Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ICU One Pager Blood Products
ICU One Pager Blood Products
Uploaded by
Abdullah Shidqul AzmiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ICU One Pager Blood Products
ICU One Pager Blood Products
Uploaded by
Abdullah Shidqul AzmiCopyright:
Available Formats
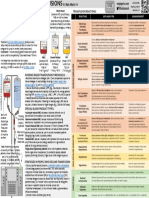
OOD PRODUCT TRANSFUSIONS
by Nick Mark MD ONE
onepagericu.c
om
Link to the
most current
DEFINITIONS: Whole blood version →
TRANSFUSION REACTIONS:
The goal of transfusion is to provide minimum O2 carrying AB+ (stored at 4°C up to 35 days) @nickmmark
Rh positive
REACTION EXPLANATION MANAGEMENT
capacity (RBCs) & sufficient platelets and clotting factors to EXP 2021-01-01 23:30 ~450 ml + 60 ml citrate
permit hemostasis. The goal is not correcting to “normal.”
A9999 20 123456 K
Good at achieving hemostasis
12
Most common immune reaction to transfusion. Prevention: APAP + H2 blockers,
Although RBC transfusions increase CaO2 they might not (contains all factors) but limited Febrile Non- Occurs within 4 hours of transfusion due to accumulated consider leukoreduced units
availability (autologous, military) Hemolytic inflammatory cytokines in the banked donor blood. May recur; Treatment: stop infusion, APAP,
normalize DO2 due to less efficient unloading of O2 in Transfusion 25% of patients who had FNHTR once had another reaction meperidine. R/o other causes.
transfused blood (2,3-BPG is degraded in storage). Reaction (FNHTR) subsequently. Notify blood bank.
Type and screen – determines blood type and detects
Occurs during or shortly after transfusion. A true emergency
antibodies in recipient (e.g., indirect Coombs test) AB+
Rh positive
AB+
Rh positive
AB+
Rh positive Occurs due to mismatch of donor antigens (often ABO/Rh) & Prevention: carefully check units
Treatment with anti-CD38 antibodies (daratumumab, EXP 2021-01-01 23:30 EXP 2021-01-01 23:30 EXP 2021-01-01 23:30 Acute Hemolytic recipient antibodies leading to hemolysis & agglutination. Treatment: Stop transfusion,
isatuximab) can cause a false positive on screen for minor A9999 20 123456 K
Transfusion S/sx: Fever, flank pain, dark urine, DIC, hypoTN, renal failure. notify blood bank, test for
12
A9999 20 123456 K A9999 20 123456 K
12
12
Reaction (AHTR) Hemolysis on labs (↓haptoglobin, ↑LDH, etc) hemolysis & DIC, aggressive IV
antigens for up to six months (notify blood bank). hydration (goal UOP > 100/hr).
Crossmatch – involves testing patient blood and specific
donor units for compatibility. Crossmatch takes ~45 min. RBCs Pooled Platelet FFP Occurs 24 hours to 30 days after transfusion due to mismatch Treatment: Notify blood bank,
(stored at 4°C up (stored at RT up (frozen -25 °C Delayed Hemolytic of minor antigens (often false negative crossmatch). 2nd repeat testing (DAT, type & screen,
In emergencies crossmatch can be skipped. Transfusion
to 42 days) to 5 days) up to 3 yrs) exposure can be faster, more severe. May have drop in Hct, etc)
In extreme emergencies non-type specific blood can be
IMMUNE MEDIATED
Reaction (DHTR) fever, minor hemolysis.
used (e.g., O- RBCs in women, O- or O+ RBCs in men). ~350 ml ~300 ml ~225 ml
↑ Hb ~1 gm/dl* ↑ Plt by ~5-7k* (*in 70 kg pt)
Usually anaphylactoid (not IgE mediated). Prevention: washed (or IgA
v1.0 (2021-07-10) CC BY-SA 3.0
EVIDENCE BASED TRANSFUSION THRESHOLDS: S/sx urticaria, maculopapular rash, pruritis, fv & hypoTN deficient) RBCs.Check for IgA
•Restrictive transfusion strategies (Hb > 7) are comparable/superior to Allergic reaction Occurs minutes to hours after transfusion, due to antibodies deficiency if recurrent anaphylaxis
against proteins on plts, leukocytes, or in plasma, including IgA Tx: epi, H2 blockers, steroids
liberal strategies in most settings including GI bleed, septic shock, (in recipients w/ IgA deficiency)
AB+
Rh positive
0.9% Sodium
cardiac surgery, TBI, and in most ICU patients.
EXP 2021-01-01 23:30
Chloride • Massive transfusion protocols (MTP) (e.g., trauma pts or massive GI Occurs 7-10 days after transfusion, due to anti-platelet Treatment: IVIG, plasmapheresis
A9999 20 123456 K
Injection USP
12
1000mL
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,
bleed) target hemodynamic stability not a specific Hb. Among patients Post Transfusion antibodies in donor blood. Causes purpura & severe
thrombocytopenia, may be life-threatening.
consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do
receiving MTP, balanced ratio (e.g., 1 RBC : 1 FFP : 1 Plt unit) is superior
eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore
Purpura (PTP)
et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad
minim veniam, quis nostrud
More common in women (85%) & Caucasians.
exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut
aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
• Platelet transfusion thresholds are disease dependent: For most
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit
in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu
fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint
occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt
in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit
diseases 10k is adequate, if bleeding or needing surgery 50k may be
anim id est laborum.
Leading cause of transfusion related death (15% mortality). Treatment: ventilatory support
required. Limited evidence for higher targets (e.g., 100k for CNS bleed) Transfusion Related TRALI resembles ARDS, onset is 4-6 hours after transfusion. may be required (use LPV), use
SPECIAL BLOOD PRODUCT TYPES: Acute Lung Injury Most common following platelet transfusion from multi- platelets from male donors for
(TRALI) parous female donors (due to anti-HLA or anti-HNA Ab) future transfusions.
•Leukocyte reduced RBC: decreases incidence of febrile rxns &
Each unit prevents allo-immunization. Also makes blood CMV-safe
Y-tubing Occurs 8-10 days post transfusion, donor leukocytes attack Prevention: use irradiated and
contains: •Gamma-irradiated RBC: reduces incidence of GVHD during
combines Transfusion immunosuppressed recipient. leukocyte reduced blood in
·Blood type transfusions; important in very immunosuppressed patients Associated Graft Sx include: fever, cutaneous eruptions, diarrhea, liver immunosuppressed recipients
blood &
·Expiration •Volume Reduced RBC: each unit comes in ~100 ml (instead of ~350 Versus Host Disease abnormalities. May progresses to pancytopenia due to Treatment: no effective treatment
crystalloid (TA-GVHD) marrow aplasia. High mortality.
·Product # ml), can reduce the incidence of febrile rxns because there are fewer
·Barcodes Filter & drip plasma proteins; can also be used in volume overloaded patients
All must be chamber (though giving diuretic is probably better) Transfusion Occurs between 0-6 hrs after transfusion. Volume overload Prevention: minimum # of units,
verified! Associated Cardiac from transfusions, particularly in patients with CHF. Presents volume reduced units, diuresis
removes •Washed RBC: plasma is replaced with crystalloid; this should be done Overload (TACO) as dyspnea potentially progressing to severe hypoxemia. Treatment: diuresis
blood clots only if there was a previous allergic reaction or in IgA deficient patients
NON-IMMUNE
(if no IgA deficient donors)
MEDIATED
Hypocalcemia Citrate in RBCs binds to serum calcium. Blood products contain Treatment: Replete calcium and
Rate of transfusion depends potassium from lysed cells. monitor for hyperkalemia.
•Single donor (apheresis) platelets: a full unit of platelets obtained Hyperkalemia
on severity of illness. In stable
patients, slower infusions (e.g. from a single donor via apheresis (in contrast to pooled platelets
typically combining 5 donors). Single donor limits antigen exposure Due to low temp of transfused products. iatrogenic Prevention/Tx: Use a blood
over 2 hrs) permits earlier Hypothermia hypothermia exacerbates coagulopathy & ↑bleeding warmer for massive transfusions
stopping. In unstable patients
consider using a rapid infuser. STRATEGIES IN PEOPLE WHO DECLINE TRANSFUSION People taking ACEi may develop hypotension due to inability Does not require intervention.
• Discuss specific reasons/concerns, understand what tx is acceptable Hypotension to break down bradykinin in transfused blood Rule out infection/hemolysis
• Correct coagulopathy (consider amicar, TXA, other products)
150 • Stop and minimize blood loss: hormonally suppress menstruation, Infection occurs due to untested organisms (rare), false negatives on testing (very rare), or bacterial contamination.
autotransfuse with cell-saver (OR) or hemothorax/chest tube (ICU) Platelets (stored at RT) are more likely to cause infections with skin flora (GPCs). RBCs (stored at 4C),
Bacterial
IINFECTION
• Minimize iatrogenic blood loss (fewer labs, less frequently, drawn in contamination are more likely to be contaminated with GNRs. Can lead to sepsis.
pediatric tubes); no "routine" labs; every test should be thoughtful
and drawn in pediatric tubes to minimize volume lost Organisms NOT tested include: Malaria, Borrellia (Lyme disease), Trypanosoma (Chagas disease),
Untested organisms Babesiosis, & vCJD (varies by country)
• Optimize hematopoesis (IV iron infusion, folate supplementation,
EPO administration)
False negative Extremely rare: HIV 1 in 2,000,000,000, HBV 1 in 100,000,000, HCV 1 in 2,000,000, HTLV 1 in 650,000
• Consider blood substitute (poly-heme)
You might also like
- тако бел PDFDocument60 pagesтако бел PDFAndrew PodshivalenkoNo ratings yet
- Panel Drawing PDFDocument40 pagesPanel Drawing PDFashutosh200967% (3)
- Imagining the Nation in Nature: Landscape Preservation and German Identity, 1885–1945From EverandImagining the Nation in Nature: Landscape Preservation and German Identity, 1885–1945No ratings yet
- Lukegarbett Bloodtypingscenario1Document2 pagesLukegarbett Bloodtypingscenario1api-340693501No ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument7 pagesCase StudyBilly Belando50% (2)
- Clinical Pathology MCQs and Ansewrs PDFDocument29 pagesClinical Pathology MCQs and Ansewrs PDFAmeer MattaNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument85 pagesMCQyasser95% (20)
- Definitions: Transfusion Reactions:: 2,3-BPG Is Degraded in StorageDocument1 pageDefinitions: Transfusion Reactions:: 2,3-BPG Is Degraded in Storagejuan ramon milanes grageraNo ratings yet
- Preliminary: Configuration Management Controlled ReferenceDocument1 pagePreliminary: Configuration Management Controlled ReferenceJesus Villoria GarciaNo ratings yet
- 1-ModelDocument1 page1-Modeljoselito navarroNo ratings yet
- Alat Pendeteksi Nominal Uang Untuk Tuna Netra Kel 6: Apk-TechDocument1 pageAlat Pendeteksi Nominal Uang Untuk Tuna Netra Kel 6: Apk-TechForza RagazziNo ratings yet
- Eng CD 2374900 A4-3077475Document4 pagesEng CD 2374900 A4-3077475Roger SuzanoNo ratings yet
- Ce133p 2 RCD ComputationDocument16 pagesCe133p 2 RCD ComputationKeroro SeighartNo ratings yet
- Smart DC Load SchematicDocument1 pageSmart DC Load SchematictxescientistNo ratings yet
- International Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocument7 pagesInternational Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringMalik RizwanNo ratings yet
- 05 Compliance Assurance Plan For May 2024 Rev 0Document3 pages05 Compliance Assurance Plan For May 2024 Rev 0sidhanathsingh5No ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram (Distribution) - CEB AnuradhapuraDocument25 pagesSingle Line Diagram (Distribution) - CEB AnuradhapuraTharindu NuwanNo ratings yet
- @ STRC 1623-ModelDocument1 page@ STRC 1623-ModelVyshnav VpNo ratings yet
- SLD PDF File111Document1 pageSLD PDF File111John Neil MitraNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 PDFDocument14 pagesLecture5 PDFante mitarNo ratings yet
- Serial Write and Read Loop: Bytes at PortDocument1 pageSerial Write and Read Loop: Bytes at PortErikChinachiAmánNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager Fluid Responsiveness v1 2Document1 pageICU One Pager Fluid Responsiveness v1 2liz mNo ratings yet
- Map r2 Ijtema 2023Document1 pageMap r2 Ijtema 2023H M Moinul IslamNo ratings yet
- Sophos PerformanceDocument148 pagesSophos Performancefake fNo ratings yet
- Preliminary: Configuration Management Controlled ReferenceDocument1 pagePreliminary: Configuration Management Controlled ReferenceJesus Villoria GarciaNo ratings yet
- Use of Crane: 5T Stahl CranesystemsDocument2 pagesUse of Crane: 5T Stahl CranesystemsАсема АселяNo ratings yet
- Aldwych NightDocument1 pageAldwych NightKairav HauradhurNo ratings yet
- 6.6 THRU' 2 Nos: Forbes & Company LimitedDocument1 page6.6 THRU' 2 Nos: Forbes & Company LimitedChandru ChristurajNo ratings yet
- Oring PerformanceDocument66 pagesOring Performancefake fNo ratings yet
- Foot Valve: Cast Iron / Stainless SteelDocument1 pageFoot Valve: Cast Iron / Stainless Steelaa abNo ratings yet
- Wiring Diagram PDFDocument1 pageWiring Diagram PDFAlexander RojasNo ratings yet
- Written Exam in Molecular Modeling: InstructionsDocument11 pagesWritten Exam in Molecular Modeling: InstructionsTalal Ahmed Awad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Carrier IdlerDocument22 pagesCarrier Idlerwawan setiawanNo ratings yet
- When Where Which Who WhoseDocument12 pagesWhen Where Which Who Whoseoummyptn13No ratings yet
- AFL Substation SolutionsDocument12 pagesAFL Substation SolutionsManali PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 2-ModelDocument1 page2-Modeljoselito navarroNo ratings yet
- FINALSDocument2 pagesFINALSjrcruzpogi0242424No ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument7 pagesCombinepdfcyrus juanezaNo ratings yet
- Power Cable Catalog (Huanghe Cables) - SummerDocument21 pagesPower Cable Catalog (Huanghe Cables) - SummerJenica Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- AX 5A1 P05 RecorteDocument1 pageAX 5A1 P05 RecorteCharlieLevittNo ratings yet
- Campus Map 2021Document2 pagesCampus Map 2021alizadehamir22No ratings yet
- 50D-BCSDocument12 pages50D-BCSCorjuc StefanNo ratings yet
- NR'S MVDC Solution: 10Kv Jiangdong MVDC For Optimizing Distribution NetworkDocument2 pagesNR'S MVDC Solution: 10Kv Jiangdong MVDC For Optimizing Distribution NetworkMoshNo ratings yet
- Ipc2022 86906Document6 pagesIpc2022 86906DarylNo ratings yet
- Lightning Strike Counter: Lightning Protection Equipment CatalogDocument1 pageLightning Strike Counter: Lightning Protection Equipment CatalogComsip400No ratings yet
- Fascinating Drums - 1° Trombon BB PDFDocument1 pageFascinating Drums - 1° Trombon BB PDFHugo Valentino Gonzalez CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 1111Document1 pageIncidence Map 1111WBKONo ratings yet
- 50D BCB 246Document10 pages50D BCB 246laura MtNo ratings yet
- M3M CornerWalkDocument40 pagesM3M CornerWalkNidhi YadavNo ratings yet
- 320N KRE ChartDocument1 page320N KRE Chartrmerchant789No ratings yet
- Page Proofs: Continuous Probability DistributionsDocument44 pagesPage Proofs: Continuous Probability DistributionsApoorva PanchalNo ratings yet
- Full Collation of The Codex Sinaiticus With New Testament (1864) - TextDocument269 pagesFull Collation of The Codex Sinaiticus With New Testament (1864) - TextQuinton Kristy BristowNo ratings yet
- MM1114761-00 HP ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM (Analogic Version)Document23 pagesMM1114761-00 HP ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM (Analogic Version)Bruno Adrover100% (1)
- Capt Front PanelDocument1 pageCapt Front PanelMrWannNo ratings yet
- D1 S2 P2 Luke BriantDocument27 pagesD1 S2 P2 Luke BriantLelosPinelos123No ratings yet
- CH 1 What Is Env HistoryDocument32 pagesCH 1 What Is Env Historydaniellema5752No ratings yet
- Response To Ms Magopeni's Grievance 2 February 2022 (002) - CEODocument32 pagesResponse To Ms Magopeni's Grievance 2 February 2022 (002) - CEOjanetNo ratings yet
- Orona Arca3 SchémasDocument38 pagesOrona Arca3 Schémasmahfoud ascenseursNo ratings yet
- Civl 316 Problem Set1 Solutions-1Document15 pagesCivl 316 Problem Set1 Solutions-1mohamed mohsenNo ratings yet
- Rate of Change Assignment: Lon DG Hee GWD Port of 7 +Document8 pagesRate of Change Assignment: Lon DG Hee GWD Port of 7 +Ezaan HaqueNo ratings yet
- Ope 4Document1 pageOpe 4CECILIA RODRIGUEZ MEDRANONo ratings yet
- Tos 03Document1 pageTos 03Maevin WooNo ratings yet
- Tabg Jec 0 000 Pro Pid 0012 - GDocument1 pageTabg Jec 0 000 Pro Pid 0012 - GAfif FadhliNo ratings yet
- HT Cable CatalogueDocument209 pagesHT Cable CataloguePeter K PaulNo ratings yet
- ISMI HOTTI - 9 (REVISI 13 - 20 Juni 2024) Agenda I 2024 (28 - 30 June 2024)Document24 pagesISMI HOTTI - 9 (REVISI 13 - 20 Juni 2024) Agenda I 2024 (28 - 30 June 2024)Abdullah Shidqul AzmiNo ratings yet
- Referat - Septic ArtritisDocument23 pagesReferat - Septic ArtritisAbdullah Shidqul AzmiNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury Is Associated With In-Hospital Mortality in Older Patients With COVID-19Document7 pagesAcute Kidney Injury Is Associated With In-Hospital Mortality in Older Patients With COVID-19Abdullah Shidqul AzmiNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategies of COVID-19-Related Hypercoagulant and Thrombotic ComplicationsDocument5 pagesPathogenesis and Treatment Strategies of COVID-19-Related Hypercoagulant and Thrombotic ComplicationsAbdullah Shidqul AzmiNo ratings yet
- 1522-1588 USMLE QuestionsDocument67 pages1522-1588 USMLE QuestionsKiran KrupaNo ratings yet
- 5 Hematologic-ExaminationsDocument12 pages5 Hematologic-ExaminationsMark Jireck AndresNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Picture (CBC) PDFDocument1 pageComplete Blood Picture (CBC) PDFRizwan yousafNo ratings yet
- The Composition of Blood: Fact Sheet: Blood PlasmaDocument1 pageThe Composition of Blood: Fact Sheet: Blood PlasmaKoshkaNo ratings yet
- 13029-Article Text-47609-1-10-20121220 PDFDocument4 pages13029-Article Text-47609-1-10-20121220 PDFtanmai nooluNo ratings yet
- Agar Plate) Agar) or EMB (Eosin Methylene Blue) Blood Agar) Agar Plate) Bile Esculin Agar) Alcohol) BCB (Document2 pagesAgar Plate) Agar) or EMB (Eosin Methylene Blue) Blood Agar) Agar Plate) Bile Esculin Agar) Alcohol) BCB (behzad bmNo ratings yet
- Untitled - 2022-12-20T191434.583Document10 pagesUntitled - 2022-12-20T191434.583Musab ali SyedNo ratings yet
- Food Borne DiseasesDocument42 pagesFood Borne DiseasesJesse LeeNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Degree of Bacterial Contamination of Different Areas of A Dental Unit Chair Used in The Clinical Practice of DentalDocument5 pagesChanges in The Degree of Bacterial Contamination of Different Areas of A Dental Unit Chair Used in The Clinical Practice of DentalAlveolar 21No ratings yet
- Unit 6 EbolaDocument6 pagesUnit 6 Ebolaapi-275689851No ratings yet
- Thypoid FeverDocument30 pagesThypoid FeverGlen Jacobs SumadihardjaNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus (Staphylococcus Aureus, Staphylococcus Epidermidis, and Staphylococcus Saprophyticus)Document27 pagesStaphylococcus (Staphylococcus Aureus, Staphylococcus Epidermidis, and Staphylococcus Saprophyticus)drparachuru100% (1)
- HEALTH 8 3rdquarterDocument2 pagesHEALTH 8 3rdquarterMarc Angelo L. SebastianNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Glycosylated HaemoglobinDocument3 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Glycosylated HaemoglobinSri ShivaNo ratings yet
- Tube Dilution MethodDocument4 pagesTube Dilution MethodDipto Kumer SarkerNo ratings yet
- Flashcards in Abo Blood GroupDocument10 pagesFlashcards in Abo Blood GroupVincent ReyesNo ratings yet
- 200 MCQs HaematologyDocument48 pages200 MCQs HaematologyHamid Iqbal100% (2)
- AnemiaDocument14 pagesAnemiaDewi MNo ratings yet
- Discussion Questions 1. Why Should The Motility Test Be Done at The Log Phase of Bacterial Growth?Document5 pagesDiscussion Questions 1. Why Should The Motility Test Be Done at The Log Phase of Bacterial Growth?Hakim RazakNo ratings yet
- Imulfex WB-SP For Leukocyte ReductionDocument2 pagesImulfex WB-SP For Leukocyte ReductiondatitoxNo ratings yet
- The Biology of TB: Bio FactsheetDocument3 pagesThe Biology of TB: Bio FactsheetNaresh MohanNo ratings yet
- Bacteria&YeastDocument13 pagesBacteria&YeastGuy SoreqNo ratings yet
- Aseptic TechniqueDocument10 pagesAseptic Techniqueanon_507843701No ratings yet
- Autoimmune - Hemolytic - Anemia - Mixed - Type-A - Case - Repo 2Document5 pagesAutoimmune - Hemolytic - Anemia - Mixed - Type-A - Case - Repo 2Afsha AnishNo ratings yet
- Massive Haemorrhage: P Donnelly B FergusonDocument18 pagesMassive Haemorrhage: P Donnelly B FergusonRizqiNo ratings yet
- The ABO Blood Groups: Phenotypes GenotypesDocument2 pagesThe ABO Blood Groups: Phenotypes GenotypesSheila Mae CabahugNo ratings yet