Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsPerformance Management
Performance Management
Uploaded by
ajithProject management lecture
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Ch13 Solutions To Book ExamplesDocument14 pagesCh13 Solutions To Book Examplesjjooeeyycc54% (13)
- Integrated Cost and Schedule Control in Project ManagementFrom EverandIntegrated Cost and Schedule Control in Project ManagementRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- EVM QuestionsDocument9 pagesEVM QuestionsBalaNo ratings yet
- A Risk Assessment ReportDocument8 pagesA Risk Assessment ReportHappi NessNo ratings yet
- Earned Value ManagementDocument3 pagesEarned Value ManagementSeenauth VeerajNo ratings yet
- 7.3.3 - Cost Variance AnalysisDocument6 pages7.3.3 - Cost Variance Analysisbigredmachine56No ratings yet
- Earned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)From EverandEarned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Practical Earned Value Analysis: 25 Project Indicators from 5 MeasurementsFrom EverandPractical Earned Value Analysis: 25 Project Indicators from 5 MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Sport Obermeyer Case EXECUTIVE SUMMARYDocument1 pageAnalysis of The Sport Obermeyer Case EXECUTIVE SUMMARYAmisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Income and Changes in Retained Earnings: - Chapter 12Document49 pagesIncome and Changes in Retained Earnings: - Chapter 12Moqadus SeharNo ratings yet
- Bankruptcy To BillionsDocument14 pagesBankruptcy To BillionsRoshin P.SNo ratings yet
- Ucp 600 & New Isbp 2013 - OctDocument4 pagesUcp 600 & New Isbp 2013 - OctReshmaShresthaNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management - The BasicsDocument18 pagesEarned Value Management - The BasicsGiles CoulsonNo ratings yet
- PM CH 15 Cost Control 21 2Document51 pagesPM CH 15 Cost Control 21 2unters yayNo ratings yet
- COST MANAGEMENT 642 - Paper 13Document31 pagesCOST MANAGEMENT 642 - Paper 13hasanNo ratings yet
- EvmDocument26 pagesEvmKaran DoshiNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii: Project Monitoring and ControlDocument75 pagesUnit - Iii: Project Monitoring and ControlyekoyesewNo ratings yet
- Project Cost ControlDocument15 pagesProject Cost ControlChuah Cheong JinNo ratings yet
- EVM Examples 26february2021Document38 pagesEVM Examples 26february2021edoNo ratings yet
- L4 May 2023 Cost & EVADocument46 pagesL4 May 2023 Cost & EVAAdam TaufikNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management: Instructor Hamza EjazDocument27 pagesEarned Value Management: Instructor Hamza EjazShaheena SanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Project Monitoring and ControlDocument30 pagesChapter 5 Project Monitoring and ControlYonas YGNo ratings yet
- Unit5 Chapter 9 Monitoring and ControlDocument55 pagesUnit5 Chapter 9 Monitoring and Controlyixem83781No ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis: Whatisit? Whydoineedit? Howdoidoit?Document44 pagesEarned Value Analysis: Whatisit? Whydoineedit? Howdoidoit?Nagendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Running Head: BCWP ANALYSIS 1Document6 pagesRunning Head: BCWP ANALYSIS 1tpitts25No ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis by John CornmanDocument17 pagesEarned Value Analysis by John CornmanElisa VadalàNo ratings yet
- 04 PM-Tricks - CostDocument27 pages04 PM-Tricks - CostMahmoud HagagNo ratings yet
- Progress Control - Earned Value: Prof. Omar El AnwarDocument11 pagesProgress Control - Earned Value: Prof. Omar El AnwarClic PointNo ratings yet
- Basics of EVM PartI-Eleanor HauptDocument0 pagesBasics of EVM PartI-Eleanor HauptCristhiams Jesus Mendez PintoNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Construction Management AND Research (PUNE) Project Cost Engineering Topic: Earned Value AnalysisDocument16 pagesNational Institute of Construction Management AND Research (PUNE) Project Cost Engineering Topic: Earned Value AnalysisJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis: Whatisit? Whydoineedit? Howdoidoit?Document44 pagesEarned Value Analysis: Whatisit? Whydoineedit? Howdoidoit?John MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sample PMP Earned Value QuestionsDocument9 pagesSample PMP Earned Value QuestionsHamza GhaffarNo ratings yet
- PMP-Cost MGMT - EVM Formaulae By-SkanchiDocument6 pagesPMP-Cost MGMT - EVM Formaulae By-Skanchiksreddy58No ratings yet
- 13 Cost ControlDocument21 pages13 Cost ControlMeQNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis Cheat Sheet 1650957417Document11 pagesEarned Value Analysis Cheat Sheet 1650957417sNo ratings yet
- PMP Exam Maths, Formulas & Equations - Sayed Mohsen-2020-04-03 00 - 50 - 54 PDFDocument48 pagesPMP Exam Maths, Formulas & Equations - Sayed Mohsen-2020-04-03 00 - 50 - 54 PDFMohamed SaaDNo ratings yet
- 15 Pengendalian Biaya 2Document15 pages15 Pengendalian Biaya 2FuadNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis-1Document15 pagesEarned Value Analysis-1Tayyiba ImranNo ratings yet
- Take-Home Quiz 2Document2 pagesTake-Home Quiz 2Deema sultanNo ratings yet
- EVMDocument26 pagesEVMmmprbjoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ControlDocument24 pagesChapter 4 - ControlArianNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Calculation: Scheduled To Be Performed by The Milestone DateDocument4 pagesEarned Value Calculation: Scheduled To Be Performed by The Milestone DatemallyavittalNo ratings yet
- Quiz Submissions - Quiz 4 - Chapter 7 (Cost Management and EVMS)Document4 pagesQuiz Submissions - Quiz 4 - Chapter 7 (Cost Management and EVMS)charlesNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management in P6Document23 pagesEarned Value Management in P6Unais1986No ratings yet
- CE131 - Lec 11 - Project Control - SolutionsDocument9 pagesCE131 - Lec 11 - Project Control - SolutionsNgoc TonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Project Evaluation and ControlDocument22 pagesChapter 8 Project Evaluation and ControlMỹ Mộc LinhNo ratings yet
- Project Control, SV, PV, and ACDocument63 pagesProject Control, SV, PV, and ACSita RamNo ratings yet
- Sample PMP Earned Value QuestionsDocument9 pagesSample PMP Earned Value QuestionsSajid ZebNo ratings yet
- Earned Value AnalysisDocument27 pagesEarned Value AnalysisMattiullahNo ratings yet
- 14 Earned Value AnalysisDocument17 pages14 Earned Value Analysisahmedrefaeeali1981No ratings yet
- CH 7 NewDocument26 pagesCH 7 Newjanahh.omNo ratings yet
- The Managerial Process Ch13Document14 pagesThe Managerial Process Ch13kristin14No ratings yet
- Do Not Sum Earned-Value-Based WBS-Element Estimates-at-CompletionDocument43 pagesDo Not Sum Earned-Value-Based WBS-Element Estimates-at-CompletionpirotteNo ratings yet
- Project Management - Earned Value Management - Primavera P6Document23 pagesProject Management - Earned Value Management - Primavera P6tohema100% (1)
- PAE AcFn621 Ch-5 Execution and MonitoringDocument45 pagesPAE AcFn621 Ch-5 Execution and MonitoringProf. Dr. Anbalagan ChinniahNo ratings yet
- Progress and Performance Measurement and EvaluationDocument26 pagesProgress and Performance Measurement and EvaluationdanishsayedNo ratings yet
- EVM - Basic FormulaDocument10 pagesEVM - Basic FormulaHuda AlShammariNo ratings yet
- Control CostDocument36 pagesControl CostSharjeel Humayun HassanNo ratings yet
- Cost Control: Cahyono Bintang Nurcahyo, ST, MTDocument33 pagesCost Control: Cahyono Bintang Nurcahyo, ST, MTFuadNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis Cheat SheetDocument11 pagesEarned Value Analysis Cheat SheetMeeraTharaMaayaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6a Earned Value ManagementDocument49 pagesTopic 6a Earned Value ManagementMohamad Zahir RazakNo ratings yet
- SC431 Lecture No.10 - Earned Value AnalysisDocument24 pagesSC431 Lecture No.10 - Earned Value AnalysisJoseph BaruhiyeNo ratings yet
- Basic Earned Value Management For Program ManagersDocument131 pagesBasic Earned Value Management For Program ManagersYoung-seok HwangNo ratings yet
- CPM-400D Calculating Estimates at Completion, Kratzert (1) - 2Document40 pagesCPM-400D Calculating Estimates at Completion, Kratzert (1) - 2NgôLanAnhNo ratings yet
- The 123s of ABC in SAP: Using SAP R/3 to Support Activity-Based CostingFrom EverandThe 123s of ABC in SAP: Using SAP R/3 to Support Activity-Based CostingNo ratings yet
- Project Audit Closure and OutsourcingDocument65 pagesProject Audit Closure and OutsourcingajithNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8, T1 2. Reducing Project Duration, Ch. 9, T1: Scheduling CostsDocument49 pagesCh. 8, T1 2. Reducing Project Duration, Ch. 9, T1: Scheduling CostsajithNo ratings yet
- Scheduling Resources and Costs: BITS PilaniDocument50 pagesScheduling Resources and Costs: BITS PilaniajithNo ratings yet
- BITS Pilani: Project ManagementDocument37 pagesBITS Pilani: Project ManagementajithNo ratings yet
- Business: Unit 6 Marketing StrategyDocument11 pagesBusiness: Unit 6 Marketing StrategyadriNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument39 pagesReportSumitNo ratings yet
- IMS International Standards Training Materials 2015 LatestDocument90 pagesIMS International Standards Training Materials 2015 LatestMahendran RajendranNo ratings yet
- NABH AdvantageDocument19 pagesNABH Advantagedr_vikasNo ratings yet
- Accenture Phygital Bank in A Year Infographic IndiaDocument1 pageAccenture Phygital Bank in A Year Infographic IndiaChetan GadiaNo ratings yet
- HRM Telenor RPRTDocument19 pagesHRM Telenor RPRTnoorirocks75% (4)
- Sailesh V Event Marketing ReportDocument27 pagesSailesh V Event Marketing Reportsailesh vasaNo ratings yet
- Italy Buying GuideDocument26 pagesItaly Buying GuideLeandro MarcattoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Integrity PetronasDocument61 pagesMechanical Integrity Petronasdefian100% (6)
- IIS263 - SAP Analytics Cloud With Focused Insights For SAP Solution ManagerDocument4 pagesIIS263 - SAP Analytics Cloud With Focused Insights For SAP Solution ManagerkiranNo ratings yet
- What Is Software QualityDocument26 pagesWhat Is Software Qualityahsan aliNo ratings yet
- Business Plan - EazypayDocument7 pagesBusiness Plan - EazypayBuchi MadukaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management : Gregory G. Dess and G. T. LumpkinDocument19 pagesStrategic Management : Gregory G. Dess and G. T. LumpkinJeramz QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Pizza HutDocument4 pagesPizza HutChieEnrileNo ratings yet
- RacDocument95 pagesRacJeffrey Rivera0% (1)
- Foreign Trade Statistics OF Bangladesh 2019-20: Volume-lIDocument164 pagesForeign Trade Statistics OF Bangladesh 2019-20: Volume-lITafsir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- 74609bos60479 FND cp2 U4Document20 pages74609bos60479 FND cp2 U4Filip JainNo ratings yet
- Commissionerate of Municipality (CMA), Tamil Nadu Circular About Tender PublicityDocument4 pagesCommissionerate of Municipality (CMA), Tamil Nadu Circular About Tender PublicitykayalonthewebNo ratings yet
- Retail Banking Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesRetail Banking Literature Reviewafmzsbnbobbgke100% (2)
- Corporate Growth Benchmarking in The Food IndustryDocument7 pagesCorporate Growth Benchmarking in The Food Industrytesfaye assefaNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument8 pagesSwot AnalysisRishma Jane ValenciaNo ratings yet
- SilversteinProperties EB5brochureDocument22 pagesSilversteinProperties EB5brochureEliot BrownNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard NpoDocument33 pagesAccounting Standard NpoArifAslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Customer FocusDocument55 pagesChapter 3 Customer FocusJennylyn RubioNo ratings yet
- The Communications Mix: What's The Difference Between The Marketing Communications Mix and The Marketing Mix?Document4 pagesThe Communications Mix: What's The Difference Between The Marketing Communications Mix and The Marketing Mix?miriam kuriaNo ratings yet
Performance Management
Performance Management
Uploaded by
ajith0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views30 pagesProject management lecture
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProject management lecture
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views30 pagesPerformance Management
Performance Management
Uploaded by
ajithProject management lecture
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 30
BITS Pilani
Pilani Campus
PROGRESS & PERFORMANCE
MANAGEMENT AND EVALUATION
CHAPTER NO 13 TEXTBOOK T1
NEED
• Control holds people accountable
• Prevents small problems from mushrooming into large
problems
• Keeps focused
• Competitive edge
• Effective control through proper information system
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
PROJECT MONITORING
INFORMATION SYSTEM
• Determining what data to be collected
• How, when and who will collect the data
• Data analysis
• Reporting current progress
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
DATA COLLECTION AND
ANALYSIS
• Actual activity duration
• Resource usage and rates
• Actual costs
• Compare :
– Planned Vs. Actual
– Scheduled Vs. Actual
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
• Data To Be Collected By
– Project Team Members
– Individual Cost Engineers
– Project Manager
• Sources
– Cash Flow
– Machine Hours
– Labor Hours
– Materials In Place
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Reports And Reporting
– Progress since last report
– Current status of project
• Schedule
• Cost
• Scope
– Cumulative trends
– Problems and issues since last report
• Action and resolution of earlier problems
• New variances and problems identified
• Corrective action planned
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
PROJECT CONTROL
PROCESS
• Setting the baseline plan
• Monitoring progress and performance
• Comparing Plan vs. Actual
• Taking actions
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
MONITORING TIME
PERFORMANCE
• Preparing Gantt Chart
– List the activities with duration
– Predecessor Relationship
– Critical Path
– Tracking Gantt Chart
• Progress
• Slippages
• Slack
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
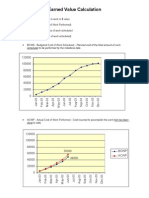
EARNED VALUE
COST/SCHEDULE SYSTEM
Time Phased Budget Baseline
Comparisons With Actual And Planned Schedule And Cost
EV: Earned Value (BCWP)
PV: Planned Value (BCWS)
AC: Actual Cost (ACWP)
CV: Cost Variance SV: Schedule Variance
BAC: Budgeted Cost at Completion
ETC: Estimated Cost to Complete Remaining Work
EAC: Estimated Cost at Completion
VAC: Cost Variance at Completion
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
COST VARIANCE CV = EV – AC
SCHEDULE VARIANCE SV = EV – PV
TIME VARIANCE TV = ST – AT
VAC = BAC - EAC
CV : IF NEGATIVE : OVERRUN
SV : IF NEGATIVE : BEHIND SCHEDULE
TV: DELAY IS NEGATIVE
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
INTEGRATED COST
SCHEDULE SYSTEM
Define The Work Using WBS
– Scope
– Work Progress
– Deliverables
– Organization Units
– Resources
– Budgets For Each Work Package
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
• Develop work and resource schedule
– Schedule resources to activities
– Time-phase work packages into network
• Develop time phased budget using work packages and
determine planned budgeted cost of the work scheduled
• At work package level, collect actual costs for the work
performed.
• Collect percent completion and compute budgeted cost
of work performed : earned value
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
TIME PHASED BUDGET
• To measure overall performance by using aggregate
performance measure called earned value
• To compare the actual and scheduled cost with planned
• Earned value is calculated by multiplying the estimated
percent physical completion of work for each task by the
planned cost for those tasks
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
WAYS TO CALCULATE
PERCENT COMPLETION
• The 50-50 estimate: fifty percent completion is assumed
when the task is begun and remaining fifty percent when
the work is complete
• The 0-100 percent rule: this rule allows the credit of work
until the task is complete
• Critical input use: this rule assigns task progress
according to the amount of critical input that has been
used
• The proportionality rule: this rule divides actual task time
to date by total scheduled task time to calculate percent
complete
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
VARIANCE ANALYSIS
• Comparing earned value with the expected schedule
value
• Comparing Earned Value With The Actual Costs
• CV = EV- AC If Negative, Overrun
• SV = EV – PV If Negative Behind Schedule
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
DEVELOPING A STATUS
REPORT
• Baseline Development
• Development Of Status Report
– Not Yet Started
– Finished
– In Process Or Partially Complete
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
PERFORMANCE INDEX
• CPI = EV / AC
• SPI = EV / PV
INDEX CPI SPI
>1.00 UNDER RUN AHEAD OF
SCHEDULE
=1.00 ON COST ON SCHEDULE
<1.00 OVER RUN BEHIND SCHEDULE
PROJECT PERCENT
COMPLETE INDEX
• Percent complete index PCIB = EV / BAC
• PCIB represents the work accomplished as percent of
the total budgeted dollars to date
• Percent complete index PCIC = AC / EAC
• PCIC represents percent complete in terms of actual
dollars spent to accomplish work to date and the actual
expected dollars for the completed project
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
FORECASTING FINAL
PROJECT COST
EAC = AC + ETC
ETC = WORK REMAINING / CPI
= (BAC – EV) / EV/AC
TCPI : TO COMPLETE PERFORMANCE INDEX (TCPI)
TCPI = (BAC – EV) / (BAC – AC)
It measures the amount of value each remaining dollar in
the budget must earn to stay within budget
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Problem no. 1
• A project to develop a country park has an actual cost in
month 17 of $350,000, A planned cost of $450,000, and
A value completed of $300,000. Find the cost and
schedule variances and the three indices.
• GIVEN : AC = 350,000 PV = 450,000
EV = 300,000
• COST VARIANCE = EV – AC
• CV = 300,000 – 350,000 = -50,000 OVERRUN
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
• SCHEDULE VARIANCE = EV – PV = 300,000 – 450,000
= -150,000 BEHIND SCHEDULE
• CPI = EV/ AC = 300,000/350,000 = 0.857
• SPI = EV / PV = 300,000 / 450,000 = 0.666
• CSI = CPI X SPI = 0.857 X 0.666 = 0.571
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
PROBLEM NO. 2
• A project to develop technology training seminars is 5
days behind schedule at day 65. It had a planned cost of
$735,000 for this point in time, but the actual cost is only
$550,000. Estimate the schedule and cost variances.
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
SOLUTION 2
GIVEN PV = 735,000 AC = 550,000 EV = 60/65 *
735,000 = 678,462
COST VARIANCE = EV – AC = 678,462 – 550,000 =
128,462 UNDERRUN
SCHEDULE VARIANCE = EV – PV = 678,462 – 735,000 =
- 56,538 BEHIND SCHEDULE
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
PROBLEM NO. 3
• For the following test marketing project at week 6,
calculate the cost schedule and time variances. Also
calculate the CPI, SPI, CSI, ETC AND EAC.
ACTIVITY PREDECE DURATI BUDGET ACTUAL %
SSOR ON COST COMPLE
TE
A - 2 300 400 100
B - 3 200 180 100
C A 2 250 300 100
D A 5 600 400 20
E B,C 4 400 200 20
SOLUTION 3
A PV 150 150
EV 150 150
B 100 100
100 100
C 125 125
125 125
D 300 300
300
E 200 200
200
TOTAL 250 150 525 125 200 0 300 200
: PV
CUM. 250 400 925 1050 1250 1250 1550 1750
AC 0 400 180 300 0 0
CUM. 0 400 580 880 880 880
EV 250 150 525 125 200 0
CUM. 250 400 925 1050 1250 1250
ON DAY 6
EV = 1250
PV = 1250
AC = 880
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
• COST VARIANCE : EV – AC = 1250 – 880 = 370
UNDERRUN
• SCHEDULE VARIANCE = EV – PV = 1250 – 1250 = 0
ON SCHEDULE
• CPI = EV/AC = 1250 / 880 = 1.42
• SPI = EV/PV = 1250 / 1250 = 1.00
• CSI = 1.42 X 1.00 = 1.42
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
• BAC = 1750 EV = 1250 CPI = 1.42
• ETC = (BAC – EV) / CPI = (1750 – 1250) / 1.42 = 352
• EAC = ETC + AC = 352 + 880 = 1232
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
You might also like
- Ch13 Solutions To Book ExamplesDocument14 pagesCh13 Solutions To Book Examplesjjooeeyycc54% (13)
- Integrated Cost and Schedule Control in Project ManagementFrom EverandIntegrated Cost and Schedule Control in Project ManagementRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- EVM QuestionsDocument9 pagesEVM QuestionsBalaNo ratings yet
- A Risk Assessment ReportDocument8 pagesA Risk Assessment ReportHappi NessNo ratings yet
- Earned Value ManagementDocument3 pagesEarned Value ManagementSeenauth VeerajNo ratings yet
- 7.3.3 - Cost Variance AnalysisDocument6 pages7.3.3 - Cost Variance Analysisbigredmachine56No ratings yet
- Earned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)From EverandEarned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Practical Earned Value Analysis: 25 Project Indicators from 5 MeasurementsFrom EverandPractical Earned Value Analysis: 25 Project Indicators from 5 MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Sport Obermeyer Case EXECUTIVE SUMMARYDocument1 pageAnalysis of The Sport Obermeyer Case EXECUTIVE SUMMARYAmisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Income and Changes in Retained Earnings: - Chapter 12Document49 pagesIncome and Changes in Retained Earnings: - Chapter 12Moqadus SeharNo ratings yet
- Bankruptcy To BillionsDocument14 pagesBankruptcy To BillionsRoshin P.SNo ratings yet
- Ucp 600 & New Isbp 2013 - OctDocument4 pagesUcp 600 & New Isbp 2013 - OctReshmaShresthaNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management - The BasicsDocument18 pagesEarned Value Management - The BasicsGiles CoulsonNo ratings yet
- PM CH 15 Cost Control 21 2Document51 pagesPM CH 15 Cost Control 21 2unters yayNo ratings yet
- COST MANAGEMENT 642 - Paper 13Document31 pagesCOST MANAGEMENT 642 - Paper 13hasanNo ratings yet
- EvmDocument26 pagesEvmKaran DoshiNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii: Project Monitoring and ControlDocument75 pagesUnit - Iii: Project Monitoring and ControlyekoyesewNo ratings yet
- Project Cost ControlDocument15 pagesProject Cost ControlChuah Cheong JinNo ratings yet
- EVM Examples 26february2021Document38 pagesEVM Examples 26february2021edoNo ratings yet
- L4 May 2023 Cost & EVADocument46 pagesL4 May 2023 Cost & EVAAdam TaufikNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management: Instructor Hamza EjazDocument27 pagesEarned Value Management: Instructor Hamza EjazShaheena SanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Project Monitoring and ControlDocument30 pagesChapter 5 Project Monitoring and ControlYonas YGNo ratings yet
- Unit5 Chapter 9 Monitoring and ControlDocument55 pagesUnit5 Chapter 9 Monitoring and Controlyixem83781No ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis: Whatisit? Whydoineedit? Howdoidoit?Document44 pagesEarned Value Analysis: Whatisit? Whydoineedit? Howdoidoit?Nagendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Running Head: BCWP ANALYSIS 1Document6 pagesRunning Head: BCWP ANALYSIS 1tpitts25No ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis by John CornmanDocument17 pagesEarned Value Analysis by John CornmanElisa VadalàNo ratings yet
- 04 PM-Tricks - CostDocument27 pages04 PM-Tricks - CostMahmoud HagagNo ratings yet
- Progress Control - Earned Value: Prof. Omar El AnwarDocument11 pagesProgress Control - Earned Value: Prof. Omar El AnwarClic PointNo ratings yet
- Basics of EVM PartI-Eleanor HauptDocument0 pagesBasics of EVM PartI-Eleanor HauptCristhiams Jesus Mendez PintoNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Construction Management AND Research (PUNE) Project Cost Engineering Topic: Earned Value AnalysisDocument16 pagesNational Institute of Construction Management AND Research (PUNE) Project Cost Engineering Topic: Earned Value AnalysisJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis: Whatisit? Whydoineedit? Howdoidoit?Document44 pagesEarned Value Analysis: Whatisit? Whydoineedit? Howdoidoit?John MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sample PMP Earned Value QuestionsDocument9 pagesSample PMP Earned Value QuestionsHamza GhaffarNo ratings yet
- PMP-Cost MGMT - EVM Formaulae By-SkanchiDocument6 pagesPMP-Cost MGMT - EVM Formaulae By-Skanchiksreddy58No ratings yet
- 13 Cost ControlDocument21 pages13 Cost ControlMeQNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis Cheat Sheet 1650957417Document11 pagesEarned Value Analysis Cheat Sheet 1650957417sNo ratings yet
- PMP Exam Maths, Formulas & Equations - Sayed Mohsen-2020-04-03 00 - 50 - 54 PDFDocument48 pagesPMP Exam Maths, Formulas & Equations - Sayed Mohsen-2020-04-03 00 - 50 - 54 PDFMohamed SaaDNo ratings yet
- 15 Pengendalian Biaya 2Document15 pages15 Pengendalian Biaya 2FuadNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis-1Document15 pagesEarned Value Analysis-1Tayyiba ImranNo ratings yet
- Take-Home Quiz 2Document2 pagesTake-Home Quiz 2Deema sultanNo ratings yet
- EVMDocument26 pagesEVMmmprbjoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ControlDocument24 pagesChapter 4 - ControlArianNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Calculation: Scheduled To Be Performed by The Milestone DateDocument4 pagesEarned Value Calculation: Scheduled To Be Performed by The Milestone DatemallyavittalNo ratings yet
- Quiz Submissions - Quiz 4 - Chapter 7 (Cost Management and EVMS)Document4 pagesQuiz Submissions - Quiz 4 - Chapter 7 (Cost Management and EVMS)charlesNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management in P6Document23 pagesEarned Value Management in P6Unais1986No ratings yet
- CE131 - Lec 11 - Project Control - SolutionsDocument9 pagesCE131 - Lec 11 - Project Control - SolutionsNgoc TonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Project Evaluation and ControlDocument22 pagesChapter 8 Project Evaluation and ControlMỹ Mộc LinhNo ratings yet
- Project Control, SV, PV, and ACDocument63 pagesProject Control, SV, PV, and ACSita RamNo ratings yet
- Sample PMP Earned Value QuestionsDocument9 pagesSample PMP Earned Value QuestionsSajid ZebNo ratings yet
- Earned Value AnalysisDocument27 pagesEarned Value AnalysisMattiullahNo ratings yet
- 14 Earned Value AnalysisDocument17 pages14 Earned Value Analysisahmedrefaeeali1981No ratings yet
- CH 7 NewDocument26 pagesCH 7 Newjanahh.omNo ratings yet
- The Managerial Process Ch13Document14 pagesThe Managerial Process Ch13kristin14No ratings yet
- Do Not Sum Earned-Value-Based WBS-Element Estimates-at-CompletionDocument43 pagesDo Not Sum Earned-Value-Based WBS-Element Estimates-at-CompletionpirotteNo ratings yet
- Project Management - Earned Value Management - Primavera P6Document23 pagesProject Management - Earned Value Management - Primavera P6tohema100% (1)
- PAE AcFn621 Ch-5 Execution and MonitoringDocument45 pagesPAE AcFn621 Ch-5 Execution and MonitoringProf. Dr. Anbalagan ChinniahNo ratings yet
- Progress and Performance Measurement and EvaluationDocument26 pagesProgress and Performance Measurement and EvaluationdanishsayedNo ratings yet
- EVM - Basic FormulaDocument10 pagesEVM - Basic FormulaHuda AlShammariNo ratings yet
- Control CostDocument36 pagesControl CostSharjeel Humayun HassanNo ratings yet
- Cost Control: Cahyono Bintang Nurcahyo, ST, MTDocument33 pagesCost Control: Cahyono Bintang Nurcahyo, ST, MTFuadNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Analysis Cheat SheetDocument11 pagesEarned Value Analysis Cheat SheetMeeraTharaMaayaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6a Earned Value ManagementDocument49 pagesTopic 6a Earned Value ManagementMohamad Zahir RazakNo ratings yet
- SC431 Lecture No.10 - Earned Value AnalysisDocument24 pagesSC431 Lecture No.10 - Earned Value AnalysisJoseph BaruhiyeNo ratings yet
- Basic Earned Value Management For Program ManagersDocument131 pagesBasic Earned Value Management For Program ManagersYoung-seok HwangNo ratings yet
- CPM-400D Calculating Estimates at Completion, Kratzert (1) - 2Document40 pagesCPM-400D Calculating Estimates at Completion, Kratzert (1) - 2NgôLanAnhNo ratings yet
- The 123s of ABC in SAP: Using SAP R/3 to Support Activity-Based CostingFrom EverandThe 123s of ABC in SAP: Using SAP R/3 to Support Activity-Based CostingNo ratings yet
- Project Audit Closure and OutsourcingDocument65 pagesProject Audit Closure and OutsourcingajithNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8, T1 2. Reducing Project Duration, Ch. 9, T1: Scheduling CostsDocument49 pagesCh. 8, T1 2. Reducing Project Duration, Ch. 9, T1: Scheduling CostsajithNo ratings yet
- Scheduling Resources and Costs: BITS PilaniDocument50 pagesScheduling Resources and Costs: BITS PilaniajithNo ratings yet
- BITS Pilani: Project ManagementDocument37 pagesBITS Pilani: Project ManagementajithNo ratings yet
- Business: Unit 6 Marketing StrategyDocument11 pagesBusiness: Unit 6 Marketing StrategyadriNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument39 pagesReportSumitNo ratings yet
- IMS International Standards Training Materials 2015 LatestDocument90 pagesIMS International Standards Training Materials 2015 LatestMahendran RajendranNo ratings yet
- NABH AdvantageDocument19 pagesNABH Advantagedr_vikasNo ratings yet
- Accenture Phygital Bank in A Year Infographic IndiaDocument1 pageAccenture Phygital Bank in A Year Infographic IndiaChetan GadiaNo ratings yet
- HRM Telenor RPRTDocument19 pagesHRM Telenor RPRTnoorirocks75% (4)
- Sailesh V Event Marketing ReportDocument27 pagesSailesh V Event Marketing Reportsailesh vasaNo ratings yet
- Italy Buying GuideDocument26 pagesItaly Buying GuideLeandro MarcattoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Integrity PetronasDocument61 pagesMechanical Integrity Petronasdefian100% (6)
- IIS263 - SAP Analytics Cloud With Focused Insights For SAP Solution ManagerDocument4 pagesIIS263 - SAP Analytics Cloud With Focused Insights For SAP Solution ManagerkiranNo ratings yet
- What Is Software QualityDocument26 pagesWhat Is Software Qualityahsan aliNo ratings yet
- Business Plan - EazypayDocument7 pagesBusiness Plan - EazypayBuchi MadukaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management : Gregory G. Dess and G. T. LumpkinDocument19 pagesStrategic Management : Gregory G. Dess and G. T. LumpkinJeramz QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Pizza HutDocument4 pagesPizza HutChieEnrileNo ratings yet
- RacDocument95 pagesRacJeffrey Rivera0% (1)
- Foreign Trade Statistics OF Bangladesh 2019-20: Volume-lIDocument164 pagesForeign Trade Statistics OF Bangladesh 2019-20: Volume-lITafsir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- 74609bos60479 FND cp2 U4Document20 pages74609bos60479 FND cp2 U4Filip JainNo ratings yet
- Commissionerate of Municipality (CMA), Tamil Nadu Circular About Tender PublicityDocument4 pagesCommissionerate of Municipality (CMA), Tamil Nadu Circular About Tender PublicitykayalonthewebNo ratings yet
- Retail Banking Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesRetail Banking Literature Reviewafmzsbnbobbgke100% (2)
- Corporate Growth Benchmarking in The Food IndustryDocument7 pagesCorporate Growth Benchmarking in The Food Industrytesfaye assefaNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument8 pagesSwot AnalysisRishma Jane ValenciaNo ratings yet
- SilversteinProperties EB5brochureDocument22 pagesSilversteinProperties EB5brochureEliot BrownNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard NpoDocument33 pagesAccounting Standard NpoArifAslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Customer FocusDocument55 pagesChapter 3 Customer FocusJennylyn RubioNo ratings yet
- The Communications Mix: What's The Difference Between The Marketing Communications Mix and The Marketing Mix?Document4 pagesThe Communications Mix: What's The Difference Between The Marketing Communications Mix and The Marketing Mix?miriam kuriaNo ratings yet