Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 08
CH 08
Uploaded by
sabyasachibba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views15 pagesOriginal Title
ch08
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views15 pagesCH 08
CH 08
Uploaded by
sabyasachibbaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
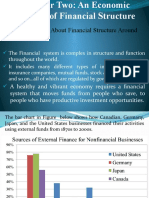
Chapter 8
An Economic
Analysis of Financial
Structure
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Sources of External Finance in Canada
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-2
Sources of Foreign External Finance
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-3
Puzzles of Financial Structure
1. Stocks are not most important source of external finance for
businesses
2. Issuing marketable securities not primary funding source for
businesses
3. Indirect finance (financial intermediation) is far more important than
direct finance
4. Banks are most important source of external finance
5. Financial system is among most heavily regulated sectors of economy
6. Only large, well established firms have access to securities markets
7. Collateral is prevalent feature of debt contracts
8. Debt contracts are typically extremely complicated legal documents
with restrictive covenants
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-4
Transaction Costs and Financial Structure
Transaction costs hinder flow of funds to people
with productive investment opportunities
Financial intermediaries make profits by
reducing transaction costs
1. Take advantage of economies of scale
Example: Mutual Funds
2. Develop expertise to lower transaction costs
Explains Puzzle 3
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-5
Adverse Selection
and Moral Hazard: Definitions
Adverse Selection:
1. Before transaction occurs
2. Potential borrowers most likely to produce adverse
outcomes are ones most likely to seek loans and be selected
Moral Hazard:
1. After transaction occurs
2. Hazard that borrower has incentives to engage in
undesirable (immoral) activities making it more likely that
won’t pay loan back
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-6
Adverse Selection
and Financial Structure
Lemons Problem in Securities Markets
1. If can’t distinguish between good and bad securities, willing
to pay only average of good and bad securities’ values.
2. Result: Good securities undervalued and firms won’t issue
them; bad securities overvalued, so too many issued.
3. Investors won’t want to buy bad securities, so market won’t
function well.
Explains Puzzle 2 and Puzzle 1.
Also explains Puzzle 6: Less asymmetric information for
well known firms, so smaller lemons problem
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-7
Tools to Help Solve Adverse
Selection (Lemons) Problem
1. Private Production and Sale of Information
Free-rider problem interferes with this solution
2. Government Regulation to Increase Information
Explains Puzzle 5
3. Financial Intermediation
A. Analogy to solution to lemons problem provided by used-car
dealers
B. Avoid free-rider problem by making private loans
Explains Puzzles 3 and 4
4. Collateral and Net Worth
Explains Puzzle 7
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-8
Moral Hazard: Debt versus Equity
Moral Hazard in Equity:
Principal-Agent Problem
1. Result of separation of ownership by stockholders (principals) from
control by managers (agents)
2. Managers act in own rather than stockholders’ interest
Tools to Help Solve the Principal-Agent Problem
1. Monitoring: production of information
2. Government regulation to increase information
3. Financial intermediation
4. Debt contracts
Explains Puzzle 1: Why debt used more than equity
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-9
Moral Hazard and Debt Markets
Moral hazard: borrower wants to take on too much risk
Tools to Help Solve Moral Hazard
1. Net worth
2. Monitoring and enforcement of restrictive
covenants
3. Financial intermediation
Banks and other intermediaries have special
advantages in monitoring
Explains Puzzles 1–4.
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-10
Summary: Asymmetric Information
Problems and Tools to Solve Them
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-11
Financial Development
and Economic Growth
Financial Repression Leads to Low Growth:
Why?
1. Poor legal system
2. Weak accounting standards
3. Government directs credit
4. Financial institutions nationalized
5. Inadequate government regulation
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-12
Financial Crises
Factors Causing Financial Crises
1. Increase in interest rates
2. Increases in uncertainty
3. Asset market effects on balance sheets
Stock market effects on net worth
Unanticipated deflation
Cash flow effects
4. Bank panics
5. Government fiscal imbalances
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-13
Events in Financial Crises in Canada
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-14
Events in
Mexican, East
Asian, and
Argentine
Financial Crises
© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8-15
You might also like
- Financial Markets and Institutions: Ninth EditionDocument59 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions: Ninth EditionShahmeer KamranNo ratings yet
- Financial Market and Institutions Ch7Document7 pagesFinancial Market and Institutions Ch7kelly0% (1)
- An Economic Analysis of Financial StructureDocument15 pagesAn Economic Analysis of Financial Structurevetushi123No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 BA 105Document27 pagesLecture 2 BA 105Boon Han TanNo ratings yet
- 3 Financial Institutions - C07Document58 pages3 Financial Institutions - C07Na PhưnNo ratings yet
- M07 MishkinEakins3427056 08 FMI C07Document58 pagesM07 MishkinEakins3427056 08 FMI C07Declan ShuitNo ratings yet
- M07 MishkinEakins3427056 08 FMI C07Document58 pagesM07 MishkinEakins3427056 08 FMI C07habiba ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document45 pagesChapter 7tientran.31211021669No ratings yet
- 8 - An Economic Analysis On Financial StructureDocument18 pages8 - An Economic Analysis On Financial StructurecihtanbioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 PDFDocument15 pagesLecture 5 PDFsuperzttNo ratings yet
- Weeks 3 and 4: Transaction Costs, Asymmetric Information and Moral HazardDocument20 pagesWeeks 3 and 4: Transaction Costs, Asymmetric Information and Moral HazardMichelle Ngan DaoNo ratings yet
- Why Do Financial Institutions ExistDocument44 pagesWhy Do Financial Institutions Existwaqar hattarNo ratings yet
- Lectures 3-4 (Chapter 8)Document22 pagesLectures 3-4 (Chapter 8)LuisLoNo ratings yet
- Finan 303Document23 pagesFinan 303khanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Week 2. QuizDocument3 pagesChapter 2. Week 2. QuizSlice LeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document23 pagesChapter 4mohamedxuseen215No ratings yet
- CH08 Mish11ge EMBFMDocument19 pagesCH08 Mish11ge EMBFMZeeruanNo ratings yet
- FI515 Homework1Document5 pagesFI515 Homework1andiemaeNo ratings yet
- Why Financial Institutions ExistDocument54 pagesWhy Financial Institutions ExistKareen WellingtonNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document66 pagesChap 3Thùy Vân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document29 pagesCH 7shubhmalhotra93No ratings yet
- Mishkin PPT Ch08Document21 pagesMishkin PPT Ch08atulkirarNo ratings yet
- Mishkin Fmi09 PPT 18Document69 pagesMishkin Fmi09 PPT 18lashia.williams69No ratings yet
- Why Do Financial Institutions ExistDocument39 pagesWhy Do Financial Institutions Existkafi100% (1)
- Chapter 8 An Economic Alaysis of Financiaal StructureDocument14 pagesChapter 8 An Economic Alaysis of Financiaal StructureSamanthaHandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document4 pagesChapter 8John FrandoligNo ratings yet
- II.1 Economic Analysis of Financial Institutions: Money, Banking and Financial MarketsDocument21 pagesII.1 Economic Analysis of Financial Institutions: Money, Banking and Financial MarketsclementNo ratings yet
- An Economic Analysis of Financial StructureDocument16 pagesAn Economic Analysis of Financial StructureAdnan NaeemNo ratings yet
- Finance and The Multinational FirmDocument13 pagesFinance and The Multinational FirmFatin AfifaNo ratings yet
- Economics 330: Money and BankingDocument23 pagesEconomics 330: Money and BankinglkjflksdfsdfNo ratings yet
- Financial IntermediationDocument45 pagesFinancial IntermediationVanessa DavisNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Basic Puzzles About Financial Structure Around The WorldDocument75 pages3.1. Basic Puzzles About Financial Structure Around The WorldNhatty WeroNo ratings yet
- Money and Banking Chapter 8Document3 pagesMoney and Banking Chapter 8Gene'sNo ratings yet
- Investments: Background and IssuesDocument35 pagesInvestments: Background and IssuesKevin GilkensonNo ratings yet
- Class 04Document3 pagesClass 04Aasim Bin BakrNo ratings yet
- Why Are Financial Institutions Special?Document31 pagesWhy Are Financial Institutions Special?Trần Nguyễn Huyền TrânNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document13 pagesCH 02sabyasachibbaNo ratings yet
- Lecture001 IBFDocument14 pagesLecture001 IBFMakhmoor SyedNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document12 pagesCH 02Kusumanchi AshishNo ratings yet
- Mishkin Chapter 7Document32 pagesMishkin Chapter 7everytimeyoulieNo ratings yet
- Reasons For Bank FailureDocument2 pagesReasons For Bank FailureBijoy SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Study Questions-AnswersDocument3 pagesCH 8 Study Questions-AnswersLiban hasanNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 - FinanceDocument11 pagesQuiz1 - Financerenata_oliver07100% (1)
- The Scope of Corporate Finance: Answers To Concept Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesThe Scope of Corporate Finance: Answers To Concept Review QuestionsHuu DuyNo ratings yet
- 2011 PPPCh8Document21 pages2011 PPPCh8BH Plus أخبار البحرينNo ratings yet
- Ross 7 e CH 01Document24 pagesRoss 7 e CH 01seshagsNo ratings yet
- An Economic Analysis of Financial StructureDocument27 pagesAn Economic Analysis of Financial StructureAlejandroArnoldoFritzRuenesNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment - Week 1 - AnswersDocument7 pagesHomework Assignment - Week 1 - AnswersTuấn Anh ĐinhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FinanceDocument18 pagesIntroduction To FinanceЛера АношинаNo ratings yet
- Asignación 1 (RMF FM)Document14 pagesAsignación 1 (RMF FM)Elia SantanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Submitted byDocument9 pagesAssignment 1: Submitted byzarin tasnimNo ratings yet
- Fianacial MarketsDocument53 pagesFianacial MarketsMostafa ElgendyNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Financial System: © 2005 Pearson Education Canada IncDocument12 pagesAn Overview of The Financial System: © 2005 Pearson Education Canada IncYasser AlmishalNo ratings yet
- FE - Tutorial 1Document2 pagesFE - Tutorial 1Carine TeeNo ratings yet
- Principles of Money & BankingDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Money & BankingMohsin KhanNo ratings yet
- Nonbank Finance: © 2005 Pearson Education Canada IncDocument9 pagesNonbank Finance: © 2005 Pearson Education Canada InchenriNo ratings yet
- ch12 Nonbank FiannaceDocument9 pagesch12 Nonbank FiannacehenriNo ratings yet
- The Role of Financial Intermediaries: Lecture No 2 Banking Techniques and OperationsDocument19 pagesThe Role of Financial Intermediaries: Lecture No 2 Banking Techniques and OperationsRoxana RusenNo ratings yet
- Ch1 FundamentalsDocument45 pagesCh1 FundamentalsFebri RahadiNo ratings yet
- Alan Kohler's The Eureka Way: Navigating the Financial Advice Minefield Without Blowing Your WealthFrom EverandAlan Kohler's The Eureka Way: Navigating the Financial Advice Minefield Without Blowing Your WealthRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Financial Institutions and MarketsDocument84 pagesFinancial Institutions and Marketsemre kutayNo ratings yet
- 5 - Stocastic Models of Investment ReturnsDocument1 page5 - Stocastic Models of Investment ReturnsAmit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Term Loan - 19225247 - 2024 - 03 - 22 - 21 - 39Document4 pagesTerm Loan - 19225247 - 2024 - 03 - 22 - 21 - 39maltemayur37No ratings yet
- Ang Tek Lian Vs CADocument1 pageAng Tek Lian Vs CAKimsey Clyde DevomaNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Housing Loan DecisionsDocument3 pagesQuestionnaire On Housing Loan Decisionsvijayadarshini vNo ratings yet
- Risk Management: Principles of Corporate FinanceDocument32 pagesRisk Management: Principles of Corporate FinanceAsad MazharNo ratings yet
- TD Bank StatementDocument3 pagesTD Bank StatementRoger kellyNo ratings yet
- List of Banks Headquarters and Taglines PDF DreamBigInstitutionDocument12 pagesList of Banks Headquarters and Taglines PDF DreamBigInstitutionWasif AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Debt Equity Ratio - MARUTI SUZUKI LTDDocument5 pagesDebt Equity Ratio - MARUTI SUZUKI LTDHaripriya AnusuyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Capital Budgeting - SolutionsDocument10 pagesChapter 10 - Capital Budgeting - Solutionsbraydenfr05No ratings yet
- Fabm 2 Quiz 1Document2 pagesFabm 2 Quiz 1Jenny HermosadoNo ratings yet
- SBI Securities Sectoral Technical Snapshot 06-12-2023Document8 pagesSBI Securities Sectoral Technical Snapshot 06-12-2023leninkumar2020No ratings yet
- Samudera Indonesia TBK - 30 Jun 2023Document115 pagesSamudera Indonesia TBK - 30 Jun 2023cahaya napitupuluNo ratings yet
- ACCA2 1 Handout No. 1 - Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocument3 pagesACCA2 1 Handout No. 1 - Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingZia May LauretaNo ratings yet
- Topic - 1 Introduction To Financial System-SummaryDocument21 pagesTopic - 1 Introduction To Financial System-SummaryAnh NguyenNo ratings yet
- WWW Simandhareducation Com Blogs Mba Vs Cpa What Is Wiser To ChooseDocument5 pagesWWW Simandhareducation Com Blogs Mba Vs Cpa What Is Wiser To Choosesrinu patroNo ratings yet
- Control Accounts Reconciliation PractiseDocument2 pagesControl Accounts Reconciliation Practisendumiso100% (1)
- Cash App January 2024 StatementAM1sDocument2 pagesCash App January 2024 StatementAM1spaschal alexNo ratings yet
- Amazon Pay BB Project v1Document85 pagesAmazon Pay BB Project v1Meenakshi Seervi100% (1)
- BDO Official ReceiptsDocument6 pagesBDO Official ReceiptsGareth TiuNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 (2802)Document4 pagesAssignment No. 1 (2802)Uzair MayaNo ratings yet
- Digitization of Indian Economy (Power Point Presentation)Document9 pagesDigitization of Indian Economy (Power Point Presentation)Gursparsh MakkerNo ratings yet
- Palepu 3e - SM - Ch01 Class Exercise QuestionDocument2 pagesPalepu 3e - SM - Ch01 Class Exercise Questionnur zakirah0% (1)
- Facturier Excel AutoDocument1,664 pagesFacturier Excel AutoxcvxccxvNo ratings yet
- Dr. Usha N. Patil MRP SummaryDocument4 pagesDr. Usha N. Patil MRP SummaryShree GuruNo ratings yet
- Statement of Financial Position SFP - PPTX MODULE2Document38 pagesStatement of Financial Position SFP - PPTX MODULE2alberto miranda100% (1)
- Financial Reporting Statements and AnalysisDocument245 pagesFinancial Reporting Statements and AnalysisSandeep Singh100% (2)
- Chanchal Infrastructure Private LimitedDocument2 pagesChanchal Infrastructure Private Limitedlalit rawatNo ratings yet
- Limitations of Ratio Analysis: Creative AccountingDocument2 pagesLimitations of Ratio Analysis: Creative AccountingGerron ThomasNo ratings yet
- Discounted Cash FlowDocument5 pagesDiscounted Cash FlowEKANGNo ratings yet