Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Audio Effects
Audio Effects
Uploaded by
Arshia Jain0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views26 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views26 pagesAudio Effects
Audio Effects
Uploaded by
Arshia JainCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 26
AUDIO EFFECTS
• Audio effects are hardware or software
devices that manipulate how an audio signal
sounds
• Time-based effects—Reverb, Delay and Echo
• Spectral effects—EQ and Panning
• Dynamic effects—Compression and Distortion
Frequencies
• All sounds — everything you hear — are
essentially vibrations that we can visualize as
waves moving up and down at different speeds,
or frequencies
• The faster the wave moves, the higher the pitch
• Measured in Hz (Hertz)
• Hertz measures how many times (i.e., the
frequency) a wave completes an up-and-down
cycle in 1 second
• The decibel (dB) is the unit of measurement
used to express volume level or loudness
• Using equalizer means that you are increasing
or decreasing the loudness of that particular
frequency.
EQUALIZATION
• the cutting or boosting of a particular
frequency (or range of frequencies) in the
frequency spectrum
• Adding some beef to low end or taking a bite
away from the treble
• By cutting or boosting certain frequencies, EQ
shapes the tone and character of your sound
• An Equalizer (EQ) divides the spectrum into
sections (called ‘bands’) that you use to cut or
boost parts of your sound
• Three band equalizers-
- Bass
- Treble
- Mid-range
• Bass and Treble = Shelving equalizers
• Mid-range= Peaking equalizers
EQUALIZATION
• Bass means low pitched Low frequency
sounds like sounds of bass guitar, kick drum,Lo
Fi sounds from synths and male baritones
• Treble means high or medium
pitched/frequency sounds like piano
sounds,acoustic guitars, cymbals and female
voices and HiFi synth sounds
• Bass frequencies start on the left,
• with midrange frequencies in the middle
• and treble on the far right (like a piano)
• Prefer peaking over shelving filters-
Peaking cuts or boosts the desirable frequencies
Shelving cuts or boosts all frequencies in bass
and treble range
Why use equalizers?
- Reduce scratch noise of old recordings
- Shelve low freq. and boost high freq. of older
recordings
- removal of hum and other unwanted
recordings
- Cutting high end will make your sound darker
- Boosting the high end will make it brighter
• Equalization not a substitute of proper
placement of microphone
• Keep in view the maximum limit of audio
mixer in handling highest possible level ( no
distortion occurs)
Artificial Reverberation
- to compensate for acoustically 'dead' studios
- only mechanical reverb devices like spring and
plate used earlier
- digital reverb devices can even be operated
remotely
Reverberation
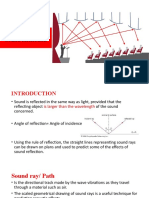
What is reverberation ?
- An echoing sound
- When you bang on a big piece of metal, you
can hear the reverberation even after you
stop banging
- The repeating, often low, booming sound that
follows the strum of an electric guitar or the
thump of a drumstick on a cymbal is called
reverberation
• Reverb occurs when a sound hits any hard
surface and reflects back to the listener at
varying times and amplitudes to create a
complex echo, which carries information
about that physical space
• The most obvious examples of reverberant
spaces are tunnels, cathedrals, halls and caves.
• Reverberation time is the time required for the
sound to “fade away” or decay in a closed space
• used in studios to add depth to sounds
• changes the perceived spectral structure of a
sound but does not alter the pitch
• one of the oldest of all audio effects
• aims to recreate the natural ambience of real
rooms and spaces
• Gives vocals more fullness and sustain, and
will have a more “natural” sound to them
• Longer decay times give the impression of
larger spaces
• Digital reverberating effects simulate or
exaggerate natural reverberations.
COMPRESSOR/LIMITER
• An audio compressor is a specialized amplifier
that reduces the gap between the loudest part
(peak) and quietest part of a signal
• Loud sounds made softer and soft sounds
made louder
• LIMITER: just a compressor that is used to
make sure a signal doesn't get much louder
than the threshold level
• Compressors are used to compress the sound
• Making more quiet sounds stand out more
• Done to sound natural on a recording
• For example: Imagine a whisper and a scream
on the same audio track. If they were the
same difference in loudness as they are in real
life, it would be very distracting!
• Compressors fix it by attenuating the loudest
parts of your signal and boosting the result so
the quieter parts are more apparent
PANNING
• the distribution of a sound signal in a stereo
(or multi-channel) field
• creates the illusion of a sound source moving
from one part of the soundstage to another
• Stereo sound systems have evolved from a
single speaker to a set of two, left and right.
This has allowed us to move from mono to
stereo sound playback
• Panning works by letting through more or less
of a signal into each speaker, creating various
spatial effects
• lets you prevent muddiness and masking in
your mix (when two sounds cover each other
up)
Echo and Delay
• Delay is an audio effect that records an audio
signal for playback a set period of time after
the original signal
• Delay can be played back in different ways to
achieve sounds such as echoes that decay
over time, or a pronounced repeated doubling
effect that adds new layers to a recording
• Most delays work by playing back the dry
signal while also playing back the wet or
‘delayed’ signal shortly after the original
• Shorter uses of delay, like slapback or doubling
effects, are useful for filling out a
performance, especially vocals or guitar
DISTORTION
• Distortion is an overloading of the audio circuit
that causes the signal to clip
• warmer” sound impression, or a harsh one
• Distortion changes your original signal by
pushing the sound to clip and compress. This
adds harmonic content and colors the sound in
a pleasant way
• makes your sound fatter and fuller
• adds complexity and body to your sound
Reference links
• https://blog.landr.com/audio-effects-plugins-g
uide
/
• http://blog.dubspot.com/understanding-audio
-effects-an-overview
/
You might also like
- Room Acoustics - Steve KindigDocument15 pagesRoom Acoustics - Steve Kindigsweeney.paraic100% (2)
- 100 QuestionsDocument44 pages100 QuestionsLara Knezić100% (1)
- How To Write A Killer Music Brief - Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesHow To Write A Killer Music Brief - Cheat Sheetdavid manuelNo ratings yet
- Sound Engineering: Professional Diploma inDocument43 pagesSound Engineering: Professional Diploma infotousNo ratings yet
- The Basics of ReverbDocument6 pagesThe Basics of ReverbIshaan EvenidaNo ratings yet
- Sound Engineering: Professional Diploma inDocument50 pagesSound Engineering: Professional Diploma infotousNo ratings yet
- Resumen de Efectos XAir X18 XR18Document9 pagesResumen de Efectos XAir X18 XR18telebaudNo ratings yet
- Sound Notes 9 BDocument3 pagesSound Notes 9 Bsmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Basic of SoundDocument54 pagesBasic of SoundRoslina Jaafar75% (4)
- Room AcousticsDocument52 pagesRoom AcousticsDavezel Zerx100% (1)
- MTA 254 Sound: Week 2Document14 pagesMTA 254 Sound: Week 2tlipfertNo ratings yet
- Week8 Day3Document49 pagesWeek8 Day3asadukimbugwe20No ratings yet
- Week 3 - Reverb Echo & SpatializationDocument64 pagesWeek 3 - Reverb Echo & Spatializationscotttian7No ratings yet
- Re Verb Quick GuideDocument2 pagesRe Verb Quick GuideMaliko MudendaNo ratings yet
- Mixing 101Document11 pagesMixing 101Lincoln WangNo ratings yet
- Noise and MusicDocument15 pagesNoise and MusicHaynes BertolNo ratings yet
- Mixing 3 - Space - Reverb: Top To BottomDocument11 pagesMixing 3 - Space - Reverb: Top To BottomLucas Ferrari RabeloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch PerceptionDocument49 pagesChapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch PerceptionmehdichitiNo ratings yet
- Research On Sonic Components in RecordingsDocument3 pagesResearch On Sonic Components in RecordingsMartika DupignyWilliamsNo ratings yet
- HometheatreDocument25 pagesHometheatreankithaNo ratings yet
- Architectural Acoustics: Building Utilities 3 - Acoustics and Lighting Systems (Topic 1)Document23 pagesArchitectural Acoustics: Building Utilities 3 - Acoustics and Lighting Systems (Topic 1)Davezel ZerxNo ratings yet
- Unit-III Radio Production and Transmission Process: Lesson 4 Recording, Broadcasting and TroubleshootingDocument14 pagesUnit-III Radio Production and Transmission Process: Lesson 4 Recording, Broadcasting and TroubleshootingpariNo ratings yet
- Design of Rooms For MusicDocument41 pagesDesign of Rooms For MusicJann BayotNo ratings yet
- Sound Engineering: Professional Diploma inDocument52 pagesSound Engineering: Professional Diploma infotousNo ratings yet
- 1.elements of MusicDocument45 pages1.elements of MusicChristian David Martinez CastilloNo ratings yet
- Perception CH 10 Basic Auditory FunctionsDocument58 pagesPerception CH 10 Basic Auditory Functionsmasscom lawNo ratings yet
- Science of Sound Dealing With Wanted and Unwanted Sounds, Assures Optimum Conditions For Producing and Listing To Speech, Music .Document37 pagesScience of Sound Dealing With Wanted and Unwanted Sounds, Assures Optimum Conditions For Producing and Listing To Speech, Music .Satyajit MalNo ratings yet
- Room Acoustics: Bouncing AroundDocument45 pagesRoom Acoustics: Bouncing AroundmanigupthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Audio)Document29 pagesChapter 6 (Audio)Ain FarahinNo ratings yet
- Bu ReviewerDocument13 pagesBu ReviewerqktfgranadaNo ratings yet
- Magic FrequenciesDocument6 pagesMagic FrequenciesSpillane AmenayereeNo ratings yet
- Hearing 1Document42 pagesHearing 1Gillian CoreyNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Physics Term 2 Lesson Presentation Week 1Document11 pagesYear 9 Physics Term 2 Lesson Presentation Week 1Pay My EveryNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Design of AuditoriumDocument12 pagesAcoustic Design of AuditoriumNur Fateha100% (3)
- Research On Sonic Components in RecordingsDocument3 pagesResearch On Sonic Components in RecordingsMartika DupignyWilliamsNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document13 pagesUnit 2Sridhar SridharanNo ratings yet
- Acoustics 101Document8 pagesAcoustics 101Charles NukesevenNo ratings yet
- Acoustics and PlumbingDocument14 pagesAcoustics and PlumbingCes Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Magic FrequenciesDocument5 pagesMagic FrequenciesJosé Edilson da Paz100% (1)
- Berklee Online Electronic Music Production Degree Major HandbookDocument15 pagesBerklee Online Electronic Music Production Degree Major HandbookHelena Santoro100% (1)
- 6 Acoustics - Room AcousticsDocument12 pages6 Acoustics - Room AcousticsMulumba ChuluNo ratings yet
- Classification and Characteristics of Musical SoundDocument8 pagesClassification and Characteristics of Musical SoundNIKHIL SOLOMON P URK19CS1045No ratings yet
- AudioFX DefinitionsDocument4 pagesAudioFX Definitions曲安琪No ratings yet
- Tabela de Frequência para Equalização - 3 - Mixing Engineers HandbookDocument4 pagesTabela de Frequência para Equalização - 3 - Mixing Engineers HandbookEgon Eduardo SNo ratings yet
- Aru 303 PresentationDocument60 pagesAru 303 PresentationMichael PachecoNo ratings yet
- Etopic 3 Audition Perceptual Aspects of SoundDocument19 pagesEtopic 3 Audition Perceptual Aspects of SoundYavereNo ratings yet
- ReverbDocument3 pagesReverbMatt GoochNo ratings yet
- Hearing: Physiology and PsychoacousticsDocument29 pagesHearing: Physiology and PsychoacousticsThắng Trần ViệtNo ratings yet
- Character of SoundDocument35 pagesCharacter of SoundVinayak DodagoudarNo ratings yet
- Room Acoustics: Binyam DerbeDocument47 pagesRoom Acoustics: Binyam DerbeHanan tarqNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Basics 1Document3 pagesSynthesis Basics 1simonballemusic100% (1)
- Building Utilities 3Document15 pagesBuilding Utilities 3Melliah PlataNo ratings yet
- EqualizersDocument8 pagesEqualizersdaniel.faitheNo ratings yet
- ACOUSTICAL DESIGN Consideration For Auditorium, Lecture Hall, Recording StudioDocument31 pagesACOUSTICAL DESIGN Consideration For Auditorium, Lecture Hall, Recording StudioPavithra SivasankaranNo ratings yet
- Sound ReflectionDocument11 pagesSound ReflectionAnnabelNo ratings yet
- Synthesis ModulesDocument2 pagesSynthesis ModulesRegina SarmientoNo ratings yet
- How to Become a Live Audio Mixer: 7 Secrets of a Hollywood Live Audio Mixer Who Does LIVE EVENTS Every Month!From EverandHow to Become a Live Audio Mixer: 7 Secrets of a Hollywood Live Audio Mixer Who Does LIVE EVENTS Every Month!No ratings yet
- RA The Book Vol 2: The Recording Architecture Book of Studio DesignFrom EverandRA The Book Vol 2: The Recording Architecture Book of Studio DesignNo ratings yet
- Sound: Shhh . . . Bang . . . POP . . . BOOM!From EverandSound: Shhh . . . Bang . . . POP . . . BOOM!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- My Ears are Special : The Science of Sound - Physics Book for Children | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandMy Ears are Special : The Science of Sound - Physics Book for Children | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Email InviteDocument3 pagesEmail InviteArshia JainNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 TOPIC 2: Corporate Communications & Public RelationsDocument21 pagesUnit 4 TOPIC 2: Corporate Communications & Public RelationsArshia JainNo ratings yet
- PB Book FairDocument5 pagesPB Book FairArshia JainNo ratings yet
- Ci - Unit 3 - Indian EconomyDocument28 pagesCi - Unit 3 - Indian EconomyArshia JainNo ratings yet
- PR ScopeDocument8 pagesPR ScopeArshia JainNo ratings yet
- SP UNIT 1 and 2Document36 pagesSP UNIT 1 and 2Arshia JainNo ratings yet
- Communication - Unit 3 - ModelsDocument23 pagesCommunication - Unit 3 - ModelsArshia JainNo ratings yet
- Cio Unit 3Document90 pagesCio Unit 3Arshia JainNo ratings yet
- Cio Unit 4Document50 pagesCio Unit 4Arshia JainNo ratings yet
- Media, Laws and Ethics UNIT 1: TOPIC 1 - Legal TerminologiesDocument18 pagesMedia, Laws and Ethics UNIT 1: TOPIC 1 - Legal TerminologiesArshia JainNo ratings yet
- Serif FontsDocument1 pageSerif FontsArshia JainNo ratings yet
- SP NotesDocument10 pagesSP NotesArshia JainNo ratings yet
- Ci - Unit 2 - Topic 2 - FederalismDocument33 pagesCi - Unit 2 - Topic 2 - FederalismArshia JainNo ratings yet
- Book Cover KrishnaDocument1 pageBook Cover KrishnaArshia JainNo ratings yet
- Media, Laws and Ethics UNIT 1: TOPIC 1 - Legal TerminologiesDocument24 pagesMedia, Laws and Ethics UNIT 1: TOPIC 1 - Legal TerminologiesArshia JainNo ratings yet
- Legal Terminologies: BillDocument5 pagesLegal Terminologies: BillArshia JainNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Roll No Student Name Hindi English Maths Physics ChemistryDocument39 pagesAssignment 1: Roll No Student Name Hindi English Maths Physics ChemistryArshia JainNo ratings yet
- 728 X 90 (Leaderboard)Document1 page728 X 90 (Leaderboard)Arshia JainNo ratings yet
- Effects of Maize-Legume Intercrops On Termite Damage To Maize, Activityof Predatoryants and Maize Yields in UgandaDocument7 pagesEffects of Maize-Legume Intercrops On Termite Damage To Maize, Activityof Predatoryants and Maize Yields in UgandasedianpoNo ratings yet
- Cement Grout AAADocument4 pagesCement Grout AAAabualamalNo ratings yet
- Blockk PDFDocument5 pagesBlockk PDFIsaias Bartolomeu SambgaNo ratings yet
- Manual Spare Parts DB540!72!07Document124 pagesManual Spare Parts DB540!72!07Gustavo CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Electronic Control of Linear-To-circular Polarization Conversion Using A Reconfigurable MetasurfaceDocument6 pages2017 - Electronic Control of Linear-To-circular Polarization Conversion Using A Reconfigurable Metasurfaceab4azizNo ratings yet
- GEA Chapter6 Economy HiresDocument37 pagesGEA Chapter6 Economy HiresMike LassaNo ratings yet
- Audi s6 2007 5.2l ManualDocument374 pagesAudi s6 2007 5.2l ManualMisael EspañaNo ratings yet
- Verb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing?: Verbs Followed by A To-InfinitiveDocument5 pagesVerb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing?: Verbs Followed by A To-InfinitiveTeodora PluskoskaNo ratings yet
- VIPER22ADocument21 pagesVIPER22AanawintaNo ratings yet
- 3b Domestic Water Meter Installation in Meter Room GuidelinesDocument10 pages3b Domestic Water Meter Installation in Meter Room GuidelinesVinish HARIDAS NAIRNo ratings yet
- 4 RPI To PCF8591 - PhotocellDocument4 pages4 RPI To PCF8591 - Photocellsatyam jadhavNo ratings yet
- Brown Et Al. 2009 Tribolium A Model For Developmental and Pest BiologyDocument9 pagesBrown Et Al. 2009 Tribolium A Model For Developmental and Pest BiologyAneel Nizar AliNo ratings yet
- Pdf&rendition 1Document61 pagesPdf&rendition 1Dulce DeNo ratings yet
- XV NATCOSEB First CircularDocument2 pagesXV NATCOSEB First CircularMn HbkNo ratings yet
- 193 Series - Hammond ChokeDocument2 pages193 Series - Hammond ChokeMario RossiNo ratings yet
- Kant's Concept of BeautyDocument14 pagesKant's Concept of BeautyVishnuNo ratings yet
- PersonificationDocument33 pagesPersonificationShane Pineda100% (2)
- Cable HDMI 10 MetrosDocument3 pagesCable HDMI 10 Metroschristian eduardoNo ratings yet
- A Top Down Approach To Mixed Signal SoC VerificationDocument15 pagesA Top Down Approach To Mixed Signal SoC VerificationSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Gesab 95131 SCR Chamber 2020-07-09Document1 pageGesab 95131 SCR Chamber 2020-07-09ilkay tomlayNo ratings yet
- Percussion Laser DrillingDocument1 pagePercussion Laser DrillingBefzzNo ratings yet
- Dialysis - Purpose, Types, Risks, and MoreDocument13 pagesDialysis - Purpose, Types, Risks, and MoreTino HelaNo ratings yet
- FPM Formula Sheet 2Document13 pagesFPM Formula Sheet 2Yolo Gamer DudeNo ratings yet
- Expeditious Retreat Press - Malevolent and Benign 1st Edition BeatiaryDocument129 pagesExpeditious Retreat Press - Malevolent and Benign 1st Edition BeatiaryJoe Conaway67% (3)
- Child - Cerebral PalsyDocument3 pagesChild - Cerebral PalsyJamie Icabandi67% (3)
- Honeywell Vesda VEP Engineering Specification Document 0219Document18 pagesHoneywell Vesda VEP Engineering Specification Document 0219Shekhar AmbreNo ratings yet
- So-Called Logical Levels WoodsmallDocument29 pagesSo-Called Logical Levels WoodsmallDan Paris100% (2)
- BS 03900 0 2010Document26 pagesBS 03900 0 2010selvaNo ratings yet
- VC - SM TransportDocument2 pagesVC - SM Transportsureshkumar mNo ratings yet