Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phonetics 8
Phonetics 8
Uploaded by
minhngocchuyenvantb0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesphonetic and phonology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentphonetic and phonology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesPhonetics 8
Phonetics 8
Uploaded by
minhngocchuyenvantbphonetic and phonology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
1.
What are the differences between a stressed and unstressed
syllable?
2. What are the factors influencing stress placement?
3. Name some of the prefixes that conventionally are
unstressed, and give examples.
4. Give an example of a word which has the stress pattern
changed when it is of different parts of speech, and establish
the rule.
5. Name some of the suffixes having no effect on the word
stress pattern, and give examples.
6. Name some of the suffixes that may receive strong stress
themselves, and give examples.
7. Name some of the suffixes causing a shift in the word stress
pattern, and give examples. 8.
8. Establish the stress pattern rule of compound nouns, and
give examples.
1. In English, how do you account for the difference between
[i:], [e] and [æ] ?
2. Diphthong moving from mid front unrounded to high front
unrounded
3. Diphthong low back rounded/ central unrounded to high
front unrounded
4. Diphthong mid back rounded to high front unrounded
5. Diphthong mid central unrounded to high back unrounded
6. Diphthong low back rounded/ central unrounded to high
back unrounded
7. Diphthong high front unrounded to mid central unrounded
8. Diphthong mid front unrounded to mid central unrounded
9. Diphthong high back unrounded to mid central unrounded
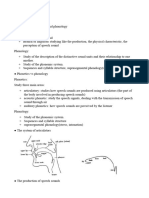
10. Bilabial sounds are produced when the …
are brought together.
11. … sounds are made when the lower lip is
raised towards the upper front teeth.
12. Dental sounds are produced by touching
the upper front teeth with the … of the tongue.
13. Alveolar sounds are made by raising the tip
of the tongue towards the ridge that is right …
the upper front teeth, called the alveolar ridge.
14. Palato-alveolar sounds are made by
raising the … of the tongue towards the part of
the palate just behind the alveolar ridge.
15. Palatal sounds are very similar to palato-
alveolar ones, they are just produced further
back towards the ….
16. Velar sounds are made by raising the … of
the tongue towards the soft palate, called the
velum.
17. Glottal sounds are produced when the air
passes through the … as it is narrowed.
18. Plosives are sounds in which there is a …
closure in the mouth, so that the air is blocked
for a fraction of a second and then released
with a small burst of sound, called a plosion (it
sounds like a very small explosion).
19. … have a closure which is not quite
complete. This means that the air is not
blocked at any point, and therefore there is no
plosion. On the other hand the obstruction is
big enough for the air to make a noise when it
passes through it, because of the friction.
20. Affricates are a combination of a plosive
and a fricative (sometimes they are called
"affricated plosives"). They begin like a plosive,
with a complete closure, but instead of a
plosion, they have a very slow …, moving
backwards to a place where a friction can be
heard (palato-alveolar).
21. Nasals resemble plosives, except that
there is a complete closure in the mouth, but
as the velum is … the air can escape through
the nasal cavity.
22. Laterals are sounds where the air escapes
around the … of the tongue.
23. Approximants are sounds where the
tongue only approaches the roof of the mouth,
so that there is not enough … to create any
friction.
24. The manners of articulation can be put into
two major groups, obtruents and sonorants. The
obstruents are …, fricatives and affricates, all
sounds with a high degree of obstruction.
Obstruents usually come in pairs, one voiceless,
one voiced. Sonorants have much less obstruction
and are all … and therefore more sonorous. They
include nasals, the …, and approximants.
25. How can you describe /r/, /w/ and /j/ using all
and only those features by which they can be
opposed to other consonants. In order to do this:
a. List all the features
b. Determine those that are redundant.
26. Give:
a. a syllable beginning with a cluster labio-dental fricative +
lateral
b. a syllable beginning with a cluster labio-dental fricative +
palatal
c. a syllable beginning with a cluster fricative + alveolar nasal
d. a syllable beginning with a cluster s + plosive + velar
e. a syllable ending with a cluster lateral +plosive + alveolar
f. a syllable ending with a cluster velar nasal + plosive
g. a syllable ending with a cluster voiced plosive + alveolar
fricative
You may have had to eliminate some of the syllables of the
exercise which are not possible in English. If you did, explain
on what basis you did so.
27. Give a clear picture of what a phoneme is
and what the problems around the definition of
the phoneme can be.
28. The autumn leaves rustled on the path.
29. Richard of York gave battle in vain.
30. We heard the cattle from a long way away.
31. He’s worried about his ankle.
32. The children were badly beaten.
33. The first train leaves at seven o’clock.
34. Have you come to enjoy the spectacle?
35. We could leave business until tomorrow.
36. Disappearance
37. Transformer
38. Captivity
Choose the word which contains a sound with its phonetic
features as stated below.
1. initial voiced fricative post-alveolar
A. giant B. job C. social D. session
2. initial cluster: plosive bilabial voiced + voiced post-alveolar approximant
A. precious B. flexible C. quality D. brother
3. final cluster: voiced nasal alveolar + voiceless plosive alveolar
A. philosophy B. student C. problem D. change
4. initial low front unrounded
A. ambulance B. apologize C. advantageous D. authority
5. final voiced labio-dental fricative
A. special B. competitive C. awareness D. occasion
Give the text to the following transcription
You might also like
- TOPIC 9 Oposiciones 2014Document10 pagesTOPIC 9 Oposiciones 2014okamideeen100% (1)
- Understanding the Concepts of English PrepositionsFrom EverandUnderstanding the Concepts of English PrepositionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Choose The Best Answer. Tick A, B, C, or D.: A. A Very Long TimeDocument13 pagesChoose The Best Answer. Tick A, B, C, or D.: A. A Very Long Timechau mai100% (1)
- Business Communication IDocument14 pagesBusiness Communication ISonam PatroNo ratings yet
- اسئلة استرشادية صوتيات قسم الترجمةDocument6 pagesاسئلة استرشادية صوتيات قسم الترجمةMasarra GhaithNo ratings yet
- Bài Kt 2 Ngữ Âm HọcDocument20 pagesBài Kt 2 Ngữ Âm HọcLệ ThứcNo ratings yet
- EX: The Phoneme /P/ in Peak and SpeakDocument5 pagesEX: The Phoneme /P/ in Peak and SpeakTuệ TâmNo ratings yet
- Review: I/ TRUE/FALSE: Decide Whether Each of The Following Statements Is TRUE or FalseDocument3 pagesReview: I/ TRUE/FALSE: Decide Whether Each of The Following Statements Is TRUE or FalsePhan Thị Cẩm LyNo ratings yet
- Phonology McqsDocument3 pagesPhonology Mcqsالاستاذ محمد زغيرNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Phonology ExamDocument6 pagesWuolah Free Phonology ExamLaura Gómez GozálvezNo ratings yet
- REVIEW 5 (New) 20-21Document5 pagesREVIEW 5 (New) 20-21WuttNo ratings yet
- Ngữ âm kiểm traDocument3 pagesNgữ âm kiểm traHoanh HuynhNo ratings yet
- REVIEW 5 (New) 20-21Document5 pagesREVIEW 5 (New) 20-21duyên phanNo ratings yet
- Trac Nghiem Ngu Am Am Vi Hoc Tieng AnhDocument19 pagesTrac Nghiem Ngu Am Am Vi Hoc Tieng AnhMary NguyenNo ratings yet
- Review 1Document7 pagesReview 1bbngoc10No ratings yet
- REVIEW 2 - NGỮ ÂM VÀ ÂM VỊ HỌCDocument3 pagesREVIEW 2 - NGỮ ÂM VÀ ÂM VỊ HỌCMinh HiếuNo ratings yet
- Ngân Hàng Câu Hỏi Môn Phonetics And Phonology (Khóa Nna-2019) A- Lý Thuyết 1. On the diagram provided, give the names for the articulatorsDocument20 pagesNgân Hàng Câu Hỏi Môn Phonetics And Phonology (Khóa Nna-2019) A- Lý Thuyết 1. On the diagram provided, give the names for the articulatorsTạ Hoàng AnhNo ratings yet
- Review Chapter 1,2,3,4,5Document8 pagesReview Chapter 1,2,3,4,5luonghoang25082004No ratings yet
- Speech OrgansDocument6 pagesSpeech OrgansPushpanathan ThiruNo ratings yet
- Phonetics: Consonants VowelsDocument2 pagesPhonetics: Consonants Vowelssami karemNo ratings yet
- Ngu Am - FinalDocument24 pagesNgu Am - FinalHuỳnh CúcNo ratings yet
- Uas Alrino Ode MasimuDocument10 pagesUas Alrino Ode MasimuArif FlouncxNo ratings yet
- Review Section 1Document5 pagesReview Section 1Đức Hoàng BùiNo ratings yet
- Review Section 1Document5 pagesReview Section 1Vân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Notes On A Course in Phonetics (Summary)Document201 pagesNotes On A Course in Phonetics (Summary)Boshra HosseinpourNo ratings yet
- Ling Mid Term RevisionDocument5 pagesLing Mid Term RevisionTrang NguyenNo ratings yet
- ÔN TẬP NGỮ ÂM - ÂM VỊ HỌC - LÝ THUYẾTDocument8 pagesÔN TẬP NGỮ ÂM - ÂM VỊ HỌC - LÝ THUYẾTTrà Nguyễn HươngNo ratings yet
- trac-nghiem-ngu-am-am-vi-hoc-tieng-anh-đã chuyển đổiDocument18 pagestrac-nghiem-ngu-am-am-vi-hoc-tieng-anh-đã chuyển đổiNguyễn ThiênNo ratings yet
- Puntos Parcial Fonetica-1Document4 pagesPuntos Parcial Fonetica-1Ax AbregúNo ratings yet
- DescriptiveDocument75 pagesDescriptiveAmani SalmanNo ratings yet
- Let Linguistics Review Test Revised QuestionnaireDocument16 pagesLet Linguistics Review Test Revised Questionnairemyraxmirror100% (1)
- Tugas PhonologyDocument4 pagesTugas PhonologyJuwita AnggreliaNo ratings yet
- ConsonantsDocument14 pagesConsonantsLinh ChiNo ratings yet
- Review 2 - NewDocument4 pagesReview 2 - Newngtr.mt2005No ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology PDFDocument62 pagesPhonetics and Phonology PDFCarlos Rojas CamachoNo ratings yet
- English Test of OralsDocument18 pagesEnglish Test of OralsAyomide VickyNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - 19.07.2022Document48 pagesModule 2 - 19.07.2022parmar003akashNo ratings yet
- Bab I PendahuluanDocument9 pagesBab I PendahuluanEka MelyanaNo ratings yet
- Uas Pak MansyurDocument5 pagesUas Pak MansyurSholahudin Al MagribiNo ratings yet
- Phoneics RecordDocument36 pagesPhoneics RecordPeddapalli NikhileshNo ratings yet
- Speech MechanismDocument3 pagesSpeech Mechanismহুমায়রা জাহানNo ratings yet
- English Communication Skills - 40-45Document6 pagesEnglish Communication Skills - 40-45nagaraja1685No ratings yet
- Introduction and Production of Speech SoundDocument31 pagesIntroduction and Production of Speech SoundNguyệt MaiNo ratings yet
- NguamDocument9 pagesNguamled56203No ratings yet
- Isi ZuluDocument3 pagesIsi ZuluSesiyabonga NgubaneNo ratings yet
- (123doc) Trac Nghiem Ngu Am Am Vi Hoc Tieng AnhDocument18 pages(123doc) Trac Nghiem Ngu Am Am Vi Hoc Tieng AnhMai Thi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Phonology QuestionDocument7 pagesPhonology QuestionA. BASHEERNo ratings yet
- Đề Cương Ngữ Âm Âm VịDocument10 pagesĐề Cương Ngữ Âm Âm Vịphanthingochuyen024No ratings yet
- Phonemes Exercises: 1. Speech Sounds AreDocument8 pagesPhonemes Exercises: 1. Speech Sounds AreNguyễn HiềnNo ratings yet
- Phonology 3: A Compiled BookDocument147 pagesPhonology 3: A Compiled BookAya Taha.MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 312a734Trần Nguyễn Thanh ThúyNo ratings yet
- Slide NG ÂmDocument240 pagesSlide NG Âmhanhnguyen23022003No ratings yet
- Organs of SpeechDocument5 pagesOrgans of Speechlittle large2100% (1)
- SegmentalsDocument43 pagesSegmentalsLeidelen Muede Maranan100% (1)
- The Sounds of EnglishDocument58 pagesThe Sounds of EnglishSara Albina0% (1)
- Voice and Accent Training ModuleDocument12 pagesVoice and Accent Training ModuleAditi GhaiNo ratings yet
- Phonetic Handout 1Document14 pagesPhonetic Handout 1Wisten MárquezNo ratings yet
- Notes PhoneticDocument8 pagesNotes PhoneticHazrin ArinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To English PhoneticsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To English PhoneticsKhair MohammadNo ratings yet
- Vowel SoundsDocument6 pagesVowel Soundskieu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Phonetics 1Document31 pagesPhonetics 1minhngocchuyenvantbNo ratings yet
- Phonetics 9Document49 pagesPhonetics 9minhngocchuyenvantbNo ratings yet
- Ielts Mock Test 2020 September - Listening Practice Test 2 v9 3220432Document27 pagesIelts Mock Test 2020 September - Listening Practice Test 2 v9 3220432minhngocchuyenvantbNo ratings yet
- Ielts Mock Test 2020 May - Listening Practice Test 1 v9 2617039Document36 pagesIelts Mock Test 2020 May - Listening Practice Test 1 v9 2617039minhngocchuyenvantbNo ratings yet
- Ielts Mock Test 2020 July - Listening Practice Test 1 v9 3080048Document29 pagesIelts Mock Test 2020 July - Listening Practice Test 1 v9 3080048minhngocchuyenvantbNo ratings yet
- Ielts Mock Test 2020 June - Listening Practice Test 1 v9 2775959Document26 pagesIelts Mock Test 2020 June - Listening Practice Test 1 v9 2775959minhngocchuyenvantbNo ratings yet
- Ielts Mock Test 2020 August - Listening Practice Test 2 v9 3210691Document29 pagesIelts Mock Test 2020 August - Listening Practice Test 2 v9 3210691minhngocchuyenvantbNo ratings yet
- Ielts Mock Test 2020 April - Listening Practice Test 2 v9 2599648Document50 pagesIelts Mock Test 2020 April - Listening Practice Test 2 v9 2599648minhngocchuyenvantbNo ratings yet
- (To Appear On Incontri Linguistici 37 (2014) : 133-44) G B M V The Nazme: A Genre of Religious Poetry of The Eritrean SahoDocument11 pages(To Appear On Incontri Linguistici 37 (2014) : 133-44) G B M V The Nazme: A Genre of Religious Poetry of The Eritrean SahoahahaNo ratings yet
- The Consonants - Fricatives - AffricatesDocument10 pagesThe Consonants - Fricatives - AffricatesThục UyênNo ratings yet
- Alif BaaDocument4 pagesAlif Baaishmam chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Ponology Summary - S6Document38 pagesPonology Summary - S6work Wafa100% (1)
- An Indonesian and Malay Grammar For StudentsDocument16 pagesAn Indonesian and Malay Grammar For StudentsDa GlouglouNo ratings yet
- 4 Phonetics 2 - Vowel Consonant - Place Manner of ArticulationDocument15 pages4 Phonetics 2 - Vowel Consonant - Place Manner of ArticulationFany WPNo ratings yet
- English Phonetic Course Assimilation & Elision: Related PapersDocument8 pagesEnglish Phonetic Course Assimilation & Elision: Related PapersẶňąÀšlňMặX-MợŞhklặNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam in SpeechDocument7 pagesMidterm Exam in Speechciedelle aranda100% (1)
- Linguistic Second AssignmentDocument3 pagesLinguistic Second AssignmentmuhammadrezaNo ratings yet
- Old and Imperial Aramaic: Margaretha FolmerDocument32 pagesOld and Imperial Aramaic: Margaretha FolmerOmar The FabulousNo ratings yet
- Mistakes in Pronunciation of The VNeseDocument12 pagesMistakes in Pronunciation of The VNeseDinh AnhNo ratings yet
- English ConsonantsDocument28 pagesEnglish ConsonantsIzzati AzmanNo ratings yet
- Q.1 Choose The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesQ.1 Choose The Correct AnswerHawraa MahdiNo ratings yet
- Self StudyDocument12 pagesSelf StudyDowran KakajanowNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linguistics: Final Exam Practice Questions: Tnagano@gc - Cuny.eduDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Linguistics: Final Exam Practice Questions: Tnagano@gc - Cuny.eduEvangeline TorremochaNo ratings yet
- Accent Training AcadsocDocument12 pagesAccent Training AcadsocHijasmine bantoloNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Christine KaoNo ratings yet
- International Phonetic AlphabetDocument25 pagesInternational Phonetic AlphabetANIME LOVERNo ratings yet
- Academic English 01 IntroductionDocument10 pagesAcademic English 01 IntroductionesayasNo ratings yet
- Manners of Articulation 2Document15 pagesManners of Articulation 2Aini AdistianiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document7 pagesChapter 3Thanh TúNo ratings yet
- Phonology IiDocument9 pagesPhonology IiMoiraAcuñaNo ratings yet
- RP Consonant Phonemes: Articulatory FeaturesDocument8 pagesRP Consonant Phonemes: Articulatory FeaturesДаниїл БодюлNo ratings yet
- Effick LanguageDocument12 pagesEffick LanguageAniekanNo ratings yet
- English Phonemic and Allophonic HandbookDocument6 pagesEnglish Phonemic and Allophonic HandbookAndrei IstrateNo ratings yet
- Language of Magick PDFDocument1 pageLanguage of Magick PDFyZdXA5MDTirXw3uvD4Y2GL9NNo ratings yet
- Phonetics ExercisesDocument5 pagesPhonetics ExercisesWei YiNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology - SampleDocument6 pagesPhonetics and Phonology - SampleNguyễn Trần Bá ToànNo ratings yet
- Jan Tavernier On The Sounds Rendered by The S-, Š - and Z - Series in ElamiteDocument20 pagesJan Tavernier On The Sounds Rendered by The S-, Š - and Z - Series in ElamitelopezNo ratings yet
- Bangime Wordlist PaperDocument32 pagesBangime Wordlist PaperSamuel EkpoNo ratings yet