Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The IT Infrastructure Componant
The IT Infrastructure Componant
Uploaded by
prakashpatelkOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The IT Infrastructure Componant
The IT Infrastructure Componant
Uploaded by
prakashpatelkCopyright:
Available Formats
IT INFRASTRUCTURE
Set of physical devices and software required to operate enterprise IT infrastructure includes investment in hardware, software, and services Services : consulting, education, and training
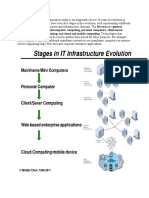
Evolution of IT infrastructure: 1950-2007
Electronic accounting machine era: 1930-1950
Specialized machines sorting computer cards, accumulating totals, printing reports
General-purpose mainframe and minicomputer era: 1959 to present
1958 IBM first mainframes introduced, eventually used to support thousands of online remote terminals 1965 less expensive DEC minicomputers introduced, allowing decentralized computing
Personal computer era: 1981 to present
1981 Introduction of IBM PC Proliferation in 80s, 90s resulted in growth of personal software Desktop clients networked to servers, with processing work split between clients and servers Network may be two-tiered or multitiered (N-tiered) Various types of servers (network, application, Web)
Client/server era: 1983 to present
Enterprise Internet computing era: 1992 to present
Move toward integrating disparate networks, applications using Internet standards and enterprise applications
IT Infrastructure components
Computer hardware platforms Computer software platforms Data management and storage Networking/ Telecommunications platforms Internet platforms Consulting and system integration services
The IT Infrastructure Ecosystem
Computer hardware platforms
Client machines Desktop PCs, mobile computing devices PDAs, laptops Servers Blade servers: ultrathin computers stored in racks Mainframes: IBM mainframe equivalent to thousands of blade servers Top chip producers: AMD, Intel, IBM Top firms: IBM, HP, Dell, Sun Microsystems
Computer software platforms
Operating systems Client level: 95% run Microsoft Windows (XP, 2000, CE, etc.) Server level: 85% run Unix or Linux
Enterprise software applications Enterprise application providers: SAP and Oracle Middleware providers: BEA
Data management and storage
Database software: IBM (DB2), Oracle, Microsoft (SQL Server), Sybase (Adaptive Server Enterprise), MySQL Physical data storage: EMC Corp (largescale systems), Seagate, Maxtor, Western Digital Storage area networks: connect multiple storage devices on dedicated network
Networking/telecommunications platforms
Telecommunication services Telecommunications, cable, telephone company charges for voice lines and Internet access MCI, AT&T, regional providers (Verizon) Network operating systems: Windows Server, Novell, Linux, Unix Network hardware providers: Cisco, Lucent, Nortel, Juniper Networks
Internet platforms
Hardware, software, management services to support company Web sites, (including Web hosting services) intranets, extranets Internet hardware server market: Dell, HP/Compaq, IBM Web development tools/suites: Microsoft (FrontPage, .NET) IBM (WebSphere) Sun (Java), independent software developers: Macromedia/Adobe, RealMedia
Consulting and system integration services
Even large firms do not have resources for full range of support for new, complex infrastructure Software integration: ensuring new infrastructure works with legacy systems Legacy systems: older TPS created for mainframes that would be too costly to replace or redesign
You might also like
- Microsoft PL-900 Exam - Questions and Answers - CertLibrary - Com-Pg1Document11 pagesMicrosoft PL-900 Exam - Questions and Answers - CertLibrary - Com-Pg1Radu Lucian Mihai0% (1)
- IT InfrastructureDocument8 pagesIT InfrastructureAkshay Mathur100% (1)
- Module 5 IT InfrastructureDocument68 pagesModule 5 IT InfrastructureAkinmulewo Ayodele50% (2)
- Introduction To Information Technology - Lecture 1 PDFDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Information Technology - Lecture 1 PDFCBAKhan75% (4)
- Handbook of Research On Digital Media andDocument771 pagesHandbook of Research On Digital Media andCIBERNONTROPPO100% (2)
- It Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesDocument53 pagesIt Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesHassan AliNo ratings yet
- IT Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies: Management Information Systems (MIS)Document17 pagesIT Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies: Management Information Systems (MIS)KillerbeeNo ratings yet
- Lec03 PDFDocument29 pagesLec03 PDFSam DariNo ratings yet
- IT InfrastructureDocument4 pagesIT InfrastructureJoy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- IT Infrastructure and EmergingDocument2 pagesIT Infrastructure and EmergingNurinda Ramadhanti PratamaNo ratings yet
- IT Concepts and Systems Analysis and Design: MCP, MCDST, MbaDocument73 pagesIT Concepts and Systems Analysis and Design: MCP, MCDST, MbaJayson AcainNo ratings yet
- Information Technology in Business: DR Hemlata GangwarDocument18 pagesInformation Technology in Business: DR Hemlata GangwarSandeep PatelNo ratings yet
- IT Infrastructure and Emerging TechDocument58 pagesIT Infrastructure and Emerging TechBima Gerry PratamaNo ratings yet
- U04 IT Infrastructure 2022 July 10 V1Document63 pagesU04 IT Infrastructure 2022 July 10 V1Noppon SETTASATIENNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document44 pagesChapter 05Joe HanNo ratings yet
- IT Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesDocument37 pagesIT Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesRhian Dennise Galanida BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- It Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies: Management Information SystemsDocument37 pagesIt Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies: Management Information SystemsShams PushanNo ratings yet
- IT InfrastructureDocument31 pagesIT InfrastructurePj Pj Pj100% (1)
- MIS Lec#4Document26 pagesMIS Lec#4جمہوری جنانNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4: It Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesDocument29 pagesLecture-4: It Infrastructure and Emerging Technologiesinsen bellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Revision InsDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Revision Ins--No ratings yet
- Dr. Samim Al Azad (SAA2) : MIS107: Computer Information SystemsDocument22 pagesDr. Samim Al Azad (SAA2) : MIS107: Computer Information SystemsGhost MailerNo ratings yet
- Session 8-9Document25 pagesSession 8-9Raveena NaiduNo ratings yet
- 2KA3 Chapter5Document62 pages2KA3 Chapter5RyanNo ratings yet
- IT InfrastructureDocument25 pagesIT InfrastructurecontactsalesuaeNo ratings yet
- Infrastucture and Emerging TechnologyDocument39 pagesInfrastucture and Emerging TechnologyAnargya Widyatama100% (1)
- Tutorial 9 AnswerDocument2 pagesTutorial 9 AnswerMEI TENG TEHNo ratings yet
- Intcom: Computer SystemDocument2 pagesIntcom: Computer SystemGenie Claire GuiuoNo ratings yet
- Yyyy y y !"y#y$# y Y!%&'yDocument7 pagesYyyy y y !"y#y$# y Y!%&'ynerdydude99No ratings yet
- Infrastructure Hardware SOFTWAREDocument40 pagesInfrastructure Hardware SOFTWAREbabyNo ratings yet
- It Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies IT InfrastructureDocument10 pagesIt Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies IT InfrastructureDIAN ARDHIANTINo ratings yet
- It InfrastructureDocument27 pagesIt InfrastructureEhtasham RazaNo ratings yet
- Presentation WPS OfficeDocument18 pagesPresentation WPS Officenajmun AlamNo ratings yet
- Platform Technologies FinalsDocument43 pagesPlatform Technologies FinalsArnel ManggaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software IT Infrastructure: Provides Platform For Supporting All Information Systems in TheDocument8 pagesChapter 4: IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software IT Infrastructure: Provides Platform For Supporting All Information Systems in TheDiep Ai NhiNo ratings yet
- Yididiya 2Document3 pagesYididiya 2Kafala LalimaNo ratings yet
- I T Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesDocument34 pagesI T Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesNavajyoti DharNo ratings yet
- Mis CH-3Document29 pagesMis CH-3Erit AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ssd2 Unit1 Computer SystemsDocument38 pagesSsd2 Unit1 Computer Systemsarman_9393No ratings yet
- Components of The Management Information System: Week.5Document21 pagesComponents of The Management Information System: Week.5Tuba MirzaNo ratings yet
- Is-Lecture 1 KKPDocument65 pagesIs-Lecture 1 KKPrahimjahan45No ratings yet
- Ch. 5 IT InfrastructureDocument22 pagesCh. 5 IT Infrastructurerahafhirzallah34No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesCloud ComputingPrashant SawnaniNo ratings yet
- Intro PPT Internet ComputingDocument23 pagesIntro PPT Internet ComputingKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- IT Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies: Cost-Effective, Efficient, Energy-Saving ComputingDocument65 pagesIT Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies: Cost-Effective, Efficient, Energy-Saving ComputingMuhamad Alvin Ariq RamadhanNo ratings yet
- By Vinay Dath .M.s ChinappaDocument16 pagesBy Vinay Dath .M.s ChinappaVinay DathNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument127 pagesIntroductionMumtaz AliNo ratings yet
- 05 Telecom MDocument27 pages05 Telecom MShukura ShuaibNo ratings yet
- IT Infrastructure and Platforms (Part I) IT Infrastructure and Platforms (Part I)Document31 pagesIT Infrastructure and Platforms (Part I) IT Infrastructure and Platforms (Part I)Umair MirzaNo ratings yet
- Network: Source DestinationDocument36 pagesNetwork: Source Destinationtriveni_palNo ratings yet
- IT Infrastructure & ComponentsDocument18 pagesIT Infrastructure & Componentsrohaibzameer001No ratings yet
- 05 TelecommDocument27 pages05 TelecommbabubmNo ratings yet
- Paul Mort ResumeDocument3 pagesPaul Mort Resumepaul5655No ratings yet
- Computer and Internet BasicsDocument51 pagesComputer and Internet Basicsromesh10008No ratings yet
- BIL101E: Linux Isn't Able To Run Microsoft ApplicationDocument4 pagesBIL101E: Linux Isn't Able To Run Microsoft ApplicationSerdarErdoğanNo ratings yet
- Living in It Era ReviewerDocument5 pagesLiving in It Era ReviewerLorenz VicenteNo ratings yet
- It InfrastructureDocument27 pagesIt InfrastructureEhtasham RazaNo ratings yet
- Parallel Scalable ModelsDocument61 pagesParallel Scalable ModelsSenthil Ganesh RNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument63 pagesInformation TechnologywahabedhiNo ratings yet
- FHSS PT 01 IntroductionDocument30 pagesFHSS PT 01 Introductionjess12castanoNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Predicate Logic-1Document70 pagesUnit 3 - Predicate Logic-1Shashank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Schrack Power PCB Relay RTH 105°C 16ADocument2 pagesSchrack Power PCB Relay RTH 105°C 16AjpbarrioNo ratings yet
- Huawei Firewall Technology BasisDocument15 pagesHuawei Firewall Technology BasisMichel HuizingNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo de Ingreso Ingles New..Document71 pagesCuadernillo de Ingreso Ingles New..Debora AzcurraNo ratings yet
- Financial Management For IT ServicesDocument10 pagesFinancial Management For IT ServicesAmeen MtNo ratings yet
- 7 JuneDocument13 pages7 Juneraj_pegasusNo ratings yet
- 415V Asb Switchboard Auto Transfer Scheme: Incomer-1 Incomer-2 Test Close Test CloseDocument2 pages415V Asb Switchboard Auto Transfer Scheme: Incomer-1 Incomer-2 Test Close Test CloseMarudavanan SomasundaramNo ratings yet
- VTL-Value: Solaris Quick Start Guide v1.3 Feb 2009Document5 pagesVTL-Value: Solaris Quick Start Guide v1.3 Feb 2009antogonisNo ratings yet
- ArchitectureDocument11 pagesArchitectureNandhanasai AletiNo ratings yet
- College Office Automation System: General ArticleDocument3 pagesCollege Office Automation System: General ArticledaniNo ratings yet
- User Guide: 300Mbps Wi-Fi Range Extender TL-WA854REDocument40 pagesUser Guide: 300Mbps Wi-Fi Range Extender TL-WA854REJohnyNo ratings yet
- InteliCharger 65 - 24 AF DatasheetDocument3 pagesInteliCharger 65 - 24 AF Datasheetjean sanchezNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual NotesDocument5 pagesSolution Manual NotesVictor Enem8% (12)
- Algorithm QuizDocument40 pagesAlgorithm QuizPronoy PronoyNo ratings yet
- CS341Tut3 PDFDocument3 pagesCS341Tut3 PDFsafSADFANo ratings yet
- Panel Data Models Stata Program and Output PDFDocument8 pagesPanel Data Models Stata Program and Output PDFcrinix7265No ratings yet
- Sage Peachtree Actian Zen V13 Support and Features LogDocument5 pagesSage Peachtree Actian Zen V13 Support and Features LogUmair AzizNo ratings yet
- Tendering For Government Contracts - A Guide For Small BusinessesDocument54 pagesTendering For Government Contracts - A Guide For Small BusinessesDavid Shanks 1No ratings yet
- Handbook For Electronic Health Records Implementation WHODocument75 pagesHandbook For Electronic Health Records Implementation WHOlaggantigganNo ratings yet
- Gmdss Tester Mrts-7 BrochureDocument2 pagesGmdss Tester Mrts-7 BrochureengrfahadkhanNo ratings yet
- Clavister Virtual CoreDocument217 pagesClavister Virtual CoreNicoleNo ratings yet
- KirbyDocument3 pagesKirbyNorhassanah UtosabuayanNo ratings yet
- BiotelemetrytelemedicineDocument57 pagesBiotelemetrytelemedicineElivongNo ratings yet
- RGX4400 User ManualDocument78 pagesRGX4400 User ManualAsriSaffuan100% (1)
- Status Profile Creation and Assignment To An Order Type in SAP PPDocument7 pagesStatus Profile Creation and Assignment To An Order Type in SAP PPHemant UNICHEMLLPNo ratings yet
- Pentium Vs 604eDocument1 pagePentium Vs 604escriNo ratings yet
- Power BiDocument198 pagesPower BidayanaNo ratings yet
- Recovering Quantitative Models of Human Information Processing With Differentiable Architecture SearchDocument8 pagesRecovering Quantitative Models of Human Information Processing With Differentiable Architecture SearchSebastian MusslickNo ratings yet