Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsLecture-8 Granulopoiesis and Its Regulation
Lecture-8 Granulopoiesis and Its Regulation
Uploaded by
adnanreshunCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Haematopoiesis: DR Rosline Hassan Hematology Department School of Medical Sciences Universiti Sains MalaysiaDocument46 pagesHaematopoiesis: DR Rosline Hassan Hematology Department School of Medical Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysialow_sernNo ratings yet
- Angle of Anterior ChamberDocument55 pagesAngle of Anterior Chamberuttam prakashNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Nuclear CardiologyDocument2 pagesAtlas of Nuclear CardiologyAmir FazelNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology MethodsDocument481 pagesEpidemiology MethodsPippo KennedyNo ratings yet
- Haematology Lecture 3+4Document20 pagesHaematology Lecture 3+4Nabeel TahirNo ratings yet
- GRANULOPOIESIS (Autosaved) .PPTX OKLADocument93 pagesGRANULOPOIESIS (Autosaved) .PPTX OKLAPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument90 pagesBone Marrow ExaminationRuxandra MesarosNo ratings yet
- 4880 MyelopoiesisDocument10 pages4880 MyelopoiesisHamilton SebastineNo ratings yet
- 4880 MyelopoiesisDocument10 pages4880 MyelopoiesisHamilton SebastineNo ratings yet
- Haematology Lecture 5+6Document25 pagesHaematology Lecture 5+6Nabeel TahirNo ratings yet
- Erythropoiesis: Awal Mir Khattak Demonstrator MLTDocument17 pagesErythropoiesis: Awal Mir Khattak Demonstrator MLTMuhammad AnasNo ratings yet
- Leukopoeisis 210325144405Document41 pagesLeukopoeisis 210325144405Gon FreecssNo ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGY 1 Hematopoiesis Notes 1Document10 pagesHEMATOLOGY 1 Hematopoiesis Notes 1sansastarkNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Hematology 2 LectureDocument8 pagesWeek 1 - Hematology 2 LectureRubenne Miles ElagasNo ratings yet
- Gran Ulo PoiesisDocument31 pagesGran Ulo Poiesisinnocentcloudz15No ratings yet
- Dr. Waluyo Rudiyanto, M.KesDocument50 pagesDr. Waluyo Rudiyanto, M.KesAsiatiNo ratings yet
- MT0831 Complete Hematology Report CompilationDocument234 pagesMT0831 Complete Hematology Report CompilationsazunaxNo ratings yet
- HEMATOPOIESISDocument9 pagesHEMATOPOIESISKIPRUTO DENNISNo ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGY Hemostasis+ (In+Hosue+Review)Document234 pagesHEMATOLOGY Hemostasis+ (In+Hosue+Review)znsntg21No ratings yet
- Hema 2Document35 pagesHema 2Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Immunology Unit 1Document14 pagesImmunology Unit 1a.parameshwari1234No ratings yet
- Heamtopoises ReviewerDocument17 pagesHeamtopoises ReviewerClyde BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Here, Only 1 Few Stages Undergo Subdivision (Sabi Ni Maam)Document6 pagesHere, Only 1 Few Stages Undergo Subdivision (Sabi Ni Maam)Jaenie Grace AliganNo ratings yet
- 5.0 LeukopoiesisDocument37 pages5.0 LeukopoiesisJunior SataNo ratings yet
- Hema-2-August-2021 (2) - 1Document35 pagesHema-2-August-2021 (2) - 1Andrew EvansNo ratings yet
- CLINPATH-01.Hematopoiesis & Morphology of Blood CellsDocument10 pagesCLINPATH-01.Hematopoiesis & Morphology of Blood CellsCharisse Angelica MacedaNo ratings yet
- Hematology 1: Topic 11Document20 pagesHematology 1: Topic 11Pamela BesanaNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic SystemDocument56 pagesHematopoietic SystemEmmanuel Tristan OlarteNo ratings yet
- Hematology L9 - ٠١٠٣٤١ - ١٠٢٧١٥Document31 pagesHematology L9 - ٠١٠٣٤١ - ١٠٢٧١٥shakib33001No ratings yet
- MegakaryopoiesisDocument41 pagesMegakaryopoiesisHazel FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- MegakaryopoiesisDocument13 pagesMegakaryopoiesisAezel CruzNo ratings yet
- 6..Wbc ParijatDocument51 pages6..Wbc ParijatSuraiya IslamNo ratings yet
- 2 HaemopoiesisDocument50 pages2 HaemopoiesisWasana Mendis100% (3)
- Leukocyte's Classification, Structure, Function, and AssessmentDocument32 pagesLeukocyte's Classification, Structure, Function, and Assessmenthayamitib11No ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Leukopoiesis-GranularDocument20 pagesLesson 8 Leukopoiesis-Granularتجربة أولىNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument107 pagesHematologyFredrich CuaNo ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis 2022 VRDocument52 pagesHematopoiesis 2022 VRvictoria tavasNo ratings yet
- 2 Haemopoiesis Medical StudentsDocument48 pages2 Haemopoiesis Medical Studentscollins ijezieNo ratings yet
- Leukocyte Development Kinetics and FunctionsDocument39 pagesLeukocyte Development Kinetics and FunctionsChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- HEMATOPOIESISDocument7 pagesHEMATOPOIESISritaoktasariNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To HeamatopoiesisDocument21 pages1 - Introduction To Heamatopoiesisdr1akram96No ratings yet
- HEMOSTASISDocument6 pagesHEMOSTASIScatuiraneljhayyyNo ratings yet
- Seminar Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Master Degree in Zoology OnDocument24 pagesSeminar Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Master Degree in Zoology OnKhushbu BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Leukocyte Structure, Function and LeukopoiesisDocument39 pagesLeukocyte Structure, Function and LeukopoiesisMarah Mazahreh100% (1)
- Leuko 1Document7 pagesLeuko 1Vince Lester LataNo ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis Part 1 Hema LecDocument4 pagesHematopoiesis Part 1 Hema LecAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Hemopoiesis PDFDocument14 pagesHemopoiesis PDFrysnawahyu13No ratings yet
- Hematology 425, LeukopoiesisDocument56 pagesHematology 425, LeukopoiesishanzukikNo ratings yet
- غير معروف Introduction to haematology-1 (Muhadharaty)Document47 pagesغير معروف Introduction to haematology-1 (Muhadharaty)aliabumrfghNo ratings yet
- HAEMOPOEISISDocument33 pagesHAEMOPOEISISKaylee NesbitNo ratings yet
- 1 LeukopoiesisDocument23 pages1 LeukopoiesisJan Victor Elico100% (3)
- Development of Blood Cells 2019Document31 pagesDevelopment of Blood Cells 2019Muhammad Anas Abbal100% (1)
- Presentation GametogenesisDocument33 pagesPresentation GametogenesisAndy ZempaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology of Circulatory SystemDocument61 pagesAnatomy Physiology of Circulatory SystemEshtiey_MegaNo ratings yet
- Hema Report PDFDocument25 pagesHema Report PDFdaliaNo ratings yet
- Blood Practical & LectureDocument28 pagesBlood Practical & Lecturetink29No ratings yet
- Blood SciencesDocument47 pagesBlood Sciencescaroline vaughanNo ratings yet
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocument28 pagesChronic Pyelonephritisarun j.rNo ratings yet
- HemopoesisDocument31 pagesHemopoesisChandra Shinoda100% (2)
- Lecture-14 MegakariopoiesisDocument16 pagesLecture-14 MegakariopoiesisadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- L 11 MeiosisDocument39 pagesL 11 MeiosissNo ratings yet
- CNS Tumors: DR Podcheko 2019Document139 pagesCNS Tumors: DR Podcheko 2019LunaLure100% (1)
- Emergency Skills Lec 1Document36 pagesEmergency Skills Lec 1adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-11 Disorders of Eosinophil and BasophilDocument12 pagesLecture-11 Disorders of Eosinophil and BasophiladnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document5 pagesPresentation 5adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-16 HemostasisDocument21 pagesLecture-16 HemostasisadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Emergency Skills Lec 3Document13 pagesEmergency Skills Lec 3adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Pneumonias Lec 4Document11 pagesPneumonias Lec 4adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-14 MegakariopoiesisDocument16 pagesLecture-14 MegakariopoiesisadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-10 Neutrophilia and NeutropeniaDocument21 pagesLecture-10 Neutrophilia and NeutropeniaadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-12 Disorders of Lymphocytes and MonocytesDocument21 pagesLecture-12 Disorders of Lymphocytes and MonocytesadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document11 pagesPresentation 2adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Math Review 3Document3 pagesMath Review 3adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document13 pagesPresentation 1adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document5 pagesPresentation 5adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 Introduction To HematologyDocument16 pagesLecture-1 Introduction To HematologyadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document8 pagesPresentation 4adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document7 pagesPresentation 3adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Relations, Graphs, and FunctionsDocument15 pagesRelations, Graphs, and FunctionsadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 Bone Marrow Structure and FunctionsDocument14 pagesLecture-2 Bone Marrow Structure and FunctionsadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation and CardioversionDocument28 pagesDefibrillation and CardioversionadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Units and DimensionsDocument6 pagesUnits and DimensionsadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Set TheoryDocument8 pagesSet TheoryadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of BLS: Shaheen Fatima Bs (Siut Karachi) MSPH (Jsmu Karachi)Document26 pagesBasic Concept of BLS: Shaheen Fatima Bs (Siut Karachi) MSPH (Jsmu Karachi)adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- R 1 Log Rolling TechniqueDocument22 pagesR 1 Log Rolling TechniqueadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Surgery For The Burned WoundDocument11 pagesSurgery For The Burned WoundadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- 3..... Secondary Survey and Its AdjunctDocument35 pages3..... Secondary Survey and Its AdjunctadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- 1.primary Survey & Adjuncts To Primary Survey & ResuscitationDocument42 pages1.primary Survey & Adjuncts To Primary Survey & ResuscitationadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- PalsDocument5 pagesPalsadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma Lec 01Document48 pagesHead Trauma Lec 01adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Truma Sllide 3Document22 pagesTruma Sllide 3adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma Lec 02Document41 pagesHead Trauma Lec 02adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- CARBUNCLEDocument11 pagesCARBUNCLEKesavanadh T M100% (1)
- A Patient's Guide To Radial Tunnel SyndromeDocument4 pagesA Patient's Guide To Radial Tunnel SyndromeKarunya Vk100% (1)
- Haemodialysis in ChildrenDocument38 pagesHaemodialysis in ChildrenValliammalShanmugam78% (9)
- Patient Safety: Dr.S.Selvakumar.M.S Hosp - Supdt-Dhqh NamakkalDocument21 pagesPatient Safety: Dr.S.Selvakumar.M.S Hosp - Supdt-Dhqh NamakkalsaravananNo ratings yet
- 2011 Primary (Arabic Board)Document25 pages2011 Primary (Arabic Board)Mustafa Ismael NayyefNo ratings yet
- First Aid Supplies BizHouse - UkDocument3 pagesFirst Aid Supplies BizHouse - UkAlex BekeNo ratings yet
- Resumen Alzheimer THDocument14 pagesResumen Alzheimer THfelix1perez-5No ratings yet
- Programa Aua San Francisco 2018Document76 pagesPrograma Aua San Francisco 2018Rosemary FranquizNo ratings yet
- Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument2 pagesEntamoeba HistolyticaEugenia Cindy JulianyNo ratings yet
- Editors, Asim Kurjak, Frank A. Chervenak. - Donald School Textbook of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology (2011., Jaypee Bros. Medical Publ.) PDFDocument1,035 pagesEditors, Asim Kurjak, Frank A. Chervenak. - Donald School Textbook of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology (2011., Jaypee Bros. Medical Publ.) PDFRaluca Haba100% (1)
- Genital Tract InfectionsDocument4 pagesGenital Tract Infectionsmed.progressNo ratings yet
- So You Want To Be A Urologist?: The First StepDocument2 pagesSo You Want To Be A Urologist?: The First StepDrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizureDocument8 pagesFebrile Seizureanon_944507650No ratings yet
- Rivanol English LeafletDocument1 pageRivanol English LeafletKazi MilonNo ratings yet
- A Way To Get FitDocument2 pagesA Way To Get FitA2 Amen, Alyza H.No ratings yet
- ACL Reconstruction BookDocument18 pagesACL Reconstruction BookSergejs JaunzemsNo ratings yet
- Examination of Thorax and LungsDocument7 pagesExamination of Thorax and LungsJohanei Mae PeraltaNo ratings yet
- LEARNING DIARY FOR NCM 105n/L-Nutrition and Diet Therapy Date: Name: Topics: Guide QuestionsDocument3 pagesLEARNING DIARY FOR NCM 105n/L-Nutrition and Diet Therapy Date: Name: Topics: Guide QuestionsWendell Gian GolezNo ratings yet
- Hyperuricemia XXXX XXXXX XxjeuneDocument32 pagesHyperuricemia XXXX XXXXX XxjeuneOziq Juga ReMa-eNo ratings yet
- Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome: Information Leaflet OnDocument8 pagesTwin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome: Information Leaflet Onshona SharupaniNo ratings yet
- Personal Hygiene and Health Care - Social and PreventiveDocument37 pagesPersonal Hygiene and Health Care - Social and Preventiveanubhav thakurNo ratings yet
- Humphrey Visual Field TestDocument1 pageHumphrey Visual Field TestMedisch 007No ratings yet
- Future Scope and Challenges For Congestive Heart Failure Moving Towards Development of PharmacotherapyDocument47 pagesFuture Scope and Challenges For Congestive Heart Failure Moving Towards Development of PharmacotherapysunhaolanNo ratings yet
- List of Hospital Performance Indicators For Accountability (Hpia)Document2 pagesList of Hospital Performance Indicators For Accountability (Hpia)Mohd syukri HashimNo ratings yet
- 30-06-2020 HMB EnglishDocument41 pages30-06-2020 HMB EnglishKirti VNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology Is The Study of Drug-Induced Changes in Mood, Sensation, ThinkingDocument5 pagesPsychopharmacology Is The Study of Drug-Induced Changes in Mood, Sensation, Thinking0921pyNo ratings yet
- CNA Body Mechanics Bed Making Comfort CareDocument32 pagesCNA Body Mechanics Bed Making Comfort CareFaith VaughnNo ratings yet
Lecture-8 Granulopoiesis and Its Regulation
Lecture-8 Granulopoiesis and Its Regulation
Uploaded by
adnanreshun0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views18 pagesOriginal Title
Lecture-8 Granulopoiesis and its regulation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views18 pagesLecture-8 Granulopoiesis and Its Regulation
Lecture-8 Granulopoiesis and Its Regulation
Uploaded by
adnanreshunCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 18
MYELOPOIESIS / GRANULOPOIESIS
AND ITS REGULATION
Awal Mir Khattak
Demonstrator MLT
B.Sc. MLT Baqai Medical University Karachi
M.Sc. Hematology Baqai Medical University Karachi
M.Phil. Medical Lab Sciences, The University of Haripur
DEFINITION
Granulopoiesis/Myelopoiesis
It is the process of proliferation,
differentiation and maturation of granulocytes
in the bone marrow
GRANULOPOIESIS
• Granulocytes arise from pluripotent hematopoietic stem
cells.
• PHSC differentiate into granulocyte-monocyte colony
forming unit (GM-CFU). This further differentiated into
granulocyte colony forming unit (G-CFU).
• G-CFU pass through successive divisions and stages and
ultimately form mature granulocytes.
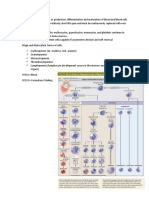
STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS
• Proliferation and maturation of myeloid series in the bone
marrow demonstrates a continuum of development from
myeloblast to the most mature granulocytes.
• Each granulocytes follow the same pattern of development
i.e. myeloblast, promyelocyte, myelocyte, metamyelocyte,
band cell and mature granulocytes.
• Each granulocyte can be distinguished at myelocyte stage
due to the appearance of specific granules.
STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS
• During maturation, there is reduction in nucleus volume,
condensation of chromatin, change in nuclear shape,
appearance and disappearance of primary granules,
appearance of secondary granules, color changes and
change in size of the cell.
• Myeloblast, promyelocyte and myelocyte; these cells
undergo mitosis and have the capability of division.
STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS
• Metamyelocytes and band cells are the components of
maturation pool. These cells do not divide.
• Segmented neutrophils stored in the bone marrow and are
released in the circulation.
• After few hours neutrophils marginate along with the vessel
wall and is termed as marginating pool. These cells leave the
circulation and enter the tissues passing through the
endothelial cells by a process known as diapedesis.
STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS
STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS
• Morphologically Granulopoiesis is divided into 6 stages
1. Myeloblast
2. Promyelocyte
3. Myelocyte
4. Metamyelocyte
5. Band cells / stab cell
6. Mature granulocytes (Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils)
STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS
1. Myeloblast (0.2-1.5%)
Size: Large (14-20 um), Shape: Round to oval, N:C: High (4:1)
Cytoplasm:
Color: Light blue
Amount: Scanty
Granule: Primary granules present
Granule color: Reddish Purple
Nucleus:
Color: Radish purple
Shape: Round to oval
Chromatin Pattern: Open
Nucleolus: 2-4 present
STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS
1. Promyelocyte (2-4)
Size: Large (15-21 um), Shape: Round to oval, N:C: High
Cytoplasm:
Color: Basophilic
Amount: Moderate
Granule: Primary granules present
Granule color: Reddish Purple
Nucleus:
Color: Radish purple
Shape: Round to oval
Chromatin Pattern: Coarse
Nucleolus: May be present
STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS
1. Myelocyte (8-16)
Size: Large (12-18 um), Shape: Round to oval, N:C: (50:50)
Cytoplasm:
Color: Light Blue
Amount: abundant
Granule: Primary + appearance of secondary granules
Granule color: Pink
Nucleus:
Color: Radish purple
Shape: Round to oval
Chromatin Pattern: Coarse
Nucleolus: Absent
STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS
1. Metamyelocyte (9-25)
Size: Large (10-18 um), Shape: Round to oval, N:C: (decrease)
Cytoplasm:
Color: Pinkish
Amount: abundant
Granule: Primary+secondary granules
Granule color: Pinkish
Nucleus:
Color: Dark purple
Shape: Kidney/horse-shoe shaped
Chromatin Pattern: Condensed
Nucleolus: Absent
STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS
1. Band Cell (9-15)
Size: Large (10-18 um), Shape: Round to oval, N:C: (decrease)
Cytoplasm:
Color: Pinkish
Amount: abundant
Granule: Primary + secondary granules
Granule color: Pinkish
Nucleus:
Color: Dark purple
Shape: Horse-shoe shaped
Chromatin Pattern: Condensed
Nucleolus: Absent
STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS
1. Segmented Neutrophil
Size: Large (10-18 um), Shape: Round to oval, N:C: (decrease)
Cytoplasm:
Color: Pink
Amount: Bbundant
Granule: Primary + secondary granules
Granule color: Pinkish
Nucleus:
Color: Dark purple
Shape: Segmented/multi lobes (2-5)
Chromatin Pattern: Condensed
Nucleolus: Absent
Regulation of Granulopoiesis
• Growth factors essential for the proliferation, growth,
development and maturation of granulocytes include
granulocyte-monocyte colony stimulating factor (GM-
CSF), granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF),
interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-11, IL-1, IL-3 and IL-5.
• Increased granulocyte and monocyte production in
response to an infection is induced by increased
production of growth factors from stromal cells and T
lymphocytes, stimulated by endotoxin, and cytokines
such as IL‐1 or tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
Regulation of Granulopoiesis
Regulation of Granulopoiesis
CLINICAL APPLICATION OF G-CSF
• G‐CSF is used as a therapeutically and administrated
intravenous or subcutaneous that increased neutrophils
count. Short‐acting G‐CSF is given daily. A longer‐acting G‐
CSF can be given once in 7–14 days.
• Indications:
• Post‐chemotherapy/radiotherapy
• Stem cell transplantation,
• Myelodysplasia
• Aplastic anemia,
• Severe benign neutropenia,
• Peripheral blood stem cell mobilisation
You might also like
- Haematopoiesis: DR Rosline Hassan Hematology Department School of Medical Sciences Universiti Sains MalaysiaDocument46 pagesHaematopoiesis: DR Rosline Hassan Hematology Department School of Medical Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysialow_sernNo ratings yet
- Angle of Anterior ChamberDocument55 pagesAngle of Anterior Chamberuttam prakashNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Nuclear CardiologyDocument2 pagesAtlas of Nuclear CardiologyAmir FazelNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology MethodsDocument481 pagesEpidemiology MethodsPippo KennedyNo ratings yet
- Haematology Lecture 3+4Document20 pagesHaematology Lecture 3+4Nabeel TahirNo ratings yet
- GRANULOPOIESIS (Autosaved) .PPTX OKLADocument93 pagesGRANULOPOIESIS (Autosaved) .PPTX OKLAPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument90 pagesBone Marrow ExaminationRuxandra MesarosNo ratings yet
- 4880 MyelopoiesisDocument10 pages4880 MyelopoiesisHamilton SebastineNo ratings yet
- 4880 MyelopoiesisDocument10 pages4880 MyelopoiesisHamilton SebastineNo ratings yet
- Haematology Lecture 5+6Document25 pagesHaematology Lecture 5+6Nabeel TahirNo ratings yet
- Erythropoiesis: Awal Mir Khattak Demonstrator MLTDocument17 pagesErythropoiesis: Awal Mir Khattak Demonstrator MLTMuhammad AnasNo ratings yet
- Leukopoeisis 210325144405Document41 pagesLeukopoeisis 210325144405Gon FreecssNo ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGY 1 Hematopoiesis Notes 1Document10 pagesHEMATOLOGY 1 Hematopoiesis Notes 1sansastarkNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Hematology 2 LectureDocument8 pagesWeek 1 - Hematology 2 LectureRubenne Miles ElagasNo ratings yet
- Gran Ulo PoiesisDocument31 pagesGran Ulo Poiesisinnocentcloudz15No ratings yet
- Dr. Waluyo Rudiyanto, M.KesDocument50 pagesDr. Waluyo Rudiyanto, M.KesAsiatiNo ratings yet
- MT0831 Complete Hematology Report CompilationDocument234 pagesMT0831 Complete Hematology Report CompilationsazunaxNo ratings yet
- HEMATOPOIESISDocument9 pagesHEMATOPOIESISKIPRUTO DENNISNo ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGY Hemostasis+ (In+Hosue+Review)Document234 pagesHEMATOLOGY Hemostasis+ (In+Hosue+Review)znsntg21No ratings yet
- Hema 2Document35 pagesHema 2Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Immunology Unit 1Document14 pagesImmunology Unit 1a.parameshwari1234No ratings yet
- Heamtopoises ReviewerDocument17 pagesHeamtopoises ReviewerClyde BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Here, Only 1 Few Stages Undergo Subdivision (Sabi Ni Maam)Document6 pagesHere, Only 1 Few Stages Undergo Subdivision (Sabi Ni Maam)Jaenie Grace AliganNo ratings yet
- 5.0 LeukopoiesisDocument37 pages5.0 LeukopoiesisJunior SataNo ratings yet
- Hema-2-August-2021 (2) - 1Document35 pagesHema-2-August-2021 (2) - 1Andrew EvansNo ratings yet
- CLINPATH-01.Hematopoiesis & Morphology of Blood CellsDocument10 pagesCLINPATH-01.Hematopoiesis & Morphology of Blood CellsCharisse Angelica MacedaNo ratings yet
- Hematology 1: Topic 11Document20 pagesHematology 1: Topic 11Pamela BesanaNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic SystemDocument56 pagesHematopoietic SystemEmmanuel Tristan OlarteNo ratings yet
- Hematology L9 - ٠١٠٣٤١ - ١٠٢٧١٥Document31 pagesHematology L9 - ٠١٠٣٤١ - ١٠٢٧١٥shakib33001No ratings yet
- MegakaryopoiesisDocument41 pagesMegakaryopoiesisHazel FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- MegakaryopoiesisDocument13 pagesMegakaryopoiesisAezel CruzNo ratings yet
- 6..Wbc ParijatDocument51 pages6..Wbc ParijatSuraiya IslamNo ratings yet
- 2 HaemopoiesisDocument50 pages2 HaemopoiesisWasana Mendis100% (3)
- Leukocyte's Classification, Structure, Function, and AssessmentDocument32 pagesLeukocyte's Classification, Structure, Function, and Assessmenthayamitib11No ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Leukopoiesis-GranularDocument20 pagesLesson 8 Leukopoiesis-Granularتجربة أولىNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument107 pagesHematologyFredrich CuaNo ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis 2022 VRDocument52 pagesHematopoiesis 2022 VRvictoria tavasNo ratings yet
- 2 Haemopoiesis Medical StudentsDocument48 pages2 Haemopoiesis Medical Studentscollins ijezieNo ratings yet
- Leukocyte Development Kinetics and FunctionsDocument39 pagesLeukocyte Development Kinetics and FunctionsChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- HEMATOPOIESISDocument7 pagesHEMATOPOIESISritaoktasariNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To HeamatopoiesisDocument21 pages1 - Introduction To Heamatopoiesisdr1akram96No ratings yet
- HEMOSTASISDocument6 pagesHEMOSTASIScatuiraneljhayyyNo ratings yet
- Seminar Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Master Degree in Zoology OnDocument24 pagesSeminar Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Master Degree in Zoology OnKhushbu BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Leukocyte Structure, Function and LeukopoiesisDocument39 pagesLeukocyte Structure, Function and LeukopoiesisMarah Mazahreh100% (1)
- Leuko 1Document7 pagesLeuko 1Vince Lester LataNo ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis Part 1 Hema LecDocument4 pagesHematopoiesis Part 1 Hema LecAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Hemopoiesis PDFDocument14 pagesHemopoiesis PDFrysnawahyu13No ratings yet
- Hematology 425, LeukopoiesisDocument56 pagesHematology 425, LeukopoiesishanzukikNo ratings yet
- غير معروف Introduction to haematology-1 (Muhadharaty)Document47 pagesغير معروف Introduction to haematology-1 (Muhadharaty)aliabumrfghNo ratings yet
- HAEMOPOEISISDocument33 pagesHAEMOPOEISISKaylee NesbitNo ratings yet
- 1 LeukopoiesisDocument23 pages1 LeukopoiesisJan Victor Elico100% (3)
- Development of Blood Cells 2019Document31 pagesDevelopment of Blood Cells 2019Muhammad Anas Abbal100% (1)
- Presentation GametogenesisDocument33 pagesPresentation GametogenesisAndy ZempaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology of Circulatory SystemDocument61 pagesAnatomy Physiology of Circulatory SystemEshtiey_MegaNo ratings yet
- Hema Report PDFDocument25 pagesHema Report PDFdaliaNo ratings yet
- Blood Practical & LectureDocument28 pagesBlood Practical & Lecturetink29No ratings yet
- Blood SciencesDocument47 pagesBlood Sciencescaroline vaughanNo ratings yet
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocument28 pagesChronic Pyelonephritisarun j.rNo ratings yet
- HemopoesisDocument31 pagesHemopoesisChandra Shinoda100% (2)
- Lecture-14 MegakariopoiesisDocument16 pagesLecture-14 MegakariopoiesisadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- L 11 MeiosisDocument39 pagesL 11 MeiosissNo ratings yet
- CNS Tumors: DR Podcheko 2019Document139 pagesCNS Tumors: DR Podcheko 2019LunaLure100% (1)
- Emergency Skills Lec 1Document36 pagesEmergency Skills Lec 1adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-11 Disorders of Eosinophil and BasophilDocument12 pagesLecture-11 Disorders of Eosinophil and BasophiladnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document5 pagesPresentation 5adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-16 HemostasisDocument21 pagesLecture-16 HemostasisadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Emergency Skills Lec 3Document13 pagesEmergency Skills Lec 3adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Pneumonias Lec 4Document11 pagesPneumonias Lec 4adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-14 MegakariopoiesisDocument16 pagesLecture-14 MegakariopoiesisadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-10 Neutrophilia and NeutropeniaDocument21 pagesLecture-10 Neutrophilia and NeutropeniaadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-12 Disorders of Lymphocytes and MonocytesDocument21 pagesLecture-12 Disorders of Lymphocytes and MonocytesadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document11 pagesPresentation 2adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Math Review 3Document3 pagesMath Review 3adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document13 pagesPresentation 1adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document5 pagesPresentation 5adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 Introduction To HematologyDocument16 pagesLecture-1 Introduction To HematologyadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document8 pagesPresentation 4adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document7 pagesPresentation 3adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Relations, Graphs, and FunctionsDocument15 pagesRelations, Graphs, and FunctionsadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 Bone Marrow Structure and FunctionsDocument14 pagesLecture-2 Bone Marrow Structure and FunctionsadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation and CardioversionDocument28 pagesDefibrillation and CardioversionadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Units and DimensionsDocument6 pagesUnits and DimensionsadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Set TheoryDocument8 pagesSet TheoryadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of BLS: Shaheen Fatima Bs (Siut Karachi) MSPH (Jsmu Karachi)Document26 pagesBasic Concept of BLS: Shaheen Fatima Bs (Siut Karachi) MSPH (Jsmu Karachi)adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- R 1 Log Rolling TechniqueDocument22 pagesR 1 Log Rolling TechniqueadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Surgery For The Burned WoundDocument11 pagesSurgery For The Burned WoundadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- 3..... Secondary Survey and Its AdjunctDocument35 pages3..... Secondary Survey and Its AdjunctadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- 1.primary Survey & Adjuncts To Primary Survey & ResuscitationDocument42 pages1.primary Survey & Adjuncts To Primary Survey & ResuscitationadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- PalsDocument5 pagesPalsadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma Lec 01Document48 pagesHead Trauma Lec 01adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Truma Sllide 3Document22 pagesTruma Sllide 3adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma Lec 02Document41 pagesHead Trauma Lec 02adnanreshunNo ratings yet
- CARBUNCLEDocument11 pagesCARBUNCLEKesavanadh T M100% (1)
- A Patient's Guide To Radial Tunnel SyndromeDocument4 pagesA Patient's Guide To Radial Tunnel SyndromeKarunya Vk100% (1)
- Haemodialysis in ChildrenDocument38 pagesHaemodialysis in ChildrenValliammalShanmugam78% (9)
- Patient Safety: Dr.S.Selvakumar.M.S Hosp - Supdt-Dhqh NamakkalDocument21 pagesPatient Safety: Dr.S.Selvakumar.M.S Hosp - Supdt-Dhqh NamakkalsaravananNo ratings yet
- 2011 Primary (Arabic Board)Document25 pages2011 Primary (Arabic Board)Mustafa Ismael NayyefNo ratings yet
- First Aid Supplies BizHouse - UkDocument3 pagesFirst Aid Supplies BizHouse - UkAlex BekeNo ratings yet
- Resumen Alzheimer THDocument14 pagesResumen Alzheimer THfelix1perez-5No ratings yet
- Programa Aua San Francisco 2018Document76 pagesPrograma Aua San Francisco 2018Rosemary FranquizNo ratings yet
- Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument2 pagesEntamoeba HistolyticaEugenia Cindy JulianyNo ratings yet
- Editors, Asim Kurjak, Frank A. Chervenak. - Donald School Textbook of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology (2011., Jaypee Bros. Medical Publ.) PDFDocument1,035 pagesEditors, Asim Kurjak, Frank A. Chervenak. - Donald School Textbook of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology (2011., Jaypee Bros. Medical Publ.) PDFRaluca Haba100% (1)
- Genital Tract InfectionsDocument4 pagesGenital Tract Infectionsmed.progressNo ratings yet
- So You Want To Be A Urologist?: The First StepDocument2 pagesSo You Want To Be A Urologist?: The First StepDrThamma ShahiNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizureDocument8 pagesFebrile Seizureanon_944507650No ratings yet
- Rivanol English LeafletDocument1 pageRivanol English LeafletKazi MilonNo ratings yet
- A Way To Get FitDocument2 pagesA Way To Get FitA2 Amen, Alyza H.No ratings yet
- ACL Reconstruction BookDocument18 pagesACL Reconstruction BookSergejs JaunzemsNo ratings yet
- Examination of Thorax and LungsDocument7 pagesExamination of Thorax and LungsJohanei Mae PeraltaNo ratings yet
- LEARNING DIARY FOR NCM 105n/L-Nutrition and Diet Therapy Date: Name: Topics: Guide QuestionsDocument3 pagesLEARNING DIARY FOR NCM 105n/L-Nutrition and Diet Therapy Date: Name: Topics: Guide QuestionsWendell Gian GolezNo ratings yet
- Hyperuricemia XXXX XXXXX XxjeuneDocument32 pagesHyperuricemia XXXX XXXXX XxjeuneOziq Juga ReMa-eNo ratings yet
- Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome: Information Leaflet OnDocument8 pagesTwin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome: Information Leaflet Onshona SharupaniNo ratings yet
- Personal Hygiene and Health Care - Social and PreventiveDocument37 pagesPersonal Hygiene and Health Care - Social and Preventiveanubhav thakurNo ratings yet
- Humphrey Visual Field TestDocument1 pageHumphrey Visual Field TestMedisch 007No ratings yet
- Future Scope and Challenges For Congestive Heart Failure Moving Towards Development of PharmacotherapyDocument47 pagesFuture Scope and Challenges For Congestive Heart Failure Moving Towards Development of PharmacotherapysunhaolanNo ratings yet
- List of Hospital Performance Indicators For Accountability (Hpia)Document2 pagesList of Hospital Performance Indicators For Accountability (Hpia)Mohd syukri HashimNo ratings yet
- 30-06-2020 HMB EnglishDocument41 pages30-06-2020 HMB EnglishKirti VNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology Is The Study of Drug-Induced Changes in Mood, Sensation, ThinkingDocument5 pagesPsychopharmacology Is The Study of Drug-Induced Changes in Mood, Sensation, Thinking0921pyNo ratings yet
- CNA Body Mechanics Bed Making Comfort CareDocument32 pagesCNA Body Mechanics Bed Making Comfort CareFaith VaughnNo ratings yet