Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UNIT 1_1707324621_5000665_presentation4
UNIT 1_1707324621_5000665_presentation4
Uploaded by
umamahesh8838Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ceragon FibeAir IP 20N Technical Description 10.9 Rev A.04Document468 pagesCeragon FibeAir IP 20N Technical Description 10.9 Rev A.04Anonymous hhzIYBNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabFrom EverandSimulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Nice Design ConsiderationsDocument178 pagesNice Design ConsiderationsMax MostwantedNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing 1ST UnitDocument8 pagesMultiplexing 1ST UnitrajveerNo ratings yet
- Multiple Xing and Communication MediaDocument13 pagesMultiple Xing and Communication MediaRanvijayNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing and SwitchingDocument26 pagesMultiplexing and SwitchingsdfasdfNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLEXINGDocument9 pagesMULTIPLEXINGabhijitraj229No ratings yet
- What Is MultiplexingDocument22 pagesWhat Is Multiplexingrashidochieng35No ratings yet
- Computer Network Unit IIIDocument12 pagesComputer Network Unit IIIPinjari Soyab ShakilNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument10 pagesMultiplexingjacob ellyNo ratings yet
- CN-lecture11 MultiplexingDocument8 pagesCN-lecture11 MultiplexingⲤʟᴏᴡɴᴛᴇʀ ᏀᴇɪꜱᴛNo ratings yet
- 2nd ModuleDocument20 pages2nd ModuleJoy SinghaNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument4 pagesMultiplexingDarmoni LaishramNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 PPT-1Document13 pagesChapter - 5 PPT-1Simran KachchhiNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument5 pagesMultiplexingTaimoor ZubairNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Multiplexing TechniqDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Multiplexing TechniqJoshua DomaNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth UtilizattionDocument22 pagesBandwidth Utilizattion82Neha PalNo ratings yet
- Types of Multiplexers: MultiplexingDocument10 pagesTypes of Multiplexers: MultiplexingShinobiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Fahad SirDocument5 pagesAssignment Fahad Sirvideos FlowNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument34 pagesMultiplexingNikhita VNo ratings yet
- VC and MultiplexingDocument4 pagesVC and MultiplexingManohar ManuNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing 200925134300Document17 pagesMultiplexing 200925134300Rom John JucutanNo ratings yet
- Multiple XingDocument30 pagesMultiple XingPrachi Arjun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 4-2 5Document17 pagesChapter-2 4-2 5bhattanushka60No ratings yet
- Multiplexing & TechniquesDocument29 pagesMultiplexing & TechniquesAnosha AmjadNo ratings yet
- MulitplextiongDocument20 pagesMulitplextiongelvis page kamunanwireNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument40 pagesMultiplexingsarika satyaNo ratings yet
- The Concept of MultiplexingDocument18 pagesThe Concept of MultiplexingsnehaNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spectrum SpreadingDocument17 pagesBandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spectrum SpreadingSuvo IslamNo ratings yet
- MUltiplexing FinalDocument6 pagesMUltiplexing FinalPratham KangraNo ratings yet
- Multiplex ErsDocument4 pagesMultiplex ErsJayaprakash DasNo ratings yet
- Idresss Sir#7 (OKDocument14 pagesIdresss Sir#7 (OKDil NawazNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3: MultiplexingDocument6 pagesAssignment # 3: MultiplexingSuper NaturalNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument5 pagesMultiplexingFarrukh BaigNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument37 pagesComputer NetworksABU SUFYANNo ratings yet
- ADC Unit 5 PPT 1Document16 pagesADC Unit 5 PPT 1Himanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is Multiplexing ?explain Its Need and Basic Format of MultiplexingDocument9 pagesWhat Is Multiplexing ?explain Its Need and Basic Format of MultiplexingVarun H SNo ratings yet
- Basic of MultiplexingDocument4 pagesBasic of MultiplexingÁñúrāG 444No ratings yet
- BECEA Time Division and Frequencydivision MultiplexingDocument10 pagesBECEA Time Division and Frequencydivision Multiplexingjaswantjangid2732No ratings yet
- Multiplexing and Multiple Access Techniques Multiplexing and Multiple Access TechniquesDocument89 pagesMultiplexing and Multiple Access Techniques Multiplexing and Multiple Access TechniquesSantosh Thapa0% (1)
- Ghazi University, Dera Ghazi KhanDocument10 pagesGhazi University, Dera Ghazi KhanIftakhar HussainNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document120 pagesTopic 3Chris DannyNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument16 pagesMultiplexingMahendran RajNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing NotesDocument5 pagesMultiplexing Notesgayathripanchumarthi30No ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument25 pagesMultiplexingisratjahanchandmoniNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument16 pagesMultiplexingAnju OzaNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer 4Document23 pagesPhysical Layer 4soumen maityNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing FDM TDM and TCM PDFDocument8 pagesMultiplexing FDM TDM and TCM PDFQuang Nghĩa VõNo ratings yet
- ECE 542 - Lecture 4Document24 pagesECE 542 - Lecture 4JohnCross DavidMaryNo ratings yet
- CH#5. MultiplexingDocument16 pagesCH#5. MultiplexingShining StarNo ratings yet
- Mux and DeMux (FOT)Document33 pagesMux and DeMux (FOT)Arjun Yadav100% (1)
- Multiplexing:: ApllicationsDocument6 pagesMultiplexing:: ApllicationsMominaIdreesNo ratings yet
- Multiple XingDocument20 pagesMultiple Xingrashidhusain112023No ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Unit 1Document7 pagesMobile Computing Unit 1smart IndiaNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication - MultiplexingDocument4 pagesAnalog Communication - MultiplexingcdrupwestNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing (Bandwidth Utilization) (Compatibility Mode)Document32 pagesMultiplexing (Bandwidth Utilization) (Compatibility Mode)Shivam KushwahaNo ratings yet
- MCC-Assignment 1-12c027Document5 pagesMCC-Assignment 1-12c027Saif ChogleNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing - Definition - Types of Multiplexing: FDM, WDM, TDMDocument14 pagesMultiplexing - Definition - Types of Multiplexing: FDM, WDM, TDMYohannis DanielNo ratings yet
- Ans:A Multiplexing Technique by Which Multiple Data Signals: Q:Briefly Explain TDM. What Is Interleaving ?Document2 pagesAns:A Multiplexing Technique by Which Multiple Data Signals: Q:Briefly Explain TDM. What Is Interleaving ?Gypsy WarheadNo ratings yet
- John Alcon D. Jerao Bsece-5 Assignment 1Document3 pagesJohn Alcon D. Jerao Bsece-5 Assignment 1justine jeraoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document121 pagesChapter 3Muhammad ZakiyNo ratings yet
- Connection Master: DatasheetDocument11 pagesConnection Master: DatasheetMd IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 1KHW002460-FOX61x-Product Features and Characteristics - pb4 PDFDocument156 pages1KHW002460-FOX61x-Product Features and Characteristics - pb4 PDFMartin AdasmeNo ratings yet
- Dialogic SDKDocument592 pagesDialogic SDKphpscottNo ratings yet
- (MCQ) Computer Communication Networks - LMT2Document14 pages(MCQ) Computer Communication Networks - LMT2raghad mejeedNo ratings yet
- Optical CDMA: Technique, Parameters and ApplicationsDocument9 pagesOptical CDMA: Technique, Parameters and ApplicationsSaurabh SalveNo ratings yet
- Smart Car PPT JejuDocument22 pagesSmart Car PPT JejuSaurabhKGuptaNo ratings yet
- I PASOLINKDocument56 pagesI PASOLINKAster Takele OfficialNo ratings yet
- Alu DWDM PDFDocument39 pagesAlu DWDM PDFShewan Alam SuhreedNo ratings yet
- M.tech - Communication Engineering and Signal ProcessingDocument19 pagesM.tech - Communication Engineering and Signal ProcessingSreeraj S J ee17d033No ratings yet
- Vmux 2100Document8 pagesVmux 2100Mohamed MoujtabaNo ratings yet
- RTN 910 Product Description (V100R001C02 - 03)Document111 pagesRTN 910 Product Description (V100R001C02 - 03)hannah8201100% (1)
- 01 iPASO 400-1000 Introduction1Document53 pages01 iPASO 400-1000 Introduction1Wubie NegaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Telecom Transmission & Switching TechniqueDocument14 pagesAssignment: Telecom Transmission & Switching TechniqueHAJRA khalidNo ratings yet
- COMM1208 Unit6 PCM SamplingDocument13 pagesCOMM1208 Unit6 PCM SamplingidatscribdNo ratings yet
- TUT2 SolDocument4 pagesTUT2 Solshini s gNo ratings yet
- (Presentation) GPON Vs EPONDocument14 pages(Presentation) GPON Vs EPONLiêm TrầnNo ratings yet
- BG Product LiDocument90 pagesBG Product LiLarba SawadogoNo ratings yet
- Brochure VR 10Document2 pagesBrochure VR 10didi100% (1)
- T1/E1 Digital Voice Port Adapter Installation and ConfigurationDocument96 pagesT1/E1 Digital Voice Port Adapter Installation and ConfigurationSergiu SergiuNo ratings yet
- Department of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab ManualDocument29 pagesDepartment of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab Manualమొక్కపాటి మాధవిNo ratings yet
- Mobicents SS7Stack User GuideDocument82 pagesMobicents SS7Stack User GuideNicTanaseNo ratings yet
- cs2 NotesDocument35 pagescs2 NotesMukul BhallaNo ratings yet
- Time Division MultiplexingDocument51 pagesTime Division MultiplexingTareq QaziNo ratings yet
- TRM Minilinktnpresentationbykhalil 170517191312 PDFDocument94 pagesTRM Minilinktnpresentationbykhalil 170517191312 PDFjamos200100% (2)
- Unit 3: Multiplexing and Switching: StructureDocument19 pagesUnit 3: Multiplexing and Switching: StructureNilesh SawantNo ratings yet
- Lista de AlarmesDocument7 pagesLista de AlarmesMarcos AlexandreNo ratings yet
- Networking Interview QuestionsDocument15 pagesNetworking Interview QuestionsArif HussainNo ratings yet
- 01 OptiX RTN 900 V100R002 Product Description 20100223 ADocument54 pages01 OptiX RTN 900 V100R002 Product Description 20100223 AJoseLuis AvilaNo ratings yet
UNIT 1_1707324621_5000665_presentation4
UNIT 1_1707324621_5000665_presentation4
Uploaded by
umamahesh8838Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT 1_1707324621_5000665_presentation4
UNIT 1_1707324621_5000665_presentation4
Uploaded by
umamahesh8838Copyright:
Available Formats
UNIT-1
Foundation of Computer Networks
1.1 Data communication Components
1.2 Representation of data and its flow Networks
1.3 Various Connection Topology
1.4 Protocols and Standards : OSI model
1.5 Transmission Control Protocol (TCP/IP):Frame Format Dr. R C Sahoo
1.6 Multiplexing - FDM, TDM and WDM Assoc. Professor
1.7 Spread Spectrum Techniques. (CSE)
TOPOLOGY : CO-1&2, BTL -1, 2
Dr. Ramesh Ch Sahoo
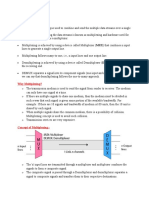
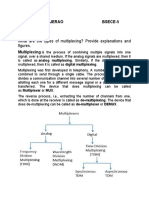
Multiplexing
It is the set of techniques that allows the simultaneous transmission
of multiple signals across a single data link.
Multiplexing is done using a device called Multiplexer (MUX) that
combine n input lines to generate one output line i.e. (many to one).
At the receiving end a device called Demultiplexer (DEMUX) is used
that separate signal into its component signals i.e. one input and
several outputs (one to many)
Advantages of Multiplexing
More than one signals can be sent over single medium or link
Effective use of the bandwidth of medium
TYPES of MULTIPLEXING
Dr. Ramesh Ch Sahoo
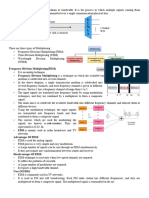
Frequency Division Multiplexing
o Frequency Division Multiplexing is a technique in which the available bandwidth of a single
transmission medium is subdivided into several channels.
o In the above diagram, a single transmission medium is subdivided into several frequency channels, and
each frequency channel is given to different devices.
o The input signals are translated into frequency bands by using modulation techniques, and they are
combined by a multiplexer to form a composite signal.
o The main aim of the FDM is to subdivide the available bandwidth into different frequency channels and
allocate them to different devices.
o Using the modulation technique, the input signals are transmitted into frequency bands and then
combined to form a composite signal.
o The carriers which are used for modulating the signals are known as sub-carriers. They are
represented as f1,f2..fn.
FDM is mainly used in radio broadcasts and TV networks
Dr. Ramesh Ch Sahoo
Advantages Of FDM:
o FDM is used for analog signals.
o FDM process is very simple and easy modulation.
o A Large number of signals can be sent through an FDM simultaneously.
o It does not require any synchronization between sender and receiver.
Disadvantages Of FDM:
o FDM technique is used only when low-speed channels are required.
o It suffers the problem of crosstalk.
o A Large number of modulators are required.
o It requires a high bandwidth channel.
Applications of FDM
FDM is used for FM & AM radio broadcasting.
AM frequency = 530 to 1700 kHz.
FM frequency = 88 to 108 MHz.
FDM is used in television broadcasting.
First generation cellular telephone also uses FDM.
Dr. Ramesh Ch Sahoo
Wave Division Multiplexing
WDM is an analog multiplexing technique.
Working is same as FDM.
In WDM different signals are optical or light signals that are transmitted through optical fiber.
Various light waves from different sources are combined to form a composite light signal that is
transmitted across the channel to the receiver.
At the receiver side, this composite light signal is broken into different light waves by Demultiplexer.
This Combining and the Splitting of light waves is done by using a PRISM. Prism bends beam of light
based on the angle of incidence and the frequency of light wave.
o At the receiving end, demultiplexer separates the signals to transmit them to their respective
destinations.
o Multiplexing and Demultiplexing can be achieved by using a prism.
o Prism can perform a role of multiplexer by combining the various optical signals to form a composite
signal, and the composite signal is transmitted through a fibre optical cable.
o Prism also performs a reverse operation, i.e., demultiplexing the signal.
Dr. Ramesh Ch Sahoo
Time Division Multiplexing
o It is a digital technique.
o In Frequency Division Multiplexing Technique, all signals operate at the same time with different
frequency, but in case of Time Division Multiplexing technique, all signals operate at the same frequency
with different time.
o In Time Division Multiplexing technique, the total time available in the channel is distributed among
different users. Therefore, each user is allocated with different time interval known as a Time slot at
which data is to be transmitted by the sender.
o A user takes control of the channel for a fixed amount of time.
o In Time Division Multiplexing technique, data is not transmitted simultaneously rather the data is
transmitted one-by-one.
o In TDM, the signal is transmitted in the form of frames. Frames contain a cycle of time slots in which
each frame contains one or more slots dedicated to each user.
o It can be used to multiplex both digital and analog signals but mainly used to multiplex digital signals.
There are two types of TDM:
o Synchronous TDM
o Asynchronous TDM
Dr. Ramesh Ch Sahoo
Synchronous TDM
o A Synchronous TDM is a technique in which time slot is preassigned to every device.
o In Synchronous TDM, each device is given some time slot irrespective of the fact that the device contains
the data or not.
o If the device does not have any data, then the slot will remain empty.
o In Synchronous TDM, signals are sent in the form of frames. Time slots are organized in the form of frames.
If a device does not have data for a particular time slot, then the empty slot will be transmitted.
o The most popular Synchronous TDM are T-1 multiplexing, ISDN multiplexing, and SONET multiplexing.
o If there are n devices, then there are n slots.
Disadvantages Of Synchronous TDM:
o The capacity of the channel is not fully utilized as the empty slots are also transmitted which is having no
data. In the above figure, the first frame is completely filled, but in the last two frames, some slots are
empty. Therefore, we can say that the capacity of the channel is not utilized efficiently.
o The speed of the transmission medium should be greater than the total speed of the input lines. An
alternative approach to the Synchronous TDM is Asynchronous Time Division Multiplexing.
Dr. Ramesh Ch Sahoo
Asynchronous TDM
o An asynchronous TDM is also known as Statistical TDM.
o An asynchronous TDM is a technique in which time slots are not fixed as in the case of Synchronous TDM. Time slots are
allocated to only those devices which have the data to send. Therefore, we can say that Asynchronous Time Division
multiplexor transmits only the data from active workstations.
o An asynchronous TDM technique dynamically allocates the time slots to the devices.
o In Asynchronous TDM, total speed of the input lines can be greater than the capacity of the channel.
o Asynchronous Time Division multiplexor accepts the incoming data streams and creates a frame that contains only data with
no empty slots.
o In Asynchronous TDM, each slot contains an address part that identifies the source of the data.
o The difference between Asynchronous TDM and Synchronous TDM is that many slots in Synchronous TDM are unutilized, but in
Asynchronous TDM, slots are fully utilized. This leads to the smaller transmission time and efficient utilization of the capacity of the
channel.
o In Synchronous TDM, if there are n sending devices, then there are n time slots. In Asynchronous TDM, if there are n sending devices,
then there are m time slots where m is less than n (m<n).
o The number of slots in a frame depends on the statistical analysis of the number of input lines.
Dr. Ramesh Ch Sahoo
You might also like
- Ceragon FibeAir IP 20N Technical Description 10.9 Rev A.04Document468 pagesCeragon FibeAir IP 20N Technical Description 10.9 Rev A.04Anonymous hhzIYBNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabFrom EverandSimulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Nice Design ConsiderationsDocument178 pagesNice Design ConsiderationsMax MostwantedNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing 1ST UnitDocument8 pagesMultiplexing 1ST UnitrajveerNo ratings yet
- Multiple Xing and Communication MediaDocument13 pagesMultiple Xing and Communication MediaRanvijayNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing and SwitchingDocument26 pagesMultiplexing and SwitchingsdfasdfNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLEXINGDocument9 pagesMULTIPLEXINGabhijitraj229No ratings yet
- What Is MultiplexingDocument22 pagesWhat Is Multiplexingrashidochieng35No ratings yet
- Computer Network Unit IIIDocument12 pagesComputer Network Unit IIIPinjari Soyab ShakilNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument10 pagesMultiplexingjacob ellyNo ratings yet
- CN-lecture11 MultiplexingDocument8 pagesCN-lecture11 MultiplexingⲤʟᴏᴡɴᴛᴇʀ ᏀᴇɪꜱᴛNo ratings yet
- 2nd ModuleDocument20 pages2nd ModuleJoy SinghaNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument4 pagesMultiplexingDarmoni LaishramNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 PPT-1Document13 pagesChapter - 5 PPT-1Simran KachchhiNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument5 pagesMultiplexingTaimoor ZubairNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Multiplexing TechniqDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Multiplexing TechniqJoshua DomaNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth UtilizattionDocument22 pagesBandwidth Utilizattion82Neha PalNo ratings yet
- Types of Multiplexers: MultiplexingDocument10 pagesTypes of Multiplexers: MultiplexingShinobiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Fahad SirDocument5 pagesAssignment Fahad Sirvideos FlowNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument34 pagesMultiplexingNikhita VNo ratings yet
- VC and MultiplexingDocument4 pagesVC and MultiplexingManohar ManuNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing 200925134300Document17 pagesMultiplexing 200925134300Rom John JucutanNo ratings yet
- Multiple XingDocument30 pagesMultiple XingPrachi Arjun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 4-2 5Document17 pagesChapter-2 4-2 5bhattanushka60No ratings yet
- Multiplexing & TechniquesDocument29 pagesMultiplexing & TechniquesAnosha AmjadNo ratings yet
- MulitplextiongDocument20 pagesMulitplextiongelvis page kamunanwireNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument40 pagesMultiplexingsarika satyaNo ratings yet
- The Concept of MultiplexingDocument18 pagesThe Concept of MultiplexingsnehaNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spectrum SpreadingDocument17 pagesBandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spectrum SpreadingSuvo IslamNo ratings yet
- MUltiplexing FinalDocument6 pagesMUltiplexing FinalPratham KangraNo ratings yet
- Multiplex ErsDocument4 pagesMultiplex ErsJayaprakash DasNo ratings yet
- Idresss Sir#7 (OKDocument14 pagesIdresss Sir#7 (OKDil NawazNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3: MultiplexingDocument6 pagesAssignment # 3: MultiplexingSuper NaturalNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument5 pagesMultiplexingFarrukh BaigNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument37 pagesComputer NetworksABU SUFYANNo ratings yet
- ADC Unit 5 PPT 1Document16 pagesADC Unit 5 PPT 1Himanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is Multiplexing ?explain Its Need and Basic Format of MultiplexingDocument9 pagesWhat Is Multiplexing ?explain Its Need and Basic Format of MultiplexingVarun H SNo ratings yet
- Basic of MultiplexingDocument4 pagesBasic of MultiplexingÁñúrāG 444No ratings yet
- BECEA Time Division and Frequencydivision MultiplexingDocument10 pagesBECEA Time Division and Frequencydivision Multiplexingjaswantjangid2732No ratings yet
- Multiplexing and Multiple Access Techniques Multiplexing and Multiple Access TechniquesDocument89 pagesMultiplexing and Multiple Access Techniques Multiplexing and Multiple Access TechniquesSantosh Thapa0% (1)
- Ghazi University, Dera Ghazi KhanDocument10 pagesGhazi University, Dera Ghazi KhanIftakhar HussainNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document120 pagesTopic 3Chris DannyNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument16 pagesMultiplexingMahendran RajNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing NotesDocument5 pagesMultiplexing Notesgayathripanchumarthi30No ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument25 pagesMultiplexingisratjahanchandmoniNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument16 pagesMultiplexingAnju OzaNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer 4Document23 pagesPhysical Layer 4soumen maityNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing FDM TDM and TCM PDFDocument8 pagesMultiplexing FDM TDM and TCM PDFQuang Nghĩa VõNo ratings yet
- ECE 542 - Lecture 4Document24 pagesECE 542 - Lecture 4JohnCross DavidMaryNo ratings yet
- CH#5. MultiplexingDocument16 pagesCH#5. MultiplexingShining StarNo ratings yet
- Mux and DeMux (FOT)Document33 pagesMux and DeMux (FOT)Arjun Yadav100% (1)
- Multiplexing:: ApllicationsDocument6 pagesMultiplexing:: ApllicationsMominaIdreesNo ratings yet
- Multiple XingDocument20 pagesMultiple Xingrashidhusain112023No ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Unit 1Document7 pagesMobile Computing Unit 1smart IndiaNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication - MultiplexingDocument4 pagesAnalog Communication - MultiplexingcdrupwestNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing (Bandwidth Utilization) (Compatibility Mode)Document32 pagesMultiplexing (Bandwidth Utilization) (Compatibility Mode)Shivam KushwahaNo ratings yet
- MCC-Assignment 1-12c027Document5 pagesMCC-Assignment 1-12c027Saif ChogleNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing - Definition - Types of Multiplexing: FDM, WDM, TDMDocument14 pagesMultiplexing - Definition - Types of Multiplexing: FDM, WDM, TDMYohannis DanielNo ratings yet
- Ans:A Multiplexing Technique by Which Multiple Data Signals: Q:Briefly Explain TDM. What Is Interleaving ?Document2 pagesAns:A Multiplexing Technique by Which Multiple Data Signals: Q:Briefly Explain TDM. What Is Interleaving ?Gypsy WarheadNo ratings yet
- John Alcon D. Jerao Bsece-5 Assignment 1Document3 pagesJohn Alcon D. Jerao Bsece-5 Assignment 1justine jeraoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document121 pagesChapter 3Muhammad ZakiyNo ratings yet
- Connection Master: DatasheetDocument11 pagesConnection Master: DatasheetMd IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 1KHW002460-FOX61x-Product Features and Characteristics - pb4 PDFDocument156 pages1KHW002460-FOX61x-Product Features and Characteristics - pb4 PDFMartin AdasmeNo ratings yet
- Dialogic SDKDocument592 pagesDialogic SDKphpscottNo ratings yet
- (MCQ) Computer Communication Networks - LMT2Document14 pages(MCQ) Computer Communication Networks - LMT2raghad mejeedNo ratings yet
- Optical CDMA: Technique, Parameters and ApplicationsDocument9 pagesOptical CDMA: Technique, Parameters and ApplicationsSaurabh SalveNo ratings yet
- Smart Car PPT JejuDocument22 pagesSmart Car PPT JejuSaurabhKGuptaNo ratings yet
- I PASOLINKDocument56 pagesI PASOLINKAster Takele OfficialNo ratings yet
- Alu DWDM PDFDocument39 pagesAlu DWDM PDFShewan Alam SuhreedNo ratings yet
- M.tech - Communication Engineering and Signal ProcessingDocument19 pagesM.tech - Communication Engineering and Signal ProcessingSreeraj S J ee17d033No ratings yet
- Vmux 2100Document8 pagesVmux 2100Mohamed MoujtabaNo ratings yet
- RTN 910 Product Description (V100R001C02 - 03)Document111 pagesRTN 910 Product Description (V100R001C02 - 03)hannah8201100% (1)
- 01 iPASO 400-1000 Introduction1Document53 pages01 iPASO 400-1000 Introduction1Wubie NegaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Telecom Transmission & Switching TechniqueDocument14 pagesAssignment: Telecom Transmission & Switching TechniqueHAJRA khalidNo ratings yet
- COMM1208 Unit6 PCM SamplingDocument13 pagesCOMM1208 Unit6 PCM SamplingidatscribdNo ratings yet
- TUT2 SolDocument4 pagesTUT2 Solshini s gNo ratings yet
- (Presentation) GPON Vs EPONDocument14 pages(Presentation) GPON Vs EPONLiêm TrầnNo ratings yet
- BG Product LiDocument90 pagesBG Product LiLarba SawadogoNo ratings yet
- Brochure VR 10Document2 pagesBrochure VR 10didi100% (1)
- T1/E1 Digital Voice Port Adapter Installation and ConfigurationDocument96 pagesT1/E1 Digital Voice Port Adapter Installation and ConfigurationSergiu SergiuNo ratings yet
- Department of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab ManualDocument29 pagesDepartment of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab Manualమొక్కపాటి మాధవిNo ratings yet
- Mobicents SS7Stack User GuideDocument82 pagesMobicents SS7Stack User GuideNicTanaseNo ratings yet
- cs2 NotesDocument35 pagescs2 NotesMukul BhallaNo ratings yet
- Time Division MultiplexingDocument51 pagesTime Division MultiplexingTareq QaziNo ratings yet
- TRM Minilinktnpresentationbykhalil 170517191312 PDFDocument94 pagesTRM Minilinktnpresentationbykhalil 170517191312 PDFjamos200100% (2)
- Unit 3: Multiplexing and Switching: StructureDocument19 pagesUnit 3: Multiplexing and Switching: StructureNilesh SawantNo ratings yet
- Lista de AlarmesDocument7 pagesLista de AlarmesMarcos AlexandreNo ratings yet
- Networking Interview QuestionsDocument15 pagesNetworking Interview QuestionsArif HussainNo ratings yet
- 01 OptiX RTN 900 V100R002 Product Description 20100223 ADocument54 pages01 OptiX RTN 900 V100R002 Product Description 20100223 AJoseLuis AvilaNo ratings yet