Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsChapter 1 The Development and Anatomy of The Female Sexual Organs
Chapter 1 The Development and Anatomy of The Female Sexual Organs
Uploaded by
anuprajsingh1212Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument4 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceSheyn Benito81% (32)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemSyed Isamil100% (1)
- Delivery Room Write UpDocument15 pagesDelivery Room Write UpDavid Calalo0% (1)
- Obstetrics - Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument12 pagesObstetrics - Anatomy & PhysiologyDexter Lendio0% (1)
- 1001 MCQ S in Physiology Including Biochemistry A D Amondikar.05576 3sampleDocument6 pages1001 MCQ S in Physiology Including Biochemistry A D Amondikar.05576 3samplenasibdinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesDocument45 pagesAnatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesMesk BanatNo ratings yet
- Urogenital (UG) Is Derived FromDocument7 pagesUrogenital (UG) Is Derived FromSushant SoniNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument75 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemProf Lina Ramli67% (3)
- Anatomy Quiz 1Document4 pagesAnatomy Quiz 1Jacob BorongNo ratings yet
- Female External GenitaliaDocument13 pagesFemale External Genitaliacyrusdaniels68No ratings yet
- Seminar RRDocument40 pagesSeminar RRkifle1921No ratings yet
- Female RSsystem 2Document90 pagesFemale RSsystem 2icliftonguytonNo ratings yet
- LECT 2anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 2Document45 pagesLECT 2anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 2Umer RafiqNo ratings yet
- 2.Gynaecology-Cyclic Changes in Cervix-Vagina.Document37 pages2.Gynaecology-Cyclic Changes in Cervix-Vagina.zekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Document49 pagesAnatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Humraz100% (1)
- Anatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryDocument89 pagesAnatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryAsma AijazNo ratings yet
- Sistem Reproduksi WanitaDocument40 pagesSistem Reproduksi WanitaTyastami T.No ratings yet
- ANATOMIDocument43 pagesANATOMIWidayuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Embryology of The Female Genital Tract & Anatomy of Female Pelvis & Fetal SkullDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Embryology of The Female Genital Tract & Anatomy of Female Pelvis & Fetal SkullBrandonRyanF.MosidinNo ratings yet
- Mullerian Duct Anamolies 0.1Document66 pagesMullerian Duct Anamolies 0.1Sonam PandayNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System 1Document9 pagesReproductive System 1Marvel NnaemekaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Embryology UterusDocument65 pagesAnatomy and Embryology UterusashwiniNo ratings yet
- Female RSystemDocument71 pagesFemale RSystemicliftonguytonNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument60 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemjeenath justin dossNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The Female Genital Tract: Pranab Chatterjee Medical College, KolkataDocument31 pagesEmbryology of The Female Genital Tract: Pranab Chatterjee Medical College, KolkataPranab Chatterjee100% (4)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyJustJ ThingsNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Female Reproductive SystemDocument54 pagesPresentation On: Female Reproductive SystemLetsShop BbsrNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument67 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Systemannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive HealthDocument276 pagesFemale Reproductive HealthviannikkkyNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reproductive FemaleDocument2 pagesAnaphy Reproductive FemaleNyna Micah CorroNo ratings yet
- Development of The Urogenital System: Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesDevelopment of The Urogenital System: Learning ObjectivesKingNo ratings yet
- DAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSDocument46 pagesDAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSAbhisek ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female ReproductionDocument108 pagesAnatomy of The Female ReproductionDaisy HamdaliNo ratings yet
- Embryology 10Document5 pagesEmbryology 10fgdhgfrhNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument40 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemSAYMABANUNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System (Yuni)Document36 pagesFemale Reproductive System (Yuni)Ayi Abdul BasithNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive OrgansDocument39 pagesThe Reproductive OrgansjoaNo ratings yet
- 23 - Development of Genital SystemDocument67 pages23 - Development of Genital SystemDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Session 4 Lecture 1 Part 1Document25 pagesSession 4 Lecture 1 Part 1avin xsroNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductive SystemDocument55 pages1 Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductive SystemMarie Cecille Soliven VarillaNo ratings yet
- Presented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONDocument67 pagesPresented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONPaul AndersonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Female Pelvic Cavity - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument1 pageAnatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Female Pelvic Cavity - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfAlonsoNo ratings yet
- Development of The Reproductive SystemDocument37 pagesDevelopment of The Reproductive SystemGodwin ZengeniNo ratings yet
- Ana-Dr. Khaled-Pelvis-Lec 6 (2) تمDocument24 pagesAna-Dr. Khaled-Pelvis-Lec 6 (2) تمasakingofhNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesReproductive Systemsugandhdon77No ratings yet
- Final Module in M101Document56 pagesFinal Module in M101J. TSNo ratings yet
- DAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSDocument36 pagesDAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSAbhisek ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Final Module in M101 1Document54 pagesFinal Module in M101 1J. TSNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Logo NotesDocument25 pagesHuman Reproduction Logo Notespajice8959No ratings yet
- Uterus Fallopian Tube and OvaryDocument35 pagesUterus Fallopian Tube and Ovaryvijaya pranaviNo ratings yet
- Unit No: Topic:: 2 Human Reproduction Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproductive System: Male and FemaleDocument31 pagesUnit No: Topic:: 2 Human Reproduction Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproductive System: Male and FemaleSavita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- CBL 2Document20 pagesCBL 2Hammad AkramNo ratings yet
- 17 Urogenital PDFDocument15 pages17 Urogenital PDFArnytha VebrianiNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument39 pagesGynecological Anatomy & Physiologynursereview100% (3)
- A Case Study About Cervical PolypsDocument8 pagesA Case Study About Cervical PolypsJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- Nurs 5343 Emergency Obstetrics CareDocument92 pagesNurs 5343 Emergency Obstetrics CareRachel BiokoNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The Reproductive TractDocument10 pagesEmbryology of The Reproductive TractsmajicnerminaNo ratings yet
- Dev of Female Reproductive SystemDocument39 pagesDev of Female Reproductive SystemOgunsusi DamilolaNo ratings yet
- Femle Reproduction OutlineDocument6 pagesFemle Reproduction OutlineNhung Nguyen100% (1)
- Female Reproductive System RecDocument13 pagesFemale Reproductive System Recloey skiiesNo ratings yet
- Female GenitaliavDocument39 pagesFemale GenitaliavKathlyn PactorananNo ratings yet
- smch34Document16 pagessmch34anuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- LipaseAcutePancreatitis_ClinicianHandoutDocument3 pagesLipaseAcutePancreatitis_ClinicianHandoutanuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Pituitary-Gland-1Document22 pagesPituitary-Gland-1anuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- NATS Final PlannerDocument1 pageNATS Final Planneranuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Lecture Planner Physics PDF Only 12th Board Booster 2024Document5 pagesLecture Planner Physics PDF Only 12th Board Booster 2024anuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Lecture Planner Organic Chemistry PDF Only 12th Board Booster 2024Document2 pagesLecture Planner Organic Chemistry PDF Only 12th Board Booster 2024anuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Palm Trees Shells PPT DesignDocument3 pagesPalm Trees Shells PPT Designanuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Genitourinary ProblemsDocument4 pagesChapter 9 Genitourinary Problemsanuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Reproduction QuestionsDocument9 pagesReproduction QuestionselizabethNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Normal Spontaneous Vaginal D EliveryDocument20 pagesA Case Study On Normal Spontaneous Vaginal D EliveryNyj QuiñoNo ratings yet
- Ovarian and Uterine Cycle - My PDocument23 pagesOvarian and Uterine Cycle - My PAzifah Zakaria100% (2)
- Menstrual CycleDocument10 pagesMenstrual CycleintanNo ratings yet
- Internal Structures Ovaries: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesInternal Structures Ovaries: Anatomy and PhysiologyshakiraNo ratings yet
- Book 2 FinalDocument115 pagesBook 2 FinalLalit JoshiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Genital Tract - IiDocument44 pagesAnatomy of Female Genital Tract - Iigksah711No ratings yet
- Histology-Reviewer (Dr. Ayochok) PDFDocument20 pagesHistology-Reviewer (Dr. Ayochok) PDFJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemanojanNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemعلي محمدNo ratings yet
- OvulationDocument2 pagesOvulationEarl CopeNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet in Science 5 Second Quarter Activity Sheet 2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet in Science 5 Second Quarter Activity Sheet 2dinnes masubay100% (3)
- 4C UterusDocument86 pages4C UterusrubenNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q3 M1 W2Document6 pagesScience10 Q3 M1 W2Chris John SantosNo ratings yet
- Supports & Innervation of UterusDocument19 pagesSupports & Innervation of UterusDr. Janarthanan V100% (1)
- AP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab SP21finalDocument14 pagesAP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab SP21finalBella DonnaAriesta LumbanGaolNo ratings yet
- Ligamentele LargiDocument2 pagesLigamentele LargiIoana IonicaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 19 - Reproductive System)Document30 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 19 - Reproductive System)Eduardo Niepes Jr.No ratings yet
- So What Is A Vulva Anyway Final BookletDocument17 pagesSo What Is A Vulva Anyway Final BookletAdrianaVeraNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument53 pagesUntitledPrincess Diane M. RagusNo ratings yet
- 23 Female Reproductive System 1213116557688874 8Document206 pages23 Female Reproductive System 1213116557688874 8Rodel AgapitoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet. Menstrual Cycle.Document5 pagesWorksheet. Menstrual Cycle.Rigel Del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System QuizDocument6 pagesReproductive System QuizMarilyn Castro Laquindanum100% (2)
- Girls and Puberty BookletDocument9 pagesGirls and Puberty Bookletఫణీంద్ర నర్సెట్టి100% (1)
- Intro On Ovulation and FertilityDocument2 pagesIntro On Ovulation and FertilitylookloNo ratings yet
- Leuk OrrheaDocument6 pagesLeuk Orrheababon3No ratings yet
- Vaginal DischargeDocument1 pageVaginal DischargeRAHMANo ratings yet
Chapter 1 The Development and Anatomy of The Female Sexual Organs
Chapter 1 The Development and Anatomy of The Female Sexual Organs
Uploaded by
anuprajsingh12120 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Chapter_1_The_development_and_anatomy_of_the_female_sexual_organs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesChapter 1 The Development and Anatomy of The Female Sexual Organs
Chapter 1 The Development and Anatomy of The Female Sexual Organs
Uploaded by
anuprajsingh1212Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
IMPORTANT MCQs Points :
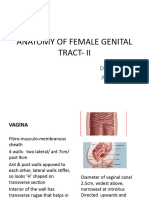
Sinovaginal bulbs : Develops into the distal one third of the
vagina
Urethral folds of the cloaca : Develops into the labia minora
Paramesonephric duct : Develops into the uterus, cervix and
proximal 2/3 of the vagina
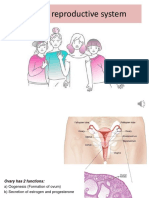
Genital ridge : Form the ovary
Para-aortic nodes : Lymphatic drainage of the ovary
Superficial inguinal and femoral nodes : Lymphatic drainage of
the lower vagina and vulva
Obturator, internal and external iliac nodes : Lymphatic drainage
of the upper vagina and cervix
Renal vein : Venous drainage from the left ovarian vein
The Fallopian tubes are lined by cilia to aid egg transport
The ovary has a central medulla of loose connective tissue and an
outer cortex covered by cuboidal germinal epithelium
www.themedicalglobe.com / www.mgElearning.net Page 1 of 4
The peritoneum overlies the all structures of abdomen except
ovaries
The round ligament ends distally in the inguinal canal
Maximum no of oogonia are formed at what age of female life :
20th week of intrauterine life
Turner syndrome : MC chromosomal anomaly in females
Main support of uterus : cervical ligaments
The cervix is narrower than the body of th uterus and is
approximately 2.5 cm in length
The main supports to the pelvic floor are the connective tissue
and levator ani muscles
Mullerian agenesis also known as Rokitansky syndrome or
Mayer–Rokitansky–Kuster–Hauser syndrome (MRKH)
The ovarian artery arises from the aorta below the renal
vein
The round ligament lies anterior to the uterus
Fallopian tubes runs in the upper margin of the broad
ligament
Long axis of uterus over long axis of cervix : anteflexion
Major nerve supply of vagina : pudendal nerve
Vagina is lined by stratified squamous epithelium
Fertilization occurs in ampullatory region of fallopian
tubes
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS:
1. Structures forming external/genitalia
www.themedicalglobe.com www.mgElearning.net Page 2 of 4
2. Structures in development of female sexual parts
3. Abnormalities of vagina
4. Relation of Uterus
5. Ureteric course in pelvis
6. Risk of ureteric damage during hysterectomy
7. Origin and insertion of pelvic diaphragm
8. Blood supply of pelvic ureter
9.Course of uterine artery
10.Branches of internal iliac artery
11.Structural problems of pelvic
organs scenarios
www.themedicalglobe.com / www.mgElearning.net Page 3 of 4
Copyrights: Medical Globe 2020
www.themedicalglobe.com / www.mgElearning.net Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument4 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceSheyn Benito81% (32)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemSyed Isamil100% (1)
- Delivery Room Write UpDocument15 pagesDelivery Room Write UpDavid Calalo0% (1)
- Obstetrics - Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument12 pagesObstetrics - Anatomy & PhysiologyDexter Lendio0% (1)
- 1001 MCQ S in Physiology Including Biochemistry A D Amondikar.05576 3sampleDocument6 pages1001 MCQ S in Physiology Including Biochemistry A D Amondikar.05576 3samplenasibdinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesDocument45 pagesAnatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesMesk BanatNo ratings yet
- Urogenital (UG) Is Derived FromDocument7 pagesUrogenital (UG) Is Derived FromSushant SoniNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument75 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemProf Lina Ramli67% (3)
- Anatomy Quiz 1Document4 pagesAnatomy Quiz 1Jacob BorongNo ratings yet
- Female External GenitaliaDocument13 pagesFemale External Genitaliacyrusdaniels68No ratings yet
- Seminar RRDocument40 pagesSeminar RRkifle1921No ratings yet
- Female RSsystem 2Document90 pagesFemale RSsystem 2icliftonguytonNo ratings yet
- LECT 2anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 2Document45 pagesLECT 2anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 2Umer RafiqNo ratings yet
- 2.Gynaecology-Cyclic Changes in Cervix-Vagina.Document37 pages2.Gynaecology-Cyclic Changes in Cervix-Vagina.zekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Document49 pagesAnatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Humraz100% (1)
- Anatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryDocument89 pagesAnatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryAsma AijazNo ratings yet
- Sistem Reproduksi WanitaDocument40 pagesSistem Reproduksi WanitaTyastami T.No ratings yet
- ANATOMIDocument43 pagesANATOMIWidayuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Embryology of The Female Genital Tract & Anatomy of Female Pelvis & Fetal SkullDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Embryology of The Female Genital Tract & Anatomy of Female Pelvis & Fetal SkullBrandonRyanF.MosidinNo ratings yet
- Mullerian Duct Anamolies 0.1Document66 pagesMullerian Duct Anamolies 0.1Sonam PandayNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System 1Document9 pagesReproductive System 1Marvel NnaemekaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Embryology UterusDocument65 pagesAnatomy and Embryology UterusashwiniNo ratings yet
- Female RSystemDocument71 pagesFemale RSystemicliftonguytonNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument60 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemjeenath justin dossNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The Female Genital Tract: Pranab Chatterjee Medical College, KolkataDocument31 pagesEmbryology of The Female Genital Tract: Pranab Chatterjee Medical College, KolkataPranab Chatterjee100% (4)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyJustJ ThingsNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Female Reproductive SystemDocument54 pagesPresentation On: Female Reproductive SystemLetsShop BbsrNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument67 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Systemannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive HealthDocument276 pagesFemale Reproductive HealthviannikkkyNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reproductive FemaleDocument2 pagesAnaphy Reproductive FemaleNyna Micah CorroNo ratings yet
- Development of The Urogenital System: Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesDevelopment of The Urogenital System: Learning ObjectivesKingNo ratings yet
- DAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSDocument46 pagesDAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSAbhisek ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female ReproductionDocument108 pagesAnatomy of The Female ReproductionDaisy HamdaliNo ratings yet
- Embryology 10Document5 pagesEmbryology 10fgdhgfrhNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument40 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemSAYMABANUNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System (Yuni)Document36 pagesFemale Reproductive System (Yuni)Ayi Abdul BasithNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive OrgansDocument39 pagesThe Reproductive OrgansjoaNo ratings yet
- 23 - Development of Genital SystemDocument67 pages23 - Development of Genital SystemDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Session 4 Lecture 1 Part 1Document25 pagesSession 4 Lecture 1 Part 1avin xsroNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductive SystemDocument55 pages1 Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductive SystemMarie Cecille Soliven VarillaNo ratings yet
- Presented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONDocument67 pagesPresented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONPaul AndersonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Female Pelvic Cavity - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument1 pageAnatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Female Pelvic Cavity - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfAlonsoNo ratings yet
- Development of The Reproductive SystemDocument37 pagesDevelopment of The Reproductive SystemGodwin ZengeniNo ratings yet
- Ana-Dr. Khaled-Pelvis-Lec 6 (2) تمDocument24 pagesAna-Dr. Khaled-Pelvis-Lec 6 (2) تمasakingofhNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesReproductive Systemsugandhdon77No ratings yet
- Final Module in M101Document56 pagesFinal Module in M101J. TSNo ratings yet
- DAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSDocument36 pagesDAMS CRS - Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DAMS Comprehensive Review Series) - DAMSAbhisek ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Final Module in M101 1Document54 pagesFinal Module in M101 1J. TSNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Logo NotesDocument25 pagesHuman Reproduction Logo Notespajice8959No ratings yet
- Uterus Fallopian Tube and OvaryDocument35 pagesUterus Fallopian Tube and Ovaryvijaya pranaviNo ratings yet
- Unit No: Topic:: 2 Human Reproduction Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproductive System: Male and FemaleDocument31 pagesUnit No: Topic:: 2 Human Reproduction Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproductive System: Male and FemaleSavita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- CBL 2Document20 pagesCBL 2Hammad AkramNo ratings yet
- 17 Urogenital PDFDocument15 pages17 Urogenital PDFArnytha VebrianiNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument39 pagesGynecological Anatomy & Physiologynursereview100% (3)
- A Case Study About Cervical PolypsDocument8 pagesA Case Study About Cervical PolypsJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- Nurs 5343 Emergency Obstetrics CareDocument92 pagesNurs 5343 Emergency Obstetrics CareRachel BiokoNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The Reproductive TractDocument10 pagesEmbryology of The Reproductive TractsmajicnerminaNo ratings yet
- Dev of Female Reproductive SystemDocument39 pagesDev of Female Reproductive SystemOgunsusi DamilolaNo ratings yet
- Femle Reproduction OutlineDocument6 pagesFemle Reproduction OutlineNhung Nguyen100% (1)
- Female Reproductive System RecDocument13 pagesFemale Reproductive System Recloey skiiesNo ratings yet
- Female GenitaliavDocument39 pagesFemale GenitaliavKathlyn PactorananNo ratings yet
- smch34Document16 pagessmch34anuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- LipaseAcutePancreatitis_ClinicianHandoutDocument3 pagesLipaseAcutePancreatitis_ClinicianHandoutanuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Pituitary-Gland-1Document22 pagesPituitary-Gland-1anuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- NATS Final PlannerDocument1 pageNATS Final Planneranuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Lecture Planner Physics PDF Only 12th Board Booster 2024Document5 pagesLecture Planner Physics PDF Only 12th Board Booster 2024anuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Lecture Planner Organic Chemistry PDF Only 12th Board Booster 2024Document2 pagesLecture Planner Organic Chemistry PDF Only 12th Board Booster 2024anuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Palm Trees Shells PPT DesignDocument3 pagesPalm Trees Shells PPT Designanuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Genitourinary ProblemsDocument4 pagesChapter 9 Genitourinary Problemsanuprajsingh1212No ratings yet
- Reproduction QuestionsDocument9 pagesReproduction QuestionselizabethNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Normal Spontaneous Vaginal D EliveryDocument20 pagesA Case Study On Normal Spontaneous Vaginal D EliveryNyj QuiñoNo ratings yet
- Ovarian and Uterine Cycle - My PDocument23 pagesOvarian and Uterine Cycle - My PAzifah Zakaria100% (2)
- Menstrual CycleDocument10 pagesMenstrual CycleintanNo ratings yet
- Internal Structures Ovaries: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesInternal Structures Ovaries: Anatomy and PhysiologyshakiraNo ratings yet
- Book 2 FinalDocument115 pagesBook 2 FinalLalit JoshiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Genital Tract - IiDocument44 pagesAnatomy of Female Genital Tract - Iigksah711No ratings yet
- Histology-Reviewer (Dr. Ayochok) PDFDocument20 pagesHistology-Reviewer (Dr. Ayochok) PDFJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemanojanNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemعلي محمدNo ratings yet
- OvulationDocument2 pagesOvulationEarl CopeNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet in Science 5 Second Quarter Activity Sheet 2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet in Science 5 Second Quarter Activity Sheet 2dinnes masubay100% (3)
- 4C UterusDocument86 pages4C UterusrubenNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q3 M1 W2Document6 pagesScience10 Q3 M1 W2Chris John SantosNo ratings yet
- Supports & Innervation of UterusDocument19 pagesSupports & Innervation of UterusDr. Janarthanan V100% (1)
- AP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab SP21finalDocument14 pagesAP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab SP21finalBella DonnaAriesta LumbanGaolNo ratings yet
- Ligamentele LargiDocument2 pagesLigamentele LargiIoana IonicaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 19 - Reproductive System)Document30 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 19 - Reproductive System)Eduardo Niepes Jr.No ratings yet
- So What Is A Vulva Anyway Final BookletDocument17 pagesSo What Is A Vulva Anyway Final BookletAdrianaVeraNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument53 pagesUntitledPrincess Diane M. RagusNo ratings yet
- 23 Female Reproductive System 1213116557688874 8Document206 pages23 Female Reproductive System 1213116557688874 8Rodel AgapitoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet. Menstrual Cycle.Document5 pagesWorksheet. Menstrual Cycle.Rigel Del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System QuizDocument6 pagesReproductive System QuizMarilyn Castro Laquindanum100% (2)
- Girls and Puberty BookletDocument9 pagesGirls and Puberty Bookletఫణీంద్ర నర్సెట్టి100% (1)
- Intro On Ovulation and FertilityDocument2 pagesIntro On Ovulation and FertilitylookloNo ratings yet
- Leuk OrrheaDocument6 pagesLeuk Orrheababon3No ratings yet
- Vaginal DischargeDocument1 pageVaginal DischargeRAHMANo ratings yet