Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6 Reactions Part 2
6 Reactions Part 2
Uploaded by
gtanews321Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Cardinal 748Document47 pagesCardinal 748Juan MontufarNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Work Method Statement For Directional DrillingDocument3 pagesWork Method Statement For Directional Drillingnice hossainNo ratings yet
- Ritual of The Rose Cross (Golden Dawn)Document4 pagesRitual of The Rose Cross (Golden Dawn)solomon5678No ratings yet
- Martyrologium Lent 2012Document60 pagesMartyrologium Lent 2012Filip100% (1)
- ReactionsDocument1 pageReactionsKunle Asekunola AbiodunNo ratings yet
- Chapter2carboncompoundsasing 150401093408 Conversion Gate01Document65 pagesChapter2carboncompoundsasing 150401093408 Conversion Gate01VinnySha SelvarajahNo ratings yet
- To Quantitative ChemistryDocument37 pagesTo Quantitative ChemistryVictor GuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 CarboncompoundsDocument71 pagesChapter2 CarboncompoundsJachinta JuliusNo ratings yet
- Let's Get Started With Chemical Properties of Alkanes - 211209 - 205756Document13 pagesLet's Get Started With Chemical Properties of Alkanes - 211209 - 205756Nikhil PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Additional Slide For Periodic Table of ElementsDocument35 pagesAdditional Slide For Periodic Table of ElementsAireen rania Ahmad ramzauddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Powerpoint PresentationDocument54 pagesChapter 7 - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Powerpoint PresentationEsther SparksNo ratings yet
- c2 Paper HandoutDocument29 pagesc2 Paper HandoutmarleypootsNo ratings yet
- Endoexothermic EnergyDocument38 pagesEndoexothermic EnergyMaram GhaziNo ratings yet
- Drying, Devolatilization & Char Oxidation of Solid Fuel: Åbo Akademi 2016: Chemistry in Combustion ProcessesDocument46 pagesDrying, Devolatilization & Char Oxidation of Solid Fuel: Åbo Akademi 2016: Chemistry in Combustion ProcessesirNo ratings yet
- 4TH QTR Reviewer GchemDocument6 pages4TH QTR Reviewer Gchemmarie parfanNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument15 pagesChemJobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- Molecules, Moles and Chemical EquationsDocument73 pagesMolecules, Moles and Chemical EquationsmjNo ratings yet
- WOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, ThermochemistryDocument30 pagesWOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Thermochemistrynur asyiqinNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 3rdsem EndTerm ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenChem2 3rdsem EndTerm ReviewerJames Andre DionedaNo ratings yet
- (SCI) Chapter 18 - Chemical ChangesDocument17 pages(SCI) Chapter 18 - Chemical ChangessanNo ratings yet
- 4-More Into LawsDocument7 pages4-More Into LawsMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Chem Chap 1Document41 pagesChem Chap 1rekha.sat29No ratings yet
- Name: Doaa Nassar Grade: 9B Teacher's Name: Ms. AfshariDocument35 pagesName: Doaa Nassar Grade: 9B Teacher's Name: Ms. AfshariDoaa NassarNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument71 pages1 Introduction To Organic ChemistryAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- 2.16 Sources of Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument36 pages2.16 Sources of Alkanes and CycloalkanesjuanNo ratings yet
- BHS CSEC Grade 11 Energy EnergeticsDocument59 pagesBHS CSEC Grade 11 Energy Energeticsabigail allenNo ratings yet
- 4470 Lecture 5 2013 PDFDocument23 pages4470 Lecture 5 2013 PDFamanpreetNo ratings yet
- Masses of Atoms and Moles - Add Together The RelativeDocument2 pagesMasses of Atoms and Moles - Add Together The Relativeapi-25909541No ratings yet
- 2324 T2 Chemistry C4 Chemical ReactionsDocument66 pages2324 T2 Chemistry C4 Chemical ReactionswilsonconcepcionNo ratings yet
- Acid and BaseDocument97 pagesAcid and Basesunidojay7No ratings yet
- Organic - Chemistry - Reactions - of - Hydrocarbons 6 Per PageDocument6 pagesOrganic - Chemistry - Reactions - of - Hydrocarbons 6 Per Pagebruno de jesus fontesNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry N PolymersDocument82 pagesOrganic Chemistry N PolymersNot IsmdanNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument19 pagesCombustionZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - 1Document40 pagesChapter 4 - 1Natnael worku100% (1)
- Chemical Properties of HydrocarbonsDocument22 pagesChemical Properties of HydrocarbonsMagaNo ratings yet
- (Short Revision Notes) : ChemistryDocument7 pages(Short Revision Notes) : ChemistryApoorv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 04 Energy Triyono1Document22 pagesChapter - 04 Energy Triyono1Natasya Dwi PutriNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2022Document30 pagesThermo 2022Yaashinie Siva SankarNo ratings yet
- 9 Chemical Reactions - Kinetics, Energetics, TypesDocument21 pages9 Chemical Reactions - Kinetics, Energetics, TypesSia handaNo ratings yet
- Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsDocument18 pagesExothermic and Endothermic ReactionsGolden TrioNo ratings yet
- Annotated: Questions and Tasks For ENERGY ProfilesDocument27 pagesAnnotated: Questions and Tasks For ENERGY ProfilesD IeadsatanisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06A - Fuels and Combustion - Fall 2020Document45 pagesLecture 06A - Fuels and Combustion - Fall 2020Huraira TahirNo ratings yet
- Week-8 Material - MOOC ISWM - Thermal Treatment and Landfill Basics - WatermarkDocument26 pagesWeek-8 Material - MOOC ISWM - Thermal Treatment and Landfill Basics - WatermarkAnindita RoyNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C7Document4 pagesAQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C7josephNo ratings yet
- Comparison of 4 Thermo ExpDocument4 pagesComparison of 4 Thermo ExpSarah WongNo ratings yet
- Energy Requirement For Solvent Regeneration in CO Capture PlantsDocument32 pagesEnergy Requirement For Solvent Regeneration in CO Capture PlantsHasanah NurNo ratings yet
- Pink Doodle Project Presentation 20240515 094832 0000Document14 pagesPink Doodle Project Presentation 20240515 094832 0000deone classesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Reactions-Acid and BasesDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Reactions-Acid and BasesJenelyn Ponce AguiloNo ratings yet
- Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesIonic Compoundsapi-25909541No ratings yet
- Notes Alkanes +alkenesDocument44 pagesNotes Alkanes +alkenesLucas “Khumalo” KaunduNo ratings yet
- Chemical Level of OrganzationDocument6 pagesChemical Level of OrganzationAbby Claire SomeraNo ratings yet
- Covid ClassDocument36 pagesCovid ClassErica Nicole C. LabialNo ratings yet
- Study of Hydrogen As An Industrial Gas: Presented By: Kamran Ashraf &Document39 pagesStudy of Hydrogen As An Industrial Gas: Presented By: Kamran Ashraf &Prabhu GovindNo ratings yet
- CEM1008F Applied Solution Chemistry Part 1 2021Document29 pagesCEM1008F Applied Solution Chemistry Part 1 2021Simlindile NgobelaNo ratings yet
- Energetics 1Document53 pagesEnergetics 1anellebrown299No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument21 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsrahNo ratings yet
- WB Ans 4Document5 pagesWB Ans 4saemin203No ratings yet
- Alkanes: Butane 2-MethylpropaneDocument7 pagesAlkanes: Butane 2-MethylpropaneAyat Al KurdiNo ratings yet
- 10 EnergeticsDocument27 pages10 EnergeticsM BNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds1Document25 pagesCarbonyl Compounds1Lyana TaylorNo ratings yet
- IM Forces ApplicationDocument38 pagesIM Forces ApplicationEmilyNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Article Debate en 6 CkäDocument5 pagesArticle Debate en 6 CkäkerstinbergekNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate Cap Structure Definition, Uses, and ExamplesDocument2 pagesInterest Rate Cap Structure Definition, Uses, and ExamplesACC200 MNo ratings yet
- Understanding Leadership and Empowerment in The Workplace: Banutu-Gomez Michael BaDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Leadership and Empowerment in The Workplace: Banutu-Gomez Michael BalopmidNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra HSC Mathematics Paper 1Document18 pagesMaharashtra HSC Mathematics Paper 1YouTibeNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Human Hair As Fiber Reinforced ConcreteDocument5 pagesExperimental Study On Human Hair As Fiber Reinforced ConcreteYogendra PatilNo ratings yet
- TOS MAPEH 10-AutoRecoveredDocument4 pagesTOS MAPEH 10-AutoRecoveredAnne Kathria Bernadette GabrielNo ratings yet
- Zohdy, Eaton & Mabey - Application of Surface Geophysics To Ground-Water Investigations - USGSDocument63 pagesZohdy, Eaton & Mabey - Application of Surface Geophysics To Ground-Water Investigations - USGSSalman AkbarNo ratings yet
- A Miniaturized Dual-Band Implantable Antenna System For Medical ApplicationsDocument5 pagesA Miniaturized Dual-Band Implantable Antenna System For Medical Applicationsrajesh yadavNo ratings yet
- Nidhi Gupta Resume UpdatedDocument4 pagesNidhi Gupta Resume Updatedshannbaby22No ratings yet
- CW DramaDocument31 pagesCW DramaBurning RoseNo ratings yet
- 9 CH 1 2024-25Document12 pages9 CH 1 2024-25Muhammad Abdullah ToufiqueNo ratings yet
- DPP 2Document3 pagesDPP 2ship-wedge00No ratings yet
- Group-8 RRL Bes-107Document16 pagesGroup-8 RRL Bes-107bj30No ratings yet
- Mountain Passes of PakistanDocument3 pagesMountain Passes of PakistanMohsin Raza Maitla0% (2)
- 2003 Animal Rights AnswersDocument5 pages2003 Animal Rights AnswersVarshLokNo ratings yet
- Heri-Azalea-management of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Mandible With SegmentalDocument14 pagesHeri-Azalea-management of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Mandible With SegmentalReniza OctafianaNo ratings yet
- Coenzymes and Prosthetic GroupsDocument35 pagesCoenzymes and Prosthetic Groupsrishigangwar2No ratings yet
- Thesis Statement For A Research Paper On CareersDocument7 pagesThesis Statement For A Research Paper On Careersyscgudvnd100% (1)
- Top Survival Tips - Kevin Reeve - OnPoint Tactical PDFDocument8 pagesTop Survival Tips - Kevin Reeve - OnPoint Tactical PDFBillLudley5100% (1)
- Single Axis Solar Tracking System: (I) PurposeDocument23 pagesSingle Axis Solar Tracking System: (I) Purposeelectrical engineeringNo ratings yet
- Military Engineer Services Notice Inviting Tender (Nit)Document14 pagesMilitary Engineer Services Notice Inviting Tender (Nit)jatanNo ratings yet
- Difference of Quantitative Research and Qualitative ResearchDocument1 pageDifference of Quantitative Research and Qualitative Researchmhel vianney bariquitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Part 2) : Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachDocument25 pagesChapter 1 (Part 2) : Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachHassan RazaNo ratings yet
- A Sad Hy Arogan Ivar An A MantraDocument9 pagesA Sad Hy Arogan Ivar An A MantraKrishNo ratings yet
- Xseries Products: Precise Measurement and Automation IntelligenceDocument12 pagesXseries Products: Precise Measurement and Automation IntelligenceRoger GracieNo ratings yet
- Oleh: Riris Retno Wulan, Mochammad MustamDocument20 pagesOleh: Riris Retno Wulan, Mochammad MustamMario100% (1)
6 Reactions Part 2
6 Reactions Part 2
Uploaded by
gtanews321Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6 Reactions Part 2
6 Reactions Part 2
Uploaded by
gtanews321Copyright:
Available Formats
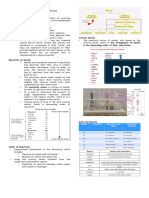
6 Reactions 2: How are chemical products
different from reactants?
Chemical reactions Combustion Thermal decomposition
• Word equations can represent a chemical reaction: • Combustion is the burning of a fuel in oxygen • A thermal decomposition reaction is one where the reactants are
• A fuel is a substance which stores energy in a chemical store broken down (decomposition) using heat (thermal energy)
O
H H O • Examples of fuels include petrol, diesel, coal and hydrogen • An example of this is with metal carbonates:
H H
C O O C O
+ + • When a carbon based fuel undergoes combustion, it will produce water zinc carbonate ➞ zinc oxide + carbon dioxide
H H O O O
carbon dioxide and carbon dioxide • We can test for this carbon dioxide clamp
methane H H
oxygen by bubbling the gas through
water methane + oxygen ➞ carbon dioxide + water
limewater, if the limewater turns
• The reactants are on the left side of the arrow and the cloudy, the gas is carbon dioxide
products are on the right side of the arrow • Hydrogen can also be used as a fuel, this is much better than traditional metal
carbonate limewater
• We use an arrow instead of an equals sign as it represents fossil fuels as it does not produce carbon dioxide:
that the reactants are changing into a new substance hydrogen + oxygen ➞ water bunsen burner
• In a reaction, the amount of each type of atom stays the
same, however they are rearranged to form a new
product Exothermic and endothermic reactions
Exothermic reactions involve a transfer of energy exothermic Endothermic reactions involve a transfer of energy endothermic
Conservation of mass from the reactants to the surroundings from the surroundings to the reactants
• In a reaction the mass will be conserved, this means that • As energy is transferred to the surroundings this • As energy is taken into the reactants a decrease
the total mass of the reactants will be equal to the total will show an increase in temperature in temperature will be shown
mass of the products • Examples of exothermic reactions include • Examples of endothermic reactions include thermal
• If it appears that some of the mass has been lost, this combustion, freezing, and condensing energy decomposition, melting, and boiling energy
means that a gas has been produced and escaped, given out taken in
accounting for the lost mass
+ + Energy level diagrams Bond energies
10 g 10 g 8g 12 g Energy level diagrams show the values of energy between the reactants and • Energy must be used to break chemical bonds, meaning that this
the products in a reaction reaction is endothermic
20 g 20g • If the energy is greater in the reactants than the products then the reaction is • Energy is given out when chemical bonds are made, meaning that
exothermic as energy has been given out to the surroundings this reaction is exothermic
• If the energy is lower in the reactants than the products then the reaction is • To see if a reaction is endothermic or exothermic, you must find the
Balanced symbol equations show the amounts of all of the endothermic as energy has been taken in from the surroundings difference in the energy needed to break and to make the bonds in
individual atoms in a reaction the reaction
• The symbols used are from the Periodic Table products • If the energy needed to break the bonds is less than the energy
reactants
• They also show: given out when making the bonds, the reaction is exothermic
energ
energ
• Formulae of reactants and products energy transfer energy transfer • If the energy needed to break the bonds is more than the energy
y
released when making the bonds, the reaction is endothermic
y
• How the atoms are rearranged reactants
products
• Relative amounts of reactants and products
2H2 + O2 ➞ 2H2O progress of reaction progress of the reaction
Exothermic Endothermic
Key Make sure you can write definitions for these key terms.
terms
balanced symbol equation chemical reaction combustion conserved conservation of mass decomposition fuel
chemical bond endothermic
energy level diagram exothermic products reactants thermal
decomposition
840824_AQA_Activate_Book2.indd 7 10/04/20 10:47 AM
You might also like
- Cardinal 748Document47 pagesCardinal 748Juan MontufarNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Work Method Statement For Directional DrillingDocument3 pagesWork Method Statement For Directional Drillingnice hossainNo ratings yet
- Ritual of The Rose Cross (Golden Dawn)Document4 pagesRitual of The Rose Cross (Golden Dawn)solomon5678No ratings yet
- Martyrologium Lent 2012Document60 pagesMartyrologium Lent 2012Filip100% (1)
- ReactionsDocument1 pageReactionsKunle Asekunola AbiodunNo ratings yet
- Chapter2carboncompoundsasing 150401093408 Conversion Gate01Document65 pagesChapter2carboncompoundsasing 150401093408 Conversion Gate01VinnySha SelvarajahNo ratings yet
- To Quantitative ChemistryDocument37 pagesTo Quantitative ChemistryVictor GuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 CarboncompoundsDocument71 pagesChapter2 CarboncompoundsJachinta JuliusNo ratings yet
- Let's Get Started With Chemical Properties of Alkanes - 211209 - 205756Document13 pagesLet's Get Started With Chemical Properties of Alkanes - 211209 - 205756Nikhil PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Additional Slide For Periodic Table of ElementsDocument35 pagesAdditional Slide For Periodic Table of ElementsAireen rania Ahmad ramzauddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Powerpoint PresentationDocument54 pagesChapter 7 - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Powerpoint PresentationEsther SparksNo ratings yet
- c2 Paper HandoutDocument29 pagesc2 Paper HandoutmarleypootsNo ratings yet
- Endoexothermic EnergyDocument38 pagesEndoexothermic EnergyMaram GhaziNo ratings yet
- Drying, Devolatilization & Char Oxidation of Solid Fuel: Åbo Akademi 2016: Chemistry in Combustion ProcessesDocument46 pagesDrying, Devolatilization & Char Oxidation of Solid Fuel: Åbo Akademi 2016: Chemistry in Combustion ProcessesirNo ratings yet
- 4TH QTR Reviewer GchemDocument6 pages4TH QTR Reviewer Gchemmarie parfanNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument15 pagesChemJobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- Molecules, Moles and Chemical EquationsDocument73 pagesMolecules, Moles and Chemical EquationsmjNo ratings yet
- WOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, ThermochemistryDocument30 pagesWOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Thermochemistrynur asyiqinNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 3rdsem EndTerm ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenChem2 3rdsem EndTerm ReviewerJames Andre DionedaNo ratings yet
- (SCI) Chapter 18 - Chemical ChangesDocument17 pages(SCI) Chapter 18 - Chemical ChangessanNo ratings yet
- 4-More Into LawsDocument7 pages4-More Into LawsMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Chem Chap 1Document41 pagesChem Chap 1rekha.sat29No ratings yet
- Name: Doaa Nassar Grade: 9B Teacher's Name: Ms. AfshariDocument35 pagesName: Doaa Nassar Grade: 9B Teacher's Name: Ms. AfshariDoaa NassarNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument71 pages1 Introduction To Organic ChemistryAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- 2.16 Sources of Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument36 pages2.16 Sources of Alkanes and CycloalkanesjuanNo ratings yet
- BHS CSEC Grade 11 Energy EnergeticsDocument59 pagesBHS CSEC Grade 11 Energy Energeticsabigail allenNo ratings yet
- 4470 Lecture 5 2013 PDFDocument23 pages4470 Lecture 5 2013 PDFamanpreetNo ratings yet
- Masses of Atoms and Moles - Add Together The RelativeDocument2 pagesMasses of Atoms and Moles - Add Together The Relativeapi-25909541No ratings yet
- 2324 T2 Chemistry C4 Chemical ReactionsDocument66 pages2324 T2 Chemistry C4 Chemical ReactionswilsonconcepcionNo ratings yet
- Acid and BaseDocument97 pagesAcid and Basesunidojay7No ratings yet
- Organic - Chemistry - Reactions - of - Hydrocarbons 6 Per PageDocument6 pagesOrganic - Chemistry - Reactions - of - Hydrocarbons 6 Per Pagebruno de jesus fontesNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry N PolymersDocument82 pagesOrganic Chemistry N PolymersNot IsmdanNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument19 pagesCombustionZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - 1Document40 pagesChapter 4 - 1Natnael worku100% (1)
- Chemical Properties of HydrocarbonsDocument22 pagesChemical Properties of HydrocarbonsMagaNo ratings yet
- (Short Revision Notes) : ChemistryDocument7 pages(Short Revision Notes) : ChemistryApoorv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 04 Energy Triyono1Document22 pagesChapter - 04 Energy Triyono1Natasya Dwi PutriNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2022Document30 pagesThermo 2022Yaashinie Siva SankarNo ratings yet
- 9 Chemical Reactions - Kinetics, Energetics, TypesDocument21 pages9 Chemical Reactions - Kinetics, Energetics, TypesSia handaNo ratings yet
- Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsDocument18 pagesExothermic and Endothermic ReactionsGolden TrioNo ratings yet
- Annotated: Questions and Tasks For ENERGY ProfilesDocument27 pagesAnnotated: Questions and Tasks For ENERGY ProfilesD IeadsatanisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06A - Fuels and Combustion - Fall 2020Document45 pagesLecture 06A - Fuels and Combustion - Fall 2020Huraira TahirNo ratings yet
- Week-8 Material - MOOC ISWM - Thermal Treatment and Landfill Basics - WatermarkDocument26 pagesWeek-8 Material - MOOC ISWM - Thermal Treatment and Landfill Basics - WatermarkAnindita RoyNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C7Document4 pagesAQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C7josephNo ratings yet
- Comparison of 4 Thermo ExpDocument4 pagesComparison of 4 Thermo ExpSarah WongNo ratings yet
- Energy Requirement For Solvent Regeneration in CO Capture PlantsDocument32 pagesEnergy Requirement For Solvent Regeneration in CO Capture PlantsHasanah NurNo ratings yet
- Pink Doodle Project Presentation 20240515 094832 0000Document14 pagesPink Doodle Project Presentation 20240515 094832 0000deone classesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Reactions-Acid and BasesDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Reactions-Acid and BasesJenelyn Ponce AguiloNo ratings yet
- Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesIonic Compoundsapi-25909541No ratings yet
- Notes Alkanes +alkenesDocument44 pagesNotes Alkanes +alkenesLucas “Khumalo” KaunduNo ratings yet
- Chemical Level of OrganzationDocument6 pagesChemical Level of OrganzationAbby Claire SomeraNo ratings yet
- Covid ClassDocument36 pagesCovid ClassErica Nicole C. LabialNo ratings yet
- Study of Hydrogen As An Industrial Gas: Presented By: Kamran Ashraf &Document39 pagesStudy of Hydrogen As An Industrial Gas: Presented By: Kamran Ashraf &Prabhu GovindNo ratings yet
- CEM1008F Applied Solution Chemistry Part 1 2021Document29 pagesCEM1008F Applied Solution Chemistry Part 1 2021Simlindile NgobelaNo ratings yet
- Energetics 1Document53 pagesEnergetics 1anellebrown299No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument21 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsrahNo ratings yet
- WB Ans 4Document5 pagesWB Ans 4saemin203No ratings yet
- Alkanes: Butane 2-MethylpropaneDocument7 pagesAlkanes: Butane 2-MethylpropaneAyat Al KurdiNo ratings yet
- 10 EnergeticsDocument27 pages10 EnergeticsM BNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds1Document25 pagesCarbonyl Compounds1Lyana TaylorNo ratings yet
- IM Forces ApplicationDocument38 pagesIM Forces ApplicationEmilyNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Article Debate en 6 CkäDocument5 pagesArticle Debate en 6 CkäkerstinbergekNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate Cap Structure Definition, Uses, and ExamplesDocument2 pagesInterest Rate Cap Structure Definition, Uses, and ExamplesACC200 MNo ratings yet
- Understanding Leadership and Empowerment in The Workplace: Banutu-Gomez Michael BaDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Leadership and Empowerment in The Workplace: Banutu-Gomez Michael BalopmidNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra HSC Mathematics Paper 1Document18 pagesMaharashtra HSC Mathematics Paper 1YouTibeNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Human Hair As Fiber Reinforced ConcreteDocument5 pagesExperimental Study On Human Hair As Fiber Reinforced ConcreteYogendra PatilNo ratings yet
- TOS MAPEH 10-AutoRecoveredDocument4 pagesTOS MAPEH 10-AutoRecoveredAnne Kathria Bernadette GabrielNo ratings yet
- Zohdy, Eaton & Mabey - Application of Surface Geophysics To Ground-Water Investigations - USGSDocument63 pagesZohdy, Eaton & Mabey - Application of Surface Geophysics To Ground-Water Investigations - USGSSalman AkbarNo ratings yet
- A Miniaturized Dual-Band Implantable Antenna System For Medical ApplicationsDocument5 pagesA Miniaturized Dual-Band Implantable Antenna System For Medical Applicationsrajesh yadavNo ratings yet
- Nidhi Gupta Resume UpdatedDocument4 pagesNidhi Gupta Resume Updatedshannbaby22No ratings yet
- CW DramaDocument31 pagesCW DramaBurning RoseNo ratings yet
- 9 CH 1 2024-25Document12 pages9 CH 1 2024-25Muhammad Abdullah ToufiqueNo ratings yet
- DPP 2Document3 pagesDPP 2ship-wedge00No ratings yet
- Group-8 RRL Bes-107Document16 pagesGroup-8 RRL Bes-107bj30No ratings yet
- Mountain Passes of PakistanDocument3 pagesMountain Passes of PakistanMohsin Raza Maitla0% (2)
- 2003 Animal Rights AnswersDocument5 pages2003 Animal Rights AnswersVarshLokNo ratings yet
- Heri-Azalea-management of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Mandible With SegmentalDocument14 pagesHeri-Azalea-management of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Mandible With SegmentalReniza OctafianaNo ratings yet
- Coenzymes and Prosthetic GroupsDocument35 pagesCoenzymes and Prosthetic Groupsrishigangwar2No ratings yet
- Thesis Statement For A Research Paper On CareersDocument7 pagesThesis Statement For A Research Paper On Careersyscgudvnd100% (1)
- Top Survival Tips - Kevin Reeve - OnPoint Tactical PDFDocument8 pagesTop Survival Tips - Kevin Reeve - OnPoint Tactical PDFBillLudley5100% (1)
- Single Axis Solar Tracking System: (I) PurposeDocument23 pagesSingle Axis Solar Tracking System: (I) Purposeelectrical engineeringNo ratings yet
- Military Engineer Services Notice Inviting Tender (Nit)Document14 pagesMilitary Engineer Services Notice Inviting Tender (Nit)jatanNo ratings yet
- Difference of Quantitative Research and Qualitative ResearchDocument1 pageDifference of Quantitative Research and Qualitative Researchmhel vianney bariquitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Part 2) : Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachDocument25 pagesChapter 1 (Part 2) : Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachHassan RazaNo ratings yet
- A Sad Hy Arogan Ivar An A MantraDocument9 pagesA Sad Hy Arogan Ivar An A MantraKrishNo ratings yet
- Xseries Products: Precise Measurement and Automation IntelligenceDocument12 pagesXseries Products: Precise Measurement and Automation IntelligenceRoger GracieNo ratings yet
- Oleh: Riris Retno Wulan, Mochammad MustamDocument20 pagesOleh: Riris Retno Wulan, Mochammad MustamMario100% (1)