Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Core Network CS Call Flow
Core Network CS Call Flow
Uploaded by
Sohaib Delloul0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesCore Network CS Call Flow
Core Network CS Call Flow
Uploaded by
Sohaib DelloulCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
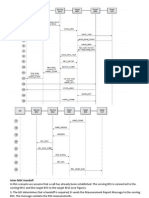
3G-UMTS Call Flow (Originating Call)
Mobile Originating (MO) Call Flow in 3G
Call Initiation:
The user dials a number on the mobile station (MS) and presses the call button.
The MS sends a Channel Request message to the Node B via the RNC (Radio Network Controller).
Radio Resource Allocation:
The Node B allocates a dedicated channel for the call and informs the MS through an Immediate Assignment message.
Call Setup Request:
The MS sends a Call Setup Request to the RNC, which then forwards it to the MSC (Mobile Switching Center).
Authentication:
The MSC initiates the authentication process, involving the MS and the HLR (Home Location Register).
The MS is authenticated using an algorithm and authentication vectors received from the HLR.
Ciphering:
Once authenticated, the MSC initiates ciphering to secure the communication channel.
The MS and MSC exchange ciphering keys and start encrypted communication.
Mobile Station Classmark Update:
The MS sends its capabilities (e.g., LAI, PLMN identity, Mobile Country Code (MCC), Mobile Network Code (MNC), Global
RNC-ID, IMSI, Mobile Station Classmark) to the MSC.
Assignment Request:
The MSC requests the RNC to establish a dedicated connection for the call.
Call Setup:
The MSC sets up the call and sends a Setup message to the called party’s MSC (if the called party is in a different network).
Routing Information:
The called party’s MSC queries its HLR to retrieve the called party’s location and routing information.
Paging:
The called party’s MSC sends a Paging message to the called party’s RNC, which then forwards it to the called party’s MS.
Call Confirmation:
The called party’s MS responds with a Page Response.
The called party’s MSC informs the calling party’s MSC that the called party is available.
Alerting:
The called party’s MS starts ringing, and an Alerting message is sent back to the calling party’s MSC, which forwards it to the
calling party’s MS.
Call Acceptance:
The called party answers the call, sending a Connect message to its MSC.
The Connect message is forwarded to the calling party’s MSC and then to the calling party’s MS.
Communication:
A voice path is established between the calling and called parties, allowing them to communicate.
Call Termination:
Either party can end the call by sending a Disconnect message.
The MSCs and RNCs release the dedicated channels and resources.
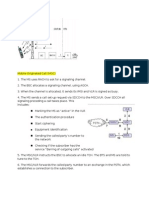
Mobile Terminating (MT) Call Flow in 3G
Incoming Call:
A call is initiated from an external network (e.g., PSTN) to a mobile subscriber.
The external network sends the call to the GMSC (Gateway MSC) of the mobile network.
HLR Query:
The GMSC queries the HLR to get the MSRN (Mobile Station Roaming Number) of the called party.
Routing:
The HLR provides the MSRN, which is used to route the call to the MSC where the called party is currently located.
Call Setup:
The serving MSC receives the call and sends a Paging message to the RNC to locate the called party’s MS.
Paging:
The RNC forwards the Paging message to the Node B, which broadcasts the paging message to the called party’s MS.
Page Response:
The called party’s MS responds with a Page Response, which is sent to the MSC via the RNC.
Call Setup Request:
The MSC sends a Call Setup message to the called party’s MS through the RNC and Node B.
Alerting:
The called party’s MS starts ringing and sends an Alerting message back to the MSC, which forwards it to the GMSC and then
to the calling party.
Call Acceptance:
The called party answers the call by sending a Connect message to the MSC.
The Connect message is forwarded to the calling party through the GMSC.
Communication:
A voice path is established, and both parties can communicate.
Call Termination:
Either party can end the call by sending a Disconnect message.
The MSC releases the resources and informs the RNC to release the radio resources.
You might also like
- Dial Plan and Call Routing Demystified On Cisco Collaboration Technologies: Cisco Unified Communication ManagerFrom EverandDial Plan and Call Routing Demystified On Cisco Collaboration Technologies: Cisco Unified Communication ManagerNo ratings yet
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationFrom EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Call Setup 2gDocument8 pagesCall Setup 2gيوسف منير محمد سعيدNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabFrom EverandSimulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- How To Connect MyPBX To TA FXO Gateway enDocument12 pagesHow To Connect MyPBX To TA FXO Gateway endodikNo ratings yet
- Call FlowsDocument14 pagesCall FlowsSandeep Reddy VajralaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Typical Call Flow in GSMDocument5 pagesSubmitted By: Typical Call Flow in GSMKiramat AzizNo ratings yet
- Mobile Originated Call and Mobile Terminated Call in GSMDocument10 pagesMobile Originated Call and Mobile Terminated Call in GSMPierreNo ratings yet
- Call From PSTN To MSDocument4 pagesCall From PSTN To MSnagendra_badamNo ratings yet
- Localization and Calling: Mobile Station International ISDN Number (MSISDN) : The Only Important NumberDocument3 pagesLocalization and Calling: Mobile Station International ISDN Number (MSISDN) : The Only Important NumberHarish SarkiNo ratings yet
- Localization and Calling: Mobile Station International ISDN Number (MSISDN) : The Only Important NumberDocument3 pagesLocalization and Calling: Mobile Station International ISDN Number (MSISDN) : The Only Important NumberHarish SarkiNo ratings yet
- GSM - SMS - Call Flow BasicsDocument7 pagesGSM - SMS - Call Flow BasicsAntony Jeba ValanNo ratings yet
- Call Flow To Simplest)Document2 pagesCall Flow To Simplest)gagan_555No ratings yet
- GSM Call FlowDocument2 pagesGSM Call Flownagendra_badamNo ratings yet
- Call Processing in GSMDocument9 pagesCall Processing in GSMjb1929835No ratings yet
- Flow Part6Document9 pagesFlow Part6Kedir HassenNo ratings yet
- Call Flow - Part5Document9 pagesCall Flow - Part5Kedir HassenNo ratings yet
- GSM Call SetupDocument6 pagesGSM Call SetupArockiaruby RubyNo ratings yet
- FLOW TELCO RevDocument3 pagesFLOW TELCO RevBurhan 'benny' RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Mobile Networks Assignment - MO - MTDocument7 pagesMobile Networks Assignment - MO - MTEkansh SelfStudyNo ratings yet
- The Typical Signaling Sequences Shows The Following FeaturesDocument5 pagesThe Typical Signaling Sequences Shows The Following FeaturesishitaNo ratings yet
- CCC C: VLR HLR AUC EIR MSC BTS BSC SCP SDP SSF SMSC MMSC Ussd Gprs Edge SGSN GGSN HSCSD IVRDocument4 pagesCCC C: VLR HLR AUC EIR MSC BTS BSC SCP SDP SSF SMSC MMSC Ussd Gprs Edge SGSN GGSN HSCSD IVRBahi HassanNo ratings yet
- Inter MSC HandoffDocument2 pagesInter MSC HandoffMrinal MondalNo ratings yet
- Basiccall Flow Part 2Document14 pagesBasiccall Flow Part 2Sneha JohnNo ratings yet
- Mobile Terminating Call Establishment Procedure in GSM: Routing Number)Document1 pageMobile Terminating Call Establishment Procedure in GSM: Routing Number)nilanshumanasNo ratings yet
- 3G Call Flow VoiceDocument2 pages3G Call Flow VoiceavinashsrinNo ratings yet
- Call Processing PDocument7 pagesCall Processing PSarika JhaNo ratings yet
- 2g-Call FlowDocument2 pages2g-Call FlowGhazwan Salih100% (3)
- GSM Mobile Terminated CallDocument2 pagesGSM Mobile Terminated CallE-Trần CmNo ratings yet
- GSM Mobile Originating Call: Request AccessDocument19 pagesGSM Mobile Originating Call: Request AccessAmit DevNo ratings yet
- SMS1 FlowDocument42 pagesSMS1 FlowIsmail Diallo100% (1)
- Moc MTCDocument3 pagesMoc MTCRaju_RNO EnggNo ratings yet
- Call ProcessingDocument25 pagesCall ProcessingFaizan KaziNo ratings yet
- Call FlowDocument4 pagesCall FlowSarwar Pasha MohammedNo ratings yet
- Messages TracingDocument8 pagesMessages Tracingnale_2No ratings yet
- GSMDocument59 pagesGSMArun Kumar0% (1)
- WC - Unit 5Document18 pagesWC - Unit 5Gopalakrishna Murthy C R100% (1)
- Mobile Phone To Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)Document1 pageMobile Phone To Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)bkvuvce8170No ratings yet
- Call FlowsDocument12 pagesCall FlowsRiyas MohamedNo ratings yet
- Call ScenarioDocument8 pagesCall Scenariomishrasaroj05No ratings yet
- GSM Call FlowsDocument59 pagesGSM Call FlowsJalal AldamaniNo ratings yet
- Vi. Call Setupphase W Ith Ms Routinganalysis, Paging, Auc, Ciphering, Eqptvalidation: OverDocument8 pagesVi. Call Setupphase W Ith Ms Routinganalysis, Paging, Auc, Ciphering, Eqptvalidation: OversudheermuthyalaNo ratings yet
- GSM Call FlowDocument3 pagesGSM Call FlowBijaya RanaNo ratings yet
- Signal TracingDocument17 pagesSignal TracingmadhunathNo ratings yet
- GSM Inter MSC Handover Call FlowDocument4 pagesGSM Inter MSC Handover Call FlowPravin YarolkarNo ratings yet
- Request Access: Cipher Mode Command MessageDocument5 pagesRequest Access: Cipher Mode Command Messageangga measNo ratings yet
- GSM Call FlowDocument3 pagesGSM Call Flowsunilchhoker11No ratings yet
- GSM Call Processing: Source: InternetDocument11 pagesGSM Call Processing: Source: InternetAditya RanjanNo ratings yet
- GSM SystSurv.Document71 pagesGSM SystSurv.Marius FerdyNo ratings yet
- Mid Term PresentationDocument25 pagesMid Term PresentationAastha BhandariNo ratings yet
- Mobile Call - 2Document30 pagesMobile Call - 2eva sharmaNo ratings yet
- GSM Call Processing and Its Security FeaturesDocument15 pagesGSM Call Processing and Its Security Featuresnaveenarora1991No ratings yet
- Call SignalingDocument9 pagesCall SignalingKedir HassenNo ratings yet
- Summary of Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Olaoluwa Osuntokun & René Pickhardt's Mastering the Lightning NetworkFrom EverandSummary of Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Olaoluwa Osuntokun & René Pickhardt's Mastering the Lightning NetworkNo ratings yet
- CISA EXAM-Testing Concept-Digital SignatureFrom EverandCISA EXAM-Testing Concept-Digital SignatureRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- 01-02 Basic Configurations CommandsDocument589 pages01-02 Basic Configurations CommandsKiKi MaNo ratings yet
- Guía de Usuario RTMS Modelo ECHODocument90 pagesGuía de Usuario RTMS Modelo ECHOgerardo.bastarNo ratings yet
- PCNSA Exam - Free Questions and Answers - ITExams - Com-15Document2 pagesPCNSA Exam - Free Questions and Answers - ITExams - Com-15amrulariffi.mppuitmsaNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Deployment in Office 365 - Checklist and Pre Requirements - Part 2 of 3Document32 pagesHybrid Deployment in Office 365 - Checklist and Pre Requirements - Part 2 of 3Eyal Doron100% (2)
- Manual Sm3 Sm5 EspañolDocument55 pagesManual Sm3 Sm5 EspañolAlejandro Oxala MederoNo ratings yet
- Ic-7851 LTDocument8 pagesIc-7851 LTandreastqNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Spectrum AnalysisDocument207 pagesFundamentals of Spectrum AnalysisGüneş ÇağlaNo ratings yet
- SnaKe CookiesDocument12 pagesSnaKe CookiesMartim SilvaNo ratings yet
- Implementing DLMS/COSEM in Smart Meters in Smart Meters: Gordan Štruklec Joško MaršićDocument14 pagesImplementing DLMS/COSEM in Smart Meters in Smart Meters: Gordan Štruklec Joško MaršićRIZ100% (1)
- B-63644en 02-03 01 PDFDocument22 pagesB-63644en 02-03 01 PDFСергей ИвановNo ratings yet
- TS90Document2 pagesTS90rajnarayan mishraNo ratings yet
- Networking Terms and DefinitionsDocument8 pagesNetworking Terms and DefinitionskgNo ratings yet
- Reliance Marketing ProjectDocument88 pagesReliance Marketing ProjectAnanyaa91% (11)
- Image Encryption and Decryption Using Aes AlgorithmDocument7 pagesImage Encryption and Decryption Using Aes AlgorithmIAEME Publication100% (5)
- Public Examination Schedule (BPUT)Document2 pagesPublic Examination Schedule (BPUT)ManishNo ratings yet
- Nokia Flexi EDGE Base Station DatasheetDocument6 pagesNokia Flexi EDGE Base Station Datasheetrogeriomb1972No ratings yet
- Integrated Device Technology - Timing SolutionsDocument63 pagesIntegrated Device Technology - Timing SolutionsIntegrated Device Technology (IDT)No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Ecom MCQDocument4 pagesUnit 4 Ecom MCQvishal GAYNo ratings yet
- Fiber-Optic Technologies - A Brief History of Fiber-Optic Communications PDFDocument17 pagesFiber-Optic Technologies - A Brief History of Fiber-Optic Communications PDFNhat Khanh BuiNo ratings yet
- 102 221 - UICC - v590Document125 pages102 221 - UICC - v590雷嘉慶No ratings yet
- 35 - Final Review Q and ADocument10 pages35 - Final Review Q and AHussein DahirNo ratings yet
- CNS Lab Manual 2019 Course - UpdatedDocument96 pagesCNS Lab Manual 2019 Course - Updatedswapnil khandareNo ratings yet
- Convergence of Voice, Video, and DataDocument40 pagesConvergence of Voice, Video, and DataFrancisco Gonzalez PachecoNo ratings yet
- Huawei SingleRAN IP Migration SolutionDocument24 pagesHuawei SingleRAN IP Migration SolutionHazem Maher100% (1)
- VoIP in RouterOS PDFDocument15 pagesVoIP in RouterOS PDFNaz LunNo ratings yet
- Please Note That Cypress Is An Infineon Technologies CompanyDocument14 pagesPlease Note That Cypress Is An Infineon Technologies CompanyPhú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument13 pagesCyber SecurityHardik AgravattNo ratings yet
- E411 - Host Interface Manual - v2.3 PDFDocument63 pagesE411 - Host Interface Manual - v2.3 PDFIvanildo JuniorNo ratings yet
- WhoisDocument3 pagesWhoisAnon13No ratings yet