Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsOrganic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by
Njabulo Ah AhCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Physical Pharmacy NotesDocument10 pagesPhysical Pharmacy NotesLorenzo Dominick Cid100% (8)
- Strip Weld OverlayDocument24 pagesStrip Weld OverlaymayataNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Definitions Finals GR12Document18 pagesChemistry Definitions Finals GR12rinaemudau50No ratings yet
- Experiment #8 Boiling Point: Laboratory Manual in Organic ChemistryDocument21 pagesExperiment #8 Boiling Point: Laboratory Manual in Organic ChemistryAria IsipNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument18 pagesOrganic ChemistryLawrence SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Funtional Group PropertiesDocument38 pagesChapter 2 Funtional Group Properties伟铭100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFAzadnikov94% (16)
- Chapter 3 Chemistry of CellsDocument12 pagesChapter 3 Chemistry of Cellsalvinlarano11No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFjacobNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Vocabulary ListDocument12 pagesBasic Chemistry Vocabulary ListBrayann InlvNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of LifeDocument44 pagesThe Chemistry of Lifecslb8No ratings yet
- L1 L2 Chemical Basis of Life - CompleteDocument38 pagesL1 L2 Chemical Basis of Life - CompleteGeethanjali SivakumarNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry Definitions: Chapter 1: Atoms, Molecules and StoichemistryDocument6 pagesAs Chemistry Definitions: Chapter 1: Atoms, Molecules and StoichemistryRamanath RamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document40 pagesLecture 1Yasir TubeNo ratings yet
- P3 Functional GroupsDocument54 pagesP3 Functional GroupsHazell SangalangNo ratings yet
- Ch03 - Introduction To Organic Molecules and Functional GroupsDocument67 pagesCh03 - Introduction To Organic Molecules and Functional GroupsFeaid Aina OrnedoNo ratings yet
- Absolute Temperature: This Is A TemperatureDocument29 pagesAbsolute Temperature: This Is A TemperatureSarah BockNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument11 pagesScience ReviewerMumay LobendinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Org. Molecules & Functional GroupsDocument43 pagesIntroduction of Org. Molecules & Functional Groups박승민No ratings yet
- IEB SAGS Chemistry DefinitionsDocument2 pagesIEB SAGS Chemistry DefinitionsYishai AbroNo ratings yet
- Chapter2:Molecular Biology: Pages (63-130)Document114 pagesChapter2:Molecular Biology: Pages (63-130)Hamzeh ZNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chem GlossaryDocument10 pagesIgcse Chem GlossaryKoniNo ratings yet
- Ch03 - Basics3Document57 pagesCh03 - Basics3Saguvij FopoNo ratings yet
- Full Org ChemDocument13 pagesFull Org ChemSOPHIA ALESNANo ratings yet
- Biochem LectureDocument24 pagesBiochem Lecturejoannenicole.maalaNo ratings yet
- Self-Check 1.1Document12 pagesSelf-Check 1.1Justine AmarantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 LectureDocument41 pagesChapter 02 Lectureplayer19No ratings yet
- Lec2 - Chemical Basis of LifeDocument58 pagesLec2 - Chemical Basis of LifeLJ LabradorNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry Definitions: 1. Relative Atomic MassDocument9 pagesAS Chemistry Definitions: 1. Relative Atomic MassTheLuckS; ラッキー矢印No ratings yet
- Biochemical Molecules Unit 2 G 11Document9 pagesBiochemical Molecules Unit 2 G 11eyosiyas tekleweyinNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document53 pagesModule 2Andrian SiscarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DefinitionDocument3 pagesChemistry DefinitionJaima Nahin NisheNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IgcseDocument31 pagesOrganic Chemistry Igcsenkoan12No ratings yet
- 5.functional GroupsDocument47 pages5.functional GroupsitsmeGYANo ratings yet
- Environmental SystemsDocument55 pagesEnvironmental SystemsPorc1234No ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Life - RevisedDocument63 pagesThe Chemistry of Life - RevisedalimeeroNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DefinitionDocument4 pagesChemistry DefinitionJaima Nahin NisheNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saDocument25 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saapi-1982440650% (2)
- Structures and Physical Properties 093652Document14 pagesStructures and Physical Properties 093652avialora6No ratings yet
- cHEMICAL RECATIONSDocument2 pagescHEMICAL RECATIONSAnam FNo ratings yet
- StotiometricrelationshipsDocument12 pagesStotiometricrelationshipsAhadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ChemicalDocument4 pagesChapter 2 ChemicalAya GhanamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions in Living Organisms OrganismsDocument30 pagesChemical Reactions in Living Organisms OrganismsanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12aDocument41 pagesChapter 12ajcvalley1No ratings yet
- 2 - A Chemistry of LifeDocument41 pages2 - A Chemistry of Lifewhether913No ratings yet
- 2 the+Chemistry+of+LifeDocument107 pages2 the+Chemistry+of+Lifegabbs_123No ratings yet
- Walang MakakaseethisDocument3 pagesWalang MakakaseethisAlissa YangNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds-2Document17 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds-2hackingraja868No ratings yet
- UNIT-I Solubility of DrugsDocument23 pagesUNIT-I Solubility of DrugsPranjul Shrivastava100% (1)
- Section 11 - Organic ChemDocument54 pagesSection 11 - Organic ChemMonique AldanaNo ratings yet
- Solids, Liquids, Gases, ReviewDocument5 pagesSolids, Liquids, Gases, ReviewnettextsNo ratings yet
- Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesOrganic CompoundsemilyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DefinitionsDocument4 pagesChemistry DefinitionsManiesegaran SagadevanNo ratings yet
- 2 - Chemistry of CellDocument41 pages2 - Chemistry of CellMira cle StarNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument16 pagesIntermolecular Forcesmaricon pocheNo ratings yet
- Biology For IMAT: 1.biochemistryDocument42 pagesBiology For IMAT: 1.biochemistryketyleenbNo ratings yet
- Boiling Point NotesDocument7 pagesBoiling Point NotesJozelle GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Acquaintance With Covalent MoleculesDocument11 pagesAcquaintance With Covalent MoleculesAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry With Boos Form 4 and 5 DefinitionsDocument4 pagesChemistry With Boos Form 4 and 5 DefinitionsFARTIN ALIA NISRINA BINTI MOHD FARID0% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument28 pagesStoichiometryDayasagar VSNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Ester Insulating Oil-Effect of Mineral Oil ContaminationDocument12 pagesSynthetic Ester Insulating Oil-Effect of Mineral Oil ContaminationSushil ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Fire Chapter2Document14 pagesFire Chapter2Debalina DassNo ratings yet
- Calcium Chloride - BrineDocument1 pageCalcium Chloride - Brinesaa6383No ratings yet
- Stnar34 MetanfetaminasDocument88 pagesStnar34 Metanfetaminashildana pachecoNo ratings yet
- 03 Plant Design and Economics Heuristics R02Document124 pages03 Plant Design and Economics Heuristics R02هادی طاهریNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids Isolation of Piperine, CaffeineDocument10 pagesAlkaloids Isolation of Piperine, CaffeineNIVEDITA PATILNo ratings yet
- EN Metallic Powder Coatings 1114Document28 pagesEN Metallic Powder Coatings 1114Станислав ПодольскийNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project - Caffeine in Tea SamplesDocument15 pagesChemistry Project - Caffeine in Tea SamplesRajuKumar100% (4)
- Full Chemistry NotesDocument21 pagesFull Chemistry NotesluckybuddyNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis and PreventionDocument76 pagesFailure Analysis and PreventionDome Stoi0% (1)
- Hydroskimming The Refinery Process 2012Document3 pagesHydroskimming The Refinery Process 2012fedemochileroNo ratings yet
- Anagrelide Dispersion SolidaDocument116 pagesAnagrelide Dispersion SolidaPedromoreno123No ratings yet
- 10.1 Galvanic CellsDocument2 pages10.1 Galvanic CellsElla LeducNo ratings yet
- U08 Notes Part2 PHDocument22 pagesU08 Notes Part2 PHapi-546066323No ratings yet
- Extra Practice CH 14 AnsDocument6 pagesExtra Practice CH 14 Ansjona chemistryNo ratings yet
- API RP 572 QuizDocument17 pagesAPI RP 572 Quizamalhaj2013No ratings yet
- Adoc - Pub - Pengaruh Penambahan Bahan Kimia Pada Tanah LempungDocument12 pagesAdoc - Pub - Pengaruh Penambahan Bahan Kimia Pada Tanah LempungDewi rahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of Cement IndustriesDocument33 pagesProduction Technology of Cement IndustriesBereket TadesseNo ratings yet
- General Organic ChemistryDocument58 pagesGeneral Organic ChemistryGauravNo ratings yet
- FF 2016 CompressedDocument215 pagesFF 2016 CompressedideyNo ratings yet
- Use of Plastic Waste in Construction of Flexible Pavement 8Document50 pagesUse of Plastic Waste in Construction of Flexible Pavement 8Ujwal Jaiswal100% (2)
- 209 425 1 SMGFFDocument10 pages209 425 1 SMGFFTeddy GunawanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/62Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/62KhairNo ratings yet
- Petrochemical Industry - Production ProcessDocument40 pagesPetrochemical Industry - Production ProcessAyie Arie AyitNo ratings yet
- Note CHP 3 Material Science 281 Uitm Em110Document40 pagesNote CHP 3 Material Science 281 Uitm Em110bino_ryeNo ratings yet
- By Dr. Amit Verma: Associate ProfessorDocument126 pagesBy Dr. Amit Verma: Associate ProfessorTalhaNo ratings yet
- S S ElectrodeDocument1 pageS S ElectrodeRajeev KhantwalNo ratings yet
- Trimethoprim: TrimethoprimumDocument3 pagesTrimethoprim: TrimethoprimumLaurențiu Mihai BălanNo ratings yet
Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by
Njabulo Ah Ah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views37 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views37 pagesOrganic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by
Njabulo Ah AhCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 37
Molar volume of gases
•Molar volume of gases: 1
mole of any gas occupies
22,4 dm3 at 0 °C (273 K) and
1 atmosphere (101,3 kPa).
Different intermolecular forces
(Van der Waal's forces)
• Dipole-dipole forces: Forces between two polar
molecules
• Induced dipole forces or London forces: Forces
between non-polar molecules
• Hydrogen bonding: Forces between molecules in
which hydrogen is covalently bonded to nitrogen,
oxygen or fluorine – a special case of dipole-dipole
forces.
Boiling point
•The stronger the
intermolecular forces, the
higher the boiling point.
Melting point
•The stronger the
intermolecular forces, the
higher the melting point.
Vapour pressure
•The stronger the
intermolecular forces, the
lower the vapour pressure.
Boiling point
•The temperature at which
the vapour pressure of a
substance equals
atmospheric pressure
Melting point
•The temperature at which
the solid and liquid phases of
a substance are at
equilibrium.
Vapour pressure
•The pressure exerted by a
vapour at equilibrium with its
liquid in a closed system.
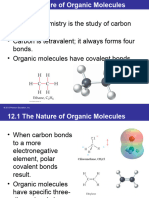
Organic molecules
•Organic molecules are
molecules containing carbon
atoms.
Molecular formula
•A chemical formula that indicates
the type of atoms and the
correct number of each in a
molecule.
Structural formula
• A structural formula of a compound shows
which atoms are attached
to which within the molecule. Atoms are
represented by their chemical symbols and
lines are used to represent ALL the bonds
that hold the atoms together.
Condensed structural formula
•This notation shows the way in
which atoms are bonded
together in the molecule, but
DOES NOT SHOW ALL bond
lines.
Hydrocarbon
Organic compounds that
consist of hydrogen and
carbon only.
Homologous series
•A series of organic compounds that
can be described by the same
general formula OR in which one
member differs from the next with
a -CH2 group
Saturated compounds
•Compounds in which there are
no multiple bonds between
Carbon atoms in their
hydrocarbon chains.
Unsaturated compounds
•Compounds with one or
more multiple bonds
between Carbon atoms in
their hydrocarbon chains.
Functional group
•A bond or an atom or a group of
atoms that determine(s) the
physical and chemical properties
of a group of organic
compounds.
Structural isomer
•Organic molecules with the
same molecular formula, but
different structural formulae.
Chain isomers
•Same molecular formula, but
different types of chains
Positional isomers
•Same molecular formula, but
different positions of the side
chain, substituents or
functional groups on the
parent chain
Functional isomers
•Same molecular formula,
but different functional
groups.
Hydro-halogenation
•The addition of a hydrogen
halide to an alkene.
Halogenation
•The reaction of a halogen
(Br2, Cℓ2 ) with a
compound.
Hydration
•The addition of water to
a compound.
Hydrogenation
•The addition of hydrogen to
an alkene.
Dehydrohalogenation of
haloalkanes
•The elimination of hydrogen and
a halogen from a haloalkane.
Dehydration of alcohols
•The elimination of water
from an alcohol.
Cracking of alkanes:
•The chemical process in
which longer chain
hydrocarbon molecules are
broken down to shorter more
useful molecules.
Hydrolysis
•The reaction of a
compound with water.
Macromolecule
•A molecule that consists of
a large number of atoms.
Polymer
•A large molecule composed
of smaller monomer units
covalently bonded to each
other in a repeating pattern
Monomer:
•Small organic molecules that
can be covalently bonded to
each other in a repeating
pattern.
Polymerisation
•A chemical reaction in
which monomer molecules
join to form a polymer.
Addition polymerisation
•A reaction in which small
molecules join to form very
large molecules by adding on
double bonds.
Addition polymer
•A polymer formed when
monomers (usually containing a
double bond) combine through
an addition reaction.
Condensation polymerisation
•Molecules of two monomers
with different functional
groups undergo condensation
reactions with the loss of small
molecules, usually water
Condensation polymer
•A polymer formed by two monomers
with different functional groups that
are linked together in a
condensation reaction in which a
small molecule, usually water, is lost.
You might also like
- Physical Pharmacy NotesDocument10 pagesPhysical Pharmacy NotesLorenzo Dominick Cid100% (8)
- Strip Weld OverlayDocument24 pagesStrip Weld OverlaymayataNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Definitions Finals GR12Document18 pagesChemistry Definitions Finals GR12rinaemudau50No ratings yet
- Experiment #8 Boiling Point: Laboratory Manual in Organic ChemistryDocument21 pagesExperiment #8 Boiling Point: Laboratory Manual in Organic ChemistryAria IsipNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument18 pagesOrganic ChemistryLawrence SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Funtional Group PropertiesDocument38 pagesChapter 2 Funtional Group Properties伟铭100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFAzadnikov94% (16)
- Chapter 3 Chemistry of CellsDocument12 pagesChapter 3 Chemistry of Cellsalvinlarano11No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFjacobNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Vocabulary ListDocument12 pagesBasic Chemistry Vocabulary ListBrayann InlvNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of LifeDocument44 pagesThe Chemistry of Lifecslb8No ratings yet
- L1 L2 Chemical Basis of Life - CompleteDocument38 pagesL1 L2 Chemical Basis of Life - CompleteGeethanjali SivakumarNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry Definitions: Chapter 1: Atoms, Molecules and StoichemistryDocument6 pagesAs Chemistry Definitions: Chapter 1: Atoms, Molecules and StoichemistryRamanath RamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document40 pagesLecture 1Yasir TubeNo ratings yet
- P3 Functional GroupsDocument54 pagesP3 Functional GroupsHazell SangalangNo ratings yet
- Ch03 - Introduction To Organic Molecules and Functional GroupsDocument67 pagesCh03 - Introduction To Organic Molecules and Functional GroupsFeaid Aina OrnedoNo ratings yet
- Absolute Temperature: This Is A TemperatureDocument29 pagesAbsolute Temperature: This Is A TemperatureSarah BockNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument11 pagesScience ReviewerMumay LobendinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Org. Molecules & Functional GroupsDocument43 pagesIntroduction of Org. Molecules & Functional Groups박승민No ratings yet
- IEB SAGS Chemistry DefinitionsDocument2 pagesIEB SAGS Chemistry DefinitionsYishai AbroNo ratings yet
- Chapter2:Molecular Biology: Pages (63-130)Document114 pagesChapter2:Molecular Biology: Pages (63-130)Hamzeh ZNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chem GlossaryDocument10 pagesIgcse Chem GlossaryKoniNo ratings yet
- Ch03 - Basics3Document57 pagesCh03 - Basics3Saguvij FopoNo ratings yet
- Full Org ChemDocument13 pagesFull Org ChemSOPHIA ALESNANo ratings yet
- Biochem LectureDocument24 pagesBiochem Lecturejoannenicole.maalaNo ratings yet
- Self-Check 1.1Document12 pagesSelf-Check 1.1Justine AmarantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 LectureDocument41 pagesChapter 02 Lectureplayer19No ratings yet
- Lec2 - Chemical Basis of LifeDocument58 pagesLec2 - Chemical Basis of LifeLJ LabradorNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry Definitions: 1. Relative Atomic MassDocument9 pagesAS Chemistry Definitions: 1. Relative Atomic MassTheLuckS; ラッキー矢印No ratings yet
- Biochemical Molecules Unit 2 G 11Document9 pagesBiochemical Molecules Unit 2 G 11eyosiyas tekleweyinNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document53 pagesModule 2Andrian SiscarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DefinitionDocument3 pagesChemistry DefinitionJaima Nahin NisheNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IgcseDocument31 pagesOrganic Chemistry Igcsenkoan12No ratings yet
- 5.functional GroupsDocument47 pages5.functional GroupsitsmeGYANo ratings yet
- Environmental SystemsDocument55 pagesEnvironmental SystemsPorc1234No ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Life - RevisedDocument63 pagesThe Chemistry of Life - RevisedalimeeroNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DefinitionDocument4 pagesChemistry DefinitionJaima Nahin NisheNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saDocument25 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saapi-1982440650% (2)
- Structures and Physical Properties 093652Document14 pagesStructures and Physical Properties 093652avialora6No ratings yet
- cHEMICAL RECATIONSDocument2 pagescHEMICAL RECATIONSAnam FNo ratings yet
- StotiometricrelationshipsDocument12 pagesStotiometricrelationshipsAhadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ChemicalDocument4 pagesChapter 2 ChemicalAya GhanamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions in Living Organisms OrganismsDocument30 pagesChemical Reactions in Living Organisms OrganismsanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12aDocument41 pagesChapter 12ajcvalley1No ratings yet
- 2 - A Chemistry of LifeDocument41 pages2 - A Chemistry of Lifewhether913No ratings yet
- 2 the+Chemistry+of+LifeDocument107 pages2 the+Chemistry+of+Lifegabbs_123No ratings yet
- Walang MakakaseethisDocument3 pagesWalang MakakaseethisAlissa YangNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds-2Document17 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds-2hackingraja868No ratings yet
- UNIT-I Solubility of DrugsDocument23 pagesUNIT-I Solubility of DrugsPranjul Shrivastava100% (1)
- Section 11 - Organic ChemDocument54 pagesSection 11 - Organic ChemMonique AldanaNo ratings yet
- Solids, Liquids, Gases, ReviewDocument5 pagesSolids, Liquids, Gases, ReviewnettextsNo ratings yet
- Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesOrganic CompoundsemilyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DefinitionsDocument4 pagesChemistry DefinitionsManiesegaran SagadevanNo ratings yet
- 2 - Chemistry of CellDocument41 pages2 - Chemistry of CellMira cle StarNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument16 pagesIntermolecular Forcesmaricon pocheNo ratings yet
- Biology For IMAT: 1.biochemistryDocument42 pagesBiology For IMAT: 1.biochemistryketyleenbNo ratings yet
- Boiling Point NotesDocument7 pagesBoiling Point NotesJozelle GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Acquaintance With Covalent MoleculesDocument11 pagesAcquaintance With Covalent MoleculesAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry With Boos Form 4 and 5 DefinitionsDocument4 pagesChemistry With Boos Form 4 and 5 DefinitionsFARTIN ALIA NISRINA BINTI MOHD FARID0% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument28 pagesStoichiometryDayasagar VSNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Ester Insulating Oil-Effect of Mineral Oil ContaminationDocument12 pagesSynthetic Ester Insulating Oil-Effect of Mineral Oil ContaminationSushil ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Fire Chapter2Document14 pagesFire Chapter2Debalina DassNo ratings yet
- Calcium Chloride - BrineDocument1 pageCalcium Chloride - Brinesaa6383No ratings yet
- Stnar34 MetanfetaminasDocument88 pagesStnar34 Metanfetaminashildana pachecoNo ratings yet
- 03 Plant Design and Economics Heuristics R02Document124 pages03 Plant Design and Economics Heuristics R02هادی طاهریNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids Isolation of Piperine, CaffeineDocument10 pagesAlkaloids Isolation of Piperine, CaffeineNIVEDITA PATILNo ratings yet
- EN Metallic Powder Coatings 1114Document28 pagesEN Metallic Powder Coatings 1114Станислав ПодольскийNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project - Caffeine in Tea SamplesDocument15 pagesChemistry Project - Caffeine in Tea SamplesRajuKumar100% (4)
- Full Chemistry NotesDocument21 pagesFull Chemistry NotesluckybuddyNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis and PreventionDocument76 pagesFailure Analysis and PreventionDome Stoi0% (1)
- Hydroskimming The Refinery Process 2012Document3 pagesHydroskimming The Refinery Process 2012fedemochileroNo ratings yet
- Anagrelide Dispersion SolidaDocument116 pagesAnagrelide Dispersion SolidaPedromoreno123No ratings yet
- 10.1 Galvanic CellsDocument2 pages10.1 Galvanic CellsElla LeducNo ratings yet
- U08 Notes Part2 PHDocument22 pagesU08 Notes Part2 PHapi-546066323No ratings yet
- Extra Practice CH 14 AnsDocument6 pagesExtra Practice CH 14 Ansjona chemistryNo ratings yet
- API RP 572 QuizDocument17 pagesAPI RP 572 Quizamalhaj2013No ratings yet
- Adoc - Pub - Pengaruh Penambahan Bahan Kimia Pada Tanah LempungDocument12 pagesAdoc - Pub - Pengaruh Penambahan Bahan Kimia Pada Tanah LempungDewi rahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of Cement IndustriesDocument33 pagesProduction Technology of Cement IndustriesBereket TadesseNo ratings yet
- General Organic ChemistryDocument58 pagesGeneral Organic ChemistryGauravNo ratings yet
- FF 2016 CompressedDocument215 pagesFF 2016 CompressedideyNo ratings yet
- Use of Plastic Waste in Construction of Flexible Pavement 8Document50 pagesUse of Plastic Waste in Construction of Flexible Pavement 8Ujwal Jaiswal100% (2)
- 209 425 1 SMGFFDocument10 pages209 425 1 SMGFFTeddy GunawanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/62Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/62KhairNo ratings yet
- Petrochemical Industry - Production ProcessDocument40 pagesPetrochemical Industry - Production ProcessAyie Arie AyitNo ratings yet
- Note CHP 3 Material Science 281 Uitm Em110Document40 pagesNote CHP 3 Material Science 281 Uitm Em110bino_ryeNo ratings yet
- By Dr. Amit Verma: Associate ProfessorDocument126 pagesBy Dr. Amit Verma: Associate ProfessorTalhaNo ratings yet
- S S ElectrodeDocument1 pageS S ElectrodeRajeev KhantwalNo ratings yet
- Trimethoprim: TrimethoprimumDocument3 pagesTrimethoprim: TrimethoprimumLaurențiu Mihai BălanNo ratings yet