in Cooperation With The Society of Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, PhilippinesShari TernolaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonography of The Neck: O. Taeymans, DVM, Dip ECVDIDocument73 pagesUltrasonography of The Neck: O. Taeymans, DVM, Dip ECVDIKSNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Adult ADHDDocument24 pagesAssessment of Adult ADHDPsydoc100% (4)
- PMMAEE Application FormDocument2 pagesPMMAEE Application FormLen-Len CobsilenNo ratings yet
- Stress and Mental HealthDocument2 pagesStress and Mental Healthspencer agbayaniNo ratings yet
- Common Respiratory Problems in Neonates & Infants 1Document46 pagesCommon Respiratory Problems in Neonates & Infants 1MichaelNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics KGMA February 2024Document98 pagesPediatrics KGMA February 2024abhijeets3011No ratings yet
- Homeopathy Mother Tinctures Internal and External UseDocument8 pagesHomeopathy Mother Tinctures Internal and External Useyogeshydd50% (2)
- Sample ProjectDocument9 pagesSample ProjectGrit WingsNo ratings yet