Professional Documents
Culture Documents
B1b Infection and Response KO
B1b Infection and Response KO
Uploaded by
aarifahschool1230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageOriginal Title
B1b Infection and Response KO (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageB1b Infection and Response KO
B1b Infection and Response KO
Uploaded by
aarifahschool123Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
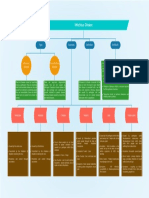
Key Terms Knowledge Organiser – Infection and Response (B1b) Stages of a drug trial
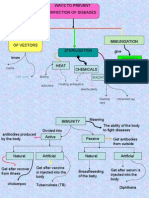
Communicable How pathogens spread:
A disease which is infectious.
disease (1) Drug tested on cells
in the lab
Pathogens Any microbe that causes disease.
(2) Drug tested on
A weakened or dead pathogen which is injected to stimulate the immune animals to see if it
Vaccine system to make antibodies. works
A cell which kills pathogens by ingesting them, producing
White blood cell (3) Drug tested on small
antibodies or producing antitoxins. group of healthy
Proteins released from white blood cells which are specific human volunteers to
Antibodies
to each pathogen and work to destroy them. see if it works in
humans
Antitoxins Chemicals released from white blood cells which neutralise toxins.
(4) Drug tested on
An immune person has the antibodies for a particular pathogen and Microbe Diseases + Symptoms patients with the
Immunity can’t get the disease. disease
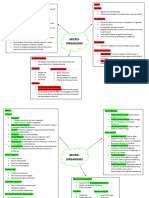
Virus (not living) Measles (itchy rash);
(5) Drug can now be
Antibiotics Chemicals that kill bacteria. HIV/AIDS (poor immune
system); Tobacco mosaic prescribed by
virus (damage to plant doctors
A design of experiment where the volunteer nor the scientist know leaves)
Double-blind who has the drug.
Bacteria Salmonella food
Placebo Something that looks like the drug, but contains no drug. poisoning (sickness);
Gonorrhoea (yellow
discharge and pain
weeing)
Carcinogen A substance which is known to cause cancer.
Fungi Athletes foot (itching);
Rose black spot (damage
Benign tumour A tumour which does not invade other parts of the body. to plant leaves)
Malignant Protist Malaria (flu-like
A tumour which will invade other parts of the body symptoms)
tumour
You might also like
- 3.1 Communicable DiseasesDocument1 page3.1 Communicable Diseaseswill hayNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesSciencex.Dilys.x xNo ratings yet
- B3 Full Revision Summary Broadsheet (Triple Only)Document2 pagesB3 Full Revision Summary Broadsheet (Triple Only)Jason akieNo ratings yet
- Infection and Response KO IRRDocument2 pagesInfection and Response KO IRROblizinNo ratings yet
- Vaccine - Inception To CulminationDocument16 pagesVaccine - Inception To CulminationYASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- B6Document2 pagesB6Hanna MalikNo ratings yet
- Fighting DiseaseDocument15 pagesFighting Diseasefatima al neyadiNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Unit 3 - Infection and ResponseDocument5 pagesGCSE Biology Unit 3 - Infection and ResponsefeyrelysNo ratings yet
- Immun e System: Chapter 31.2 Page 885Document21 pagesImmun e System: Chapter 31.2 Page 885JanaNo ratings yet
- Immune System and Disorders: Infectious DiseasesDocument28 pagesImmune System and Disorders: Infectious DiseasesanasNo ratings yet
- Human HealthDocument31 pagesHuman Health2375606245No ratings yet
- A1 GC Poster Template (Landscape) (修正版3) - 副本Document1 pageA1 GC Poster Template (Landscape) (修正版3) - 副本wanzhen0527No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Diseases & Immunity - Cecilia Benita 2Document19 pagesChapter 10 - Diseases & Immunity - Cecilia Benita 2simplyjisungNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument10 pagesCommunicable Diseasemyjr54bx4mNo ratings yet
- Mahmud RAHMAN - Edexcel - Biology - Health, Disease and The Development of Medicines - KnowIT - GCSE 2Document49 pagesMahmud RAHMAN - Edexcel - Biology - Health, Disease and The Development of Medicines - KnowIT - GCSE 2Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Micro 303-محولDocument12 pagesChapter Two Micro 303-محولshimaa dewedarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing (Midterm Topic 3)Document7 pagesFundamentals of Nursing (Midterm Topic 3)Manuel, Precious Marie B.No ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument6 pagesInfectious DiseasesAlexa QuizomNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease XI312 RAMADocument1 pageInfectious Disease XI312 RAMAMuhammad NaufalNo ratings yet
- General Biology Unit 6Document76 pagesGeneral Biology Unit 6waktolabokaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Week34 ReviewerDocument20 pagesPharma Week34 ReviewerDT1029No ratings yet
- EXPANDED PROGRAM IMMUNIZATION - Self ReviewerDocument6 pagesEXPANDED PROGRAM IMMUNIZATION - Self ReviewerIana CastigadorNo ratings yet
- Vaccination (20 Marks) How Are We Protected From Disease?: Task 1Document3 pagesVaccination (20 Marks) How Are We Protected From Disease?: Task 1KareemNo ratings yet
- Immunity and InfectionDocument26 pagesImmunity and InfectionfikowowNo ratings yet
- BioA4 24. Infectious DiseasesDocument7 pagesBioA4 24. Infectious Diseasesthanks btNo ratings yet
- Med Dia Lec Oct. 26Document15 pagesMed Dia Lec Oct. 26Enha PenNo ratings yet
- Plant Disease QP - AQA Biology GCSEDocument13 pagesPlant Disease QP - AQA Biology GCSEjivesh.karthigayanNo ratings yet
- Key Terms For Prevention and TreatmentDocument1 pageKey Terms For Prevention and Treatmentmariabour.enNo ratings yet
- Bacteria and Viruses PowerPointDocument43 pagesBacteria and Viruses PowerPointGastonMuñozAzulGmgNo ratings yet
- Hand Out AntibioticsDocument13 pagesHand Out AntibioticsMinhwa KimNo ratings yet
- 33x PDFDocument12 pages33x PDFHassan mohamad Al-bayateNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics ChartDocument8 pagesAntibiotics Chartapi-523306558No ratings yet
- Prevention of DiseasesDocument6 pagesPrevention of DiseasesbahacdNo ratings yet
- Escherichia Coli: Done By: Tamara Khalel, Majd Shweiki, Aya SulimanDocument8 pagesEscherichia Coli: Done By: Tamara Khalel, Majd Shweiki, Aya SulimanSalih TahsinNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Treating VirusesDocument4 pages11.2 Treating VirusesZJC 2333No ratings yet
- Anti-Infective AgentsDocument7 pagesAnti-Infective AgentsAlyssaGrandeMontimor100% (1)
- Microbial Control Sterilization & DisinfectionDocument10 pagesMicrobial Control Sterilization & DisinfectionMatt CloudNo ratings yet
- Final Brochure Health ScienceDocument2 pagesFinal Brochure Health Scienceapi-313269355No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Infectn 10Document5 pagesAnatomy of Infectn 10Nyxa AbdullaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112-Mod5Document6 pagesNCM 112-Mod5Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument24 pagesImmune SystemGaurav RathiNo ratings yet
- Pharma - Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument6 pagesPharma - Chemotherapeutic AgentsSae YanNo ratings yet
- National Center For Complementary and Integrative HealthDocument1 pageNational Center For Complementary and Integrative HealthKaisy MaramotNo ratings yet
- What Are TheyDocument1 pageWhat Are TheyDanna CruzNo ratings yet
- BAD MEDICINE Final ReportDocument25 pagesBAD MEDICINE Final ReporttimNo ratings yet
- Anti Hiv Using Nano RobotsDocument8 pagesAnti Hiv Using Nano RobotsBharadwaj Santhosh50% (2)
- Presentación 30Document1 pagePresentación 308vkzhpymgdNo ratings yet
- Topic 13 Full Doc j22 DDocument45 pagesTopic 13 Full Doc j22 DabdulwahabibnfayazNo ratings yet
- Micro OrganismsDocument5 pagesMicro Organismsnikitaria1603No ratings yet
- Funda MidtermDocument21 pagesFunda MidtermTrisha ApalisNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases of The Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageCommunicable Diseases of The Reproductive SystemSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of TBDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of TBEddie Lou GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of VaccineDocument2 pagesThe Benefits of VaccineNav AriNo ratings yet
- 2016 EdExcel Biology Topic 5 Health Disease and MedicinesDocument40 pages2016 EdExcel Biology Topic 5 Health Disease and MedicinesShilpa RKNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases QP - AQA Biology GCSEDocument18 pagesCommunicable Diseases QP - AQA Biology GCSEjivesh.karthigayanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Fundamentals in Nursing PracticeDocument4 pagesLaboratory Fundamentals in Nursing PracticedaclangiaNo ratings yet
- Funda Finals ReviewerDocument23 pagesFunda Finals Reviewerchloepaxton030No ratings yet
- Green Illustrative Circular Economy Infographic 2Document1 pageGreen Illustrative Circular Economy Infographic 2nazzlor08No ratings yet
- Herbal Antibiotics and Antivirals: Herbal Medicine to Heal Yourself NaturallyFrom EverandHerbal Antibiotics and Antivirals: Herbal Medicine to Heal Yourself NaturallyNo ratings yet
- Methods in The Time of COVID-19: The Vital Role of Qualitative InquiriesDocument5 pagesMethods in The Time of COVID-19: The Vital Role of Qualitative Inquiriesjahan namaNo ratings yet
- Aids 2013Document404 pagesAids 2013kovaron80No ratings yet
- Oncology BulletsDocument11 pagesOncology BulletsDonaJeanNo ratings yet
- Iuliana-Alexandra Radu - MG II Tema 1the Hospital-Medical VocabularyDocument4 pagesIuliana-Alexandra Radu - MG II Tema 1the Hospital-Medical VocabularyIuliana RaduNo ratings yet
- Varicella Zoster InfectionDocument68 pagesVaricella Zoster InfectionChristelle Brookshiel Demayo Marba100% (1)
- Navarro, JC CHN Rle 50 Items QuizDocument16 pagesNavarro, JC CHN Rle 50 Items QuizClint NavarroNo ratings yet
- Aids Quiz: The Answer Is DDocument4 pagesAids Quiz: The Answer Is DagarhemantNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Spore Forming Microorganisms of Medical ImportanceDocument30 pagesAnaerobic Spore Forming Microorganisms of Medical ImportanceVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument10 pagesImmune Systemailyn regaladoNo ratings yet
- Infection Control ManualDocument206 pagesInfection Control Manualastha singhNo ratings yet
- Escleritis EpiescleritisDocument16 pagesEscleritis EpiescleritisAngeloCarpioNo ratings yet
- Verorab PDFDocument3 pagesVerorab PDFNurul ArsitaNo ratings yet
- MCQ 3Document21 pagesMCQ 3Robert Edwards100% (1)
- Medical Statistics Exersice 1Document6 pagesMedical Statistics Exersice 1Нурпери НуралиеваNo ratings yet
- June 5, 2015 Strathmore TimesDocument36 pagesJune 5, 2015 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 6212 Assessment 2 Executive SummaryDocument4 pagesNURS FPX 6212 Assessment 2 Executive SummaryCarolyn HarkerNo ratings yet
- Model OL Exam English Essays Topics 2022Document10 pagesModel OL Exam English Essays Topics 2022nova katuneriyaNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesDaftar PustakaStephanie KusbiantoNo ratings yet
- BELLO DOCsDocument98 pagesBELLO DOCsPia Loraine BacongNo ratings yet
- Congenital RubellaDocument15 pagesCongenital RubellaShanaz AlvikhaNo ratings yet
- Asepsis & Infection ControlDocument26 pagesAsepsis & Infection ControlDominic SantosNo ratings yet
- Unit IB5: Biological AgentsDocument41 pagesUnit IB5: Biological Agentssamer alrawashdehNo ratings yet
- Critical Care - Criteria For Admission & Role of NurseDocument64 pagesCritical Care - Criteria For Admission & Role of NurseProf. Ramsharan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Management PlanDocument21 pagesCommunicable Disease Management PlanRaza Muhammad SoomroNo ratings yet
- A Little Red Lie - Quinton MeilDocument19 pagesA Little Red Lie - Quinton MeilQuinton K. MeilNo ratings yet
- Priyanka Pradhan: A Project Work On Study of Pathogenic Bacteria From Brackish Waters of Chilika Lake, OdishaDocument33 pagesPriyanka Pradhan: A Project Work On Study of Pathogenic Bacteria From Brackish Waters of Chilika Lake, Odishapraanya kishoreNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Jeronimus - Personality and The Coronavirus Pandemic - A Journal of The Plague YearDocument91 pages2020 - Jeronimus - Personality and The Coronavirus Pandemic - A Journal of The Plague YearBassem KamelNo ratings yet
- Dermatologycal Preparations PDFDocument268 pagesDermatologycal Preparations PDFVando F. Sardi100% (1)
- Netter's Internal Medicine 2nd Ed 17Document19 pagesNetter's Internal Medicine 2nd Ed 17Panagiotis SouldatosNo ratings yet
- SANCHEZ Et Al Medical Frontliners 2022 1Document801 pagesSANCHEZ Et Al Medical Frontliners 2022 1Andreagale GoNo ratings yet