Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HTS diagnostic flowcharts poster version 3 (003)
HTS diagnostic flowcharts poster version 3 (003)
Uploaded by
wadson chirwaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HTS diagnostic flowcharts poster version 3 (003)
HTS diagnostic flowcharts poster version 3 (003)
Uploaded by
wadson chirwaCopyright:
Available Formats
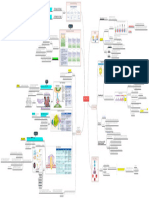
2023 Malawi HIV, Syphilis and Hepati ti s B Integrated Rapid Testi ng and Counselling Guidelines
HIV Testing Client Flow in the 2023 Registers 2023 HIV Diagnostic Algorithm for: Never tested, Last self-test (neg, pos, inc), Last professional test (neg, inc, exp infant) 2023 HIV Diagnostic Algorithm for Last Professional Positive Clients
Has the client ever been tested for HIV? If yes, was the most recent test:
Diagnostic Algorithm Recency Surveillance * Diagnostic Algorithm
Self-test or professional test? Documented results are preferred, but reported results are acceptable.
Blood Draw 1
Blood Draw 1
* Syphilis and hepatitis B tests are done in parallel with
Document previous test status in Initial Testing Register.
Regardless of previous test status: all clients follow the full serial 3-test algorithm HIV test 1 in certain entry points. Recency testing is only
Syphilis done in selected facilities
HIV Test 1 HIV Test 1
Hepatitis B * R = reactive
LT = long-term
Rec = recent R = reactive
Most recent: Most recent: NR R NR= non-reactive NR R
Never tested Neg = negative NR= non-reactive
Self-test Professional test
I n f or me d Co ns e nt
Blood Draw 2
Blood Draw 2
Negative, Initial positive*, New Recency
HIV Test 2 HIV Test 2
Negative, Positive or Invalid
Positive, New inconclusive, Test
Exposed infant, Positive or NR R LT Neg NR R
Inconclusive re-test Rec
Blood Draw 3
Blood Draw 3
Initial Register
HIV Test 1 HIV Test 1 HIV Test 3 DBS for VL HIV Test 1 HIV Test 3
* Initial Positive: Clients with a
NR R NR R <
positive HIV test 1 result 1000 1000 NR R NR R
(entered in the Initial Testing +
Interpretation
Interpre tation
HIV Test 1 positive Register) who did not complete
͞Initial positive͟Ύ the full 3-test algorithm Long-term Recent
(confirmatory testing). This may Negative Inconclusive Positive (Ignore) Negative Inconclusive Positive
Infection Infection
happen with community-based
testing.
Confirmatory Register
HIV Test 2, 3, 1, Recency
Result Given
Result Given
New New Positive Inconclusive Positive
Negative None
Inconclusive or Exp. Infant Re-test Re-test
New inconclusive, New positive, Patients on ART
HIV negative
Inconcl. re-test Positive re-test (once per year)
Repeat whole 3- Start ART as soon Continue / start ART as soon as client is ready
High risk event in last 72hrs: PEP, re- (No routine follow-up) Repeat whole 3-test algorithm after 2 weeks
test algorithm as client is ready (within 2 weeks). HIV exposed infant if client is <12
Referral
Referral
test after 4 weeks If repeat is still inconclusive: DBS for reference lab
after 2 weeks (within 2 weeks) months. All children under 24 months who start or
** Self- tests may be Ongoing risk: re-test after 12 months DBS result provides final diagnosis, except:
Send DBS to Ref. If repeat is still HIV exposed *All children under 24 months who start or re-start ART re-start ART need a confirmatory DNA-PCR using a
distributed for use by Client on PrEP: re-test 3-monthly If DBS is negative and client is on ART: interrupt ART, repeat
Lab if repeat Index register inconclusive: DBS infant if client is need a confirmatory DNA-PCR using a new DBS sample. new DBS sample. This should be collected on the
partners or others, regardless Refer high-risk for VMMC, PrEP, etc. 3-test algorithm after 3 months.
inconclusive for reference lab <12 months* This should be collected on the day of starting ART. day of starting ART.
of the recipients own HIV
status. However, never give
self-tests for self-use by
clients with a previous
positive or inconclusive test Contact Register
result.
Syphilis Screening Hepatitis B (surface antigen) screening
2023 Diagnostic Algorithm 2023 Diagnostic Algorithm
Self-test Distribution
Register**
Need for HBV
syphilis te st
Ne ed for
test
Not eligible Eligible* Not eligible Eligible*
HIV Risk Assessment
Syphilis test
HBV test
Hepatitis B surface
Syphilis Rapid Test
antigen rapid test
Low risk Ongoing risk High risk
(moderate)
No sex / abstinence Any of the 6 substantial risk factors defining PrEP need, but client is NR R NR R
Consistent and correct Stable partner with not, or not consistently, using PrEP:
HBV infection
Ask: previous
treatment?
condom use with all unknown HIV 1. Current or recent STI: in last 6 months, self-report or clinical
Treated for syphilis Never treated for
risk
partners status without diagnosis Low High*
in the past syphilis before
Consistent PrEP use* (any other high-risk 2. Transactional sex: paid or received money or goods for
partners) sexual partners condomless sex (incl. sex workers and clients)
Stable known HIV Born / breast 3. Condomless sex with a known HIV infected regular partner who is
negative partner who feeding from HIV not on ART or with viraemia 1000+ on their most recent VL result
Refer to lab for
HIV status***
confirmation
does not engage in risky infected mother on 4. Condomless sex with regular partner with unknown HIV status Lab tests for active Lab tests not
behaviour ART who has other high-risk sexual partners. infection** available*** HIV negative or
inconclusive HIV positive
Stable HIV infected 5. Condomless anal intercourse with non-regular partner NR R
partner who is taking ART 6. Injecting drug use with needle sharing
with viral load <1000 Rape (regardless of HIV status of perpetrator)
copies/ml on their most Condomless sex with non-regular partner (known pos. or unknown
Other tests and re- Full course of 3 Enroll in HBV clinic
recent result. HIV status) No syphilis treatment. Enroll in HBV clinic
test appointment HBV vaccinations for reporting.
Referral
Referral
Occupational exposure: needle stick injury, etc. Other tests and re-test for diagnostic
Treat for Syphilis based on risk (unless already Start or continue
Born / breastfeeding from HIV infected mother not on ART appointment based on risk follow-up /
assessment and completed in the ART for HIV and
assessment and guidelines treatment HBV
guidelines past)
*Consistent PrEP use means taking oral or injectable PrEP exactly as prescribed for the minimum required time before and after all risky acts (see PrEP guidelines)
* Eligibility for HBV testing: see Table 5 in Integrated Testing Guidelines for who and when to test for Hepatitis B.
* Eligibility for syphilis testing: see Table 5 in Integrated Testing Guidelines for who and when to test for syphilis.
** Table 5 shows high risk groups who should be referred for a course of 3 HBV vaccinations unless they have
But: condomless sex carries high risk of unwanted pregnancy ** Lab test for active infection: Clients with a previous syphilis infection usually have a positive rapid test for life, even previously completed 3 HBV vaccinations: FSW, TG, MSW, MSM, PWID, prisoners, PrEP clients, children 0-14 years born
ART and PrEP are and STIs if the infection was cured. Additional lab tests (RPR or VDRL) are needed to confirm a new, active syphilis infection. to HBV positive women, STI patients, general population at ongoing HIV risk or after high-risk event, health workers,
!
very effective Some STIs can not be cured and may cause ugly sores on *** Lab tests not available: Lab tests for confirmation of active syphilis infection may not be available at all sites. In sex partners of HBV index clients, sex partners of STI patients, presumed hepatitis patients, in-patients.
HIV prevention genitals, long-term suffering, cancer and death (hepatitis this case, refer for presumptive syphilis treatment to ensure that any potentially new syphilis infection is treated. *** HIV status must be ascertained for all HBV positive clients. Perform a new HIV test using the full 3-test algorithm
methods if used B, herpes simplex, HPV, HTLV) unless the client is already known to be HIV positive.
consistently Even curable STIs are often missed, causing infertility,
stillbirth, nerve and brain damage, etc.
You might also like
- Testing_Algorithms Revised March 2024Document35 pagesTesting_Algorithms Revised March 2024wadson chirwaNo ratings yet
- Package Insert Determine HIV 1 2 Ag Ab ComboDocument22 pagesPackage Insert Determine HIV 1 2 Ag Ab ComboSutiniNo ratings yet
- IAFP STEC Poster - v03Document1 pageIAFP STEC Poster - v03chiralicNo ratings yet
- Statistics Formula TablesDocument8 pagesStatistics Formula TablesSamantha RodriguezNo ratings yet
- PMT HPS SmartSensors Analytical Instruments BrochureDocument8 pagesPMT HPS SmartSensors Analytical Instruments BrochureSharad GargNo ratings yet
- Rapide Test PDFDocument6 pagesRapide Test PDFMusa abidinNo ratings yet
- ND ST: Indicator Label Means of Measurement of Labelled Product/analyteDocument2 pagesND ST: Indicator Label Means of Measurement of Labelled Product/analytejana encaboNo ratings yet
- OSIS12 H. Pylori Antibody NouDocument4 pagesOSIS12 H. Pylori Antibody Nouwilder sarceñoNo ratings yet
- Immuno and Sero Midterm LabDocument1 pageImmuno and Sero Midterm LabSuk Yeong SongNo ratings yet
- Hiv Testing in The Era of Prep:: When The Tests Are DiscordantDocument17 pagesHiv Testing in The Era of Prep:: When The Tests Are DiscordantAldren GilanaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Validation of HIV Rapid Tests For Recent - IAS - EYDocument16 pagesLaboratory Validation of HIV Rapid Tests For Recent - IAS - EYkiwkiwNo ratings yet
- PN 91134 Rev. B Package Insert A1CNow EN - DE - FR - IT - Pro IFCCDocument2 pagesPN 91134 Rev. B Package Insert A1CNow EN - DE - FR - IT - Pro IFCCKepala HitamNo ratings yet
- 27 Pekeliling KPK 1-2011-CARTA ALIR - UJIAN PENGESAHAN HIVDocument20 pages27 Pekeliling KPK 1-2011-CARTA ALIR - UJIAN PENGESAHAN HIVsiti nur aishah jalilNo ratings yet
- Anigen Rapid Test Kit: Caniv-4Document1 pageAnigen Rapid Test Kit: Caniv-4cleoinNo ratings yet
- Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc.: ADVIA Centaur XP Version 1.0.EC and 1.0.ED Test DefinitionsDocument12 pagesSiemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc.: ADVIA Centaur XP Version 1.0.EC and 1.0.ED Test DefinitionsОлександрNo ratings yet
- OG7 V3 Prime Mover Inspection Checklist Jun 2015Document2 pagesOG7 V3 Prime Mover Inspection Checklist Jun 2015Asela Bandara100% (1)
- Law of TortsDocument12 pagesLaw of TortsGrossAlasNo ratings yet
- Holahan Sloan Poster YaleDocument1 pageHolahan Sloan Poster Yaleapi-416977976No ratings yet
- Real-Time Alerting System For COVID-19 and Other Stress Events Using Wearable DataDocument26 pagesReal-Time Alerting System For COVID-19 and Other Stress Events Using Wearable DataLuiz Folha FlaskNo ratings yet
- Wa0001.Document2 pagesWa0001.akashcool470No ratings yet
- Surveilence Hais: Dr. Elsye Maria Rosa, M.KepDocument9 pagesSurveilence Hais: Dr. Elsye Maria Rosa, M.KepEni MuchlisohNo ratings yet
- Information Zur Anwendung Der Selbsttests Xiamen Boson Biotech - Rapid Sars-Cov-2 Antigen TestDocument3 pagesInformation Zur Anwendung Der Selbsttests Xiamen Boson Biotech - Rapid Sars-Cov-2 Antigen TestmaxvaneykNo ratings yet
- Cepheid Xpert Xpress CoV 2 Plus Comparison EUA 0923 English HIRDocument2 pagesCepheid Xpert Xpress CoV 2 Plus Comparison EUA 0923 English HIRaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Serumindexliste Für COBAS INTEGRA Systeme - V22Document11 pagesSerumindexliste Für COBAS INTEGRA Systeme - V22Waleed YaserNo ratings yet
- Ra For Concreate Floor BreakingDocument5 pagesRa For Concreate Floor Breakingshamshad ahamedNo ratings yet
- Algoritme Tes Serologi Toxoplasma (ARUP Laboratories 2010)Document1 pageAlgoritme Tes Serologi Toxoplasma (ARUP Laboratories 2010)Endang Frida SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Symposium Board 1Document1 pageSymposium Board 1api-482373029No ratings yet
- Preference For Long Acting Injectable (Lai) Antiretrovirals For Hiv Treatment or Prep in ArgentinaDocument1 pagePreference For Long Acting Injectable (Lai) Antiretrovirals For Hiv Treatment or Prep in ArgentinaAli CamelliNo ratings yet
- Brochure Canine Babesia AbDocument2 pagesBrochure Canine Babesia AbPatricia LupuNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Phosphatase Opt - Au400Document2 pagesAlkaline Phosphatase Opt - Au400Nghi NguyenNo ratings yet
- The 3rd Generation of ONE STEP Antibodies To HIV-1/HIV-2 TestDocument2 pagesThe 3rd Generation of ONE STEP Antibodies To HIV-1/HIV-2 TestFensi AndraNo ratings yet
- 【Brochure】Getein 1100Document6 pages【Brochure】Getein 1100Aomago Spy GadgetsNo ratings yet
- Elecsys® Anti-HAV IgM Immunoassay For The Qualitative Detection of IgM Antibodies Against HAVDocument4 pagesElecsys® Anti-HAV IgM Immunoassay For The Qualitative Detection of IgM Antibodies Against HAVLAMA LAMANo ratings yet
- Departments of Neurology, James J. Peters Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Bronx, NY, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NYDocument1 pageDepartments of Neurology, James J. Peters Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Bronx, NY, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NYyuliNo ratings yet
- EUA Genabio rapidkitOTC ifuHT - 0Document6 pagesEUA Genabio rapidkitOTC ifuHT - 0Alexander StewartNo ratings yet
- Guide Test Strip Insert - 85125 - 09074937004 - WEBDocument2 pagesGuide Test Strip Insert - 85125 - 09074937004 - WEBErsa BayungNo ratings yet
- Argene Covid-19 Solutions Ce Marked - 9321502 007-Gb-A 3 0Document2 pagesArgene Covid-19 Solutions Ce Marked - 9321502 007-Gb-A 3 0Yaser MNo ratings yet
- Usaid An Icn Hemocue Population 2022Document1 pageUsaid An Icn Hemocue Population 2022Samson DesieNo ratings yet
- MODULE B TBPresentation3Document62 pagesMODULE B TBPresentation3Jerommy MalweleNo ratings yet
- 175-300 T3 AccuLite CLIA Rev 4Document2 pages175-300 T3 AccuLite CLIA Rev 4cxjvxsogzbNo ratings yet
- LEPU Antigen Selftesting Brochure-MinDocument7 pagesLEPU Antigen Selftesting Brochure-Minleopa78No ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument16 pagesEconomicsGrossAlasNo ratings yet
- Program Medicine and Supplies Stock Status Reporting TemplateDocument11 pagesProgram Medicine and Supplies Stock Status Reporting TemplateTadiwos BelihuNo ratings yet
- INGUN GKS Katalog DE PDFDocument178 pagesINGUN GKS Katalog DE PDFJuanilloNo ratings yet
- 007 GB A Argene Covid19 RespiratoryDocument2 pages007 GB A Argene Covid19 RespiratorySachinNo ratings yet
- RA For SPT Test (Reviewed)Document5 pagesRA For SPT Test (Reviewed)shamshad ahamedNo ratings yet
- Hep ABC - Lab DiagnosisDocument15 pagesHep ABC - Lab DiagnosisjunaidiabdhalimNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Info Sheet SBM PDFDocument2 pagesPregnancy Info Sheet SBM PDFRameesa KhanNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Testing Overview Molecular Antigen Antibody 0920Document2 pagesCovid 19 Testing Overview Molecular Antigen Antibody 0920ArdityaNo ratings yet
- Catcment Area Meeting PPT TemplateDocument31 pagesCatcment Area Meeting PPT TemplateEssie MohammedNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Testing For COVID-19 - Dr. Trilis Yulianti, M.kesDocument20 pagesLaboratory Testing For COVID-19 - Dr. Trilis Yulianti, M.kesYayax RakhmanNo ratings yet
- Asha Monthly Reports - Aprial MonthDocument64 pagesAsha Monthly Reports - Aprial MonthSamuel SourabNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of RightsDocument23 pagesCharacteristics of RightsArnav LekharaNo ratings yet
- Anti Streptolysin o - Au400Document2 pagesAnti Streptolysin o - Au400Nghi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Post Market Review of Antigen and Rapid Antigen Tests TableDocument33 pagesPost Market Review of Antigen and Rapid Antigen Tests Tableray mantaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment FormDocument12 pagesHealth Assessment Formmiha3la33No ratings yet
- Mappa MicroDocument1 pageMappa MicroCarlotta RanalliNo ratings yet
- Pathology Last 10 YearsDocument20 pagesPathology Last 10 YearsVastya RishiNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument24 pagesCommunicationwadson chirwaNo ratings yet
- OSH450 Documents W02 Water Quality Testing FormDocument2 pagesOSH450 Documents W02 Water Quality Testing Formwadson chirwaNo ratings yet
- Index Testing -ME Register ADocument33 pagesIndex Testing -ME Register Awadson chirwaNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Morphology - 6.Document24 pagesMammalian Morphology - 6.wadson chirwaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - 1Document13 pagesCourse Outline - 1wadson chirwaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Elevation On Distribution of Female Bats in The Black Hills, South DakotaDocument7 pagesEffect of Elevation On Distribution of Female Bats in The Black Hills, South Dakotawadson chirwaNo ratings yet
- Eurasia Research Pharma Corporation: e Effective SupersedesDocument10 pagesEurasia Research Pharma Corporation: e Effective SupersedesErine FelipeNo ratings yet
- Forensci Medicine Test 2Document12 pagesForensci Medicine Test 2Bashiru SelemaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice 1-Pre-Board Exam-Vmuf-College of Nursing-Revalida 2021Document52 pagesNursing Practice 1-Pre-Board Exam-Vmuf-College of Nursing-Revalida 2021Dyanne Bautista67% (3)
- HPV Amostras AlternativasDocument6 pagesHPV Amostras Alternativasnathaliasantosx3No ratings yet
- SWMS Sample - Safe Work MethodDocument8 pagesSWMS Sample - Safe Work Methodsupasart100% (1)
- Opium: Retail and Wholesale Prices and Purity Levels: Breakdown by Drug, Region and Country or TerritoryDocument19 pagesOpium: Retail and Wholesale Prices and Purity Levels: Breakdown by Drug, Region and Country or TerritoryboombaNo ratings yet
- The Fault in Our Stars-Extract 1-2 QuestionsDocument6 pagesThe Fault in Our Stars-Extract 1-2 QuestionsNathaly Yessenia Luque CruzNo ratings yet
- Anti-Hangover ShotsDocument10 pagesAnti-Hangover ShotsSaniya ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Coconut Climbing MachineDocument2 pagesCoconut Climbing MachineVon A. Damirez100% (1)
- English 7 q1 m7 EditedDocument11 pagesEnglish 7 q1 m7 EditedShei La Ma RieNo ratings yet
- CNCS Organization Assessment Tool Final 082517 508 0Document29 pagesCNCS Organization Assessment Tool Final 082517 508 0Nicole TaylorNo ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Examination SyllabusDocument122 pagesUPSC Civil Services Examination SyllabusnityagpkNo ratings yet
- ReseachDocument20 pagesReseachLila GrayNo ratings yet
- 07 One Missing StrokeDocument10 pages07 One Missing StrokeMiura AngNo ratings yet
- Drug Desensitization PenicillinDocument19 pagesDrug Desensitization PenicillinpdahlianaNo ratings yet
- ANCC NCPD ManualDocument58 pagesANCC NCPD Manualshadi alshadafanNo ratings yet
- Migraine & Cluster HeadachesDocument12 pagesMigraine & Cluster HeadachesBigabwa BernardNo ratings yet
- Tele Med and Tele NursingDocument14 pagesTele Med and Tele NursingVineeta Jose100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 2 - MELC 2: Discipline and Ideas in Applied Social SciencesDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Quarter 2 - MELC 2: Discipline and Ideas in Applied Social Sciencesgayle gallaza100% (1)
- Controlling Behavior: Pam Britton Reese Nena C. ChallennerDocument32 pagesControlling Behavior: Pam Britton Reese Nena C. ChallennerZarghoona0% (1)
- Cartão de Vacina CovidDocument2 pagesCartão de Vacina CovidEvanildo MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Swimmer Syndrome in WildlifeDocument2 pagesSwimmer Syndrome in WildlifeALicjaNo ratings yet
- Shampoo BarDocument1 pageShampoo BarrezaNo ratings yet
- Fibromyalgia: Annals of Internal MedicineDocument16 pagesFibromyalgia: Annals of Internal MedicineTeofanes PonceNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment And Analysis/ ـرطاـخملـا مييق ــت: Excavation WorksDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment And Analysis/ ـرطاـخملـا مييق ــت: Excavation WorksSibgathullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- AB Lounge 2 ManualDocument13 pagesAB Lounge 2 ManualStacy MinnsNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Test - Q4 English 5Document4 pagesQuarterly Test - Q4 English 5Bem JazzelNo ratings yet
- The Shadow From A Buddhist PerspectiveDocument14 pagesThe Shadow From A Buddhist PerspectiveGuilherme SimãoNo ratings yet
- Luma - Health Insurance Quotation - May Kabyar Oo (3 Options)Document3 pagesLuma - Health Insurance Quotation - May Kabyar Oo (3 Options)Kabyar MayNo ratings yet
- Polarization Index Report Mar22Document22 pagesPolarization Index Report Mar22Nicola RovettaNo ratings yet