Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsJAW CYST.PPT (1)
JAW CYST.PPT (1)
Uploaded by
sahibpir02Jaw cyst bds iqra university notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Odontogenic CystDocument16 pagesOdontogenic CystMahsaNo ratings yet
- Oral Radiology Principles and Interpretation 7th Ed PDFDocument14 pagesOral Radiology Principles and Interpretation 7th Ed PDFLaura Victoria Alvarez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- BDS10011 Cystic Lesions of Bone 2Document50 pagesBDS10011 Cystic Lesions of Bone 2habibahafez282No ratings yet
- cysts 1-مدمجDocument306 pagescysts 1-مدمجأمال داودNo ratings yet
- CYST - نسخةDocument71 pagesCYST - نسخةKHALED WALEEDNo ratings yet
- د.نجاة Cyst-7 (Muhadharaty) 1Document28 pagesد.نجاة Cyst-7 (Muhadharaty) 1بكر الدوريNo ratings yet
- Oral CystDocument47 pagesOral CystmelNo ratings yet
- CystDocument59 pagesCystHarshini DonepudiNo ratings yet
- CystsDocument180 pagesCystsDinesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Special Lecture 11Document15 pagesSpecial Lecture 11HussainNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The JawsDocument75 pagesCysts of The JawsSwetha KaripineniNo ratings yet
- l17 Management of CystsDocument55 pagesl17 Management of CystsJu JuNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts and Tumor of The JawsDocument149 pagesOdontogenic Cysts and Tumor of The JawsAnooda MazenNo ratings yet
- 3 CYSTS of The Soft Tissues and The Jaws PDFDocument28 pages3 CYSTS of The Soft Tissues and The Jaws PDFmarianaffernandes10No ratings yet
- RAMON - Cystic LesionDocument28 pagesRAMON - Cystic Lesionjamaica faith ramonNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic and Non Odontogenic Cysts of The Oral CavityDocument115 pagesOdontogenic and Non Odontogenic Cysts of The Oral CavitySalwa AboelmagdNo ratings yet
- Cyst of The JawsDocument13 pagesCyst of The Jawstthtn6c8pbNo ratings yet
- PDF Cyst 1-2Document122 pagesPDF Cyst 1-2Sadek MohamedNo ratings yet
- Omr Seminar CystDocument51 pagesOmr Seminar CystJohann GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Dental Radiology LectureDocument31 pagesDental Radiology LectureAbdullahayad farouqNo ratings yet
- Cysts MainDocument43 pagesCysts MainharshiniNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts and TumorsDocument273 pagesOdontogenic Cysts and TumorsAliImadAlKhasaki82% (11)
- Cysts MainDocument43 pagesCysts MainharshiniNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The JawsDocument28 pagesCysts of The JawsMladen PazinNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts: Dr. Amin AbusallamahDocument82 pagesOdontogenic Cysts: Dr. Amin Abusallamahmabula masungaNo ratings yet
- 3,3 - Cyst of Jaws and Oral Soft TissuesDocument19 pages3,3 - Cyst of Jaws and Oral Soft Tissuesحمزة تلاحمةNo ratings yet
- Dentigerous CystDocument25 pagesDentigerous CystDr. Deepanshi SutariaNo ratings yet
- Cyst of The JawDocument60 pagesCyst of The Jawafzanwahab100% (2)
- Odontogenic Cysts of The JAW: Seminar Presented byDocument31 pagesOdontogenic Cysts of The JAW: Seminar Presented byankita sethi100% (1)
- Cysts of The Oral CavityDocument270 pagesCysts of The Oral CavitySally Mahfouz100% (6)
- Seminar On Radicular CystDocument7 pagesSeminar On Radicular CystKhalid Mahmud Arifin100% (2)
- Cysts of The Jaws and Neck: Wil Dustin P. SinlaoDocument46 pagesCysts of The Jaws and Neck: Wil Dustin P. Sinlaojamaica faith ramonNo ratings yet
- Cysts Part2Document63 pagesCysts Part2abdelrahman amrNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystDocument16 pagesOdontogenic CystMahsaNo ratings yet
- Oral Surgery Benign Cysts P.2Document33 pagesOral Surgery Benign Cysts P.2abbasmazaal1234No ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystsDocument5 pagesOdontogenic CystsBH ASMRNo ratings yet
- Introduction Cysts of JawsDocument62 pagesIntroduction Cysts of JawsFatima Siddiqui100% (1)
- 7 Cysts of The Jaws 1 SlideDocument53 pages7 Cysts of The Jaws 1 SlideMohammed BohaliqahNo ratings yet
- Cyst 1Document59 pagesCyst 1محمد ربيعيNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystsDocument63 pagesOdontogenic CystsshabeelpnNo ratings yet
- Cyst Final-1Document120 pagesCyst Final-1drjatinNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystsDocument28 pagesOdontogenic Cystsووويويويةءتؤوبةين للاNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document43 pagesChapter 5mohmedNo ratings yet
- Eruption Cyst 22Document40 pagesEruption Cyst 22Taki EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Pseudocyst: R Gaushini Bds Cri Department of Oral and Maxilofacial PathologyDocument23 pagesPseudocyst: R Gaushini Bds Cri Department of Oral and Maxilofacial PathologyGautam RamuvelNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The Oral RegionDocument14 pagesCysts of The Oral RegionJASTHER LLOYD TOMANENGNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystsDocument54 pagesOdontogenic CystssamsoomaustNo ratings yet
- Cysts DentalDocument23 pagesCysts DentalApollo DentalNo ratings yet
- Introduction Cysts of JawsDocument62 pagesIntroduction Cysts of JawsEnass Alhadi50% (2)
- Odontogenic CystsDocument63 pagesOdontogenic CystsFaraz MohammedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1(2)Document9 pagesLecture 1(2)photo copyhemnNo ratings yet
- Cystak Diagnosztikája AngolDocument36 pagesCystak Diagnosztikája AngolErdeli StefaniaNo ratings yet
- 07 CystsDocument16 pages07 CystsNathnael GebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The JawDocument14 pagesCysts of The Jawluke swanepoelNo ratings yet
- Radicular CystDocument45 pagesRadicular CystPriyanka GanesanNo ratings yet
- Sebaceous Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSebaceous Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZFrom EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- The Dental Pulp: Biology, Pathology, and Regenerative TherapiesFrom EverandThe Dental Pulp: Biology, Pathology, and Regenerative TherapiesNo ratings yet
- Common Causes of Swelling in The Oral CavityDocument12 pagesCommon Causes of Swelling in The Oral CavityScribdNo ratings yet
- Radicular Cyst With Primary Mandibular Molar A RarDocument5 pagesRadicular Cyst With Primary Mandibular Molar A RargarciadeluisaNo ratings yet
- Radiography Jaw LesionsDocument19 pagesRadiography Jaw LesionssrikantnairNo ratings yet
- 4.radiolucent Inflammatory Jaw Lesions A TwentyyearDocument7 pages4.radiolucent Inflammatory Jaw Lesions A TwentyyearMihaela TuculinaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Oral CavityDocument4 pagesDiseases of Oral CavityStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- JaypeeDigital - Ebook ReaderDocument40 pagesJaypeeDigital - Ebook ReaderHanin AbukhiaraNo ratings yet
- Kramer 1992Document7 pagesKramer 1992Elite Dental AcademyNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kasus Tambahan 3 - Khairin Yonni (12730)Document6 pagesJurnal Kasus Tambahan 3 - Khairin Yonni (12730)Khairin YonniNo ratings yet
- Radicular CystDocument45 pagesRadicular CystPriyanka GanesanNo ratings yet
- MSQ. Oral Pathology. Dr. Hiwa KareemDocument13 pagesMSQ. Oral Pathology. Dr. Hiwa KareemAmmar YasirNo ratings yet
- CYSTSDocument3 pagesCYSTSfr.faisal8265No ratings yet
- Oral Pathology Vimal K Sikri Colour Guides, MCQ's Arpit SikriDocument585 pagesOral Pathology Vimal K Sikri Colour Guides, MCQ's Arpit SikriKrish NatbhanjanNo ratings yet
- Cysts and Odontogenic Tumors1 2Document41 pagesCysts and Odontogenic Tumors1 2Seca mandiNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The Oral RegionDocument14 pagesCysts of The Oral RegionJASTHER LLOYD TOMANENGNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystsDocument63 pagesOdontogenic CystsshabeelpnNo ratings yet
- Oral Path CramDocument10 pagesOral Path CramHarjotBrarNo ratings yet
- Dentigerous CystDocument16 pagesDentigerous CystMudjiono MudjionoNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Sinus 1Document61 pagesMaxillary Sinus 1saksheeNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystDocument16 pagesOdontogenic CystMahsaNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts: Dr. Amin AbusallamahDocument82 pagesOdontogenic Cysts: Dr. Amin Abusallamahmabula masungaNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Management of Impacted CanineDocument7 pagesOrthodontic Management of Impacted CanineplsssssNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts of The JAW: Seminar Presented byDocument31 pagesOdontogenic Cysts of The JAW: Seminar Presented byankita sethi100% (1)
- Differential Diagnosis of Pericoronal RadiolucenciesDocument30 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Pericoronal RadiolucenciesakNo ratings yet
- Dentigerous CystDocument25 pagesDentigerous CystDr. Deepanshi SutariaNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumor Ameloblastoma: Presented By: Ankita Singh Bds Final Year Roll No 37Document73 pagesOdontogenic Tumor Ameloblastoma: Presented By: Ankita Singh Bds Final Year Roll No 37ankita sethiNo ratings yet
- CEOT in ChildDocument7 pagesCEOT in ChildlilaNo ratings yet
- Case #1: Case Study Assignment Assignment #3Document10 pagesCase #1: Case Study Assignment Assignment #3api-536664543No ratings yet
- Gambaran Kista Dentigerous Gigi Premolar Rahang Atas Pada Radiograf CBCT: Laporan KasusDocument6 pagesGambaran Kista Dentigerous Gigi Premolar Rahang Atas Pada Radiograf CBCT: Laporan KasusSurya DimastiarNo ratings yet
- Quistes OdontogénicosDocument15 pagesQuistes OdontogénicosYsabel GutierrezNo ratings yet
JAW CYST.PPT (1)
JAW CYST.PPT (1)
Uploaded by
sahibpir020 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views16 pagesJaw cyst bds iqra university notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentJaw cyst bds iqra university notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views16 pagesJAW CYST.PPT (1)
JAW CYST.PPT (1)
Uploaded by
sahibpir02Jaw cyst bds iqra university notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
Presented by ; Dr.
Irfan Ali Khan
Topic : Jaw cyst
Subject: Periodontology
Oral pathology
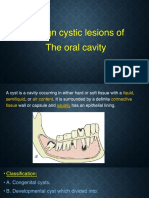
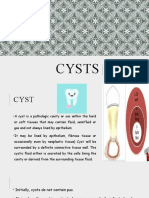
Definition
• A cyst is an epithelial lined cavity that fills with
fluid or soft material.
• Chronic swelling are the most common cause
of jaw cyst.
• Cyst are more common in jaw than any other
bone because of the many remnants of
odontogenic epithelium remaining in the
tissues.
Types of cyst
• 1.True Cysts: that which is lined by
epithelium .
• E.g : Dentigerous cyst, Radicular cyst.
• 2.Pseudo cysts: not lined by epithelium,
• Eg ; solitary bone cyst, aneurysmal bone
cyst.
Key factors of Cyst Formation
• Proliferation of epithelial lining;
• Infection from pulp
chamber induces inflammation and
proliferation of the epithelial rests.
• Hydrostatic pressure of cystic fluid;
• The cysts attain a balloon
like shape because cystic fluid contain
inflammatory exudate
Cont,d
• and contain concentration of protein
which exert osmotic pressure.
• Bone resorbing factors;
• cyst tissue in culture release
PGE2 and PGE3 which contribute in cystic
growth.
General clinical symptoms of cyst
• Cyst usually asymptomatic but some
symptoms may occure like this;
• Swelling
• Displacement or loosening of tooth
• Pain(if infected)
• Eggshell cracking
Diagnosis
• Your doctor may recommend tests prior to
treatment. These test may include:
• Imaging studies, such as X-ray, CT or MRI
• A biopsy to remove a sample of tumor or cyst
cells for laboratory analysis
• Your doctor uses this information to put
together a treatment plan that's best for you
and the most effective option for treating your
tumor or cyst
Treatment
• Enucleation (cystectomy);
• Removal of the entire cyst. Enucleation of
cysts should be performed with care in an attempt
to remove the cyst in one piece without
fragmentation.
• Marsupialization;
• The creation of a window into the wall of a
cyst, allowing the contents to be drained. The
window is left open, and the lack of pressure within
the cyst causes the lesion to shrink, as the
surrounding bone starts to fill in again
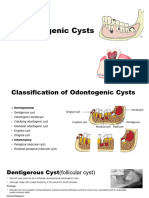
Classification of cyst
• Epithelial cyst are classified in the following
manner;
• (A) Odontogenic cyst;
• (1) Developmental Odontogenic Cyst;
Keratocyst.
Dentigerous cyst(follicular cyst).
Eruption cyst .
Lateral periodontal cyst.
• Gingival cyst of adult.
classification
• (2) Inflammatory Odontogenic Cyst
Radicular cyst
Residual cyst.
• (B) Non-odontogenic Cysts
Nasopalatine cyst
Nasolabial cyst.
Gobulomaxillary cyst.
• Keratocyst;
• Odontogenic keratocyst (OKC) is the cyst
arising from the cell rests of dental lamina. It most
often affects the posterior mandible.
Odontogenic keratocysts make up around 19% of
jaw cysts.
• Dentigerous cyst;
• A dentigerous cyst is an odontogenic cyst -
associated with the crown of an unerupted (or
partially erupted) tooth. The cyst cavity is lined by
epithelial cells derived from the reduced enamel
epithelium of the tooth forming organ.
Eruption cyst;
Eruption cysts are benign cysts that appear on
the mucosa of a tooth shortly before its eruption.
They may disappear by themselves but if they hurt,
bleed or are infected they may require surgical
treatment(marsupialization).
Radicular cyst;
A radicular cyst is generally inflammatory
odontogenic cyst and defined as a cyst arising from
epithelial remnants (cells of Malassez) in the
periodontal ligament as a consequence of
inflammation, usually following the death of the
dental pulp.
• Residual cyst;
• A residual cyst, as the name implies,
ق
is a radicular, lateral periodotal, dentigerous
or any other cyst that has persisted() ب ر رارafter
it’s associated tooth has been lost. Residual
cysts commonly affect the maxillary region.
Usually, residual cysts are asymptomatic.
Non-odontogenic cysts
• Nasopalatine cyst;
• The nasopalatine cyst is the most
common epithelial and nonodontogenic cyst of the
maxilla. The cyst originates from epithelial
remnants from the nasopalatine duct. The cyst is
commonly asymptomatic and associated with
swelling that usually located in the midline of
anterior palate.
• Nasolabial cyst;
• Nasolabial cyst is a rare nonodontogenics,
• soft-tissue cyst occurring in the sublabial area
and anterior maxillary region. The patient
usually presents with a slowly enlarging
asymptomatic swelling.
• Globulomaxillary cyst;
The globulomaxillary cyst is
a cyst that appears between a maxillary lateral
incisor and the adjacent canine. It exhibits as an
"inverted pear-shaped radiolucency" on
radiographs, or X-ray films.
The globulomaxillary cyst often causes the
roots of adjacent teeth to diverge.
You might also like
- Odontogenic CystDocument16 pagesOdontogenic CystMahsaNo ratings yet
- Oral Radiology Principles and Interpretation 7th Ed PDFDocument14 pagesOral Radiology Principles and Interpretation 7th Ed PDFLaura Victoria Alvarez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- BDS10011 Cystic Lesions of Bone 2Document50 pagesBDS10011 Cystic Lesions of Bone 2habibahafez282No ratings yet
- cysts 1-مدمجDocument306 pagescysts 1-مدمجأمال داودNo ratings yet
- CYST - نسخةDocument71 pagesCYST - نسخةKHALED WALEEDNo ratings yet
- د.نجاة Cyst-7 (Muhadharaty) 1Document28 pagesد.نجاة Cyst-7 (Muhadharaty) 1بكر الدوريNo ratings yet
- Oral CystDocument47 pagesOral CystmelNo ratings yet
- CystDocument59 pagesCystHarshini DonepudiNo ratings yet
- CystsDocument180 pagesCystsDinesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Special Lecture 11Document15 pagesSpecial Lecture 11HussainNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The JawsDocument75 pagesCysts of The JawsSwetha KaripineniNo ratings yet
- l17 Management of CystsDocument55 pagesl17 Management of CystsJu JuNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts and Tumor of The JawsDocument149 pagesOdontogenic Cysts and Tumor of The JawsAnooda MazenNo ratings yet
- 3 CYSTS of The Soft Tissues and The Jaws PDFDocument28 pages3 CYSTS of The Soft Tissues and The Jaws PDFmarianaffernandes10No ratings yet
- RAMON - Cystic LesionDocument28 pagesRAMON - Cystic Lesionjamaica faith ramonNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic and Non Odontogenic Cysts of The Oral CavityDocument115 pagesOdontogenic and Non Odontogenic Cysts of The Oral CavitySalwa AboelmagdNo ratings yet
- Cyst of The JawsDocument13 pagesCyst of The Jawstthtn6c8pbNo ratings yet
- PDF Cyst 1-2Document122 pagesPDF Cyst 1-2Sadek MohamedNo ratings yet
- Omr Seminar CystDocument51 pagesOmr Seminar CystJohann GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Dental Radiology LectureDocument31 pagesDental Radiology LectureAbdullahayad farouqNo ratings yet
- Cysts MainDocument43 pagesCysts MainharshiniNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts and TumorsDocument273 pagesOdontogenic Cysts and TumorsAliImadAlKhasaki82% (11)
- Cysts MainDocument43 pagesCysts MainharshiniNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The JawsDocument28 pagesCysts of The JawsMladen PazinNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts: Dr. Amin AbusallamahDocument82 pagesOdontogenic Cysts: Dr. Amin Abusallamahmabula masungaNo ratings yet
- 3,3 - Cyst of Jaws and Oral Soft TissuesDocument19 pages3,3 - Cyst of Jaws and Oral Soft Tissuesحمزة تلاحمةNo ratings yet
- Dentigerous CystDocument25 pagesDentigerous CystDr. Deepanshi SutariaNo ratings yet
- Cyst of The JawDocument60 pagesCyst of The Jawafzanwahab100% (2)
- Odontogenic Cysts of The JAW: Seminar Presented byDocument31 pagesOdontogenic Cysts of The JAW: Seminar Presented byankita sethi100% (1)
- Cysts of The Oral CavityDocument270 pagesCysts of The Oral CavitySally Mahfouz100% (6)
- Seminar On Radicular CystDocument7 pagesSeminar On Radicular CystKhalid Mahmud Arifin100% (2)
- Cysts of The Jaws and Neck: Wil Dustin P. SinlaoDocument46 pagesCysts of The Jaws and Neck: Wil Dustin P. Sinlaojamaica faith ramonNo ratings yet
- Cysts Part2Document63 pagesCysts Part2abdelrahman amrNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystDocument16 pagesOdontogenic CystMahsaNo ratings yet
- Oral Surgery Benign Cysts P.2Document33 pagesOral Surgery Benign Cysts P.2abbasmazaal1234No ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystsDocument5 pagesOdontogenic CystsBH ASMRNo ratings yet
- Introduction Cysts of JawsDocument62 pagesIntroduction Cysts of JawsFatima Siddiqui100% (1)
- 7 Cysts of The Jaws 1 SlideDocument53 pages7 Cysts of The Jaws 1 SlideMohammed BohaliqahNo ratings yet
- Cyst 1Document59 pagesCyst 1محمد ربيعيNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystsDocument63 pagesOdontogenic CystsshabeelpnNo ratings yet
- Cyst Final-1Document120 pagesCyst Final-1drjatinNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystsDocument28 pagesOdontogenic Cystsووويويويةءتؤوبةين للاNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document43 pagesChapter 5mohmedNo ratings yet
- Eruption Cyst 22Document40 pagesEruption Cyst 22Taki EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Pseudocyst: R Gaushini Bds Cri Department of Oral and Maxilofacial PathologyDocument23 pagesPseudocyst: R Gaushini Bds Cri Department of Oral and Maxilofacial PathologyGautam RamuvelNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The Oral RegionDocument14 pagesCysts of The Oral RegionJASTHER LLOYD TOMANENGNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystsDocument54 pagesOdontogenic CystssamsoomaustNo ratings yet
- Cysts DentalDocument23 pagesCysts DentalApollo DentalNo ratings yet
- Introduction Cysts of JawsDocument62 pagesIntroduction Cysts of JawsEnass Alhadi50% (2)
- Odontogenic CystsDocument63 pagesOdontogenic CystsFaraz MohammedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1(2)Document9 pagesLecture 1(2)photo copyhemnNo ratings yet
- Cystak Diagnosztikája AngolDocument36 pagesCystak Diagnosztikája AngolErdeli StefaniaNo ratings yet
- 07 CystsDocument16 pages07 CystsNathnael GebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The JawDocument14 pagesCysts of The Jawluke swanepoelNo ratings yet
- Radicular CystDocument45 pagesRadicular CystPriyanka GanesanNo ratings yet
- Sebaceous Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSebaceous Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZFrom EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- The Dental Pulp: Biology, Pathology, and Regenerative TherapiesFrom EverandThe Dental Pulp: Biology, Pathology, and Regenerative TherapiesNo ratings yet
- Common Causes of Swelling in The Oral CavityDocument12 pagesCommon Causes of Swelling in The Oral CavityScribdNo ratings yet
- Radicular Cyst With Primary Mandibular Molar A RarDocument5 pagesRadicular Cyst With Primary Mandibular Molar A RargarciadeluisaNo ratings yet
- Radiography Jaw LesionsDocument19 pagesRadiography Jaw LesionssrikantnairNo ratings yet
- 4.radiolucent Inflammatory Jaw Lesions A TwentyyearDocument7 pages4.radiolucent Inflammatory Jaw Lesions A TwentyyearMihaela TuculinaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Oral CavityDocument4 pagesDiseases of Oral CavityStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- JaypeeDigital - Ebook ReaderDocument40 pagesJaypeeDigital - Ebook ReaderHanin AbukhiaraNo ratings yet
- Kramer 1992Document7 pagesKramer 1992Elite Dental AcademyNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kasus Tambahan 3 - Khairin Yonni (12730)Document6 pagesJurnal Kasus Tambahan 3 - Khairin Yonni (12730)Khairin YonniNo ratings yet
- Radicular CystDocument45 pagesRadicular CystPriyanka GanesanNo ratings yet
- MSQ. Oral Pathology. Dr. Hiwa KareemDocument13 pagesMSQ. Oral Pathology. Dr. Hiwa KareemAmmar YasirNo ratings yet
- CYSTSDocument3 pagesCYSTSfr.faisal8265No ratings yet
- Oral Pathology Vimal K Sikri Colour Guides, MCQ's Arpit SikriDocument585 pagesOral Pathology Vimal K Sikri Colour Guides, MCQ's Arpit SikriKrish NatbhanjanNo ratings yet
- Cysts and Odontogenic Tumors1 2Document41 pagesCysts and Odontogenic Tumors1 2Seca mandiNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The Oral RegionDocument14 pagesCysts of The Oral RegionJASTHER LLOYD TOMANENGNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystsDocument63 pagesOdontogenic CystsshabeelpnNo ratings yet
- Oral Path CramDocument10 pagesOral Path CramHarjotBrarNo ratings yet
- Dentigerous CystDocument16 pagesDentigerous CystMudjiono MudjionoNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Sinus 1Document61 pagesMaxillary Sinus 1saksheeNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystDocument16 pagesOdontogenic CystMahsaNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts: Dr. Amin AbusallamahDocument82 pagesOdontogenic Cysts: Dr. Amin Abusallamahmabula masungaNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Management of Impacted CanineDocument7 pagesOrthodontic Management of Impacted CanineplsssssNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts of The JAW: Seminar Presented byDocument31 pagesOdontogenic Cysts of The JAW: Seminar Presented byankita sethi100% (1)
- Differential Diagnosis of Pericoronal RadiolucenciesDocument30 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Pericoronal RadiolucenciesakNo ratings yet
- Dentigerous CystDocument25 pagesDentigerous CystDr. Deepanshi SutariaNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumor Ameloblastoma: Presented By: Ankita Singh Bds Final Year Roll No 37Document73 pagesOdontogenic Tumor Ameloblastoma: Presented By: Ankita Singh Bds Final Year Roll No 37ankita sethiNo ratings yet
- CEOT in ChildDocument7 pagesCEOT in ChildlilaNo ratings yet
- Case #1: Case Study Assignment Assignment #3Document10 pagesCase #1: Case Study Assignment Assignment #3api-536664543No ratings yet
- Gambaran Kista Dentigerous Gigi Premolar Rahang Atas Pada Radiograf CBCT: Laporan KasusDocument6 pagesGambaran Kista Dentigerous Gigi Premolar Rahang Atas Pada Radiograf CBCT: Laporan KasusSurya DimastiarNo ratings yet
- Quistes OdontogénicosDocument15 pagesQuistes OdontogénicosYsabel GutierrezNo ratings yet