Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AFM - L2 - S1 New-2
AFM - L2 - S1 New-2
Uploaded by
najig59163Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AFM - L2 - S1 New-2
AFM - L2 - S1 New-2
Uploaded by
najig59163Copyright:
Available Formats
19AUOC1001
Automotive Fundamentals and
Manufacturing
Online Lecture-23
BHARATHIRAJA R
ASSISTANT PROFESSOR [MECH]
Dr.Mahalingam College of Engineering &
Technology - Pollachi
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Course Type : Open Elective Course Categories : Mastery Courses
Total Hours-45 IIIrd Year
[2019-2023 Batch]
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Course Outcome
Explain the functions and quality parameters of given
sub-systems in Electrical and Electronic System of
automotive products.
Learning Outcome 2
Explain the charging system of the automotive vehicle.
•Different types of charging system used in the automotive
vehicle
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
UNIT IV
ELECTRICAL AND
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Charging System
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
Introduction
Charging system maintains the charge in the
vehicle's battery, and also provides electrical energy
to electrical loads while the engine is running.
Charging system in two-wheelers consist of the
magneto, regulator, battery and the interconnecting
wiring.
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
Why Charging System?
It is to provide necessary electrical power to the
electrical parts which are used for :
Homologation Requirements
•Horn
•Headlamp, Indicators, Brake lamp, etc.
•Speedometer indications
Night Driving Conditions
•Position lamps
Engine electric start
•Convenient starting
DC Ignition
•Enhanced start-ability and spark
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
Functions of Charging System
The charging system has a primary function of
maintaining the battery in an optimum charged
condition.
Secondary functions are
•Enable functioning of electrical loads without battery
also.
•Provide the required output with minimum ripple and
voltage spikes.
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
Functional Block Diagram
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
Power Generation
In motor vehicles the mechanical power generated by
engine via manual kicking or Auxiliary electrical storage
such as Battery can be utilized to generate power.
This is done by means of a Magneto, which is a single
phase AC generator with permanent magnets.
In this case, permanent magnets act as rotor and
winding across limbs as stator through which electrical
output is taken.
Electrical power generated depends on engine speed.
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
Power Conditioning
The two important functions of this stage are:
1.Regulation
2.Rectification
Regulation – To control the power supplied to the
electrical loads.
-Linear or switching regulators.
Rectification – AC to DC conversion.
(with power semiconductor devices)
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
Auxiliary Storage
Auxiliary storage is necessary to store energy for using
electrical loads in the engine OFF condition.
• A battery can be used as an auxiliary energy storage
device.
• The capacity required depends on the DC loads in
each vehicle.
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
Subsystem Parts
Magneto Assembly
Regulator cum Rectifier Unit
Battery
External capacitor (in RTR-FI)
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
Magneto
The Magneto is used for
•Generating and providing power for the lamps, horn,
battery, etc on the vehicle in running condition.
•Generating and providing power for creating spark in the
spark plug for vehicles with AC ignition system.
•Acting as a flywheel, thereby providing inertia and also
minimizing torque transients in the engine.
•Providing ignition timing signal through the pulser coil
and rotor pip.
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
How a Magneto Works?
•The Magneto works on the principle of
a single phase AC Generator.
•The basic law that governs the AC
generator principle is the Faraday’s Law
Hence whenever there is a relative motion between the conductor and
the magnetic field, electricity can be produced.
In a magneto, permanent magnets are fitted on the rotating part
(rotor) which creates a varying magnetic field.
The conductors (copper windings) are wound on the stationary part.
Whenever the windings experience a change in the magnetic field, a
voltage is developed. The rate of change (acceleration and speed) of
the engine are vital factors that affect the output of magneto.
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
Magneto Assembly
•Rotating part of magneto assy.
Holds magnets
•Provides inertia
•Contains the pip for ignition timing
Stationary part of magneto assy
has windings to cut the magnetic field
Contains :
•Charging coil
•Lighting coil
•Source coil (only for AC ignition systems)
•Pulser coil
Video
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
RR Unit
The Regulator cum Rectifier unit is used for
Giving a Controlled AC voltage output - For loads which operate
only when engine is running.
Converting AC to controlled DC output – For loads which can
operate when engine is OFF.
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
R.R. Unit - Regulation
• Regulation means controlling the output voltage within a
specified limit (ie.,14 ± 0.5 V).
• The two configurations that can be used for regulation
are:
Shunt
Preferred for generators that do not produce excess
current when shunted.
More heat is produced at low loads
Series
Only the necessary load current runs at any time.
The result is less heating when operated low electrical
load.
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
R.R. Unit - Rectification
Rectification means conversion of AC to DC power. The two
configurations that can be used for rectification are:
Full Wave: Half Wave:
•Both the halves of the sine •Only the positive half of the sine
wave are utilized. wave is utilized.
•Better efficiency as the power •Half the efficiency of the full wave
utilization is more. configuration.
•Used in Apache RTR-FI, Flame •Used in Star, Scooty, Apache RTR
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
R.R. Unit – Connection Diagram
Dept of Mech LO 4.2 19AUOC1001-AFM
Battery
The battery supplies electricity when the:
ENGINE IS OFF:
Electricity from the battery is used to operate lighting, accessories, or
other electrical systems when the engine is not running.
ENGINE IS STARTING:
Electricity from the battery is used to operate the starter motor and to
provide current for the ignition system during engine cranking.
ENGINE IS RUNNING:
Electricity from the battery is needed to supplement the charging
system when the vehicle's electrical load requirements exceed the
charging system's ability to produce electricity. Both the battery and
the magneto supply electricity when demand is high.
Typical automotive batteries have a nominal voltage of 12V.
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Battery - Types
PRIMARY CELL:
Because the chemical reaction totally destroys
one of the metals after a period of time, primary
cells cannot be recharged. Small batteries such
as flashlight and radio batteries are primary
cells. Under this there are types like Zinc
Chloride, Mercury, alkaline, etc.
SECONDARY CELL:
By applying current to the battery in the reverse
direction, the battery materials can be restored,
thus recharging the battery. This process is called
charging. Automotive lead-acid batteries are
secondary cells and can be recharged. Under this
there are types like NiMH, Pb acid, Li Ion, etc
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Lead Acid Battery - Construction
Lead acid battery is widely used in automobiles.
Lead acid battery is the popular choice in automotive Contains
a diluted sulfuric acid electrolyte and positive and negative
electrodes, in the form of several plates.
A battery is separated into several cells (usually six in the case
of automobile batteries), and in each cell there are several
battery elements, all bathed in the electrolyte solution.
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Lead Acid Battery - Construction
Principle
•Changes Chemical Energy to Electrical Energy (Chemical Compound
Alkali, salt or acid solution is capable of Conducting Electricity)
• Two dissimilar Plates(Eg. Lead & Lead Peroxide) immersed in the
Electrolyte solution causes Electricity
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Battery - Types
Batteries can be produced as Wet-Charged, such as current
automotive batteries are today, or they can be Dry-Charged,
where an electrolyte solution is added when put into service.
WET-CHARGED: The lead-acid battery is filled with electrolyte
and charged when it is built. During storage, a slow chemical
reaction will cause self-discharge. Periodic charging is required.
Most batteries sold today are wet charged.
DRY-CHARGED: The battery is built, charged, washed and dried,
sealed, and shipped without electrolyte. It can be stored for up to
18 months. When put into use, electrolyte and charging are
required. Batteries of this type have a long shelf life. Some
motorcycle batteries are typically dry charged batteries (eg.
Export).
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Battery Terminologies
1.Ampere-Hour Rating
5Ahr ----------- 5 Amps * 1 hr
0.5Amps * 10hrs
2.High Rate Discharge Rating
•Discharge current is 40 A. for 5Ah Battery,
•Voltage After 5 Sec. Is 9.8V
•Discharge final Voltage is 6V after at least 78 Sec.
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Types of Charging
A wide variety of schemes exist for charging lead-acid
batteries. The common methods are :
1.Constant Voltage : In this method, a constant voltage
input is maintained throughout the charging process. This
enables high initial current to the battery as the potential
difference is high in the initial stage.
2.Constant Current : In this method, a uniform current is
supplied throughout the charging process. This eliminates
imbalances of the cells.
In two wheelers, charging is predominantly constant
voltage mode at the suitable engine rpm.
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Quality Characteristics
Magneto
1.Output voltage
2.Rated rpm
3.Power output
4.Taper Matching
5.Stator Mounting
6.Amount of Unbalance
If the unbalance is high, the rotor will wobble which leads to
•Less power from magneto and hence improper ignition leading to loss
of power and mileage and more emission.
•Leads to engine vibration because of torque variation
If taper matching is less
•There will not be proper locking of rotor with crankshaft and hence
damage to both crankshaft and rotor.
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Quality Characteristics
RR Unit
1.Output voltage (with & without Battery)
2.Rated rpm
3.Battery charging current
4.Spike level
5.Load Regulation
6.Mounting on chassis
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Quality Characteristics
Battery
1.Open circuit Voltage
2.Specific gravity
3.Battery Life
4.Electrolyte level
5.Discharge capacity
Achieving Quality characteristics @ design stage
1.Design Specifications
2.Charge balance test
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Design Specifications
Major quality characteristics are the output voltage and current in the
charging system
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Design Specifications
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
Charge Balance test
A method to capture the parameters of charging system such as
Voltage, Current and Temperature of the battery.
The measuring system captures the Real-time Capacity (Ampere-
hour) of the battery.
System captures the data at minimum intervals ( more than 30
samples / minute).
Dept of Mech 19AUOC1001-AFM
You might also like
- Viktor Schauberger Living Energies With Callum CoatsDocument312 pagesViktor Schauberger Living Energies With Callum CoatsJason Verbelli98% (46)
- Presentation On Power Factor ImprovementDocument21 pagesPresentation On Power Factor Improvementmahin100% (2)
- Dokumen - Tips Process Integration and Intensification Saving Energy Water and Resources 58adc6097048aDocument12 pagesDokumen - Tips Process Integration and Intensification Saving Energy Water and Resources 58adc6097048asamandondonNo ratings yet
- Power Transformer Test ProcedureDocument13 pagesPower Transformer Test ProcedureDebdeep Mondal100% (1)
- Botswana Power SectorDocument19 pagesBotswana Power SectorJeremiah MatongotiNo ratings yet
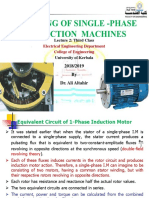
- AFM - L2 - S1 New-1Document33 pagesAFM - L2 - S1 New-1najig59163No ratings yet
- AFM - L1 - S3 NewDocument13 pagesAFM - L1 - S3 Newnajig59163No ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency in Electrical UtilitiesDocument82 pagesEnergy Efficiency in Electrical Utilitiesmanorajcv100% (1)
- Single Phase Inductive LoadDocument40 pagesSingle Phase Inductive LoadJULIET MOKWUGWONo ratings yet
- Final - Lect6 - DC MachineDocument30 pagesFinal - Lect6 - DC MachineNice TanatadNo ratings yet
- Dip Ee 404 Industrial Drives Lab ManualDocument46 pagesDip Ee 404 Industrial Drives Lab ManualNeeraj Kumar SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- MT6801 PDFDocument118 pagesMT6801 PDFSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document43 pagesPresentation 1Shreya RathoreNo ratings yet
- EE8401 2M QB EM-II - by EasyEngineering - Net 2Document30 pagesEE8401 2M QB EM-II - by EasyEngineering - Net 2Lokey LokeshNo ratings yet
- May 2009 Sync Motor Excitation ADocument59 pagesMay 2009 Sync Motor Excitation AZul AtfiNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument25 pagesDC MotorDeandre LaingNo ratings yet
- Automotive Charging System: Chapter FourDocument23 pagesAutomotive Charging System: Chapter FourIsaac TesfayeNo ratings yet
- 2L Single Phase IM PDFDocument28 pages2L Single Phase IM PDFAli AltahirNo ratings yet
- Universal Motor - PPSXDocument29 pagesUniversal Motor - PPSXPerfil Web JdcortestwebNo ratings yet
- Charging System12345Document48 pagesCharging System12345Hriday AryaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines IIDocument236 pagesElectrical Machines IIKhadar A. FarahNo ratings yet
- ECE 252 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: Lesson 19. MotorsDocument9 pagesECE 252 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: Lesson 19. MotorsPhillip ChirongweNo ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument157 pagesElectricalnaguNo ratings yet
- Plant Utilities & Maintenance: .: Karte 01.aDocument33 pagesPlant Utilities & Maintenance: .: Karte 01.aHidayat StafaNo ratings yet
- Amplidyne Homopolar and Servo MachinesDocument6 pagesAmplidyne Homopolar and Servo MachinesAchuilNo ratings yet
- Transformer Training (SNC Lavalin - District Cooling Project) - R01Document174 pagesTransformer Training (SNC Lavalin - District Cooling Project) - R01MohammedNo ratings yet
- Single Phase I.M-FinalDocument15 pagesSingle Phase I.M-Final47DEESUBRATA KAYALNo ratings yet
- Electric-Locomotive SAIDocument30 pagesElectric-Locomotive SAIMy bestie is my enemyNo ratings yet
- Railway WorkshopDocument38 pagesRailway WorkshopPrateek SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Automatic Side Stand Braking Mechanism For Two WheelerDocument28 pagesFabrication of Automatic Side Stand Braking Mechanism For Two Wheelergnana muruganNo ratings yet
- ECE Electrical Engineering 2 Marks PDFDocument22 pagesECE Electrical Engineering 2 Marks PDFsivagamiNo ratings yet
- Brushed DC Motor Control Using The MC68HC16Z1: Freescale SemiconductorDocument16 pagesBrushed DC Motor Control Using The MC68HC16Z1: Freescale SemiconductorWaqas KhanNo ratings yet
- Permanent Magnet DC Criteria: Motors Design and Operation AdvantagesDocument7 pagesPermanent Magnet DC Criteria: Motors Design and Operation Advantagesdjole07No ratings yet
- Recent Advances of IPM Motor Drives in Power Electronics WorldDocument8 pagesRecent Advances of IPM Motor Drives in Power Electronics WorldIan SilveiraNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 InvertersDocument15 pagesUNIT 5 InverterssavitaNo ratings yet
- Course: Industrial Electrician: Day 4: TopicsDocument37 pagesCourse: Industrial Electrician: Day 4: TopicsKiyoshi Jiro MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Systems CH 5Document46 pagesElectromechanical Systems CH 5fabrice mellantNo ratings yet
- AC and DC MotorDocument13 pagesAC and DC MotorrikechNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument20 pagesInduction MotorC V VIJAY KUMASRNo ratings yet
- History of CLW: Chittaranjan Locomotive Works. CLW Is The Proud Recipient of The SafetyDocument10 pagesHistory of CLW: Chittaranjan Locomotive Works. CLW Is The Proud Recipient of The SafetyRahul SinhaNo ratings yet
- Lectures of Week#1Document33 pagesLectures of Week#1HASSANNo ratings yet
- Eac Unit Ii PFDocument32 pagesEac Unit Ii PFRajesh BhaskarlaNo ratings yet
- 17me655 Module 3.2Document10 pages17me655 Module 3.2VinayakNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1Document21 pagesDC Motor Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1Abir LovesickNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorsDocument22 pagesInduction MotorsErick MUANDA TULUME100% (1)
- Train LightingDocument5 pagesTrain Lightingsanket100% (1)
- Automotive Electrical SystemDocument25 pagesAutomotive Electrical SystemW Mohd Zailimi Abdullah100% (3)
- Ee-120 Ac MachineDocument6 pagesEe-120 Ac Machinesmk30150No ratings yet
- AJITIIIIIIIDocument20 pagesAJITIIIIIIIValin paruNo ratings yet
- Ael WppiDocument8 pagesAel WppiAHMED EL HAMRINo ratings yet
- Regenerative Braking of Series-Wound Brushed DC Electric Motors For Electric VehiclesDocument6 pagesRegenerative Braking of Series-Wound Brushed DC Electric Motors For Electric Vehiclesbeastlt12No ratings yet
- Electric MotorDocument40 pagesElectric MotorhmiwukcyNo ratings yet
- Ac GeneratorsDocument2 pagesAc GeneratorsDarshan PatilNo ratings yet
- 01 - 02 - 28 AprilDocument13 pages01 - 02 - 28 AprilTahmid TamzidNo ratings yet
- Electrical System 3126Document8 pagesElectrical System 3126GerardoNo ratings yet
- Mech Electrical PowerDocument6 pagesMech Electrical PowerJezrael Kim SaquingNo ratings yet
- 61 - DieselEngine Black StartDocument12 pages61 - DieselEngine Black StartLincoln Eng100% (1)
- EE-246 Machiness - 2012Document47 pagesEE-246 Machiness - 2012Noman NisarNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Electric Car Using Field Oriented Controlled Switched Reluctance MotorDocument5 pagesSpeed Control of Electric Car Using Field Oriented Controlled Switched Reluctance MotorInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Guide For The Selection and Application of Energy-Efficient Motors PDFDocument10 pagesGuide For The Selection and Application of Energy-Efficient Motors PDFEliseu RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1v9mhtc2qjzNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Efficiency Calculation Formula Amp EquationDocument8 pagesDC Motor Efficiency Calculation Formula Amp EquationPeter Tendai MakaraNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseFrom EverandPower Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- AFM - L2 - S1 NewDocument15 pagesAFM - L2 - S1 Newnajig59163No ratings yet
- AFM - L3 - S1 NewDocument15 pagesAFM - L3 - S1 Newnajig59163No ratings yet
- AFM - L4 - S1 NewDocument15 pagesAFM - L4 - S1 Newnajig59163No ratings yet
- AFM - L1 - S2 NewDocument27 pagesAFM - L1 - S2 Newnajig59163No ratings yet
- AFM - L1 - S3 NewDocument13 pagesAFM - L1 - S3 Newnajig59163No ratings yet
- AFM - L2 - S1 New-1Document33 pagesAFM - L2 - S1 New-1najig59163No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877705814031701 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S1877705814031701 Mainnajig59163No ratings yet
- User Manual: HGM6400 Automatic Genset Controller (With J1939 Interface)Document37 pagesUser Manual: HGM6400 Automatic Genset Controller (With J1939 Interface)nhocti007No ratings yet
- IEEMADocument9 pagesIEEMAAsok M ReddyNo ratings yet
- 1.7 Capstone Jim Crouse EnglishDocument40 pages1.7 Capstone Jim Crouse EnglishJuan Carlos BeleñoNo ratings yet
- Solar Electric System DesignDocument37 pagesSolar Electric System DesignMayank Porwal100% (2)
- English 9 Unit7 Saving Energy Test 4Document4 pagesEnglish 9 Unit7 Saving Energy Test 4Vân AnhNo ratings yet
- ASTRA For Padmamitra Awards 2023 Material - RevMKA V FINALDocument19 pagesASTRA For Padmamitra Awards 2023 Material - RevMKA V FINALandi mamanNo ratings yet
- BiodiselDocument14 pagesBiodiselPrabhat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering EE-101 Tutorial + Assignment - 4 Topic: - Three PhaseDocument1 pageBasic Electrical Engineering EE-101 Tutorial + Assignment - 4 Topic: - Three PhaseSH RanaNo ratings yet
- Siklus Brayton Contoh:: P P T TDocument7 pagesSiklus Brayton Contoh:: P P T TDicky PasaribuNo ratings yet
- SteamTurbineanalysisms KumanaIETC20173 27 17Document9 pagesSteamTurbineanalysisms KumanaIETC20173 27 17Vivek DomadiyaNo ratings yet
- 2Document4 pages2Arnel Pamaos Lopiba MontañezNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Noise MitigationDocument11 pagesWind Turbine Noise Mitigationvicky bahiratNo ratings yet
- Divided Wall Column 498Document3 pagesDivided Wall Column 498GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Susceptibility Method For Piping VibrationDocument13 pagesDynamic Susceptibility Method For Piping VibrationA. Venugopal100% (1)
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument71 pagesWork, Energy and PowerSaurav DuttNo ratings yet
- Standard 3.3 QuizDocument5 pagesStandard 3.3 QuizMichael LiangNo ratings yet
- English For The Energy Industry-OXFORDDocument84 pagesEnglish For The Energy Industry-OXFORDytmfm5zfycNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and InductorsDocument31 pagesCapacitors and InductorsJucimar BrilhanteNo ratings yet
- Empr - QCS 2014Document3 pagesEmpr - QCS 2014sahilNo ratings yet
- Instructions To Students: Information For CandidatesDocument6 pagesInstructions To Students: Information For CandidatesMukhtaar CaseNo ratings yet
- Motor Starting Analysis - MJDocument5 pagesMotor Starting Analysis - MJCatrina FedericoNo ratings yet
- 110Document16 pages110A FirdausNo ratings yet
- RHINO Installation Instructions For PSB24-060-P Power SupplyDocument2 pagesRHINO Installation Instructions For PSB24-060-P Power SupplyJuan BragaNo ratings yet
- PF - TypeC GasOil Burner - Astec - 0922Document2 pagesPF - TypeC GasOil Burner - Astec - 0922Jehison EscobarNo ratings yet
- Fourth RevisionDocument7 pagesFourth Revisionladderelectricals22No ratings yet
- Dometic Service ManualDocument31 pagesDometic Service ManualNanook100% (1)