Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsElias Fatima Yushra Gout and Hyperthyroidism
Elias Fatima Yushra Gout and Hyperthyroidism
Uploaded by
Jason AbudaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Governor's Study Group On Efficiency in State GovernmentDocument12 pagesGovernor's Study Group On Efficiency in State GovernmentMike Cason67% (3)
- Lecture On Metabolic DisordersDocument56 pagesLecture On Metabolic DisordersRoselily Flores CoquillaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisorderDocument20 pagesThyroid DisorderNadun MethwadaneNo ratings yet
- Hypothyriodism - Medicose Nursing AcademyDocument15 pagesHypothyriodism - Medicose Nursing AcademyRawal Rafiq LeghariNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Disorders General LectureDocument34 pagesEndocrinology Disorders General LecturejawadNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders 22 April 2019Document105 pagesThyroid Disorders 22 April 2019jialeongNo ratings yet
- SymptomsDocument4 pagesSymptomsannaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders: Aprilia Indra K, M.BiotechDocument36 pagesEndocrine Disorders: Aprilia Indra K, M.BiotechFifiana AngeliaNo ratings yet
- Week 16 EndocrineDocument55 pagesWeek 16 EndocrineEditha LucasNo ratings yet
- SymptomsDocument4 pagesSymptomsannaNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Endocrine Disorders PPTDocument36 pages7.3 Endocrine Disorders PPTLorelie AsisNo ratings yet
- 2.endocrine (Pt.2)Document50 pages2.endocrine (Pt.2)عمر حليم omar haleemNo ratings yet
- Overview of Endocrine SystemDocument29 pagesOverview of Endocrine Systemufjn4nfogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Clients With Tyroid DisordersDocument40 pagesNursing Management of Clients With Tyroid DisordersRIZKINo ratings yet
- Thyroid EmergenciesDocument22 pagesThyroid EmergenciesAvian CamelotNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorder: Aishah Idham Aishah MunirahDocument47 pagesThyroid Disorder: Aishah Idham Aishah Munirahmunii28No ratings yet
- Hyper and Hypothyroidism Endemic (Iodine-Deficient) Goiter Thyroid Cancer The Parathyroid Glands Hyperparathyroidism Hypoparathyroidism EtcDocument25 pagesHyper and Hypothyroidism Endemic (Iodine-Deficient) Goiter Thyroid Cancer The Parathyroid Glands Hyperparathyroidism Hypoparathyroidism EtcTaate MohammedNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine DisordersDocument55 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine Disorderseliza marie luisNo ratings yet
- THYROID YunitaDocument81 pagesTHYROID YunitaPandu KusumawardhanyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument7 pagesThyroid DisordersRohitNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders: Presented By:-Drashti Chudasama Guided By:-Dr. Milan SirDocument44 pagesThyroid Disorders: Presented By:-Drashti Chudasama Guided By:-Dr. Milan SirDrashti ChudasamaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland: Dr. Humairah Medina Liza Lubis, M. Ked (PA), SP - PADocument138 pagesThyroid Gland: Dr. Humairah Medina Liza Lubis, M. Ked (PA), SP - PARizky anandaNo ratings yet
- KP 3 Aktivitas Fisik Dan Gaya Hidup Sehat - Prof. Dr. Dr. Gusbakti SP - KKLPDocument27 pagesKP 3 Aktivitas Fisik Dan Gaya Hidup Sehat - Prof. Dr. Dr. Gusbakti SP - KKLPacalNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Muscular-Skeletal System: Unit - 4Document20 pagesDisorders of Muscular-Skeletal System: Unit - 4ArenPrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders: Hyperthyroidism HypothyroidismDocument66 pagesThyroid Disorders: Hyperthyroidism HypothyroidismGabz GabbyNo ratings yet
- ThyrotoxicosisDocument42 pagesThyrotoxicosisShaw Khan100% (7)
- What Is Adrenal InsufficiencyDocument17 pagesWhat Is Adrenal InsufficiencygammuacNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine Systyem NDocument93 pagesThe Endocrine Systyem NMuh YaminNo ratings yet
- Prac Theme 2.5Document182 pagesPrac Theme 2.5alkalicharanNo ratings yet
- Pathologic Conditios of Endocrine Disorder.Document42 pagesPathologic Conditios of Endocrine Disorder.ramoli1988No ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism Vs HyperthyroidismDocument23 pagesHyperthyroidism Vs HyperthyroidismElla Marie CruzadaNo ratings yet
- Archivo en Ingles-Patologias TiroideasDocument4 pagesArchivo en Ingles-Patologias Tiroideasesther avilaNo ratings yet
- Standar Asuhan Keperawatan Diabetes Mellitus: PresentationDocument39 pagesStandar Asuhan Keperawatan Diabetes Mellitus: PresentationpuspitaNo ratings yet
- Caring For Patients With Cardiac Disorders (OUTLINE)Document55 pagesCaring For Patients With Cardiac Disorders (OUTLINE)JamNo ratings yet
- PDF 2Document23 pagesPDF 2Vahid KhaveNo ratings yet
- Geriatrics...... DR Mazhar (03066980980)Document44 pagesGeriatrics...... DR Mazhar (03066980980)azamneha341No ratings yet
- HypercalcemiaDocument11 pagesHypercalcemiaShizuka Marycris Amane100% (1)
- Thyroid DisordersDocument66 pagesThyroid DisordersJOY SANDHYA JOSEPH (RA2123003011002)No ratings yet
- 2017 A3 What Can Acupuncture Help WithDocument2 pages2017 A3 What Can Acupuncture Help WithmayxzineNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Gout: by JuhairinaDocument39 pagesNutrition For Gout: by Juhairinadesy100% (1)
- Below The Knee AmputationDocument76 pagesBelow The Knee AmputationDarell M. Book50% (2)
- Tuto Patho Endo 1Document2 pagesTuto Patho Endo 1SIVAJOTHY A/P SIVALINGAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Renal DisordersSDocument29 pagesRenal DisordersSpastrokateNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Diagnostic Text and Some DiseasesDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Diagnostic Text and Some Diseasesevangelo22656100% (1)
- Thyroid DisorderDocument16 pagesThyroid DisorderfahadNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Emergencies: Heidi Chamberlain Shea, MDDocument32 pagesThyroid Emergencies: Heidi Chamberlain Shea, MDAstrini Retno PermatasariNo ratings yet
- Im DkaDocument16 pagesIm DkaTrisNo ratings yet
- Definition of AtherosclerosisDocument9 pagesDefinition of AtherosclerosischiabixuanNo ratings yet
- Physio Psych Module 5Document73 pagesPhysio Psych Module 5Sonal ChandraNo ratings yet
- Medical Therapy in GoiterDocument43 pagesMedical Therapy in GoiterIka Niswatul ChamidahNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism and HyperthyroidismDocument39 pagesHypothyroidism and HyperthyroidismnatekumandraNo ratings yet
- Thyroid 32Document19 pagesThyroid 32Srinivas SrinuNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Disease of HeartDocument34 pagesInflammatory Disease of HeartLoma Waghmare (Jadhav)No ratings yet
- Gynecologic ProblemsDocument76 pagesGynecologic Problemsairahibrahim23No ratings yet
- BEST PWP! InjuryManagementDocument39 pagesBEST PWP! InjuryManagementAdilene Manzo LeyvaNo ratings yet
- Science Group ReportDocument14 pagesScience Group ReportCzedhryx Cody CamuyagNo ratings yet
- Patients With Adrenal DisordersDocument17 pagesPatients With Adrenal DisordersTsarina Diana TanNo ratings yet
- GeriatricsDocument44 pagesGeriatricsfashion4hub4No ratings yet
- Struma Nodusa: Pembimbing: Dr. Rizapahlevi., M.Si., SP.BDocument45 pagesStruma Nodusa: Pembimbing: Dr. Rizapahlevi., M.Si., SP.BAndre Pradnyana100% (1)
- Adult Health NursingDocument16 pagesAdult Health NursingKomal Ramzan100% (1)
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractapi-3747282No ratings yet
- Most Important Terms & Conditions: Schedule of ChargesDocument18 pagesMost Important Terms & Conditions: Schedule of ChargesVINAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Local Plans FinalDocument21 pagesLocal Plans FinalManuel CassarNo ratings yet
- Visual Examination ProcedureDocument23 pagesVisual Examination ProcedureEdAlmNo ratings yet
- AGBS Ingles 2023Document15 pagesAGBS Ingles 20239fk72y9xy4No ratings yet
- Surgery III MCQS 2023Document4 pagesSurgery III MCQS 2023mariam100% (1)
- Spandan HR ManualDocument46 pagesSpandan HR ManualBotanic Hair Oil100% (1)
- Waste Water - Coke PlantDocument13 pagesWaste Water - Coke PlantSejla Becirovic Cehajic100% (1)
- OOP SE-203: Submitted By: - ANUJ 2K20/SE/21 - Anurag Munshi 2K20/Se/25Document9 pagesOOP SE-203: Submitted By: - ANUJ 2K20/SE/21 - Anurag Munshi 2K20/Se/25Anurag Munshi 25No ratings yet
- Release NotesDocument14 pagesRelease NotesJonathan RodríguezNo ratings yet
- 01section 1 Invitation For TenderersDocument2 pages01section 1 Invitation For TenderersFeteneNo ratings yet
- Kipor KDE Silent GeneratorDocument4 pagesKipor KDE Silent GeneratorbacNo ratings yet
- The Daily Tar Heel For April 10, 2012Document8 pagesThe Daily Tar Heel For April 10, 2012The Daily Tar HeelNo ratings yet
- Poker Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesPoker Cheat Sheet: by ViamaolpNo ratings yet
- Atb164 Re4r01a, R4a-El Nissan ...... Planetary FailureDocument4 pagesAtb164 Re4r01a, R4a-El Nissan ...... Planetary FailureAleNo ratings yet
- 220 Transition Cement SDSDocument9 pages220 Transition Cement SDSKevin MaciasNo ratings yet
- Memory Structures of An ABAP Program and FunctionsDocument1 pageMemory Structures of An ABAP Program and FunctionsardaNo ratings yet
- Block Brute Force Attack in Mikrotik RouterDocument1 pageBlock Brute Force Attack in Mikrotik RouterPedro HernandezNo ratings yet
- Written Exam-Guleng, Adrian AngelicoDocument21 pagesWritten Exam-Guleng, Adrian AngelicoAdrian Esico GulengNo ratings yet
- TP MicroprocessorDocument10 pagesTP MicroprocessorAnshuman Swaroop DasNo ratings yet
- Basic Floor Plans SolutionDocument9 pagesBasic Floor Plans SolutionAlice KrodeNo ratings yet
- EMT Refresher FlyerDocument2 pagesEMT Refresher FlyerBillR.YoungNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument11 pagesTransmission LinesAnirban Z100% (1)
- Augmented Seventh Chord - WikipediaDocument3 pagesAugmented Seventh Chord - WikipediaAla2 PugaciovaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 2 QuestionsPham Thi Hong ThuyNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Civil Engineering and ArchitectureDocument7 pagesDifference Between Civil Engineering and ArchitectureLin ZawNo ratings yet
- APRO Banking Gateway For Oracle Financials CloudDocument2 pagesAPRO Banking Gateway For Oracle Financials Cloudsohaibmuzaffar007No ratings yet
- Solid Pad Mount Switchgear - 150123 V2.0Document8 pagesSolid Pad Mount Switchgear - 150123 V2.0Edwin Quispe50% (2)
- Extrusive Intrusive: What Are Igneous Rocks?Document6 pagesExtrusive Intrusive: What Are Igneous Rocks?Edna BernabeNo ratings yet
Elias Fatima Yushra Gout and Hyperthyroidism
Elias Fatima Yushra Gout and Hyperthyroidism
Uploaded by
Jason Abuda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views19 pagesOriginal Title
Elias Fatima Yushra Gout and Hyperthyroidism (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views19 pagesElias Fatima Yushra Gout and Hyperthyroidism
Elias Fatima Yushra Gout and Hyperthyroidism
Uploaded by
Jason AbudaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
Gout
Presented by: Fatima Yushra I. Elias
What is Gout?
Gout is a common and complex
form of arthritis that can affect anyone.
It's characterized by sudden, severe
attacks of pain, swelling, redness and
tenderness in one or more joints, most
often in the big toe.
Pathophysiology
• Hyperuricemia
• Urate Crystal Deposition
• Inflammation
Risk Factor
Gout occurs when urate crystals
accumulate in your joint, causing the
inflammation and intense pain of a gout
attack. Urate crystals can form when you
have high levels of uric acid in your
blood. Your body produces uric acid
when it breaks down purines —
substances that are found naturally in
your body.
Causes
• Diet
• Weight
• Medical conditions
• Certain medications
• Family history of gout
• Age and sex
• Recent surgery or trauma
Diagnosis
• Joint fluid test
• Blood test
• X-ray imaging
• Ultrasound
• Dual-energy computerized tomography
(DECT)
Signs And Symptoms
• Intense joint pain
• Lingering discomfort
• Inflammation and redness
• Limited range of motion
Pharmacologic Treatment
Medications to treat gout attacks
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
• Colchicine
• Corticosteroids
Medications that Medications that
improve uric acid block uric acid
removal production
Non-Pharmacologic Treatment
• Choose healthier beverages
• Avoid foods high in purines
• Exercise regularly and lose weight
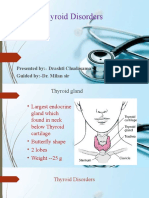
Hyperthyroidism
Presented by: Fatima Yushra I. Elias
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is a common
thyroid disorder with multiple underlying
etiologies. This disease is characterized by
excess thyroid hormone production.
Hyperthyroidism can be overt or
subclinical.
Pathophysiology
• Graves Disease
• Toxic Multinodular Goiter
• Toxic Adenoma
• Iodine-Induced Hyperthyroidism
(Jod-Basedow Phenomenon)
• Amiodarone-Induced
Thyrotoxicosis
• Thyroiditis
Risk Factor
• Graves' disease
• Overactive thyroid nodules
• Thyroiditis
Causes
• Genetics
• A personal history of certain
chronic illnesses
• A recent pregnancy
Diagnosis
• Medical history and physical exam
• Blood test
• Radioiodine scan and uptake test
• Thyroid ultrasound
Signs And Symptoms
• Losing weight without trying. • Changes in bowel patterns, especially more-
frequent bowel movements.
• Fast heartbeat, a condition called tachycardia.
• Enlarged thyroid gland, sometimes called a goiter,
• Irregular heartbeat, also called arrhythmia.
which may appear as a swelling at the base of the
• Pounding of the heart, sometimes called heart neck.
palpitations. • Tiredness.
• Increased hunger.
• Muscle weakness.
• Nervousness, anxiety and irritability.
• Sleep problems.
• Tremor
• Warm, moist skin.
• Sweating.
• Thinning skin.
• Changes in menstrual cycles.
• Fine, brittle hair.
• Increased sensitivity to heat.
Pharmacologic Treatment
• Anti-thyroid medications
• Beta-blockers
• Radioactive iodine therapy
• Surgery
Non-Pharmacologic Treatment
• Dietary changes
• Stress management
• Exercise
• Support groups
You might also like
- Governor's Study Group On Efficiency in State GovernmentDocument12 pagesGovernor's Study Group On Efficiency in State GovernmentMike Cason67% (3)
- Lecture On Metabolic DisordersDocument56 pagesLecture On Metabolic DisordersRoselily Flores CoquillaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisorderDocument20 pagesThyroid DisorderNadun MethwadaneNo ratings yet
- Hypothyriodism - Medicose Nursing AcademyDocument15 pagesHypothyriodism - Medicose Nursing AcademyRawal Rafiq LeghariNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Disorders General LectureDocument34 pagesEndocrinology Disorders General LecturejawadNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders 22 April 2019Document105 pagesThyroid Disorders 22 April 2019jialeongNo ratings yet
- SymptomsDocument4 pagesSymptomsannaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders: Aprilia Indra K, M.BiotechDocument36 pagesEndocrine Disorders: Aprilia Indra K, M.BiotechFifiana AngeliaNo ratings yet
- Week 16 EndocrineDocument55 pagesWeek 16 EndocrineEditha LucasNo ratings yet
- SymptomsDocument4 pagesSymptomsannaNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Endocrine Disorders PPTDocument36 pages7.3 Endocrine Disorders PPTLorelie AsisNo ratings yet
- 2.endocrine (Pt.2)Document50 pages2.endocrine (Pt.2)عمر حليم omar haleemNo ratings yet
- Overview of Endocrine SystemDocument29 pagesOverview of Endocrine Systemufjn4nfogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Clients With Tyroid DisordersDocument40 pagesNursing Management of Clients With Tyroid DisordersRIZKINo ratings yet
- Thyroid EmergenciesDocument22 pagesThyroid EmergenciesAvian CamelotNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorder: Aishah Idham Aishah MunirahDocument47 pagesThyroid Disorder: Aishah Idham Aishah Munirahmunii28No ratings yet
- Hyper and Hypothyroidism Endemic (Iodine-Deficient) Goiter Thyroid Cancer The Parathyroid Glands Hyperparathyroidism Hypoparathyroidism EtcDocument25 pagesHyper and Hypothyroidism Endemic (Iodine-Deficient) Goiter Thyroid Cancer The Parathyroid Glands Hyperparathyroidism Hypoparathyroidism EtcTaate MohammedNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine DisordersDocument55 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine Disorderseliza marie luisNo ratings yet
- THYROID YunitaDocument81 pagesTHYROID YunitaPandu KusumawardhanyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument7 pagesThyroid DisordersRohitNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders: Presented By:-Drashti Chudasama Guided By:-Dr. Milan SirDocument44 pagesThyroid Disorders: Presented By:-Drashti Chudasama Guided By:-Dr. Milan SirDrashti ChudasamaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland: Dr. Humairah Medina Liza Lubis, M. Ked (PA), SP - PADocument138 pagesThyroid Gland: Dr. Humairah Medina Liza Lubis, M. Ked (PA), SP - PARizky anandaNo ratings yet
- KP 3 Aktivitas Fisik Dan Gaya Hidup Sehat - Prof. Dr. Dr. Gusbakti SP - KKLPDocument27 pagesKP 3 Aktivitas Fisik Dan Gaya Hidup Sehat - Prof. Dr. Dr. Gusbakti SP - KKLPacalNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Muscular-Skeletal System: Unit - 4Document20 pagesDisorders of Muscular-Skeletal System: Unit - 4ArenPrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders: Hyperthyroidism HypothyroidismDocument66 pagesThyroid Disorders: Hyperthyroidism HypothyroidismGabz GabbyNo ratings yet
- ThyrotoxicosisDocument42 pagesThyrotoxicosisShaw Khan100% (7)
- What Is Adrenal InsufficiencyDocument17 pagesWhat Is Adrenal InsufficiencygammuacNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine Systyem NDocument93 pagesThe Endocrine Systyem NMuh YaminNo ratings yet
- Prac Theme 2.5Document182 pagesPrac Theme 2.5alkalicharanNo ratings yet
- Pathologic Conditios of Endocrine Disorder.Document42 pagesPathologic Conditios of Endocrine Disorder.ramoli1988No ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism Vs HyperthyroidismDocument23 pagesHyperthyroidism Vs HyperthyroidismElla Marie CruzadaNo ratings yet
- Archivo en Ingles-Patologias TiroideasDocument4 pagesArchivo en Ingles-Patologias Tiroideasesther avilaNo ratings yet
- Standar Asuhan Keperawatan Diabetes Mellitus: PresentationDocument39 pagesStandar Asuhan Keperawatan Diabetes Mellitus: PresentationpuspitaNo ratings yet
- Caring For Patients With Cardiac Disorders (OUTLINE)Document55 pagesCaring For Patients With Cardiac Disorders (OUTLINE)JamNo ratings yet
- PDF 2Document23 pagesPDF 2Vahid KhaveNo ratings yet
- Geriatrics...... DR Mazhar (03066980980)Document44 pagesGeriatrics...... DR Mazhar (03066980980)azamneha341No ratings yet
- HypercalcemiaDocument11 pagesHypercalcemiaShizuka Marycris Amane100% (1)
- Thyroid DisordersDocument66 pagesThyroid DisordersJOY SANDHYA JOSEPH (RA2123003011002)No ratings yet
- 2017 A3 What Can Acupuncture Help WithDocument2 pages2017 A3 What Can Acupuncture Help WithmayxzineNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Gout: by JuhairinaDocument39 pagesNutrition For Gout: by Juhairinadesy100% (1)
- Below The Knee AmputationDocument76 pagesBelow The Knee AmputationDarell M. Book50% (2)
- Tuto Patho Endo 1Document2 pagesTuto Patho Endo 1SIVAJOTHY A/P SIVALINGAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Renal DisordersSDocument29 pagesRenal DisordersSpastrokateNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Diagnostic Text and Some DiseasesDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Diagnostic Text and Some Diseasesevangelo22656100% (1)
- Thyroid DisorderDocument16 pagesThyroid DisorderfahadNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Emergencies: Heidi Chamberlain Shea, MDDocument32 pagesThyroid Emergencies: Heidi Chamberlain Shea, MDAstrini Retno PermatasariNo ratings yet
- Im DkaDocument16 pagesIm DkaTrisNo ratings yet
- Definition of AtherosclerosisDocument9 pagesDefinition of AtherosclerosischiabixuanNo ratings yet
- Physio Psych Module 5Document73 pagesPhysio Psych Module 5Sonal ChandraNo ratings yet
- Medical Therapy in GoiterDocument43 pagesMedical Therapy in GoiterIka Niswatul ChamidahNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism and HyperthyroidismDocument39 pagesHypothyroidism and HyperthyroidismnatekumandraNo ratings yet
- Thyroid 32Document19 pagesThyroid 32Srinivas SrinuNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Disease of HeartDocument34 pagesInflammatory Disease of HeartLoma Waghmare (Jadhav)No ratings yet
- Gynecologic ProblemsDocument76 pagesGynecologic Problemsairahibrahim23No ratings yet
- BEST PWP! InjuryManagementDocument39 pagesBEST PWP! InjuryManagementAdilene Manzo LeyvaNo ratings yet
- Science Group ReportDocument14 pagesScience Group ReportCzedhryx Cody CamuyagNo ratings yet
- Patients With Adrenal DisordersDocument17 pagesPatients With Adrenal DisordersTsarina Diana TanNo ratings yet
- GeriatricsDocument44 pagesGeriatricsfashion4hub4No ratings yet
- Struma Nodusa: Pembimbing: Dr. Rizapahlevi., M.Si., SP.BDocument45 pagesStruma Nodusa: Pembimbing: Dr. Rizapahlevi., M.Si., SP.BAndre Pradnyana100% (1)
- Adult Health NursingDocument16 pagesAdult Health NursingKomal Ramzan100% (1)
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractapi-3747282No ratings yet
- Most Important Terms & Conditions: Schedule of ChargesDocument18 pagesMost Important Terms & Conditions: Schedule of ChargesVINAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Local Plans FinalDocument21 pagesLocal Plans FinalManuel CassarNo ratings yet
- Visual Examination ProcedureDocument23 pagesVisual Examination ProcedureEdAlmNo ratings yet
- AGBS Ingles 2023Document15 pagesAGBS Ingles 20239fk72y9xy4No ratings yet
- Surgery III MCQS 2023Document4 pagesSurgery III MCQS 2023mariam100% (1)
- Spandan HR ManualDocument46 pagesSpandan HR ManualBotanic Hair Oil100% (1)
- Waste Water - Coke PlantDocument13 pagesWaste Water - Coke PlantSejla Becirovic Cehajic100% (1)
- OOP SE-203: Submitted By: - ANUJ 2K20/SE/21 - Anurag Munshi 2K20/Se/25Document9 pagesOOP SE-203: Submitted By: - ANUJ 2K20/SE/21 - Anurag Munshi 2K20/Se/25Anurag Munshi 25No ratings yet
- Release NotesDocument14 pagesRelease NotesJonathan RodríguezNo ratings yet
- 01section 1 Invitation For TenderersDocument2 pages01section 1 Invitation For TenderersFeteneNo ratings yet
- Kipor KDE Silent GeneratorDocument4 pagesKipor KDE Silent GeneratorbacNo ratings yet
- The Daily Tar Heel For April 10, 2012Document8 pagesThe Daily Tar Heel For April 10, 2012The Daily Tar HeelNo ratings yet
- Poker Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesPoker Cheat Sheet: by ViamaolpNo ratings yet
- Atb164 Re4r01a, R4a-El Nissan ...... Planetary FailureDocument4 pagesAtb164 Re4r01a, R4a-El Nissan ...... Planetary FailureAleNo ratings yet
- 220 Transition Cement SDSDocument9 pages220 Transition Cement SDSKevin MaciasNo ratings yet
- Memory Structures of An ABAP Program and FunctionsDocument1 pageMemory Structures of An ABAP Program and FunctionsardaNo ratings yet
- Block Brute Force Attack in Mikrotik RouterDocument1 pageBlock Brute Force Attack in Mikrotik RouterPedro HernandezNo ratings yet
- Written Exam-Guleng, Adrian AngelicoDocument21 pagesWritten Exam-Guleng, Adrian AngelicoAdrian Esico GulengNo ratings yet
- TP MicroprocessorDocument10 pagesTP MicroprocessorAnshuman Swaroop DasNo ratings yet
- Basic Floor Plans SolutionDocument9 pagesBasic Floor Plans SolutionAlice KrodeNo ratings yet
- EMT Refresher FlyerDocument2 pagesEMT Refresher FlyerBillR.YoungNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument11 pagesTransmission LinesAnirban Z100% (1)
- Augmented Seventh Chord - WikipediaDocument3 pagesAugmented Seventh Chord - WikipediaAla2 PugaciovaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 2 QuestionsPham Thi Hong ThuyNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Civil Engineering and ArchitectureDocument7 pagesDifference Between Civil Engineering and ArchitectureLin ZawNo ratings yet
- APRO Banking Gateway For Oracle Financials CloudDocument2 pagesAPRO Banking Gateway For Oracle Financials Cloudsohaibmuzaffar007No ratings yet
- Solid Pad Mount Switchgear - 150123 V2.0Document8 pagesSolid Pad Mount Switchgear - 150123 V2.0Edwin Quispe50% (2)
- Extrusive Intrusive: What Are Igneous Rocks?Document6 pagesExtrusive Intrusive: What Are Igneous Rocks?Edna BernabeNo ratings yet