Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsSpiro Meter
Spiro Meter
Uploaded by
aboosh1699Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Enron Case StudyDocument3 pagesEnron Case StudycharleejaiNo ratings yet
- Grady McMurtry The Millenial Glow Myth and Magic in The Marxist Ethics V 1.0.5 PDFDocument130 pagesGrady McMurtry The Millenial Glow Myth and Magic in The Marxist Ethics V 1.0.5 PDFMoreno KrvavacNo ratings yet
- Biology IIRespiratory SystemDocument28 pagesBiology IIRespiratory SystemSustiguer Estelle FaithNo ratings yet
- Lung Volume & CapacitiesDocument32 pagesLung Volume & CapacitiesGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Volumes: - Used To Assess A Person's Respiratory StatusDocument8 pagesRespiratory Volumes: - Used To Assess A Person's Respiratory StatusMohammed Qasim Al-WataryNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument34 pagesRespiratory Systemrenzvalorant28No ratings yet
- Lab 07 Respiratory SystemsDocument5 pagesLab 07 Respiratory SystemsameeschwittersNo ratings yet
- Lung VolumesDocument4 pagesLung VolumesLdv1 1No ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestDocument34 pagesPulmonary Function TestmukeshmscNo ratings yet
- Practical PhysiologyDocument14 pagesPractical PhysiologyOmar AymanNo ratings yet
- 1.lung Volume and CapacityDocument3 pages1.lung Volume and CapacityDr. K. YAMUNA DEVI Asst.Prof-BME DeptNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and Capacities Tutorial 2010ghgDocument17 pagesLung Volumes and Capacities Tutorial 2010ghgKelvinNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument15 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesIrfanNo ratings yet
- Bio20 - Unit D - 12 - Notes - SpirometerDocument10 pagesBio20 - Unit D - 12 - Notes - SpirometerJhalak GargNo ratings yet
- Spirometry RV and RCDocument19 pagesSpirometry RV and RCMâřâh MöHămmădNo ratings yet
- 3 Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument20 pages3 Lung Volumes and CapacitiesNimra TariqNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Respiration IIIDocument13 pagesBreathing and Respiration IIIAshrith KumarNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument2 pagesLung Volumes and Capacitiesclaribel0303No ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument16 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesMoses DumbuyaNo ratings yet
- CHECK HALF Respiratory Volumes and CapacitiesDocument4 pagesCHECK HALF Respiratory Volumes and CapacitiesRoss GellerNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument13 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesTanmayee MuppaneniNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Volumes and CapacitiesDocument34 pagesPulmonary Volumes and Capacitiesahang.aliNo ratings yet
- Practical Physiology RRS ResDocument9 pagesPractical Physiology RRS Resmina mounirNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument41 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gases538 varsha vishnoiNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Respiratory System (Spirometry)Document20 pagesPhysiology of The Respiratory System (Spirometry)Frances de JesusNo ratings yet
- Assigment of PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAssigment of Physiologyabdirizak Haji MohammedNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION PHYSIOLOGY Sept 2022 IntakeDocument94 pagesRESPIRATION PHYSIOLOGY Sept 2022 IntakeKing kakaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Tests - DR MoiseDocument39 pagesPulmonary Function Tests - DR MoisemathemoisemedNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الجاهزة 4،5 فسيو بلك التنفسيDocument43 pagesالمحاضرة الجاهزة 4،5 فسيو بلك التنفسيbessan alfqeatNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes: Navigation SearchDocument8 pagesLung Volumes: Navigation SearchAisha AlderNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Volumes Capacities and Lung DiseasesDocument14 pagesRespiratory Volumes Capacities and Lung DiseasesRoss GellerNo ratings yet
- Physiology-2 by Ahmed AboulyazeedDocument20 pagesPhysiology-2 by Ahmed AboulyazeedMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Lung Volume and CapacityDocument13 pagesLung Volume and CapacityPlzstudylav SyedNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology: Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument35 pagesRespiratory Physiology: Lung Volumes and CapacitiesNur Faizah Ahmad AriffNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestDocument24 pagesPulmonary Function Testfkrishna445No ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument3 pagesRespiration Noteseshoukat353No ratings yet
- Lung Volumes Alveolar VentilationDocument30 pagesLung Volumes Alveolar Ventilationz nameNo ratings yet
- Physiology AsignmentDocument5 pagesPhysiology AsignmentAnasAbdelaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Volumes & CapacitiesDocument13 pagesRespiratory Volumes & CapacitiesharshabhuvanmahendranNo ratings yet
- Lung Vol, Capacity and BMRDocument24 pagesLung Vol, Capacity and BMRMAKHANANI CHAUKENo ratings yet
- 1 Pulmonary Diagnostic and Therapeutic Interventions - First-1Document27 pages1 Pulmonary Diagnostic and Therapeutic Interventions - First-1Zohour AlowisyNo ratings yet
- L - 2 Physiology of Respiration IIDocument25 pagesL - 2 Physiology of Respiration IIkaukab azimNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFT)Document30 pagesPulmonary Function Tests (PFT)براءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Lung Volume and CapacitiesDocument14 pagesLung Volume and CapacitiesAhmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument24 pagesPulmonary Function TestsAman UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 CPPTDocument27 pagesLecture 1 CPPTDr. Rabail MalikNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument27 pagesRespiratory SystemMartin OrtillanaNo ratings yet
- DR - Hari Singh Gour Vishwavidyalaya: Department of Pharmaceutical SciencesDocument32 pagesDR - Hari Singh Gour Vishwavidyalaya: Department of Pharmaceutical SciencesNiyati GuptaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PhysiologyDocument11 pagesRespiratory PhysiologywalterNo ratings yet
- Breating and ExchangeDocument3 pagesBreating and Exchangedamon salvatoreNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Test PFTDocument24 pagesPulmonary Function Test PFTyogithajeganathan5197No ratings yet
- SpirometryDocument63 pagesSpirometryAries DocNo ratings yet
- Spirometry Testing - What Is A SpirometerDocument11 pagesSpirometry Testing - What Is A SpirometerFatima Sherrisa SaliNo ratings yet
- HSCI 103 Lab 4 HandoutDocument4 pagesHSCI 103 Lab 4 HandoutMatthewFlecknoeNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument43 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesChinmaya SNo ratings yet
- PHS 211 RespiratoryDocument72 pagesPHS 211 RespiratoryEmma OsabohienNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Volumes and CapacitiesDocument20 pagesPulmonary Volumes and Capacitiesalice_lim01No ratings yet
- Lung Capacities and VolumesDocument2 pagesLung Capacities and VolumeslucasNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesKULDocument32 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesKULWhy DharmawanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System & ParametersDocument35 pagesRespiratory System & Parametersrobert robNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation For Respiratory MechanicsDocument73 pagesInstrumentation For Respiratory MechanicsSoniya CsNo ratings yet
- Metta - Philosophy - Practice of - Universal LoveDocument24 pagesMetta - Philosophy - Practice of - Universal LoveTharaka Nadeeshan100% (1)
- Deionization: Cost Reduction and Operating Results of An Ro/Edi Treatment SystemDocument4 pagesDeionization: Cost Reduction and Operating Results of An Ro/Edi Treatment SystemjonnelNo ratings yet
- Buffered Anaesthetic S: DR Shazeena QaiserDocument25 pagesBuffered Anaesthetic S: DR Shazeena QaiserShazeena OfficialNo ratings yet
- Your Contacts From TelephoneDocument73 pagesYour Contacts From TelephoneEly IEJINo ratings yet
- Mobile Offshore Drilling Units 2016: Rules For Building and ClassingDocument9 pagesMobile Offshore Drilling Units 2016: Rules For Building and ClassingneoNo ratings yet
- III Year A EEEDocument2 pagesIII Year A EEEshenbagaraman cseNo ratings yet
- New Year Around The World 1Document22 pagesNew Year Around The World 1Sang LêNo ratings yet
- Driscoll WordsDocument55 pagesDriscoll WordsMatthew James DriscollNo ratings yet
- Live Outside The BoxDocument2 pagesLive Outside The BoxKrishnaKumarDeepNo ratings yet
- 5 - Emergency MotionDocument14 pages5 - Emergency MotionTyler LofallNo ratings yet
- Ajax Asynchronous Javascript + XML: "A Fundamental Shift in What'S Possible On The Web"Document60 pagesAjax Asynchronous Javascript + XML: "A Fundamental Shift in What'S Possible On The Web"lucasNo ratings yet
- China Pakistan Economic Corridor CPEC IsDocument12 pagesChina Pakistan Economic Corridor CPEC IsNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Week Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesComprehension Week Lesson Planapi-339960745No ratings yet
- Nep Schools - VZM Dist - 26072021Document27 pagesNep Schools - VZM Dist - 26072021WHO IS ITNo ratings yet
- Public Space Thesis ArchitectureDocument5 pagesPublic Space Thesis Architecturestephaniejohnsonsyracuse100% (2)
- Santiago v. Gonzalez PDFDocument2 pagesSantiago v. Gonzalez PDFGervin ArquizalNo ratings yet
- Brakes MCQDocument8 pagesBrakes MCQSathistrnpcNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Statcon QuizDocument18 pagesReviewer For Statcon QuizShella Hannah SalihNo ratings yet
- Akash Karia - Anti-Procrastination For Writers - The Writer's Guide To Stop Procrastinating, Start Writing and Create A Daily Writing Ritual-AkashKaria - Com (2014) PDFDocument99 pagesAkash Karia - Anti-Procrastination For Writers - The Writer's Guide To Stop Procrastinating, Start Writing and Create A Daily Writing Ritual-AkashKaria - Com (2014) PDFNeman AshrafNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Research Methods For ManagementDocument19 pagesAssignment - Research Methods For Managementnatashashaikh93No ratings yet
- Nandan CoffeeDocument18 pagesNandan CoffeegautamNo ratings yet
- Barson - Ligula PaperDocument4 pagesBarson - Ligula PaperIonela ConstandacheNo ratings yet
- (1899) (Vol. 2) A Sailor's Life Under Four SovereignsDocument364 pages(1899) (Vol. 2) A Sailor's Life Under Four SovereignsHerbert Hillary Booker 2ndNo ratings yet
- Rego Multiport A8574AGDocument2 pagesRego Multiport A8574AGCristobal CherigoNo ratings yet
- Cpec GeographyDocument2 pagesCpec GeographyaNo ratings yet
- Motion Regarding Admission of Out of Court Statement 1Document2 pagesMotion Regarding Admission of Out of Court Statement 1WXMINo ratings yet
- Unit 19 p3Document10 pagesUnit 19 p3api-344079053No ratings yet
- Document Analysis Worksheet: Analyze A PaintingDocument4 pagesDocument Analysis Worksheet: Analyze A PaintingPatrick SanchezNo ratings yet
Spiro Meter
Spiro Meter
Uploaded by
aboosh16990 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views16 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views16 pagesSpiro Meter
Spiro Meter
Uploaded by
aboosh1699Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
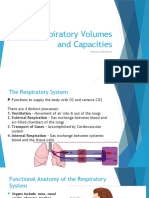
Spirometry
Spiro - from the Greek for ‘breathing. Metry –measurement.
SPIROMETRY – the measurement of breathing.
• The measurement of the flow and
volume of air entering and leaving
the lungs.
• Volume: records the amount of air exhaled or
inhaled within a certain time
• Flow: measures how fast the air flows in or out
as the volume of air inhaled or exhaled
increases.
• Spirometry can be used to measure pulmonary
(lung) functions.
Lung diseases
✔ Lung disease is often divided into two categories
• Obstructive Disorders • Restrictive Disorders
– Characterized by a limitation – Characterized by reduced
of expiratory airflow so that lung volumes/decreased lung
airways cannot empty as compliance
rapidly compared to normal Examples:
(such as through narrowed – tuberculosis
airways from bronchospasm, – Silicosis (lung fibrosis caused by
inflammation, etc….) the inhalation of dust containing
Examples: silica.)
– Asthma (airways narrow and swell – Obesity (cause mechanical
and produce extra mucus).
– Emphysema (air sacs of the lungs are
compression of the diaphragm )
damaged and enlarged, causing
breathlessness)
Pulmonary Function Testing
Normal values dependent upon:
▪ Individual variation according to age, height, ethnicity and
gender
- Height - Tall people have larger lungs
- Age - Respiratory function declines with age
- Sex - Lung volumes smaller in females
- Race - Studies show Blacks and Asians have smaller lung
volumes (-12%)
Pulmonary Function Tests
• Lung volumes and Capacities
– Tidal Volume : 500ml
– Inspiratory Reserve Volume(IRV): 3000ml
– Expiratory Reserve Volume(ERV): 1000ml
– Functional residual capacity(FRC): ERV+RV =2200ml
– Total lung capacity(TLC): 5700-6000ml
– Residual volume(RV): 1200ml
– Vital Capacity(VC): Tv+IRV+ERV=4500ml
Types of Spirometers
• Small hand-held spirometers:
Inexpensive and quick to use but
no print out
✔ Tidal Volume: volume of air inspired & expired with each normal
breath. Normal TV is approximately 500 ml
✔ Inspiratory Reserve Volume :Additional volume that can be
inspired above tidal volume . Normal IRV is approximately 3000
ml
✔Expiratory Reserve Volume :Additional volume that can be expired
below tidal volume . Normal ERV is approximately 1000 ml
✔ Residual Volume :the volume of air remaining in the lungs after
forced expiration . Normal R.V is approximately 1200 ml can not
be measured with spirometry
✔ Functional Residual Capacity:Is R.V+ ERV. Normal FRC is
approximately 2200 ml. can not be measured with spirometry
✔ Vital Capacity: Is IRV+TV+ ERV. Normal VC is approximately
4500 ml .
✔ Total lung Capacity:Is VC+RV. Normal TLC is approximately 5700
ml. Is the maximum volume to which lungs can be expanded with
greatest possible efforts. can not be measured with spirometry
Equations Volume (liters) Definition Volume/Capacity
Volume/Capacity Definition Volume (liters) Equations
Amount of air inhaled
Tidal volume (TV) 0.5 –
during a normal breath
Amount of air that can be
Expiratory reserve volume
exhaled after a normal 1.2 –
(ERV)
exhalation
Amount of air that can be
Inspiratory reserve volume
further inhaled after a 3.1 –
(IRV)
normal inhalation
Air left in the lungs after a
Residual volume (RV) 1.2 –
forced exhalation
Maximum amount of air
that can be moved in or out
Vital capacity (VC) 4.8 ERV+TV+IRV
of the lungs in a single
respiratory cycle
Volume of air that can be
Inspiratory capacity (IC) inhaled in addition to a 3.6 TV+IRV
normal exhalation
Functional residual Volume of air remaining
2.4 ERV+RV
capacity (FRC) after a normal exhalation
Total volume of air in the
Total lung capacity (TLC) lungs after a maximal 6.0 RV+ERV+TV+IRV
inspiration
You might also like
- Enron Case StudyDocument3 pagesEnron Case StudycharleejaiNo ratings yet
- Grady McMurtry The Millenial Glow Myth and Magic in The Marxist Ethics V 1.0.5 PDFDocument130 pagesGrady McMurtry The Millenial Glow Myth and Magic in The Marxist Ethics V 1.0.5 PDFMoreno KrvavacNo ratings yet
- Biology IIRespiratory SystemDocument28 pagesBiology IIRespiratory SystemSustiguer Estelle FaithNo ratings yet
- Lung Volume & CapacitiesDocument32 pagesLung Volume & CapacitiesGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Volumes: - Used To Assess A Person's Respiratory StatusDocument8 pagesRespiratory Volumes: - Used To Assess A Person's Respiratory StatusMohammed Qasim Al-WataryNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument34 pagesRespiratory Systemrenzvalorant28No ratings yet
- Lab 07 Respiratory SystemsDocument5 pagesLab 07 Respiratory SystemsameeschwittersNo ratings yet
- Lung VolumesDocument4 pagesLung VolumesLdv1 1No ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestDocument34 pagesPulmonary Function TestmukeshmscNo ratings yet
- Practical PhysiologyDocument14 pagesPractical PhysiologyOmar AymanNo ratings yet
- 1.lung Volume and CapacityDocument3 pages1.lung Volume and CapacityDr. K. YAMUNA DEVI Asst.Prof-BME DeptNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and Capacities Tutorial 2010ghgDocument17 pagesLung Volumes and Capacities Tutorial 2010ghgKelvinNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument15 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesIrfanNo ratings yet
- Bio20 - Unit D - 12 - Notes - SpirometerDocument10 pagesBio20 - Unit D - 12 - Notes - SpirometerJhalak GargNo ratings yet
- Spirometry RV and RCDocument19 pagesSpirometry RV and RCMâřâh MöHămmădNo ratings yet
- 3 Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument20 pages3 Lung Volumes and CapacitiesNimra TariqNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Respiration IIIDocument13 pagesBreathing and Respiration IIIAshrith KumarNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument2 pagesLung Volumes and Capacitiesclaribel0303No ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument16 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesMoses DumbuyaNo ratings yet
- CHECK HALF Respiratory Volumes and CapacitiesDocument4 pagesCHECK HALF Respiratory Volumes and CapacitiesRoss GellerNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument13 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesTanmayee MuppaneniNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Volumes and CapacitiesDocument34 pagesPulmonary Volumes and Capacitiesahang.aliNo ratings yet
- Practical Physiology RRS ResDocument9 pagesPractical Physiology RRS Resmina mounirNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument41 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gases538 varsha vishnoiNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Respiratory System (Spirometry)Document20 pagesPhysiology of The Respiratory System (Spirometry)Frances de JesusNo ratings yet
- Assigment of PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAssigment of Physiologyabdirizak Haji MohammedNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION PHYSIOLOGY Sept 2022 IntakeDocument94 pagesRESPIRATION PHYSIOLOGY Sept 2022 IntakeKing kakaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Tests - DR MoiseDocument39 pagesPulmonary Function Tests - DR MoisemathemoisemedNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الجاهزة 4،5 فسيو بلك التنفسيDocument43 pagesالمحاضرة الجاهزة 4،5 فسيو بلك التنفسيbessan alfqeatNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes: Navigation SearchDocument8 pagesLung Volumes: Navigation SearchAisha AlderNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Volumes Capacities and Lung DiseasesDocument14 pagesRespiratory Volumes Capacities and Lung DiseasesRoss GellerNo ratings yet
- Physiology-2 by Ahmed AboulyazeedDocument20 pagesPhysiology-2 by Ahmed AboulyazeedMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Lung Volume and CapacityDocument13 pagesLung Volume and CapacityPlzstudylav SyedNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology: Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument35 pagesRespiratory Physiology: Lung Volumes and CapacitiesNur Faizah Ahmad AriffNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestDocument24 pagesPulmonary Function Testfkrishna445No ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument3 pagesRespiration Noteseshoukat353No ratings yet
- Lung Volumes Alveolar VentilationDocument30 pagesLung Volumes Alveolar Ventilationz nameNo ratings yet
- Physiology AsignmentDocument5 pagesPhysiology AsignmentAnasAbdelaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Volumes & CapacitiesDocument13 pagesRespiratory Volumes & CapacitiesharshabhuvanmahendranNo ratings yet
- Lung Vol, Capacity and BMRDocument24 pagesLung Vol, Capacity and BMRMAKHANANI CHAUKENo ratings yet
- 1 Pulmonary Diagnostic and Therapeutic Interventions - First-1Document27 pages1 Pulmonary Diagnostic and Therapeutic Interventions - First-1Zohour AlowisyNo ratings yet
- L - 2 Physiology of Respiration IIDocument25 pagesL - 2 Physiology of Respiration IIkaukab azimNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFT)Document30 pagesPulmonary Function Tests (PFT)براءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Lung Volume and CapacitiesDocument14 pagesLung Volume and CapacitiesAhmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument24 pagesPulmonary Function TestsAman UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 CPPTDocument27 pagesLecture 1 CPPTDr. Rabail MalikNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument27 pagesRespiratory SystemMartin OrtillanaNo ratings yet
- DR - Hari Singh Gour Vishwavidyalaya: Department of Pharmaceutical SciencesDocument32 pagesDR - Hari Singh Gour Vishwavidyalaya: Department of Pharmaceutical SciencesNiyati GuptaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PhysiologyDocument11 pagesRespiratory PhysiologywalterNo ratings yet
- Breating and ExchangeDocument3 pagesBreating and Exchangedamon salvatoreNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Test PFTDocument24 pagesPulmonary Function Test PFTyogithajeganathan5197No ratings yet
- SpirometryDocument63 pagesSpirometryAries DocNo ratings yet
- Spirometry Testing - What Is A SpirometerDocument11 pagesSpirometry Testing - What Is A SpirometerFatima Sherrisa SaliNo ratings yet
- HSCI 103 Lab 4 HandoutDocument4 pagesHSCI 103 Lab 4 HandoutMatthewFlecknoeNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument43 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesChinmaya SNo ratings yet
- PHS 211 RespiratoryDocument72 pagesPHS 211 RespiratoryEmma OsabohienNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Volumes and CapacitiesDocument20 pagesPulmonary Volumes and Capacitiesalice_lim01No ratings yet
- Lung Capacities and VolumesDocument2 pagesLung Capacities and VolumeslucasNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesKULDocument32 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesKULWhy DharmawanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System & ParametersDocument35 pagesRespiratory System & Parametersrobert robNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation For Respiratory MechanicsDocument73 pagesInstrumentation For Respiratory MechanicsSoniya CsNo ratings yet
- Metta - Philosophy - Practice of - Universal LoveDocument24 pagesMetta - Philosophy - Practice of - Universal LoveTharaka Nadeeshan100% (1)
- Deionization: Cost Reduction and Operating Results of An Ro/Edi Treatment SystemDocument4 pagesDeionization: Cost Reduction and Operating Results of An Ro/Edi Treatment SystemjonnelNo ratings yet
- Buffered Anaesthetic S: DR Shazeena QaiserDocument25 pagesBuffered Anaesthetic S: DR Shazeena QaiserShazeena OfficialNo ratings yet
- Your Contacts From TelephoneDocument73 pagesYour Contacts From TelephoneEly IEJINo ratings yet
- Mobile Offshore Drilling Units 2016: Rules For Building and ClassingDocument9 pagesMobile Offshore Drilling Units 2016: Rules For Building and ClassingneoNo ratings yet
- III Year A EEEDocument2 pagesIII Year A EEEshenbagaraman cseNo ratings yet
- New Year Around The World 1Document22 pagesNew Year Around The World 1Sang LêNo ratings yet
- Driscoll WordsDocument55 pagesDriscoll WordsMatthew James DriscollNo ratings yet
- Live Outside The BoxDocument2 pagesLive Outside The BoxKrishnaKumarDeepNo ratings yet
- 5 - Emergency MotionDocument14 pages5 - Emergency MotionTyler LofallNo ratings yet
- Ajax Asynchronous Javascript + XML: "A Fundamental Shift in What'S Possible On The Web"Document60 pagesAjax Asynchronous Javascript + XML: "A Fundamental Shift in What'S Possible On The Web"lucasNo ratings yet
- China Pakistan Economic Corridor CPEC IsDocument12 pagesChina Pakistan Economic Corridor CPEC IsNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Week Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesComprehension Week Lesson Planapi-339960745No ratings yet
- Nep Schools - VZM Dist - 26072021Document27 pagesNep Schools - VZM Dist - 26072021WHO IS ITNo ratings yet
- Public Space Thesis ArchitectureDocument5 pagesPublic Space Thesis Architecturestephaniejohnsonsyracuse100% (2)
- Santiago v. Gonzalez PDFDocument2 pagesSantiago v. Gonzalez PDFGervin ArquizalNo ratings yet
- Brakes MCQDocument8 pagesBrakes MCQSathistrnpcNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Statcon QuizDocument18 pagesReviewer For Statcon QuizShella Hannah SalihNo ratings yet
- Akash Karia - Anti-Procrastination For Writers - The Writer's Guide To Stop Procrastinating, Start Writing and Create A Daily Writing Ritual-AkashKaria - Com (2014) PDFDocument99 pagesAkash Karia - Anti-Procrastination For Writers - The Writer's Guide To Stop Procrastinating, Start Writing and Create A Daily Writing Ritual-AkashKaria - Com (2014) PDFNeman AshrafNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Research Methods For ManagementDocument19 pagesAssignment - Research Methods For Managementnatashashaikh93No ratings yet
- Nandan CoffeeDocument18 pagesNandan CoffeegautamNo ratings yet
- Barson - Ligula PaperDocument4 pagesBarson - Ligula PaperIonela ConstandacheNo ratings yet
- (1899) (Vol. 2) A Sailor's Life Under Four SovereignsDocument364 pages(1899) (Vol. 2) A Sailor's Life Under Four SovereignsHerbert Hillary Booker 2ndNo ratings yet
- Rego Multiport A8574AGDocument2 pagesRego Multiport A8574AGCristobal CherigoNo ratings yet
- Cpec GeographyDocument2 pagesCpec GeographyaNo ratings yet
- Motion Regarding Admission of Out of Court Statement 1Document2 pagesMotion Regarding Admission of Out of Court Statement 1WXMINo ratings yet
- Unit 19 p3Document10 pagesUnit 19 p3api-344079053No ratings yet
- Document Analysis Worksheet: Analyze A PaintingDocument4 pagesDocument Analysis Worksheet: Analyze A PaintingPatrick SanchezNo ratings yet