Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fall BUBT FI - Class-01 (1B) 19.10.11
Fall BUBT FI - Class-01 (1B) 19.10.11
Uploaded by
ashiqazamkhanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sop 28 - Sales and MarketingDocument8 pagesSop 28 - Sales and Marketingnice guy100% (3)
- Financial Market and InstitutionsDocument43 pagesFinancial Market and Institutionsdhiviraj100% (3)
- Assignment - Financial MarketsDocument9 pagesAssignment - Financial MarketsTaruntej Singh100% (3)
- The Kenyan Financial SystemDocument90 pagesThe Kenyan Financial SystemBondoobiero87% (15)
- Deposit Confirmation/Renewal AdviceDocument1 pageDeposit Confirmation/Renewal Advicedeepak pandeyNo ratings yet
- Case Study Bank of The Philippine Island PDFDocument3 pagesCase Study Bank of The Philippine Island PDF김서연100% (1)
- Role of Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument25 pagesRole of Financial Markets and InstitutionsvlaciarNo ratings yet
- Business and The Financial Markets Chapter 03Document50 pagesBusiness and The Financial Markets Chapter 03James KuruvalakaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets, Institutions, and InstrumentsDocument58 pagesFinancial Markets, Institutions, and InstrumentsDaniela MercadoNo ratings yet
- Financial Environment: Financial Markets of PakistanDocument26 pagesFinancial Environment: Financial Markets of PakistanMuneeb UmairNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsDocument40 pagesLecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsKurt Anne SanchezNo ratings yet
- Jamila Mufazzal - Chapter002.pptx (BF)Document49 pagesJamila Mufazzal - Chapter002.pptx (BF)jamila mufazzalNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions 1Document29 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions 1Hamza Iqbal100% (1)
- Financial Markets and Institutions: Required Reading: Mishkin, Chapter 1 andDocument43 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions: Required Reading: Mishkin, Chapter 1 andVivek Roy100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsDocument40 pagesLecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsPerbielyn BasinilloNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument29 pagesFinancial Markets and InstitutionsAdriana Del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets - Chapter 1 PDFDocument19 pagesFinancial Markets - Chapter 1 PDFBuzon Kyle BluNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions, Markets, & Money, 10 Edition: Power Point Slides ForDocument56 pagesFinancial Institutions, Markets, & Money, 10 Edition: Power Point Slides Forsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- 1.financial Services-An Overview-FinalDocument26 pages1.financial Services-An Overview-FinalSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Financial Instruments Institutions and MarketsDocument37 pagesModule 1 Financial Instruments Institutions and MarketsMary Gwyneth PerezNo ratings yet
- Financial Environment - Lecture2Document20 pagesFinancial Environment - Lecture2mehnaz kNo ratings yet
- Overview of Market Participants and Financial InnovationDocument52 pagesOverview of Market Participants and Financial Innovationlinda zyongweNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstrumentDocument30 pagesFinancial Markets and InstrumentAbdul Fattaah Bakhsh 1837065No ratings yet
- 1-Bond MarketDocument85 pages1-Bond Marketdharmtamanna80% (5)
- Financial EnvironmentDocument30 pagesFinancial EnvironmentIan TattaoNo ratings yet
- Neha Siddique 02-111201-222 BBA-4B Fundamentals of Finance: Integrated Case StudyDocument8 pagesNeha Siddique 02-111201-222 BBA-4B Fundamentals of Finance: Integrated Case StudyArishfa khanNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and Markets: Prof. Manisha SanghviDocument85 pagesFinancial Institutions and Markets: Prof. Manisha SanghviinderpretationNo ratings yet
- Mahran Final 2 Organized (1) RemovedDocument15 pagesMahran Final 2 Organized (1) RemovedAhmed Adly MohamedNo ratings yet
- W2. NotesDocument14 pagesW2. NotesCristelyn TomasNo ratings yet
- 1financial Management EnvironmentDocument2 pages1financial Management Environmentchautsi preciousNo ratings yet
- Capital MarketDocument41 pagesCapital MarketAhmed Jan DahriNo ratings yet
- Topic 8: The Australian Financial Markets: Week 8 NotesDocument3 pagesTopic 8: The Australian Financial Markets: Week 8 NotesJakeNo ratings yet
- FINANCEDocument5 pagesFINANCEAARTI MaidNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Financial MarketsDocument6 pagesThe Role of The Financial Marketsrosalyn mauricioNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document37 pagesCH 1xyzNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument21 pagesBusiness Finance: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleNOVELYN QUILNATNo ratings yet
- Madura Chapter 1 PDFDocument36 pagesMadura Chapter 1 PDFMahmoud AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Canadian Financial SystemDocument22 pagesWeek 1 - Canadian Financial SystemDinusha FernandoNo ratings yet
- (NR) Financial Markets and InstitutionDocument8 pages(NR) Financial Markets and InstitutionMichael MendozaNo ratings yet
- Let'S Go Back To The Past: Quiz For The Last Lesson DiscussedDocument26 pagesLet'S Go Back To The Past: Quiz For The Last Lesson DiscussedReina Mae Martinez RiegoNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document54 pagesChap 2Yeshiwork GirmaNo ratings yet
- Financial Market Premid ANS KEY161413805Document4 pagesFinancial Market Premid ANS KEY161413805LeaGabrielleAbbyFariolaNo ratings yet
- Industry Profile of Financial Service IndustryDocument7 pagesIndustry Profile of Financial Service IndustryMedha SinghNo ratings yet
- Purple Gradient 3D Bold Modern Investing Tips PresentationDocument47 pagesPurple Gradient 3D Bold Modern Investing Tips PresentationJana Beni Carolyn R. SabadoNo ratings yet
- FIN - 605 - Lecture NotesDocument195 pagesFIN - 605 - Lecture NotesDebendra Nath PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Banking and Finance: Guy Hargreaves ACE-102Document38 pagesIntroduction To Banking and Finance: Guy Hargreaves ACE-102Riri FahraniNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and MarketsDocument6 pagesFinancial Institutions and MarketsFarrah Jane BitacNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Financial System: Group1: Michelle Santiago ReighlynroseteDocument23 pagesOverview of The Financial System: Group1: Michelle Santiago ReighlynroseteJoan Pearl SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Mutual FundsDocument15 pagesMutual FundsMirchi RiyazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Financial Market EnvironmentDocument4 pagesChapter 2 - The Financial Market EnvironmentWahyu MahardikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Environment - SystemsDocument29 pagesChapter 2 Environment - SystemsMasum BillahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1mark sanadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document2 pagesLesson 3Safh SalazarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Phương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 1-Indian Financial SystemDocument30 pages1-Indian Financial SystempallavimakkanNo ratings yet
- Finman7.Module Sir RhomarkDocument69 pagesFinman7.Module Sir RhomarkLeynard ColladoNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets.Document32 pagesCapital Markets.api-3727090No ratings yet
- Mutual FundsDocument8 pagesMutual FundsaltraxiNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds - The Mutual Fund Retirement Plan For Long - Term Wealth BuildingFrom EverandMutual Funds - The Mutual Fund Retirement Plan For Long - Term Wealth BuildingNo ratings yet
- Equity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2From EverandEquity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Job Description: Send Me Jobs Like ThisDocument2 pagesJob Description: Send Me Jobs Like Thispradhan13No ratings yet
- 02 B1 - 91 - Multi - Branch - 12Document41 pages02 B1 - 91 - Multi - Branch - 12Cristhian MercadoNo ratings yet
- Wallstreetjournaleurope 20170425 The Wall Street Journal EuropeDocument22 pagesWallstreetjournaleurope 20170425 The Wall Street Journal EuropestefanoNo ratings yet
- E Bussiness AssignmentDocument40 pagesE Bussiness Assignmentsateesh_ims09100% (3)
- Ethical Practices of Financial Services OrganisationsDocument20 pagesEthical Practices of Financial Services OrganisationsKrutika Likhite100% (1)
- BCDocument2 pagesBCKathrine CruzNo ratings yet
- SIM Audit 421 Problem Week 4-5Document33 pagesSIM Audit 421 Problem Week 4-5Kristelle MarieNo ratings yet
- BLW/INV38/04/2020: Note: This Invoice Is Not Valid Whitout Our Official StampDocument2 pagesBLW/INV38/04/2020: Note: This Invoice Is Not Valid Whitout Our Official StampAnisa YosivaNo ratings yet
- Travis Sims UnionbankDocument4 pagesTravis Sims UnionbankJonathan Seagull LivingstonNo ratings yet
- Qabco English TestDocument19 pagesQabco English TestFA AyNo ratings yet
- HSL Weekly Insight: Retail ResearchDocument5 pagesHSL Weekly Insight: Retail ResearchumaganNo ratings yet
- Ey Shifting Focus Risk Culture at The Forefront of BankingDocument86 pagesEy Shifting Focus Risk Culture at The Forefront of BankingChristian AquinoNo ratings yet
- Sammy Gicheha - Bank StatementDocument6 pagesSammy Gicheha - Bank StatementJason MoutiNo ratings yet
- IPO PreparationDocument4 pagesIPO Preparationdeshmukh_muzammil1917No ratings yet
- A Brief Report EnglishDocument10 pagesA Brief Report EnglishJohn BernalNo ratings yet
- RR PDFDocument1 pageRR PDFسید محمد ہارون باچاNo ratings yet
- Arthur Kitson - A Fraudulent StandardDocument262 pagesArthur Kitson - A Fraudulent StandardmrpoissonNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Deploying Microsoft Dynamics AX Opening BalancesDocument4 pagesBest Practices For Deploying Microsoft Dynamics AX Opening Balancesearnestgoh3635No ratings yet
- Foreign Fund Management China 11Document89 pagesForeign Fund Management China 11Ning JiaNo ratings yet
- Infra Emkay 151014Document113 pagesInfra Emkay 151014SUKHSAGAR1969No ratings yet
- Mymaxicare Rates 2021Document2 pagesMymaxicare Rates 2021Ariane ComboyNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document2 pagesChap 2Siva SankariNo ratings yet
- Payment Bank Impact On Digital BankingDocument78 pagesPayment Bank Impact On Digital BankingSudharshan Reddy P0% (1)
- Unit 4 Banking PDFDocument14 pagesUnit 4 Banking PDFakashNo ratings yet
- NetbankDocument3 pagesNetbankjambroo100% (1)
- Ponzi SCams in IndiaDocument7 pagesPonzi SCams in IndiaVignesh KymalNo ratings yet
- RiskCalc 3.1 WhitepaperDocument36 pagesRiskCalc 3.1 Whitepaperiver2340_729926247No ratings yet
Fall BUBT FI - Class-01 (1B) 19.10.11
Fall BUBT FI - Class-01 (1B) 19.10.11
Uploaded by
ashiqazamkhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fall BUBT FI - Class-01 (1B) 19.10.11
Fall BUBT FI - Class-01 (1B) 19.10.11
Uploaded by
ashiqazamkhanCopyright:
Available Formats
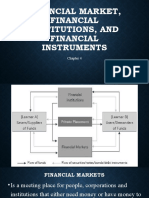
CHAPTER 1
ROLE OF FINANCIAL MARKETS AND INSTITUTIONS
FUNCTION OF FINANCIAL MARKETS
A financial market is a market in which financial assets (securities) can be purchased or sold Financial markets facilitate transfers of funds from person or business without investment opportunities (i.e., Lender-Savers, or Surplus Unit) to those who have them (i.e., Borrower-Spenders, or Deficit Unit)
SEGMENTS OF FINANCIAL MARKETS
Direct Financing
Funds are transferred directly from ultimate savers to ultimate borrowers
Indirect Financing
A financial "intermediary" transforms financial claims with one set of characteristics into financial claims with other characteristics e.g. deposits are used to make loans.
3
TRANSFER OF FUNDS ON FINANCIAL MARKET
FUNCTION OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES
Provide customers with liquidity service Help to repackage the risk
Willing to create and sell assets with lesser risk to one party in order to buy assets with greater risk form another party This process is referred to as asset transformation
TYPES OF FINANCIAL MARKETS
Financial markets can be distinguished by the maturity structure and trading structure of its securities Financial markets can be thought as the following types: Money versus capital markets
Primary versus secondary markets Organized versus over-the-counter markets Open versus negotiated market
6
TYPES OF FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Money versus Capital markets
The flow of short-term funds is facilitated by money
markets
The flow of long-term funds is facilitated by capital
markets
Organized versus Over-the-counter markets
A visible marketplace for secondary market transactions
is an organized exchange
Some transactions occur in the over-the-counter (OTC)
market (a telecommunications network)
7
TYPES OF FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Primary versus Secondary markets
Primary markets facilitate the issuance of new securities
E.g.: the sale of new corporate stock or new Treasury securities Secondary Markets facilitate the trading of existing securities
E.g., the sale of existing stock Securities traded in secondary markets should be liquid
TYPES OF FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Knowledge of financial markets is power
Decide which markets to use to achieve our
investment goals or financing needs
Decide which markets to use as part of your job Avoid common mistakes in investing and borrowing
SECURITIES TRADED IN FINANCIAL MARKETS
Money Market Securities
Money market securities are debt securities
with a maturity of one year or less Characteristics: Liquid Low expected return Low degree of risk
10
SECURITIES TRADED IN FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Capital Market Securities
Capital market securities are those with a
maturity of more than one year Bonds and mortgages Stocks Capital market securities have a higher expected return and more risk than money market securities
11
SECURITIES TRADED IN FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Bonds and Mortgages
Bonds are long-term debt obligations issued by
corporations and government agencies Mortgages are long-term debt obligations created to finance the purchase of real estate Bonds and mortgages specify the amount and timing of interest and principal payments
12
SECURITIES TRADED IN FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Stocks
Stocks (equity) are certificates representing
partial ownership in corporations Investors may earn a return by receiving dividends and capital gains Stocks have a higher expected return and higher risk than long-term debt securities
13
SECURITIES TRADED IN FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Derivative Securities
Derivative securities are financial contracts whose
values are derived from the values of underlying assets
Speculating with derivatives allow investors to
benefit from increases or decreases in the underlying asset
Risk management with derivatives generates gains
if the value of the underlying security declines
14
ROLE OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS IN FINANCIAL MARKETS
Role of Depository Institutions
Depository institutions accept deposits from
surplus units and provide credit to deficit units Depository institutions are popular because: Deposits are liquid They customize loans They accept the risk of loans They have expertise in evaluating creditworthiness They diversify their loans
15
ROLE OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS IN FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Commercial Banks
Are the most dominant depository institution Offer a wide variety of deposit accounts Transfer deposited funds by providing direct
loans or purchasing debt securities
Serve both the public and the private sector
16
ROLE OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS IN FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Savings institutions
savings banks
Include savings and loan associations (S&Ls) and
Are mostly owned by depositors (mutual) Concentrate on residential mortgage loans
Credit unions
Are nonprofit organizations Restrict their business to credit union members Tend to be much smaller than other depository
institutions
17
ROLE OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS IN FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Role of nondepository financial institutions
sources other than deposits
Nondepository institutions generate funds from
Types of nondepository financial institutions
Mutual funds Securities firms Insurance companies Pension funds Finance companies Leasing companies
18
ROLE OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS IN FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Mutual Funds
Sell shares to surplus units Use funds to purchase a portfolio of securities
Some focus on capital market securities (e.g.,
stocks or bonds) Money market mutual funds concentrate on money market securities
19
ROLE OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS IN FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Securities firms
Broker
function
Execute securities transactions between two
parties Charge a fee in the form of a bid-ask spread
Investment banking Dealer
function
function
Underwrite newly issued securities
Securities firms make a market in specific
securities by adjusting their inventory
20
ROLE OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS IN FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Insurance Companies
Provide insurance policies to individuals and firms
for death, illness, and damage to property Charge premiums Invest in stocks or bonds issued by corporations
Finance companies
Obtain funds by issuing securities Lend funds to individuals and small businesses
21
ROLE OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS IN FINANCIAL MARKETS (CONTD)
Pension Funds
Offered by most corporations and government
agencies Manage funds until they are withdrawn from the retirement account Invest in stocks or bonds issued by corporations or in bonds issued by the government
Leasing Companies
Give leases to businesses and individuals
22
COMPARISON OF ROLES AMONG FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Deposits
Depository Institutions Finance Companies
Individual Surplus Units Securities
Purchase Shares
Purchase
Mutual Funds Insurance Companies
Deficit Units
Policyholders
Premiums
Employers Employees
Employee Contributions
Pension Funds
23
OVERVIEW OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Competition between financial institutions
the value of their owners Present value of future cash flows Depends on: Growth and profitability Degree of risk
24
Financial institutions should operate to maximize
OVERVIEW OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS (CONTD)
Consolidation of financial institutions
opportunities to capitalize on: Economies of scale Economies of scope Mergers have resulted in financial conglomerates Consolidation may increase expected cash flows or reduce risk, or both
25
Reduction in regulations has resulted in more
You might also like
- Sop 28 - Sales and MarketingDocument8 pagesSop 28 - Sales and Marketingnice guy100% (3)
- Financial Market and InstitutionsDocument43 pagesFinancial Market and Institutionsdhiviraj100% (3)
- Assignment - Financial MarketsDocument9 pagesAssignment - Financial MarketsTaruntej Singh100% (3)
- The Kenyan Financial SystemDocument90 pagesThe Kenyan Financial SystemBondoobiero87% (15)
- Deposit Confirmation/Renewal AdviceDocument1 pageDeposit Confirmation/Renewal Advicedeepak pandeyNo ratings yet
- Case Study Bank of The Philippine Island PDFDocument3 pagesCase Study Bank of The Philippine Island PDF김서연100% (1)
- Role of Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument25 pagesRole of Financial Markets and InstitutionsvlaciarNo ratings yet
- Business and The Financial Markets Chapter 03Document50 pagesBusiness and The Financial Markets Chapter 03James KuruvalakaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets, Institutions, and InstrumentsDocument58 pagesFinancial Markets, Institutions, and InstrumentsDaniela MercadoNo ratings yet
- Financial Environment: Financial Markets of PakistanDocument26 pagesFinancial Environment: Financial Markets of PakistanMuneeb UmairNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsDocument40 pagesLecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsKurt Anne SanchezNo ratings yet
- Jamila Mufazzal - Chapter002.pptx (BF)Document49 pagesJamila Mufazzal - Chapter002.pptx (BF)jamila mufazzalNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions 1Document29 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions 1Hamza Iqbal100% (1)
- Financial Markets and Institutions: Required Reading: Mishkin, Chapter 1 andDocument43 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions: Required Reading: Mishkin, Chapter 1 andVivek Roy100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsDocument40 pagesLecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsPerbielyn BasinilloNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument29 pagesFinancial Markets and InstitutionsAdriana Del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets - Chapter 1 PDFDocument19 pagesFinancial Markets - Chapter 1 PDFBuzon Kyle BluNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions, Markets, & Money, 10 Edition: Power Point Slides ForDocument56 pagesFinancial Institutions, Markets, & Money, 10 Edition: Power Point Slides Forsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- 1.financial Services-An Overview-FinalDocument26 pages1.financial Services-An Overview-FinalSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Financial Instruments Institutions and MarketsDocument37 pagesModule 1 Financial Instruments Institutions and MarketsMary Gwyneth PerezNo ratings yet
- Financial Environment - Lecture2Document20 pagesFinancial Environment - Lecture2mehnaz kNo ratings yet
- Overview of Market Participants and Financial InnovationDocument52 pagesOverview of Market Participants and Financial Innovationlinda zyongweNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstrumentDocument30 pagesFinancial Markets and InstrumentAbdul Fattaah Bakhsh 1837065No ratings yet
- 1-Bond MarketDocument85 pages1-Bond Marketdharmtamanna80% (5)
- Financial EnvironmentDocument30 pagesFinancial EnvironmentIan TattaoNo ratings yet
- Neha Siddique 02-111201-222 BBA-4B Fundamentals of Finance: Integrated Case StudyDocument8 pagesNeha Siddique 02-111201-222 BBA-4B Fundamentals of Finance: Integrated Case StudyArishfa khanNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and Markets: Prof. Manisha SanghviDocument85 pagesFinancial Institutions and Markets: Prof. Manisha SanghviinderpretationNo ratings yet
- Mahran Final 2 Organized (1) RemovedDocument15 pagesMahran Final 2 Organized (1) RemovedAhmed Adly MohamedNo ratings yet
- W2. NotesDocument14 pagesW2. NotesCristelyn TomasNo ratings yet
- 1financial Management EnvironmentDocument2 pages1financial Management Environmentchautsi preciousNo ratings yet
- Capital MarketDocument41 pagesCapital MarketAhmed Jan DahriNo ratings yet
- Topic 8: The Australian Financial Markets: Week 8 NotesDocument3 pagesTopic 8: The Australian Financial Markets: Week 8 NotesJakeNo ratings yet
- FINANCEDocument5 pagesFINANCEAARTI MaidNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Financial MarketsDocument6 pagesThe Role of The Financial Marketsrosalyn mauricioNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document37 pagesCH 1xyzNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument21 pagesBusiness Finance: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleNOVELYN QUILNATNo ratings yet
- Madura Chapter 1 PDFDocument36 pagesMadura Chapter 1 PDFMahmoud AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Canadian Financial SystemDocument22 pagesWeek 1 - Canadian Financial SystemDinusha FernandoNo ratings yet
- (NR) Financial Markets and InstitutionDocument8 pages(NR) Financial Markets and InstitutionMichael MendozaNo ratings yet
- Let'S Go Back To The Past: Quiz For The Last Lesson DiscussedDocument26 pagesLet'S Go Back To The Past: Quiz For The Last Lesson DiscussedReina Mae Martinez RiegoNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document54 pagesChap 2Yeshiwork GirmaNo ratings yet
- Financial Market Premid ANS KEY161413805Document4 pagesFinancial Market Premid ANS KEY161413805LeaGabrielleAbbyFariolaNo ratings yet
- Industry Profile of Financial Service IndustryDocument7 pagesIndustry Profile of Financial Service IndustryMedha SinghNo ratings yet
- Purple Gradient 3D Bold Modern Investing Tips PresentationDocument47 pagesPurple Gradient 3D Bold Modern Investing Tips PresentationJana Beni Carolyn R. SabadoNo ratings yet
- FIN - 605 - Lecture NotesDocument195 pagesFIN - 605 - Lecture NotesDebendra Nath PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Banking and Finance: Guy Hargreaves ACE-102Document38 pagesIntroduction To Banking and Finance: Guy Hargreaves ACE-102Riri FahraniNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and MarketsDocument6 pagesFinancial Institutions and MarketsFarrah Jane BitacNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Financial System: Group1: Michelle Santiago ReighlynroseteDocument23 pagesOverview of The Financial System: Group1: Michelle Santiago ReighlynroseteJoan Pearl SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Mutual FundsDocument15 pagesMutual FundsMirchi RiyazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Financial Market EnvironmentDocument4 pagesChapter 2 - The Financial Market EnvironmentWahyu MahardikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Environment - SystemsDocument29 pagesChapter 2 Environment - SystemsMasum BillahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1mark sanadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document2 pagesLesson 3Safh SalazarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Phương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 1-Indian Financial SystemDocument30 pages1-Indian Financial SystempallavimakkanNo ratings yet
- Finman7.Module Sir RhomarkDocument69 pagesFinman7.Module Sir RhomarkLeynard ColladoNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets.Document32 pagesCapital Markets.api-3727090No ratings yet
- Mutual FundsDocument8 pagesMutual FundsaltraxiNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds - The Mutual Fund Retirement Plan For Long - Term Wealth BuildingFrom EverandMutual Funds - The Mutual Fund Retirement Plan For Long - Term Wealth BuildingNo ratings yet
- Equity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2From EverandEquity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Job Description: Send Me Jobs Like ThisDocument2 pagesJob Description: Send Me Jobs Like Thispradhan13No ratings yet
- 02 B1 - 91 - Multi - Branch - 12Document41 pages02 B1 - 91 - Multi - Branch - 12Cristhian MercadoNo ratings yet
- Wallstreetjournaleurope 20170425 The Wall Street Journal EuropeDocument22 pagesWallstreetjournaleurope 20170425 The Wall Street Journal EuropestefanoNo ratings yet
- E Bussiness AssignmentDocument40 pagesE Bussiness Assignmentsateesh_ims09100% (3)
- Ethical Practices of Financial Services OrganisationsDocument20 pagesEthical Practices of Financial Services OrganisationsKrutika Likhite100% (1)
- BCDocument2 pagesBCKathrine CruzNo ratings yet
- SIM Audit 421 Problem Week 4-5Document33 pagesSIM Audit 421 Problem Week 4-5Kristelle MarieNo ratings yet
- BLW/INV38/04/2020: Note: This Invoice Is Not Valid Whitout Our Official StampDocument2 pagesBLW/INV38/04/2020: Note: This Invoice Is Not Valid Whitout Our Official StampAnisa YosivaNo ratings yet
- Travis Sims UnionbankDocument4 pagesTravis Sims UnionbankJonathan Seagull LivingstonNo ratings yet
- Qabco English TestDocument19 pagesQabco English TestFA AyNo ratings yet
- HSL Weekly Insight: Retail ResearchDocument5 pagesHSL Weekly Insight: Retail ResearchumaganNo ratings yet
- Ey Shifting Focus Risk Culture at The Forefront of BankingDocument86 pagesEy Shifting Focus Risk Culture at The Forefront of BankingChristian AquinoNo ratings yet
- Sammy Gicheha - Bank StatementDocument6 pagesSammy Gicheha - Bank StatementJason MoutiNo ratings yet
- IPO PreparationDocument4 pagesIPO Preparationdeshmukh_muzammil1917No ratings yet
- A Brief Report EnglishDocument10 pagesA Brief Report EnglishJohn BernalNo ratings yet
- RR PDFDocument1 pageRR PDFسید محمد ہارون باچاNo ratings yet
- Arthur Kitson - A Fraudulent StandardDocument262 pagesArthur Kitson - A Fraudulent StandardmrpoissonNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Deploying Microsoft Dynamics AX Opening BalancesDocument4 pagesBest Practices For Deploying Microsoft Dynamics AX Opening Balancesearnestgoh3635No ratings yet
- Foreign Fund Management China 11Document89 pagesForeign Fund Management China 11Ning JiaNo ratings yet
- Infra Emkay 151014Document113 pagesInfra Emkay 151014SUKHSAGAR1969No ratings yet
- Mymaxicare Rates 2021Document2 pagesMymaxicare Rates 2021Ariane ComboyNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document2 pagesChap 2Siva SankariNo ratings yet
- Payment Bank Impact On Digital BankingDocument78 pagesPayment Bank Impact On Digital BankingSudharshan Reddy P0% (1)
- Unit 4 Banking PDFDocument14 pagesUnit 4 Banking PDFakashNo ratings yet
- NetbankDocument3 pagesNetbankjambroo100% (1)
- Ponzi SCams in IndiaDocument7 pagesPonzi SCams in IndiaVignesh KymalNo ratings yet
- RiskCalc 3.1 WhitepaperDocument36 pagesRiskCalc 3.1 Whitepaperiver2340_729926247No ratings yet