Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anemia and Its Types
Anemia and Its Types
Uploaded by
nihalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nur 145 Answer KeyDocument36 pagesNur 145 Answer KeyJhoanna Marie VillaverdeNo ratings yet
- MediCall Past Papers PDFDocument1,224 pagesMediCall Past Papers PDFarsalan67% (3)
- Physiology Question BankDocument9 pagesPhysiology Question BankShriyaNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia Pada Anak: Pembimbing: Dr. Aulia SP A, (K) Meriani SilabanDocument44 pagesThalassemia Pada Anak: Pembimbing: Dr. Aulia SP A, (K) Meriani SilabanMeriani Damaris SilabanNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 - Anemia 5Document25 pagesTopic 10 - Anemia 5Vince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia: Dr. Rino Arianto Marswita, SP - PDDocument45 pagesThalassemia: Dr. Rino Arianto Marswita, SP - PDAnonymous Eox0rG4xA100% (1)
- Thalassemia LectureDocument45 pagesThalassemia LectureBomber ENo ratings yet
- Thalassemia Final 1Document8 pagesThalassemia Final 1Kartick PalNo ratings yet
- MGD Eta1 Revision: Coagulation Cascade, Haemoglobinopathies & Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument16 pagesMGD Eta1 Revision: Coagulation Cascade, Haemoglobinopathies & Chromosomal AbnormalitiesAdiShineNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia Seminar Final 161117182232Document124 pagesThalassemia Seminar Final 161117182232interna MANADONo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument6 pagesSickle Cell AnemiaJoshua PioneloNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Seminar: Dr. Aysha Sabiha Dr. Maimuna Sayeed Dr. Sharmin Akter Luna Residents (Phase-A)Document124 pagesWelcome To Seminar: Dr. Aysha Sabiha Dr. Maimuna Sayeed Dr. Sharmin Akter Luna Residents (Phase-A)interna MANADONo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaDocument8 pagesThalassemiaMonish NavaneethanNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaDocument15 pagesThalassemianareshk260377No ratings yet
- Cme Anemia and ThalassemiaDocument80 pagesCme Anemia and Thalassemianurhadirah94No ratings yet
- Thallasemia: Shinta O WardhaniDocument12 pagesThallasemia: Shinta O WardhaniTonny Aldo Aprillino100% (1)
- Thalassemia: BASICS - 3 Types of HBDocument5 pagesThalassemia: BASICS - 3 Types of HBBhavya agarwalNo ratings yet
- 3-InTRODUCTION - ThalassemiaDocument12 pages3-InTRODUCTION - Thalassemiayeshitla amsaluNo ratings yet
- 4 Genetics DiseaseDocument40 pages4 Genetics Diseasemouid0.2003No ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Alterations in Oxygen Carrying Capacity (Hematologic Disorder)Document30 pagesCare of Clients With Alterations in Oxygen Carrying Capacity (Hematologic Disorder)Michael John CanlasNo ratings yet
- HEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Document31 pagesHEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia: Dr. VenkateshDocument74 pagesThalassemia: Dr. Venkateshinterna MANADONo ratings yet
- Thalassemia PND MaisuriDocument38 pagesThalassemia PND MaisuriariniNo ratings yet
- THALASSEMIADocument7 pagesTHALASSEMIAJann April ManalaysayNo ratings yet
- 3525-Article Text-13140-1-10-20200722Document12 pages3525-Article Text-13140-1-10-20200722Uzma KhanNo ratings yet
- The Thalassemias: December 2014Document7 pagesThe Thalassemias: December 2014Joscelind SunaryoNo ratings yet
- THALASSEMIADocument33 pagesTHALASSEMIAMirzi Cuison100% (1)
- Clinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateDocument3 pagesClinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateqselmmNo ratings yet
- Alpha-Thalassemia: Renzo Galanello, MD, and Antonio Cao, MDDocument6 pagesAlpha-Thalassemia: Renzo Galanello, MD, and Antonio Cao, MDLink BuiNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument131 pagesCardioKnowrienel OhmsNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia SyndromesDocument11 pagesThalassemia SyndromesTrishenth FonsekaNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiasDocument50 pagesThalassemiassamaNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia and Related HemoglobinopathiesDocument6 pagesThalassemia and Related HemoglobinopathiesMelly SyafridaNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobinopathies & Thalasemia Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesHemoglobinopathies & Thalasemia Learning ObjectivesFatima AhmedNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia PDFDocument88 pagesThalassemia PDFshabrinaerin100% (1)
- Thalassemiais ShafiqDocument70 pagesThalassemiais ShafiqIAMSANWAR019170No ratings yet
- Genetic Disease Tables-2Document8 pagesGenetic Disease Tables-2Joe JosephNo ratings yet
- Talasemia HemoglobinopatiDocument103 pagesTalasemia Hemoglobinopatisanti kristianiNo ratings yet
- Beta-Thalassemia: Authors: Antonio Cao, MD Renzo Galanello, MDDocument33 pagesBeta-Thalassemia: Authors: Antonio Cao, MD Renzo Galanello, MDUMMID WashimNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia: by DR PP GevaoDocument46 pagesThalassemia: by DR PP GevaoAbubakar JallohNo ratings yet
- ThalasemiaDocument48 pagesThalasemianeelam aliNo ratings yet
- Abnormal FBC 1.16 Feb 2016Document5 pagesAbnormal FBC 1.16 Feb 2016jyothi vallabhaneniNo ratings yet
- Beta Thalassemia - A Review: Jha R, Jha SDocument9 pagesBeta Thalassemia - A Review: Jha R, Jha SSajjad Hossain ShuvoNo ratings yet
- 4 - Alfa Thalassemia SyndromesDocument10 pages4 - Alfa Thalassemia Syndromesyeshitla amsaluNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Causative DiseasesDocument3 pagesCirrhosis Causative DiseasesMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Haemoglobinopathies - ThalassaemiaDocument49 pagesHaemoglobinopathies - ThalassaemiaRaymond LundaNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia An OverviewDocument4 pagesThalassemia An OverviewLink BuiNo ratings yet
- Beta Thalassemia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument16 pagesBeta Thalassemia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchFrancis GathiraNo ratings yet
- Thalassemias and HemoglobinopathiesDocument63 pagesThalassemias and HemoglobinopathiesMahmod_Al_Bust_4830No ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument2 pagesAnemiaRed DiggerNo ratings yet
- Hematology Anemia Clinical Manifestations of Anemia MECHANISM OF ANEMIA (How It Develops)Document10 pagesHematology Anemia Clinical Manifestations of Anemia MECHANISM OF ANEMIA (How It Develops)Jüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaDocument10 pagesThalassemiaAmanda Scarlet100% (1)
- ThalassemiaDocument44 pagesThalassemiaYASSER2009FREE89% (18)
- Hemolytic Anemia's ThalassemiaDocument60 pagesHemolytic Anemia's Thalassemiadx8ybd5ry9No ratings yet
- Mendel Law: Autosomal RecessiveDocument11 pagesMendel Law: Autosomal RecessivemuhammadfahmanNo ratings yet
- 2 Premarital CounselingDocument23 pages2 Premarital CounselingMark BirthNo ratings yet
- Thalassemi ADocument23 pagesThalassemi Ainterna MANADO100% (1)
- Athalassaemia: A Genotype-Phenotype Correlation and ManagementDocument10 pagesAthalassaemia: A Genotype-Phenotype Correlation and ManagementDina Sabilah AssegafNo ratings yet
- TABLE 135 - Mood Stabilizing MedicationsDocument1 pageTABLE 135 - Mood Stabilizing MedicationsDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Beta Thalassemia by Sylvester: DefinitionDocument9 pagesBeta Thalassemia by Sylvester: DefinitionAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Alpha and Betha Thalassemia (Muncie, 2009)Document8 pagesAlpha and Betha Thalassemia (Muncie, 2009)widyafandriNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandThalassemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2021 QuestionsDocument112 pages2021 QuestionsMohammad Alrefai100% (1)
- Dr. Ritu Verma Synopsiss FullDocument42 pagesDr. Ritu Verma Synopsiss Fulldrrituverma1No ratings yet
- Approach To The Adult With Anemia PDFDocument37 pagesApproach To The Adult With Anemia PDFAmjad SaudNo ratings yet
- IVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesDocument151 pagesIVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (2)
- Approachtohemolyticanemia 131001003025 Phpapp02Document63 pagesApproachtohemolyticanemia 131001003025 Phpapp02adnansirajNo ratings yet
- Hematology CasesDocument10 pagesHematology Casesuyes100% (1)
- MCQ2 QuestionDocument100 pagesMCQ2 Question9hjk6wpxyfNo ratings yet
- Sideroblastic AnemiaDocument18 pagesSideroblastic AnemiaSonam Joshi100% (2)
- PATHology Questions MGR Medical UniversityDocument40 pagesPATHology Questions MGR Medical UniversityPONNUSAMY P50% (2)
- Research ArticleDocument17 pagesResearch ArticleRidho TjanNo ratings yet
- 41 How To Cure DiseaseDocument60 pages41 How To Cure DiseaseEdie M Murgia50% (2)
- Hema, Gut Take Home TestDocument6 pagesHema, Gut Take Home TestNom NomNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentTed Cipriano VistaNo ratings yet
- Stereological Analysis of Terminal Villi of The Placentas of Pregnant Woman With Sideropenic AnemiaDocument5 pagesStereological Analysis of Terminal Villi of The Placentas of Pregnant Woman With Sideropenic Anemiasanbin007No ratings yet
- (K5-1) Kuliah Anemia Hemolitik (Dr. Riza)Document21 pages(K5-1) Kuliah Anemia Hemolitik (Dr. Riza)Puti Callistha IchsanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: For The Primary Care PhysicianDocument54 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: For The Primary Care PhysicianFlavia PolodeanuNo ratings yet
- Ancy Lost OmaDocument41 pagesAncy Lost OmaMuhmmad TahaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Geriatric Assessment of Hip FractureDocument14 pagesRapid Geriatric Assessment of Hip FractureJuliana Moreno LadinoNo ratings yet
- Classification of AnemiaDocument8 pagesClassification of AnemiaHelao SilasNo ratings yet
- A. Maternal Adaptation in PregnancyDocument32 pagesA. Maternal Adaptation in PregnancyFely Gunay100% (2)
- Vitamins: Ghubaya College of Pharmacy 9485500085Document2 pagesVitamins: Ghubaya College of Pharmacy 9485500085Ghubaya CopNo ratings yet
- 2809 250 PBDocument8 pages2809 250 PBAndi RahmadNo ratings yet
- Hematologymnemonics 151002194222 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument8 pagesHematologymnemonics 151002194222 Lva1 App6891 PDFpadmaNo ratings yet
- Immunology ExamsDocument120 pagesImmunology ExamsThanuja SureshNo ratings yet
- 2 Drug Study - PanganadamanDocument5 pages2 Drug Study - PanganadamanNornisah H. PangandamanNo ratings yet
- Obsos 2Document10 pagesObsos 2Depri AndreansyaNo ratings yet
- 7th March 2020 Plab 1 MockDocument32 pages7th March 2020 Plab 1 MockZoha QureshiNo ratings yet
Anemia and Its Types
Anemia and Its Types
Uploaded by
nihalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anemia and Its Types
Anemia and Its Types
Uploaded by
nihalCopyright:
Available Formats
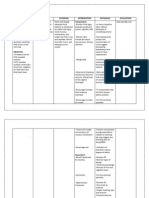
ANEMIA AND ITS TYPES
ANEMIA: TYPES
THALESSEMIA Grk. Thalassa; (the sea)
Hemoglobin conc. below a set point* α- thalassemia β- thalassemia
Depends upon Inherited blood disorder when body
• Age doesn’t make enough Hemoglobin Defect in α chain genes Defect in β chain genes
• Gender
• Physiological status 1 gene (no symp) trait 1 gene (mild sym) β-
• Smoking habits thalassemia minor
• altitudes HISTORY 2 genes (mild sym) α- 2 genes (mod-severe
Cut Off Values Of Hb Gene mutation that cause Thalassemia arose as partial thalassemia minor sym)
(WHO, 2018) protection against Malaria Mod- β-thalassemia
intermedia
Mild 10-lower limit Affects people more with ancestral links to parts of
Sev- β-thalassemia
world with prevalent Malaria (Africa, Southern Europe,
Moderate 8-10 g/dl West, East & South Asia)
major/ Cooley’s
anemia
Severe 6.5-7.9 g/dl
3 genes (mod-sev sym) -
GENETICS Hemoglobin H disease
TYPES OF ANEMIA
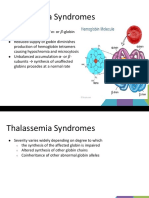
Hb 4 chains •• 2 α 4 genes (hydrops -
2β • CBC fetalis)
4 genes(2 from each parent)
• Hb Life long transfusions
TREATMENT
If defect in any of the Electrophoresis Blood Transfusion
genes, the result will • Every 4 months
be Thalassemia • 2-4 weeks (major)
Genetic Testing Iron chelation (removal of excess
iron)
SIGN & SYMPTOMS
Asymptomatic: No symp, or mostly fatigue Iron supplements
Mild-Moderate: Growth prob, delayed
puberty, osteoporosis Bone marrow/ stem cell transplant
(only cure to thalassemia)
Severe: All mild-moderate
symptoms plus Poor appetite, jaundice, dark PRESENTED BY Luspatercept (injection given every 3
Bakht Nihal Khan, Shafaat Haroon, Komail, Aqsa, Ahmad Zeb, weeks for RBC production)
urine, irregular facial appearance Abdal Khan, Mehr Ali
You might also like
- Nur 145 Answer KeyDocument36 pagesNur 145 Answer KeyJhoanna Marie VillaverdeNo ratings yet
- MediCall Past Papers PDFDocument1,224 pagesMediCall Past Papers PDFarsalan67% (3)
- Physiology Question BankDocument9 pagesPhysiology Question BankShriyaNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia Pada Anak: Pembimbing: Dr. Aulia SP A, (K) Meriani SilabanDocument44 pagesThalassemia Pada Anak: Pembimbing: Dr. Aulia SP A, (K) Meriani SilabanMeriani Damaris SilabanNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 - Anemia 5Document25 pagesTopic 10 - Anemia 5Vince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia: Dr. Rino Arianto Marswita, SP - PDDocument45 pagesThalassemia: Dr. Rino Arianto Marswita, SP - PDAnonymous Eox0rG4xA100% (1)
- Thalassemia LectureDocument45 pagesThalassemia LectureBomber ENo ratings yet
- Thalassemia Final 1Document8 pagesThalassemia Final 1Kartick PalNo ratings yet
- MGD Eta1 Revision: Coagulation Cascade, Haemoglobinopathies & Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument16 pagesMGD Eta1 Revision: Coagulation Cascade, Haemoglobinopathies & Chromosomal AbnormalitiesAdiShineNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia Seminar Final 161117182232Document124 pagesThalassemia Seminar Final 161117182232interna MANADONo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument6 pagesSickle Cell AnemiaJoshua PioneloNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Seminar: Dr. Aysha Sabiha Dr. Maimuna Sayeed Dr. Sharmin Akter Luna Residents (Phase-A)Document124 pagesWelcome To Seminar: Dr. Aysha Sabiha Dr. Maimuna Sayeed Dr. Sharmin Akter Luna Residents (Phase-A)interna MANADONo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaDocument8 pagesThalassemiaMonish NavaneethanNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaDocument15 pagesThalassemianareshk260377No ratings yet
- Cme Anemia and ThalassemiaDocument80 pagesCme Anemia and Thalassemianurhadirah94No ratings yet
- Thallasemia: Shinta O WardhaniDocument12 pagesThallasemia: Shinta O WardhaniTonny Aldo Aprillino100% (1)
- Thalassemia: BASICS - 3 Types of HBDocument5 pagesThalassemia: BASICS - 3 Types of HBBhavya agarwalNo ratings yet
- 3-InTRODUCTION - ThalassemiaDocument12 pages3-InTRODUCTION - Thalassemiayeshitla amsaluNo ratings yet
- 4 Genetics DiseaseDocument40 pages4 Genetics Diseasemouid0.2003No ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Alterations in Oxygen Carrying Capacity (Hematologic Disorder)Document30 pagesCare of Clients With Alterations in Oxygen Carrying Capacity (Hematologic Disorder)Michael John CanlasNo ratings yet
- HEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Document31 pagesHEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia: Dr. VenkateshDocument74 pagesThalassemia: Dr. Venkateshinterna MANADONo ratings yet
- Thalassemia PND MaisuriDocument38 pagesThalassemia PND MaisuriariniNo ratings yet
- THALASSEMIADocument7 pagesTHALASSEMIAJann April ManalaysayNo ratings yet
- 3525-Article Text-13140-1-10-20200722Document12 pages3525-Article Text-13140-1-10-20200722Uzma KhanNo ratings yet
- The Thalassemias: December 2014Document7 pagesThe Thalassemias: December 2014Joscelind SunaryoNo ratings yet
- THALASSEMIADocument33 pagesTHALASSEMIAMirzi Cuison100% (1)
- Clinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateDocument3 pagesClinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateqselmmNo ratings yet
- Alpha-Thalassemia: Renzo Galanello, MD, and Antonio Cao, MDDocument6 pagesAlpha-Thalassemia: Renzo Galanello, MD, and Antonio Cao, MDLink BuiNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument131 pagesCardioKnowrienel OhmsNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia SyndromesDocument11 pagesThalassemia SyndromesTrishenth FonsekaNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiasDocument50 pagesThalassemiassamaNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia and Related HemoglobinopathiesDocument6 pagesThalassemia and Related HemoglobinopathiesMelly SyafridaNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobinopathies & Thalasemia Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesHemoglobinopathies & Thalasemia Learning ObjectivesFatima AhmedNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia PDFDocument88 pagesThalassemia PDFshabrinaerin100% (1)
- Thalassemiais ShafiqDocument70 pagesThalassemiais ShafiqIAMSANWAR019170No ratings yet
- Genetic Disease Tables-2Document8 pagesGenetic Disease Tables-2Joe JosephNo ratings yet
- Talasemia HemoglobinopatiDocument103 pagesTalasemia Hemoglobinopatisanti kristianiNo ratings yet
- Beta-Thalassemia: Authors: Antonio Cao, MD Renzo Galanello, MDDocument33 pagesBeta-Thalassemia: Authors: Antonio Cao, MD Renzo Galanello, MDUMMID WashimNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia: by DR PP GevaoDocument46 pagesThalassemia: by DR PP GevaoAbubakar JallohNo ratings yet
- ThalasemiaDocument48 pagesThalasemianeelam aliNo ratings yet
- Abnormal FBC 1.16 Feb 2016Document5 pagesAbnormal FBC 1.16 Feb 2016jyothi vallabhaneniNo ratings yet
- Beta Thalassemia - A Review: Jha R, Jha SDocument9 pagesBeta Thalassemia - A Review: Jha R, Jha SSajjad Hossain ShuvoNo ratings yet
- 4 - Alfa Thalassemia SyndromesDocument10 pages4 - Alfa Thalassemia Syndromesyeshitla amsaluNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Causative DiseasesDocument3 pagesCirrhosis Causative DiseasesMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Haemoglobinopathies - ThalassaemiaDocument49 pagesHaemoglobinopathies - ThalassaemiaRaymond LundaNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia An OverviewDocument4 pagesThalassemia An OverviewLink BuiNo ratings yet
- Beta Thalassemia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument16 pagesBeta Thalassemia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchFrancis GathiraNo ratings yet
- Thalassemias and HemoglobinopathiesDocument63 pagesThalassemias and HemoglobinopathiesMahmod_Al_Bust_4830No ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument2 pagesAnemiaRed DiggerNo ratings yet
- Hematology Anemia Clinical Manifestations of Anemia MECHANISM OF ANEMIA (How It Develops)Document10 pagesHematology Anemia Clinical Manifestations of Anemia MECHANISM OF ANEMIA (How It Develops)Jüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaDocument10 pagesThalassemiaAmanda Scarlet100% (1)
- ThalassemiaDocument44 pagesThalassemiaYASSER2009FREE89% (18)
- Hemolytic Anemia's ThalassemiaDocument60 pagesHemolytic Anemia's Thalassemiadx8ybd5ry9No ratings yet
- Mendel Law: Autosomal RecessiveDocument11 pagesMendel Law: Autosomal RecessivemuhammadfahmanNo ratings yet
- 2 Premarital CounselingDocument23 pages2 Premarital CounselingMark BirthNo ratings yet
- Thalassemi ADocument23 pagesThalassemi Ainterna MANADO100% (1)
- Athalassaemia: A Genotype-Phenotype Correlation and ManagementDocument10 pagesAthalassaemia: A Genotype-Phenotype Correlation and ManagementDina Sabilah AssegafNo ratings yet
- TABLE 135 - Mood Stabilizing MedicationsDocument1 pageTABLE 135 - Mood Stabilizing MedicationsDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Beta Thalassemia by Sylvester: DefinitionDocument9 pagesBeta Thalassemia by Sylvester: DefinitionAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Alpha and Betha Thalassemia (Muncie, 2009)Document8 pagesAlpha and Betha Thalassemia (Muncie, 2009)widyafandriNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandThalassemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2021 QuestionsDocument112 pages2021 QuestionsMohammad Alrefai100% (1)
- Dr. Ritu Verma Synopsiss FullDocument42 pagesDr. Ritu Verma Synopsiss Fulldrrituverma1No ratings yet
- Approach To The Adult With Anemia PDFDocument37 pagesApproach To The Adult With Anemia PDFAmjad SaudNo ratings yet
- IVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesDocument151 pagesIVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (2)
- Approachtohemolyticanemia 131001003025 Phpapp02Document63 pagesApproachtohemolyticanemia 131001003025 Phpapp02adnansirajNo ratings yet
- Hematology CasesDocument10 pagesHematology Casesuyes100% (1)
- MCQ2 QuestionDocument100 pagesMCQ2 Question9hjk6wpxyfNo ratings yet
- Sideroblastic AnemiaDocument18 pagesSideroblastic AnemiaSonam Joshi100% (2)
- PATHology Questions MGR Medical UniversityDocument40 pagesPATHology Questions MGR Medical UniversityPONNUSAMY P50% (2)
- Research ArticleDocument17 pagesResearch ArticleRidho TjanNo ratings yet
- 41 How To Cure DiseaseDocument60 pages41 How To Cure DiseaseEdie M Murgia50% (2)
- Hema, Gut Take Home TestDocument6 pagesHema, Gut Take Home TestNom NomNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentTed Cipriano VistaNo ratings yet
- Stereological Analysis of Terminal Villi of The Placentas of Pregnant Woman With Sideropenic AnemiaDocument5 pagesStereological Analysis of Terminal Villi of The Placentas of Pregnant Woman With Sideropenic Anemiasanbin007No ratings yet
- (K5-1) Kuliah Anemia Hemolitik (Dr. Riza)Document21 pages(K5-1) Kuliah Anemia Hemolitik (Dr. Riza)Puti Callistha IchsanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: For The Primary Care PhysicianDocument54 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: For The Primary Care PhysicianFlavia PolodeanuNo ratings yet
- Ancy Lost OmaDocument41 pagesAncy Lost OmaMuhmmad TahaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Geriatric Assessment of Hip FractureDocument14 pagesRapid Geriatric Assessment of Hip FractureJuliana Moreno LadinoNo ratings yet
- Classification of AnemiaDocument8 pagesClassification of AnemiaHelao SilasNo ratings yet
- A. Maternal Adaptation in PregnancyDocument32 pagesA. Maternal Adaptation in PregnancyFely Gunay100% (2)
- Vitamins: Ghubaya College of Pharmacy 9485500085Document2 pagesVitamins: Ghubaya College of Pharmacy 9485500085Ghubaya CopNo ratings yet
- 2809 250 PBDocument8 pages2809 250 PBAndi RahmadNo ratings yet
- Hematologymnemonics 151002194222 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument8 pagesHematologymnemonics 151002194222 Lva1 App6891 PDFpadmaNo ratings yet
- Immunology ExamsDocument120 pagesImmunology ExamsThanuja SureshNo ratings yet
- 2 Drug Study - PanganadamanDocument5 pages2 Drug Study - PanganadamanNornisah H. PangandamanNo ratings yet
- Obsos 2Document10 pagesObsos 2Depri AndreansyaNo ratings yet
- 7th March 2020 Plab 1 MockDocument32 pages7th March 2020 Plab 1 MockZoha QureshiNo ratings yet