Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Artifacts
Artifacts
Uploaded by
hamza.mahmood.khan2030 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views25 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views25 pagesArtifacts
Artifacts
Uploaded by
hamza.mahmood.khan203Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 25
ARTIFACTS
Lecture notes by:
Dr. Shumail Mukhtar
Definition:
Ultrasound imaging artifacts are echoes on the display
that do not properly represent the structures being imaged.
There are many types of artifacts, some can be caused by
improper control settings, or by equipment malfunction.
Understanding the physical properties responsible for
various acoustic artifacts permits sonographers to
recognize them with greater certainty and avoid them
when necessary.
Following is the list of some common artifacts with a brief
explanation.
Spatial resolution:
Spatialresolution refers to the ability of an imaging
modality to differentiate two adjacent structures as
being distinct from one another.
Poor spatial resolution is an artifact since a failure to
resolve adjacent interfaces means a loss of detail, and
two closely spaced interfaces are displayed as one echo
rather than two.
Axial resolution:
Axial resolution artifacts occur when the imaging
system is not capable of resolving two-point reflectors
in an axial direction.
Mathematically, it is equal to half the spatial pulse
length.
Axial resolution is high when the spatial pulse length is
short.
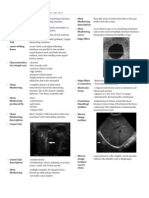
Beam width artifact:
This occurs when a reflective object located beyond the
widened ultrasound beam, after the focal zone, creates
false detectable echoes that are displayed as overlapping
the structure of interest.
Itcan be reduced by adjusting the focal zone,
diminishing the gain settings, and viewing the structure
through multiple acoustic windows at different angles.
Slice thickness artifact:
This is similar to the beam width artifact but occurs due
to the thickness of the beam.
Slice thickness determines the trade-off in image quality
between spatial resolution (how clearly you can
differentiate small changes in the image) and image
noise (the standard deviation of the image).
Increased slice thickness will result in decreased spatial
resolution and image noise.
Reverberation:
Itis caused by echoes bouncing back and forth between
two strong interfaces before returning to the transducer
for detection.
Its appearance is multiple equidistantly spaced linear
reflections like a ladder.
Itcan be reduced by adjusting the transducer angle of
incidence or by decreasing the distance between the
reflective structure and the transducer.
Ring down artifact:
Ultrasound energy causes resonant vibrations of the air
bubbles. It is generated when a small column of fluid
between the gas bubbles is caused to resonate when
struck with a pulse of ultrasound. Also known as
resonance artifact.
Itoccurs posterior to the collections of gas (e.g. portal
venous gas, gas in abscess, bowel)
Itappears as a line or series of parallel bands extending
posteriorly to a gas collection.
Comet tail artifact:
Itis a form of reverberation, two reflective interfaces,
and thus sequential echoes are so closely spaced that
individual signals are not perceivable in the image.
Itoccurs due to surgical clips, and copper intrauterine
devices.
The appearance is a series of multiple, closely spaced
small bands of echoes.
Itcan be prevented by changing the beam angle or with
an alternate window.
Ghosting artifact:
Sound is refracted and the degree of this change in
direction is dependent on both the angle of the incident
ultrasound beam and the difference in velocity between
the two media.
The speed of sound varies in different tissues.
Thisappears as a duplication of a structure appearing
wider on the ultrasound image.
It can be prevented by changing the angle.
Mirror image artifact:
The return of the sound beams is delayed, and therefore the
structures from which these delayed beams are reflected are
displayed at a greater depth than their true anatomic depth.
Appears as a duplicated structure equidistant from a
strongly reflective interface.
It occurs around the diaphragm with liver lesions or the
liver itself being duplicated.
Its prevention includes scanning from different angles, by
adjusting the focal zone or scanning from multiple
windows.
You might also like
- Ultrasound PhysicsDocument9 pagesUltrasound PhysicsawansurfNo ratings yet
- Physics of UltarasoundDocument195 pagesPhysics of Ultarasoundhossam62683% (6)
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Riphah College of Science & Technology Faculty of Engineering & Applied SciencesDocument6 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Riphah College of Science & Technology Faculty of Engineering & Applied Sciencesallrounder fightNo ratings yet
- Mark H. Apostadero, MDDocument81 pagesMark H. Apostadero, MDYuan LiNo ratings yet
- US Artifacts - University of ChicagoDocument101 pagesUS Artifacts - University of Chicagoludiegues752No ratings yet
- Ultrasound ArtifactsDocument34 pagesUltrasound ArtifactsPatricio Alejandro Montalvo Ramos100% (1)
- Point-Of-Care Ultrasonography For ObstetricsDocument22 pagesPoint-Of-Care Ultrasonography For Obstetricssalah subbahNo ratings yet
- EchohandbookhscDocument126 pagesEchohandbookhscMr-deligent Abdalmohsen100% (1)
- Artefacts in LtrasoundDocument16 pagesArtefacts in Ltrasoundtvm1018No ratings yet
- A Scan BiometryDocument19 pagesA Scan BiometryJeanna Salima100% (1)
- Artifacts Od Ultrasound - HellerDocument7 pagesArtifacts Od Ultrasound - HellerMythily VedhagiriNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound PrinciplesDocument21 pagesUltrasound PrinciplesOMAR khaledNo ratings yet
- A Scan Biometery-PrintDocument16 pagesA Scan Biometery-PrintSadegh ShebaniNo ratings yet
- Physics of USGDocument24 pagesPhysics of USGdrdeyanNo ratings yet
- Basicsofultrasound 170807183128Document145 pagesBasicsofultrasound 170807183128Bunga FaridaNo ratings yet
- AstrophysicsDocument55 pagesAstrophysicsrbtlch1nNo ratings yet
- 2006 Physics NotesDocument7 pages2006 Physics NotesnealNo ratings yet
- Artifacts Interpretation 3Document12 pagesArtifacts Interpretation 3Hikmat UllahNo ratings yet
- Interferences and Types of ProbesDocument48 pagesInterferences and Types of ProbesyahyaNo ratings yet
- B-Scan Ocular UltrasoundDocument29 pagesB-Scan Ocular UltrasoundJeanna SalimaNo ratings yet
- E405 ph4Document2 pagesE405 ph4Marc OlivaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Based LearningDocument17 pagesPhysics Project Based Learningphanindra vulliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To UltrasonographyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Ultrasonographyrobinmilton1998No ratings yet
- Physics of Light and Microscopy (Autosaved)Document95 pagesPhysics of Light and Microscopy (Autosaved)sharada thiagarajanNo ratings yet
- ResonatorDocument10 pagesResonatorMariana Carrillo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- ULTRASOUND Suad - KHDocument14 pagesULTRASOUND Suad - KHxibsjddhsNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Physics and Safety ImplicationsDocument36 pagesFundamental Physics and Safety ImplicationsalgeboriNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound BasicsDocument2 pagesUltrasound Basicspiano543No ratings yet
- Intro To Light MicrosDocument9 pagesIntro To Light MicrosRendi PermanaNo ratings yet
- Radar Is A Detection System That UsesDocument18 pagesRadar Is A Detection System That UsesJonesha DaquitaNo ratings yet
- Physics ST AssignmentDocument9 pagesPhysics ST Assignmentsalmasharif082No ratings yet
- Part 2Document30 pagesPart 2ReshmaNo ratings yet
- Diffraction Note at A LevelDocument11 pagesDiffraction Note at A LevelBryan SutantoNo ratings yet
- Optics Notes 1-12-2024Document5 pagesOptics Notes 1-12-2024vihaanrawal2No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Ultrasound ImagingDocument11 pagesFundamentals of Ultrasound ImagingAryan Shukla100% (2)
- PHY370 Chapter 3 PDFDocument50 pagesPHY370 Chapter 3 PDFaisyahNo ratings yet
- Physical Principles of Abdominal Ultrasonography, Part 1 - Basics of Ultrasound Transducers and Image Formation - Today's Veterinary PracticeDocument10 pagesPhysical Principles of Abdominal Ultrasonography, Part 1 - Basics of Ultrasound Transducers and Image Formation - Today's Veterinary PracticeDalia ExtrapolisNo ratings yet
- Artifacts PPT OKDocument46 pagesArtifacts PPT OKCharles SiregarNo ratings yet
- Physics Board Project Rough Class 11Document17 pagesPhysics Board Project Rough Class 11Sandil KumarNo ratings yet
- How Does Ultrasound Work?Document7 pagesHow Does Ultrasound Work?shishichanNo ratings yet
- Journal of Light Microscopy: Rendi Permana (1903112399)Document13 pagesJournal of Light Microscopy: Rendi Permana (1903112399)Rendi PermanaNo ratings yet
- Lasers: Sub.:PhysicsDocument33 pagesLasers: Sub.:PhysicsVinay AdlakhaNo ratings yet
- Image Quality - v1Document50 pagesImage Quality - v1Fouzia NoorNo ratings yet
- Phase Contrast MicrosDocument7 pagesPhase Contrast Micros9791617898No ratings yet
- Ne Form of Energy Into Another For ExampleDocument4 pagesNe Form of Energy Into Another For ExampleKenny Then Soon HungNo ratings yet
- Electronic SurveyingDocument63 pagesElectronic Surveyingadedejidamilare2019No ratings yet
- ArtifactDocument3 pagesArtifactfeiflyfly100% (1)
- Medical Imaging (Chapter 32 TB)Document6 pagesMedical Imaging (Chapter 32 TB)Deewas PokhNo ratings yet
- 2013 Physics Assessment TaskDocument9 pages2013 Physics Assessment TasknealNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Unit 1Document65 pagesPaper 1 Unit 1sagar narkarNo ratings yet
- A Scan BiometryDocument28 pagesA Scan Biometrysolex_No ratings yet
- Optical FiberDocument177 pagesOptical FiberManish ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- DiffractionDocument2 pagesDiffractionAlexie AlmohallasNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonography Machine: SR - No Topic Name Page NoDocument30 pagesUltrasonography Machine: SR - No Topic Name Page NoLakhan YogiNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Laser TerminologyDocument27 pagesGlossary of Laser TerminologyRosário BeatoNo ratings yet
- Propagation of Light: Physical Science - Week 3ADocument28 pagesPropagation of Light: Physical Science - Week 3AJen JvsjvsNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of CTDocument77 pagesBasic Principles of CTcroydubsNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument13 pagesBiology ProjectHome MarufNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge About X-RayDocument2 pagesBasic Knowledge About X-Raysanjeeb88No ratings yet
- Astm E127 20 Fabrication and Control of Flat Bottomed Hole Ultrasonic Standard Reference Blocks Apiasme Practice Test PDFDocument16 pagesAstm E127 20 Fabrication and Control of Flat Bottomed Hole Ultrasonic Standard Reference Blocks Apiasme Practice Test PDFDinesh KanwaluNo ratings yet
- Particle Fluid Separation: Filtration: CHE 509: Introduction To Particle TechnologyDocument32 pagesParticle Fluid Separation: Filtration: CHE 509: Introduction To Particle TechnologyJane Eilyza AballaNo ratings yet
- Normed Linear Space-1Document16 pagesNormed Linear Space-1P R SAMBHU RAJNo ratings yet
- DS RE AK-8 Governor-Test-Stand eDocument2 pagesDS RE AK-8 Governor-Test-Stand esantiagoyepezNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Fast Recovery RectifiersDocument2 pagesData Sheet: Fast Recovery RectifiersCarlos Evangelista SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air System For Thermal Power ProjectsDocument21 pagesCompressed Air System For Thermal Power Projectsjkhan_7243840% (1)
- Phy Lab Rep 2.1 Linear AirtrackDocument4 pagesPhy Lab Rep 2.1 Linear AirtrackMGunNicholasNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 5Document6 pagesLab Report 5Rajput JanjuaNo ratings yet
- HFP Ap-As: FeaturesDocument13 pagesHFP Ap-As: FeaturesmohamedNo ratings yet
- Steam DistributionDocument16 pagesSteam DistributionHaris PrawotoNo ratings yet
- Simulación Optimizada Del Tiempo de La Parte Superior Del Cuerpo en La Producción de La Velocidad de La Cabeza Del Bate en El Bateo deDocument9 pagesSimulación Optimizada Del Tiempo de La Parte Superior Del Cuerpo en La Producción de La Velocidad de La Cabeza Del Bate en El Bateo dejhonattan sandovalNo ratings yet
- CFD - NotepadDocument1 pageCFD - NotepadLalith KumarNo ratings yet
- Enggzc112 May05 An PDFDocument3 pagesEnggzc112 May05 An PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual For Transmission Monitor RSUK0919: ORSUK0919Document31 pagesOperation Manual For Transmission Monitor RSUK0919: ORSUK0919Baena75No ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Periodic MotionDocument33 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Periodic MotionSalinas SalinasNo ratings yet
- Potential of Sintered Friction Linings in Synchronizers - enDocument15 pagesPotential of Sintered Friction Linings in Synchronizers - enPedro Ivo Meirinho GalvãoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 2Document5 pagesTutorial Chapter 2AmmyNo ratings yet
- f607 Chauvin PDFDocument4 pagesf607 Chauvin PDFsilveriserNo ratings yet
- Helicoidal StairDocument5 pagesHelicoidal Stairdeepak tom babuNo ratings yet
- Column Interaction CurvesDocument58 pagesColumn Interaction Curvesdbircs1981No ratings yet
- Communications & Power Industries TriodeDocument2 pagesCommunications & Power Industries TriodeathinabebaNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE PROBLEMS Fluid Mechanics Pump DeNeversDocument2 pagesSAMPLE PROBLEMS Fluid Mechanics Pump DeNeversGeorge Isaac McQuilesNo ratings yet
- CE120-02 Lecture 3 - Elevation Measurement by LevellingDocument38 pagesCE120-02 Lecture 3 - Elevation Measurement by LevellingJP PunsalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Physical WorldDocument10 pagesChapter-1 Physical WorldSparshiNo ratings yet
- Modeling of an electrolyzer for а hybrid power supply systemDocument3 pagesModeling of an electrolyzer for а hybrid power supply systemashoaib3No ratings yet
- Frigoboat Manual Rev 19aDocument19 pagesFrigoboat Manual Rev 19aDavid GPNo ratings yet
- Elimination Reactions: C C H X KOH Alcohol C C KX O HDocument14 pagesElimination Reactions: C C H X KOH Alcohol C C KX O HSreehari ES100% (1)
- MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST 0018 - 170102 I. Choose The Word Whose Underlined Part Is Pronounced DifferentlyDocument4 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE TEST 0018 - 170102 I. Choose The Word Whose Underlined Part Is Pronounced DifferentlyNguyễn Thu TrangNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physics Class XiDocument6 pagesSample Paper Physics Class XiBhaskar JhaNo ratings yet