Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(WUWM) Research Symp Pres
(WUWM) Research Symp Pres
Uploaded by
michaelcamus123Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Case 8 - Western Pharmaceutical - ADocument5 pagesCase 8 - Western Pharmaceutical - Amohamed mohamedgalal100% (2)
- Asci Scmbok Edition 1Document26 pagesAsci Scmbok Edition 1Amalia NurrahmahNo ratings yet
- Topaz Annual Report 2017 PDFDocument92 pagesTopaz Annual Report 2017 PDFEhsan AlimNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management Tata MotorDocument25 pagesSupply Chain Management Tata MotorArpit JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Oracle OPM WMS White PaperDocument5 pagesOracle OPM WMS White Paper1lvlupNo ratings yet
- ERP Implementation in Food IndustryDocument7 pagesERP Implementation in Food IndustryKavan ChhedaNo ratings yet
- And Key Concepts: End-To-End Supply Chain Planning FrameworkDocument44 pagesAnd Key Concepts: End-To-End Supply Chain Planning FrameworkBrayan Quispe CorcinoNo ratings yet
- Big Data Analytics Supply Chain PerformanceDocument16 pagesBig Data Analytics Supply Chain PerformanceGokan GoNo ratings yet
- Week 15 Strategic Challenges and Change For Supply ChainsDocument31 pagesWeek 15 Strategic Challenges and Change For Supply ChainsSaiparnNo ratings yet
- Future Supply Chain Data Consumer Goods RetailDocument32 pagesFuture Supply Chain Data Consumer Goods RetailRB100% (1)
- Merging Anomalous Data Usage in Wireless Mobile Telecommunication: Business Analytics With A Strategy-Focused Data-Driven Approach For SustainabilityDocument7 pagesMerging Anomalous Data Usage in Wireless Mobile Telecommunication: Business Analytics With A Strategy-Focused Data-Driven Approach For Sustainabilityniket mehtaNo ratings yet
- Operation Management Specialization SyllabusDocument18 pagesOperation Management Specialization SyllabusDivyeshNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument8 pagesBrochureswapzNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledlaadla3951No ratings yet
- IM Wise Analytics-491004f03d-PpDocument20 pagesIM Wise Analytics-491004f03d-PpIrfan HanifNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Short Courses: About UsDocument2 pagesSupply Chain Short Courses: About Ussutawijaya_masNo ratings yet
- Big Data Computing and Clouds: Trends and Future DirectionsDocument44 pagesBig Data Computing and Clouds: Trends and Future DirectionsJobi VijayNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 13 07101Document22 pagesSustainability 13 07101Riya GuptaNo ratings yet
- 4064 4086.pptmDocument22 pages4064 4086.pptmchandru.scubeNo ratings yet
- Trac360 WhitepaperDocument13 pagesTrac360 WhitepaperNhư Nguyễn Trần ThảoNo ratings yet
- Big Data For Supply Chain Management Opportunities and ChallengesDocument7 pagesBig Data For Supply Chain Management Opportunities and ChallengesRinda nurulNo ratings yet
- Course 2 Module 03 Lesson 6Document12 pagesCourse 2 Module 03 Lesson 6ducNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Design and Enterprise Data Warehouse DevelopmentDocument12 pagesRelational Database Design and Enterprise Data Warehouse DevelopmentducNo ratings yet
- Industrial Marketing Management 90 (2020) 493-507Document15 pagesIndustrial Marketing Management 90 (2020) 493-507albeiro beltranNo ratings yet
- AHP Based Data Mining For Customer Segmentation Based On Customer Lifetime ValueDocument7 pagesAHP Based Data Mining For Customer Segmentation Based On Customer Lifetime ValueIIR indiaNo ratings yet
- CLSCM BrochureDocument4 pagesCLSCM Brochureictberger102No ratings yet
- Chap 1Document45 pagesChap 1Prasad DhanikondaNo ratings yet
- Global Supply-Chain Strategy and Global CompetitivenessDocument14 pagesGlobal Supply-Chain Strategy and Global CompetitivenessgiovanniNo ratings yet
- S2017 Hubble ExpansionDocument25 pagesS2017 Hubble ExpansionYanxuan QinNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument2 pagesSupply Chain ManagementAshish SwainNo ratings yet
- Data Mining: Concepts and TechniquesDocument15 pagesData Mining: Concepts and TechniquesHira BaigNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project Presentation - Smart SalesDocument16 pagesFinal Year Project Presentation - Smart SalesMayank JhaNo ratings yet
- Big data With MLDocument19 pagesBig data With MLtusharadri123No ratings yet
- GSCI Supply Chain Integration Strategy WPDocument48 pagesGSCI Supply Chain Integration Strategy WPAlfredo PanceronNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentzonaira IoBMNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Ds Project Report FinalDocument20 pagesGroup 2 Ds Project Report FinalDaddy MewariNo ratings yet
- Rancang Bangun Aplikasi Data Mining Pada Penjualan Distro Bloods Berbasis Web Menggunakan Algoritma AprioriDocument8 pagesRancang Bangun Aplikasi Data Mining Pada Penjualan Distro Bloods Berbasis Web Menggunakan Algoritma AprioriJurnal JTIK (Jurnal Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi)No ratings yet
- Keegan 5e 06Document29 pagesKeegan 5e 06api-3695734100% (1)
- Basma Supply Chain AssDocument13 pagesBasma Supply Chain AssBasma ShaalanNo ratings yet
- Xlri Ba BrochureDocument16 pagesXlri Ba BrochureSudipto PaulNo ratings yet
- Predictive Big Data Analytics For Supply Chain Demand Forecasting: Methods, Applications, and Research OpportunitiesDocument22 pagesPredictive Big Data Analytics For Supply Chain Demand Forecasting: Methods, Applications, and Research Opportunitiesgoutam1235No ratings yet
- Comviva DSDP 360 Deg Marketing PlanDocument22 pagesComviva DSDP 360 Deg Marketing PlanTuhina JhaNo ratings yet
- Deloitte NL Cip FMCG Analytics FrameworkDocument50 pagesDeloitte NL Cip FMCG Analytics FrameworkPulokesh Ghosh100% (1)
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument6 pagesSupply Chain ManagementrahulpetermbaNo ratings yet
- Shipement Price: PredictionDocument35 pagesShipement Price: Predictionamey bhirangeNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: During Uncertain TimesDocument8 pagesSupply Chain Management: During Uncertain TimesAkhil AhemadNo ratings yet
- MIT-SCM 2021 Research JournalDocument15 pagesMIT-SCM 2021 Research JournalJorge TininiNo ratings yet
- 1646 5994 3 PBDocument11 pages1646 5994 3 PBRubel RezaNo ratings yet
- Big Data and The Information Management SystemDocument9 pagesBig Data and The Information Management SystemRico MartenstyaroNo ratings yet
- Outlook SIPDocument11 pagesOutlook SIPakhil pillaiNo ratings yet
- Gujarat University, Ahmedabad - MBA (Supply Chain Management)Document16 pagesGujarat University, Ahmedabad - MBA (Supply Chain Management)Exim 2021No ratings yet
- D2 Itibaev KairatDocument22 pagesD2 Itibaev KairatIvana WijayaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Demand ForecastingDocument13 pagesTerm Paper Demand Forecastinggoutam1235No ratings yet
- Vol 11 3Document5 pagesVol 11 3bhuvanesh.cse23No ratings yet
- Presentation Dr. Francis Lau (For Participants)Document20 pagesPresentation Dr. Francis Lau (For Participants)AISYA AURANo ratings yet
- The SAC Higg IndexDocument40 pagesThe SAC Higg IndexRanjit SamalNo ratings yet
- Big Data and Analytics in The Automotive IndustryDocument16 pagesBig Data and Analytics in The Automotive IndustryDhwanit ThakorNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Customer Churn Prediction in Telecom Industry Using Decision Trees and Logistic RegressionDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Customer Churn Prediction in Telecom Industry Using Decision Trees and Logistic RegressionD DNo ratings yet
- CSCP Content V5Document6 pagesCSCP Content V5cameron.preneshreeNo ratings yet
- Expert@StratergyDocument21 pagesExpert@Stratergyjai123shriganeshNo ratings yet
- Review and Analysis of Artificial Intelligence Methods For DemandDocument6 pagesReview and Analysis of Artificial Intelligence Methods For DemandPurushotam KumarNo ratings yet
- Avid EverywhereDocument12 pagesAvid EverywheremauroboteroNo ratings yet
- Topic10 - Data MiningDocument29 pagesTopic10 - Data Miningmiragelimited91No ratings yet
- ST7. MAR - PlaceDocument8 pagesST7. MAR - PlaceUyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- Arpita Paul DWDM2024Document10 pagesArpita Paul DWDM2024aakashshaw01No ratings yet
- Returnables Processing (BDW) - Process Diagrams PDFDocument3 pagesReturnables Processing (BDW) - Process Diagrams PDFNavjyot SinghviNo ratings yet
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) - Based Modular Integrated Construction Risk Management - Critical Survey and Future NeedsDocument15 pagesBuilding Information Modeling (BIM) - Based Modular Integrated Construction Risk Management - Critical Survey and Future NeedsChristopher StevenNo ratings yet
- Cold Chain ValidationDocument20 pagesCold Chain Validationvijay narayan100% (2)
- Certificate in Logistics ManagementDocument2 pagesCertificate in Logistics ManagementRifwan FadiansyahNo ratings yet
- DRP PlanningDocument30 pagesDRP PlanningRaja Sekhar RaaviNo ratings yet
- ESCS Corporate PresentationDocument37 pagesESCS Corporate PresentationDeathless LoveNo ratings yet
- Presentation Isa s95Document32 pagesPresentation Isa s95Do Van TuNo ratings yet
- Jump To Country: (Internal Link To Company) (External Link To Member)Document216 pagesJump To Country: (Internal Link To Company) (External Link To Member)kevinNo ratings yet
- Hero MotoCorp - Process CheatsheetDocument1 pageHero MotoCorp - Process CheatsheetShreshtha MittalNo ratings yet
- WMS+Location+Manager+User+Guide+ +WIP+DocDocument21 pagesWMS+Location+Manager+User+Guide+ +WIP+Docir4w4nNo ratings yet
- BatDocument14 pagesBatnakibosmanNo ratings yet
- Dissertation ReworkedDocument48 pagesDissertation ReworkedBelùr PrathyushNo ratings yet
- SurveyDocument8 pagesSurveyEdwardArribaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain and LogisticDocument7 pagesSupply Chain and LogisticJeryl GandecilaNo ratings yet
- CNH Industrial QPS 08018 Rev DDocument79 pagesCNH Industrial QPS 08018 Rev DCarlos PedrosoNo ratings yet
- Industry 40 Implications in Logistics An OverviewDocument9 pagesIndustry 40 Implications in Logistics An OverviewDimitri KaramazovNo ratings yet
- LGT - Outlook For Supply Chain and Logistics ManagementDocument4 pagesLGT - Outlook For Supply Chain and Logistics ManagementWency Bringino Alterado NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Snapdeal PDFDocument7 pagesSnapdeal PDFAMIT BANSALNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 6Document8 pagesLaboratory Exercise 6JH EscobarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting - Dayag 2015 - Chapter 13 - Problem III - IVDocument2 pagesAdvanced Accounting - Dayag 2015 - Chapter 13 - Problem III - IVJohn Carlos DoringoNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Desertation - JeetuDocument9 pagesSynopsis Desertation - JeetuJeetu RamNo ratings yet
- 0-3-2 E-KanbanDocument33 pages0-3-2 E-Kanbanprasetyo ilhamNo ratings yet
- Materials Manager Competency ModelDocument24 pagesMaterials Manager Competency ModelSaikumar SelaNo ratings yet
- Doctoral Dissertations in Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementDocument5 pagesDoctoral Dissertations in Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementWriteMyPaperForMeFastSingaporeNo ratings yet
(WUWM) Research Symp Pres
(WUWM) Research Symp Pres
Uploaded by
michaelcamus123Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(WUWM) Research Symp Pres
(WUWM) Research Symp Pres
Uploaded by
michaelcamus123Copyright:
Available Formats
Orchestrating the Future of Food Supply Chains
A System Dynamics Approach to Analyzing Food Waste in
Wholesale Markets
Food and Retail Operations Lab
Furqan Khalil Syed
Advisors: Dr. Christopher Mejia
Prof. Dr. Sara Grobbelaar
Motivation and Background
1.3 Billion tonnes of food
wasted every year
750 million people at risk of
severe food insecurity
How can we match the dynamic consumption patterns to food sources to ensure accessibility,
affordability and availability for all?
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 2
Research Objectives
Food is lost along every stage in the food value chain:
On-farm post
Transport,
Pre harvest / Harvest / harvest/ Wholesale
storage, Retail Consumption
Pre Slaughter Slaughter slaughter Markets
distribution
operations
Stages of food systems
1. What significant Supply Chain factors may help address overarching challenges around food
waste in wholesale markets?
2. What are the strategic and operational levers and some recommendations that can help fight
food loss and waste?
We aim not to solve specific challenges of specific wholesale markets but devise a framework
that can support the process of analyzing issues and developing mitigation schemes.
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 3
Methodology and Results
Process and Quantitative
Primary Data SD Simulation
Stakeholder Data
Collection Framework Model
Mapping Collection
Identifying and Semi-structured Publicly available Causal Loop Simulate SD model with
developing key interviews data Diagram supporting data
partners
Behavioral WS Market sourced Develop Stock and Devise Intervention
Surveys Flow Model Schemes
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 4
Methodology and Results
Process and Quantitative
Primary Data SD Simulation
Stakeholder Data
Collection Framework Model
Mapping Collection
Identifying and Semi-structured Publicly available Causal Loop Simulate SD model with
developing key interviews data Diagram supporting data
partners
Behavioral WS Market sourced Develop Stock and Devise Intervention
Surveys Flow Model Schemes
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 5
Process Mapping and Primary Data Collection
Primary Partner Hamburg, Germany
World Union of Wholesale Markets (WUWM) Paris, France
Barcelona, Spain Piraeus, Greece
A broad network of WS markets that aims to create a
more inclusive, sustainable and high quality Mexico City
international food system
Melbourne,
Australia
3 dimensions:
Strategy and
Market Operations Key Challenges
Objectives
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 6
Methodology and Results
Process and Quantitative
Primary Data SD Simulation
Stakeholder Data
Collection Framework Model
Mapping Collection
Identifying and Semi-structured Publicly available Causal Loop Simulate SD model with
developing key interviews data Diagram supporting data
partners
Behavioral WS Market sourced Develop Stock and Devise Intervention
Surveys Flow Model Schemes
System Dynamics framework capturing 70 + interrelated factors (or variables)
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 7
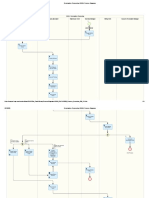
Simplified SD Model for Wholesale Market Operations
Physical Flow Endogenous Variables
Partnerships with
Tax Incentives Causal impact Stock Variables
foodbanks
Terminal Flow Variables
Decision Variables
Food Recovery Taxes Exogenous (Driving)
variables
Supply from Wholesale Wholesale Operational
Sales Income
farms Market Inventory Market Cash Expenditure
Food Waste Infrastructure
Willingness to Investment
invest
Invest in
Inventory Total Inventory
Product Price Cold
Capacity Need Capacity
Storage
Refrigeration Invest in Cold Storage
Product Shelf-life Product Quality
Capacity Need Capacity Capacity
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 8
Simplified SD Model for Wholesale Market Operations
Physical Flow Endogenous Variables
Partnerships with
Tax Incentives Causal impact Stock Variables
foodbanks
Terminal Flow Variables
Decision Variables
Food Recovery Taxes Exogenous (Driving)
variables
Supply from Wholesale Wholesale Operational
Sales Income
farms Market Inventory Market Cash Expenditure
Food Waste Infrastructure
Willingness to Investment
invest
Invest in
Inventory Total Inventory
Product Price Cold
Capacity Need Capacity
Storage
Refrigeration Invest in Cold Storage
Product Shelf-life Product Quality
Capacity Need Capacity Capacity
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 9
Simplified SD Model for Wholesale Market Operations
Physical Flow Endogenous Variables
Partnerships with
Tax Incentives Causal impact Stock Variables
foodbanks
Terminal Flow Variables
Decision Variables
Food Recovery Taxes Exogenous (Driving)
variables
Supply from Wholesale Wholesale Operational
Sales Income
farms Market Inventory Market Cash Expenditure
Food Waste Infrastructure
Willingness to Investment
invest
Invest in
Inventory Total Inventory
Product Price Cold
Capacity Need Capacity
Storage
Refrigeration Invest in Cold Storage
Product Shelf-life Product Quality
Capacity Need Capacity Capacity
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 10
Simplified SD Model for Wholesale Market Operations
Physical Flow Endogenous Variables
Partnerships with
Tax Incentives Causal impact Stock Variables
foodbanks
Terminal Flow Variables
Decision Variables
Food Recovery Taxes Exogenous (Driving)
variables
Supply from Wholesale Wholesale Operational
Sales Income
farms Market Inventory Market Cash Expenditure
Food Waste Infrastructure
Willingness to Investment
invest
Invest in
Inventory Total Inventory
Product Price Cold
Capacity Need Capacity
Storage
Refrigeration Invest in Cold Storage
Product Shelf-life Product Quality
Capacity Need Capacity Capacity
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 11
Simplified SD Model for Wholesale Market Operations
Physical Flow Endogenous Variables
Partnerships with
Tax Incentives Causal impact Stock Variables
foodbanks
Terminal Flow Variables
Decision Variables
Food Recovery Taxes Exogenous (Driving)
variables
Supply from Wholesale Wholesale Operational
Sales Income
farms Market Inventory Market Cash Expenditure
Food Waste Infrastructure
Willingness to Investment
invest
Invest in
Inventory Total Inventory
Product Price Cold
Capacity Need Capacity
Storage
Refrigeration Invest in Cold Storage
Product Shelf-life Product Quality
Capacity Need Capacity Capacity
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 12
Simplified SD Model for Wholesale Market Operations
Physical Flow Endogenous Variables
Partnerships with
Tax Incentives Causal impact Stock Variables
foodbanks
Terminal Flow Variables
Decision Variables
Food Recovery Taxes Exogenous (Driving)
variables
Supply from Wholesale Wholesale Operational
Sales Income
farms Market Inventory Market Cash Expenditure
Food Waste Infrastructure
Willingness to Investment
invest
Invest in
Inventory Total Inventory
Product Price Cold
Capacity Need Capacity
Storage
Refrigeration Invest in Cold Storage
Product Shelf-life Product Quality
Capacity Need Capacity Capacity
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 13
Simplified SD Model for Wholesale Market Operations
Physical Flow Endogenous Variables
Partnerships with
Tax Incentives Causal impact Stock Variables
foodbanks
Terminal Flow Variables
Decision Variables
Food Recovery Taxes Exogenous (Driving)
variables
Supply from Wholesale Wholesale Operational
Sales Income
farms Market Inventory Market Cash Expenditure
Food Waste Infrastructure
Willingness to Investment
invest
Hi Lo
Invest in
Inventory Total Inventory
Product Price Cold
Capacity Need Capacity
Storage
Refrigeration Invest in Cold Storage
Product Shelf-life Product Quality
Capacity Need Capacity Capacity
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 14
Methodology and Results
Process and Quantitative
Primary Data SD Simulation
Stakeholder Data
Collection Framework Model
Mapping Collection
Identifying and Semi-structured Publicly available Causal Loop Simulate SD model with
developing key interviews data Diagram supporting data
partners
Behavioral WS Market sourced Develop Stock and Devise Intervention
Surveys Flow Model Schemes
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 15
Simulating the model
7 Scenarios developed to explore model dynamics
Baseline Panic buying
Growing yield without infrastructure investment Perishability
Growing yield with infrastructure investment Intermittent Supply shock
Partnerships with foodbanks
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 16
Seasonal supply with/out Infrastructure Investment
Partnerships with Willingness to invest LOW Supply from
Product Shelf-life
foodbanks NO 2-10 d Willingness to invest HIGH farms
Simulation run over 1000 days No infrastructure investment High infrastructure investment
Key Insights:
• A growing yield triggers investment in merchandise capacity and cold storage
• Food loss is significantly reduced as cold chain and additional capacity are developed
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 17
Intermittent Supply (with active partnerships)
Supply from
Partnerships with Willingness to farms
Product Shelf-life HIGH
foodbanks YES 2-10 d Invest
Supply from
farms
Simulation run over 1000 days Intermittent Supply Seasonal Supply
Key Insights:
• Sudden changes in supply can cause the system to “overreact”
• Delay in market response causes the demand – and therefore stock to trail behind supply peaks
• With established partnerships with foodbanks, potential loss shifts to recovery
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 18
Key Contributions
A framework capturing dynamics of wholesale market supply chains
Key insights for wholesale markets:
Partnerships with foodbanks
Proactive infrastructure investment
Strategic management of supply & demand
Use of systems thinking in wholesale market supply chains
Foundational work for future research
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 19
Thank you!
System Dynamics Models
Cash flow
Inventory
Demand
Infrastructure
© 2022 MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics | Page 21
You might also like
- Case 8 - Western Pharmaceutical - ADocument5 pagesCase 8 - Western Pharmaceutical - Amohamed mohamedgalal100% (2)
- Asci Scmbok Edition 1Document26 pagesAsci Scmbok Edition 1Amalia NurrahmahNo ratings yet
- Topaz Annual Report 2017 PDFDocument92 pagesTopaz Annual Report 2017 PDFEhsan AlimNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management Tata MotorDocument25 pagesSupply Chain Management Tata MotorArpit JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Oracle OPM WMS White PaperDocument5 pagesOracle OPM WMS White Paper1lvlupNo ratings yet
- ERP Implementation in Food IndustryDocument7 pagesERP Implementation in Food IndustryKavan ChhedaNo ratings yet
- And Key Concepts: End-To-End Supply Chain Planning FrameworkDocument44 pagesAnd Key Concepts: End-To-End Supply Chain Planning FrameworkBrayan Quispe CorcinoNo ratings yet
- Big Data Analytics Supply Chain PerformanceDocument16 pagesBig Data Analytics Supply Chain PerformanceGokan GoNo ratings yet
- Week 15 Strategic Challenges and Change For Supply ChainsDocument31 pagesWeek 15 Strategic Challenges and Change For Supply ChainsSaiparnNo ratings yet
- Future Supply Chain Data Consumer Goods RetailDocument32 pagesFuture Supply Chain Data Consumer Goods RetailRB100% (1)
- Merging Anomalous Data Usage in Wireless Mobile Telecommunication: Business Analytics With A Strategy-Focused Data-Driven Approach For SustainabilityDocument7 pagesMerging Anomalous Data Usage in Wireless Mobile Telecommunication: Business Analytics With A Strategy-Focused Data-Driven Approach For Sustainabilityniket mehtaNo ratings yet
- Operation Management Specialization SyllabusDocument18 pagesOperation Management Specialization SyllabusDivyeshNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument8 pagesBrochureswapzNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledlaadla3951No ratings yet
- IM Wise Analytics-491004f03d-PpDocument20 pagesIM Wise Analytics-491004f03d-PpIrfan HanifNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Short Courses: About UsDocument2 pagesSupply Chain Short Courses: About Ussutawijaya_masNo ratings yet
- Big Data Computing and Clouds: Trends and Future DirectionsDocument44 pagesBig Data Computing and Clouds: Trends and Future DirectionsJobi VijayNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 13 07101Document22 pagesSustainability 13 07101Riya GuptaNo ratings yet
- 4064 4086.pptmDocument22 pages4064 4086.pptmchandru.scubeNo ratings yet
- Trac360 WhitepaperDocument13 pagesTrac360 WhitepaperNhư Nguyễn Trần ThảoNo ratings yet
- Big Data For Supply Chain Management Opportunities and ChallengesDocument7 pagesBig Data For Supply Chain Management Opportunities and ChallengesRinda nurulNo ratings yet
- Course 2 Module 03 Lesson 6Document12 pagesCourse 2 Module 03 Lesson 6ducNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Design and Enterprise Data Warehouse DevelopmentDocument12 pagesRelational Database Design and Enterprise Data Warehouse DevelopmentducNo ratings yet
- Industrial Marketing Management 90 (2020) 493-507Document15 pagesIndustrial Marketing Management 90 (2020) 493-507albeiro beltranNo ratings yet
- AHP Based Data Mining For Customer Segmentation Based On Customer Lifetime ValueDocument7 pagesAHP Based Data Mining For Customer Segmentation Based On Customer Lifetime ValueIIR indiaNo ratings yet
- CLSCM BrochureDocument4 pagesCLSCM Brochureictberger102No ratings yet
- Chap 1Document45 pagesChap 1Prasad DhanikondaNo ratings yet
- Global Supply-Chain Strategy and Global CompetitivenessDocument14 pagesGlobal Supply-Chain Strategy and Global CompetitivenessgiovanniNo ratings yet
- S2017 Hubble ExpansionDocument25 pagesS2017 Hubble ExpansionYanxuan QinNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument2 pagesSupply Chain ManagementAshish SwainNo ratings yet
- Data Mining: Concepts and TechniquesDocument15 pagesData Mining: Concepts and TechniquesHira BaigNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project Presentation - Smart SalesDocument16 pagesFinal Year Project Presentation - Smart SalesMayank JhaNo ratings yet
- Big data With MLDocument19 pagesBig data With MLtusharadri123No ratings yet
- GSCI Supply Chain Integration Strategy WPDocument48 pagesGSCI Supply Chain Integration Strategy WPAlfredo PanceronNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentzonaira IoBMNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Ds Project Report FinalDocument20 pagesGroup 2 Ds Project Report FinalDaddy MewariNo ratings yet
- Rancang Bangun Aplikasi Data Mining Pada Penjualan Distro Bloods Berbasis Web Menggunakan Algoritma AprioriDocument8 pagesRancang Bangun Aplikasi Data Mining Pada Penjualan Distro Bloods Berbasis Web Menggunakan Algoritma AprioriJurnal JTIK (Jurnal Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi)No ratings yet
- Keegan 5e 06Document29 pagesKeegan 5e 06api-3695734100% (1)
- Basma Supply Chain AssDocument13 pagesBasma Supply Chain AssBasma ShaalanNo ratings yet
- Xlri Ba BrochureDocument16 pagesXlri Ba BrochureSudipto PaulNo ratings yet
- Predictive Big Data Analytics For Supply Chain Demand Forecasting: Methods, Applications, and Research OpportunitiesDocument22 pagesPredictive Big Data Analytics For Supply Chain Demand Forecasting: Methods, Applications, and Research Opportunitiesgoutam1235No ratings yet
- Comviva DSDP 360 Deg Marketing PlanDocument22 pagesComviva DSDP 360 Deg Marketing PlanTuhina JhaNo ratings yet
- Deloitte NL Cip FMCG Analytics FrameworkDocument50 pagesDeloitte NL Cip FMCG Analytics FrameworkPulokesh Ghosh100% (1)
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument6 pagesSupply Chain ManagementrahulpetermbaNo ratings yet
- Shipement Price: PredictionDocument35 pagesShipement Price: Predictionamey bhirangeNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: During Uncertain TimesDocument8 pagesSupply Chain Management: During Uncertain TimesAkhil AhemadNo ratings yet
- MIT-SCM 2021 Research JournalDocument15 pagesMIT-SCM 2021 Research JournalJorge TininiNo ratings yet
- 1646 5994 3 PBDocument11 pages1646 5994 3 PBRubel RezaNo ratings yet
- Big Data and The Information Management SystemDocument9 pagesBig Data and The Information Management SystemRico MartenstyaroNo ratings yet
- Outlook SIPDocument11 pagesOutlook SIPakhil pillaiNo ratings yet
- Gujarat University, Ahmedabad - MBA (Supply Chain Management)Document16 pagesGujarat University, Ahmedabad - MBA (Supply Chain Management)Exim 2021No ratings yet
- D2 Itibaev KairatDocument22 pagesD2 Itibaev KairatIvana WijayaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Demand ForecastingDocument13 pagesTerm Paper Demand Forecastinggoutam1235No ratings yet
- Vol 11 3Document5 pagesVol 11 3bhuvanesh.cse23No ratings yet
- Presentation Dr. Francis Lau (For Participants)Document20 pagesPresentation Dr. Francis Lau (For Participants)AISYA AURANo ratings yet
- The SAC Higg IndexDocument40 pagesThe SAC Higg IndexRanjit SamalNo ratings yet
- Big Data and Analytics in The Automotive IndustryDocument16 pagesBig Data and Analytics in The Automotive IndustryDhwanit ThakorNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Customer Churn Prediction in Telecom Industry Using Decision Trees and Logistic RegressionDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Customer Churn Prediction in Telecom Industry Using Decision Trees and Logistic RegressionD DNo ratings yet
- CSCP Content V5Document6 pagesCSCP Content V5cameron.preneshreeNo ratings yet
- Expert@StratergyDocument21 pagesExpert@Stratergyjai123shriganeshNo ratings yet
- Review and Analysis of Artificial Intelligence Methods For DemandDocument6 pagesReview and Analysis of Artificial Intelligence Methods For DemandPurushotam KumarNo ratings yet
- Avid EverywhereDocument12 pagesAvid EverywheremauroboteroNo ratings yet
- Topic10 - Data MiningDocument29 pagesTopic10 - Data Miningmiragelimited91No ratings yet
- ST7. MAR - PlaceDocument8 pagesST7. MAR - PlaceUyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- Arpita Paul DWDM2024Document10 pagesArpita Paul DWDM2024aakashshaw01No ratings yet
- Returnables Processing (BDW) - Process Diagrams PDFDocument3 pagesReturnables Processing (BDW) - Process Diagrams PDFNavjyot SinghviNo ratings yet
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) - Based Modular Integrated Construction Risk Management - Critical Survey and Future NeedsDocument15 pagesBuilding Information Modeling (BIM) - Based Modular Integrated Construction Risk Management - Critical Survey and Future NeedsChristopher StevenNo ratings yet
- Cold Chain ValidationDocument20 pagesCold Chain Validationvijay narayan100% (2)
- Certificate in Logistics ManagementDocument2 pagesCertificate in Logistics ManagementRifwan FadiansyahNo ratings yet
- DRP PlanningDocument30 pagesDRP PlanningRaja Sekhar RaaviNo ratings yet
- ESCS Corporate PresentationDocument37 pagesESCS Corporate PresentationDeathless LoveNo ratings yet
- Presentation Isa s95Document32 pagesPresentation Isa s95Do Van TuNo ratings yet
- Jump To Country: (Internal Link To Company) (External Link To Member)Document216 pagesJump To Country: (Internal Link To Company) (External Link To Member)kevinNo ratings yet
- Hero MotoCorp - Process CheatsheetDocument1 pageHero MotoCorp - Process CheatsheetShreshtha MittalNo ratings yet
- WMS+Location+Manager+User+Guide+ +WIP+DocDocument21 pagesWMS+Location+Manager+User+Guide+ +WIP+Docir4w4nNo ratings yet
- BatDocument14 pagesBatnakibosmanNo ratings yet
- Dissertation ReworkedDocument48 pagesDissertation ReworkedBelùr PrathyushNo ratings yet
- SurveyDocument8 pagesSurveyEdwardArribaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain and LogisticDocument7 pagesSupply Chain and LogisticJeryl GandecilaNo ratings yet
- CNH Industrial QPS 08018 Rev DDocument79 pagesCNH Industrial QPS 08018 Rev DCarlos PedrosoNo ratings yet
- Industry 40 Implications in Logistics An OverviewDocument9 pagesIndustry 40 Implications in Logistics An OverviewDimitri KaramazovNo ratings yet
- LGT - Outlook For Supply Chain and Logistics ManagementDocument4 pagesLGT - Outlook For Supply Chain and Logistics ManagementWency Bringino Alterado NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Snapdeal PDFDocument7 pagesSnapdeal PDFAMIT BANSALNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 6Document8 pagesLaboratory Exercise 6JH EscobarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting - Dayag 2015 - Chapter 13 - Problem III - IVDocument2 pagesAdvanced Accounting - Dayag 2015 - Chapter 13 - Problem III - IVJohn Carlos DoringoNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Desertation - JeetuDocument9 pagesSynopsis Desertation - JeetuJeetu RamNo ratings yet
- 0-3-2 E-KanbanDocument33 pages0-3-2 E-Kanbanprasetyo ilhamNo ratings yet
- Materials Manager Competency ModelDocument24 pagesMaterials Manager Competency ModelSaikumar SelaNo ratings yet
- Doctoral Dissertations in Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementDocument5 pagesDoctoral Dissertations in Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementWriteMyPaperForMeFastSingaporeNo ratings yet