Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ganglia of Head&Neck (ANATOMY)
Ganglia of Head&Neck (ANATOMY)
Uploaded by
shubhra.choudhary220 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views10 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views10 pagesGanglia of Head&Neck (ANATOMY)
Ganglia of Head&Neck (ANATOMY)
Uploaded by
shubhra.choudhary22Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
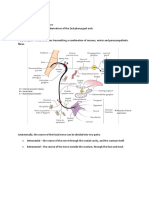
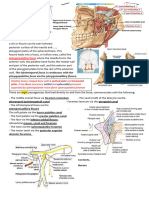
Parasympathetic Ganglia
of head and neck
Submandibular ganglion
Lies superficial to hyoglossus muscle in the
submandibular region.
Functionally it is connected to the facial nerve while
topographically it is related to the lingual br of
mandibular nerve.
Roots
Sensory – Lingual nerve
Sympathetic – derived from the nerve plexus around
the facial artery.
Secretomotor pathway – Superior salivatory nucleus
(pons) ---- Facial nerve ---- Geniculate ganglion
-----Chorda tympani nerve ----- Lingual nerve
-------- submandibular ganglion (fibres relay) ----
post ganglionic fibres supply the submandibular gland.
Otic ganglion
It lies deep to the trunk of the mandibular nerve in the
infratemporal fossa just distil to the foramen ovale.
Functionally related to 9th nerve but topographically
related to mandibular nerve.
Roots
Parasympathetic (secretomotor) – Preganglionic fibers
start in the inferior salivatory nucleus --9th nerve --
tympanic br --tympanic plexus --lesser petrosal
nerve --otic ganglion --- auriculotemporal nerve --
parotid gland.
Sympathetic (vasomotor) – Preganglionic fibers arise
from lateral horn of thoracic segments of spinal cord.
They relay in superior cervical sympathetic ganglion.
Postganglionic fibers form a plexus around the MMa
and reach the gland.
Sensory – auriculotemporal nerve.
Pterygopalatine ganglion
It is the largest parasympathetic peripheral ganglion.
It serves as a relay station for the secretomotor fibers
to the lacrimal gland and to the mucous glands of the
nose, paranasal sinuses, palate and pharynx.
Functionally connected to facial nerve but
topographically related to maxillary nerve (5th nerve).
Roots
Parasympathetic – The preganglionic fibers arising from
the lacrimatory nucleus in the pons pass thru the facial
nerve --- geniculate ganglion ---- greater petrosal
nerve ---nerve of pterygoid canal to reach the
pterygopalatine ganglion. The fibers relay in the
ganglion. The postganglionic fibers traverse thru the
maxillary nerve and its zygomatic branch to reach the
lacrimal br of ophthalmic nerve - lacrymal gl.
Sympathetic root – This is vasoconstrictive.
Postganglionic fibers arising from the superior cervical
sympathetic ganglion form a plexus around the internal
carotid artery --deep petrosal nerve --nerve of
pterygoid canal - pterygopalatine ganglion.
They pass thru thru ganglion without relay and then
follow the same path as the parasym. fibres to reach the
lacrimal gl.
Sensory root – Comes from maxillary nerve.
Ciliary ganglion
It is a peripheral parasympathetic ganglion placed in
the course of 3rd nerve.
It lies near the apex of the orbit between the optic
nerve and lateral rectus muscle.
Roots
Motor root – Preganglionic fibers begin in the edinger
westphal nucleus ---3rd nerve -----ciliary gangliion
------ postganglionic fibers pass thru the short ciliary
nerves and supply the sphincter pupillae and ciliaris
muscle.
Sensory root – comes from the nasociliary nerve (5 th
nerve) and contains sensory fibers for the eyeball.
Sympathetic root is a branch from the internal carotid
plexus. They pass thru the ganglion without relay and
thru the short ciliary branches supply the bloosd vessels
of eyeball and dilator pupillae muscle.
You might also like
- Cranial Nerves - Function and Dysfunctions, 3E (2010) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Document262 pagesCranial Nerves - Function and Dysfunctions, 3E (2010) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Alvaro RivCalle87% (15)
- MCQs On Complete DenturesDocument20 pagesMCQs On Complete Denturesمحمد العراقي87% (47)
- Tajweed Course - Articulation PointsDocument29 pagesTajweed Course - Articulation Pointsapi-19863350100% (2)
- Cranial Nerves WordDocument26 pagesCranial Nerves WordAMR WALIDNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic GangliaDocument16 pagesParasympathetic GangliaPriya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- PARASYMPATHETIC GANGLION in Head and NeckDocument53 pagesPARASYMPATHETIC GANGLION in Head and NeckDEEP SABNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve and Its Applied AspectsDocument198 pagesTrigeminal Nerve and Its Applied AspectsArun MamachanNo ratings yet
- 3.trigeminal NerveDocument81 pages3.trigeminal NerverajaniNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve Anatomy & Course in Middle EAR: Done by Thasni T U Roll No 102 Vignesh Sunil Roll No 105 7 SEMDocument60 pagesFacial Nerve Anatomy & Course in Middle EAR: Done by Thasni T U Roll No 102 Vignesh Sunil Roll No 105 7 SEM102 .Thasni T.U . 6th sem100% (1)
- Trigeminal NerveDocument126 pagesTrigeminal NerveAsha Praveena100% (4)
- Seminar - Ganglia of Head & Neck 27-05-2020Document52 pagesSeminar - Ganglia of Head & Neck 27-05-2020Chandra dimpleNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic GangliaDocument2 pagesParasympathetic GangliaPeterkingNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON Trigeminal Nerve & Applied Anatomy: DR - Neha Mds 1 YearDocument37 pagesSeminar ON Trigeminal Nerve & Applied Anatomy: DR - Neha Mds 1 YearMAYANK MITTALNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument48 pagesTrigeminal NervebhalaashokkumarNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve: Presented by DR Harees Shabir JR I Departmant of PedodonticsDocument77 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: Presented by DR Harees Shabir JR I Departmant of PedodonticsHarees ShabirNo ratings yet
- Describe The Different Types of Ganglia in The Head and NeckDocument2 pagesDescribe The Different Types of Ganglia in The Head and Neckmp658t952dNo ratings yet
- Pterygopalatine GanglionDocument15 pagesPterygopalatine Ganglionalphonsajoshy2020No ratings yet
- 9pterygopalatine FossaDocument9 pages9pterygopalatine FossaAaaNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument92 pagesTrigeminal Nervemounika50% (4)
- Trigeminal NerveDocument62 pagesTrigeminal NervevimalspiderNo ratings yet
- The Glossopharyngeal Nerve (N. Glossopharyngeus Ninth Nerve)Document15 pagesThe Glossopharyngeal Nerve (N. Glossopharyngeus Ninth Nerve)viorel79No ratings yet
- Facial Nerve.. EditedDocument61 pagesFacial Nerve.. EditedmfaisalzargarNo ratings yet
- Nervous IntermediusDocument1 pageNervous IntermediusGhaly AmirNo ratings yet
- 3 TrigeminalwordDocument26 pages3 TrigeminalwordrajaniNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal and Facial NerveDocument121 pagesTrigeminal and Facial NerveFadilaNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument74 pagesTrigeminal NerveSanat KhanapuriNo ratings yet
- The Facial Nerve NotesDocument5 pagesThe Facial Nerve NotesSimphiwe CebisaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic N.SDocument7 pagesAutonomic N.SAjigotto ubiq.No ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiDocument76 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiAlexAlxNo ratings yet
- Petrosal NervesDocument12 pagesPetrosal NervesDeepika RathnaNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve 2Document87 pagesFacial Nerve 2bhavyaNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument51 pagesFacial NerveSwijalNo ratings yet
- 12 Cranial NervesDocument13 pages12 Cranial Nervesapi-303065931No ratings yet
- 1 Nervous SystemDocument34 pages1 Nervous SystemMarius MarinNo ratings yet
- L3 Infratemporal RegionDocument29 pagesL3 Infratemporal RegionMohammad HilmiNo ratings yet
- The Wand - Atlas Nerve CompressedDocument23 pagesThe Wand - Atlas Nerve CompressedAmina AganovićNo ratings yet
- Lect11-Facial Nerve (CNVII)Document17 pagesLect11-Facial Nerve (CNVII)Nayela AkramNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument76 pagesTrigeminal Nerveanhca4519No ratings yet
- Sympathetic Pathway (Thoracolumnar Outflow)Document3 pagesSympathetic Pathway (Thoracolumnar Outflow)NellyWataNo ratings yet
- CR NervesDocument14 pagesCR Nervesapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Mandibular NerveDocument23 pagesHuman Anatomy Mandibular Nerveمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- The Trigeminal NerveDocument83 pagesThe Trigeminal NerveRicha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- The Facial NerveDocument6 pagesThe Facial NerveRahul Raj SNo ratings yet
- Frog Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesFrog Nervous SystemBeaNo ratings yet
- 8 Mandibular NerveDocument6 pages8 Mandibular NerveAaaNo ratings yet
- Reporters: Marawh, Qasem Bin Jahlan, Salem Samantha BallesterosDocument56 pagesReporters: Marawh, Qasem Bin Jahlan, Salem Samantha Ballesterosjamaica faith ramonNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument23 pagesFacial NerveAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Sep 06, 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan Sep 06, 2023Isha RaghuNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System WordDocument4 pagesPeripheral Nervous System WordJesi QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument128 pagesFacial NervevaneetNo ratings yet
- 5TH NERVE STDDocument36 pages5TH NERVE STDAayusha ChipaluNo ratings yet
- Brainstem by GasheguDocument47 pagesBrainstem by Gashegugatete samNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument4 pagesFacial NerveAppas SahaNo ratings yet
- Pterygd and OrbitDocument10 pagesPterygd and OrbitAmbg GhalyNo ratings yet
- Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyDocument5 pagesNeuroembryology and NeurohistologyCZARINA TUAZONNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve: BY Alvi Fatima Mds 1 Year Dept of Prevantive and Pediatric DentistryDocument69 pagesFacial Nerve: BY Alvi Fatima Mds 1 Year Dept of Prevantive and Pediatric DentistryHarees Shabir100% (1)
- Lec 9 AtrigeminalDocument2 pagesLec 9 AtrigeminalOodettaNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve: by Dr.P.PriyaDocument15 pagesFacial Nerve: by Dr.P.Priyapreeth_tNo ratings yet
- Sacral PlexusDocument61 pagesSacral Plexusbunnydhaliwal100% (3)
- ANAPHYSIODocument2 pagesANAPHYSIOtimmisarmientoNo ratings yet
- PBL 3 MDSC 2002 Upper or LowerDocument15 pagesPBL 3 MDSC 2002 Upper or LoweradaumedNo ratings yet
- 8 Brainstem 2Document20 pages8 Brainstem 2sjs6r8wwv9No ratings yet
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet
- Hearing and EquilibriumDocument30 pagesHearing and EquilibriumabdirizakNo ratings yet
- Hypo BrochureDocument2 pagesHypo Brochurea604No ratings yet
- Perilymph FistulaDocument4 pagesPerilymph FistulavieeveeNo ratings yet
- A Textbook of Orthodontics 3rd Ed. - T D FosterDocument351 pagesA Textbook of Orthodontics 3rd Ed. - T D FosterAjay Patel0% (1)
- Referred PainDocument18 pagesReferred Painapi-3710331No ratings yet
- MastoidectomyDocument110 pagesMastoidectomySangam AdhikariNo ratings yet
- OralMechanismExamKit 1Document11 pagesOralMechanismExamKit 1ABELIZ DURANT MUNIZNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Facial NerveDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Facial NerveMohammed Rahmath100% (1)
- 01 - Embryology and Introduction To The Nervous System - AMDDocument10 pages01 - Embryology and Introduction To The Nervous System - AMDLiza Elaine Ulep CawasNo ratings yet
- How To Draw A Rat - Easy Drawing ArtDocument14 pagesHow To Draw A Rat - Easy Drawing Artcount ossieNo ratings yet
- Fetal SkullDocument34 pagesFetal SkullNeelofur Ibran Ali86% (22)
- Regla de Los Cuatro para Las Lesiones de Tallo CerebralDocument4 pagesRegla de Los Cuatro para Las Lesiones de Tallo CerebralLeonardo PgNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Tanjong Rambutan 31250, Tanjong Rambutan Science Form 2Document5 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Tanjong Rambutan 31250, Tanjong Rambutan Science Form 2Jannah SulaimanNo ratings yet
- The Power of MindDocument5 pagesThe Power of MindAshley Pelayo Buduan100% (1)
- Script On AssessmentDocument14 pagesScript On AssessmentissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Muscle Deprogramming - An Orthodontist's Perspective: Batra Laxman Ra Angshuman B LlachDocument5 pagesMuscle Deprogramming - An Orthodontist's Perspective: Batra Laxman Ra Angshuman B LlachJulio Cesar AlvearNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Facial: ExpressionDocument34 pagesMuscles of Facial: ExpressionAhmed AlrashidNo ratings yet
- Cavum Orbita: Oleh: M. Dony HermawanDocument3 pagesCavum Orbita: Oleh: M. Dony HermawanMuhammad Dony HermawanNo ratings yet
- DC-TMD Examform International 2013-05-12Document2 pagesDC-TMD Examform International 2013-05-12sorcNo ratings yet
- Mandibular MovementDocument56 pagesMandibular MovementSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Ent AssessmentDocument23 pagesEnt AssessmentPdianghunNo ratings yet
- Salivary GlandsDocument28 pagesSalivary GlandsMohammed FaragNo ratings yet
- Rapid MaxillaryDocument24 pagesRapid MaxillaryDon George GeojanNo ratings yet
- Orthognathic Surgery Types and Indications: Mousa Ibrahim MousaDocument42 pagesOrthognathic Surgery Types and Indications: Mousa Ibrahim MousahashimalarwliaNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Care For Clients With Cognitive and Perceptual Disorder 1Document93 pagesModule 1: Care For Clients With Cognitive and Perceptual Disorder 1Woot RootNo ratings yet
- Language, Orientation, Memory, Attention Span and Calculation, LOCDocument7 pagesLanguage, Orientation, Memory, Attention Span and Calculation, LOCYessamin Paith RoderosNo ratings yet
- MENDONÇA, Et Al. 2006 The Girl From The Church of The Sacrament. A Case of Congenital Syphilis in XVIII Century LisbonDocument10 pagesMENDONÇA, Et Al. 2006 The Girl From The Church of The Sacrament. A Case of Congenital Syphilis in XVIII Century LisbonMercedesNo ratings yet