Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparative graph
Comparative graph
Uploaded by
Hong Nhung0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesComparative graph
Comparative graph
Uploaded by
Hong NhungCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
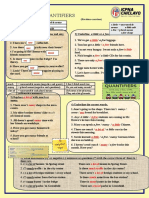
Comparative graph
A graph or table without a trend.
You should compare and contrast the data given in the graph/table
General structure
• Write an introduction to the topic of the graph in your own
words. (Paragraph 1)
• Give an overview of the main ideas in the graph. (Paragraph
2)
• Describe the most important details, including numbers
(Paragraph 3 and 4)
Understanding and interpreting the graph
Before you start, think about these questions:
1. What will you write in the introduction?
2. What are the main differences between the objects stated in
the graph?
3. How could you group the data?
4. What grammar and vocabulary will you need to use?
Understanding and interpreting the graph
Decide whether these statements about
the graph are True (T) or False (F)
1. On a typical Saturday, Bernie’s Buns is
generally busier than Lovely Loaves.
2. Doughnuts are by far the most
popular item among customer in both
stores.
3. The second-best selling item in
Bernie’s Buns is cookies.
4. Fresh loaves are the least popular
snack overall.
5. Toasted sandwiches are as popular as
cookies.
6. Lovely Loaves sells slightly more
salads than Bernie’s Buns.
Language for making comparisons
1. Grammatical structures:
- Equal comparison: as……as….
- Comparatives Combine with adverbs showing the amount of
differences: much, a lot, slightly, a bit,
- Superlatives considerably, a little, far
Ex: Lovely Loaves’ revenue of selling cookies is
considerably higher than Bernie’s Buns’.
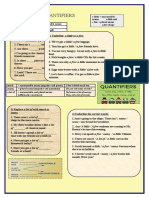
Language for making comparisons
2. Linking words
a. Contrasting words:
- while, whereas, meanwhile, however, nevertheless,…
- But, yet, by contrast, in contrast, …
b. Comparing words:
- Both … and …,
- Not only … but also…, similar, likewise,
- … same as …
c. Others:
- Despite/ Inspite of/ Although
- Except for, Apart from…
Language for making comparisons
3. Amounts, quantities and other measurements
• Quantity = number
• Amount
• Figure = value = data
• Rate = ratio = percentage
• Proportion = portion
• Half/ double/ triple
• A half (n) = halve (v)
• Double = twice as much as
Ex: The number of students in University A was double/ twice as much as the
University B.
• Double (v) = rise two-fold
You might also like
- Daily Lesson Log For Cohesive DevicesDocument7 pagesDaily Lesson Log For Cohesive DevicesDaisy Tacay100% (10)
- Comparatives and Superlatives PDFDocument23 pagesComparatives and Superlatives PDFJua Redey0% (3)
- SOF Level 2 NSO Class 3Document5 pagesSOF Level 2 NSO Class 3Pallavi Goel100% (2)
- Internet Explorer 8 Basics ManualDocument0 pagesInternet Explorer 8 Basics ManualAdriana BarjovanuNo ratings yet
- OnlineDocument12 pagesOnlinejadransko more0% (1)
- English Class: Teacher Lina Paula Cuartasesión B1Document14 pagesEnglish Class: Teacher Lina Paula Cuartasesión B1Lina Paula Alvarez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Name: Mauricio Ipiales Date:20/03/2022 Subject: English Teacher: Roberto Analuisa QuevedoDocument4 pagesName: Mauricio Ipiales Date:20/03/2022 Subject: English Teacher: Roberto Analuisa QuevedoMauricio IpialesNo ratings yet
- Com 2Document2 pagesCom 2MontseNANo ratings yet
- QuantifiersDocument1 pageQuantifiersANTHONY ZAMORANo ratings yet
- Speaking Part 1 RevisionDocument14 pagesSpeaking Part 1 RevisionNhân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Working With QUANTIFIERS: A Little A Few A Little Few A Few A Little A FewDocument1 pageWorking With QUANTIFIERS: A Little A Few A Little Few A Few A Little A FewCristina MendozaNo ratings yet
- Research Leveling: Automation EnglishDocument24 pagesResearch Leveling: Automation EnglishErik MonteroNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Class MaterialDocument78 pagesUnit 2 Class Materialdiana angelaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed S-V Agreement Day1Document2 pagesSemi-Detailed S-V Agreement Day1Gwyn CalanocNo ratings yet
- GIAO TRINH (FINAL) - A1 A2-Unit 4Document11 pagesGIAO TRINH (FINAL) - A1 A2-Unit 4Minh Thuận NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Untuk Bahasa Indonesia PDFDocument85 pagesBahasa Inggris Untuk Bahasa Indonesia PDFdamarNo ratings yet
- Presentations British English TeacherDocument13 pagesPresentations British English Teacheranglais pourtousNo ratings yet
- Anh 10 Global - Bài Giảng Điện Tử Unit 1 - Lesson 7 - Communication - CultureDocument17 pagesAnh 10 Global - Bài Giảng Điện Tử Unit 1 - Lesson 7 - Communication - CultureGV Chuyen Ha Long Truong Thi Thu HuongNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in English 7: I. Listening StrategiesDocument2 pagesSummative Test in English 7: I. Listening StrategiesCheeney Keith Burgos100% (1)
- WorksheetsDocument40 pagesWorksheetsJulliana SantosNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - 38-44 PDFDocument7 pagesUnit 3 - 38-44 PDFDavid MucollariNo ratings yet
- Presentations American English StudentDocument7 pagesPresentations American English StudentJackie HoffmanNo ratings yet
- Eng8 Q2 Mod4 Comparing Contrasting Opinions Using Transitions ModifiedDocument8 pagesEng8 Q2 Mod4 Comparing Contrasting Opinions Using Transitions ModifiedErich Cloe EscobidoNo ratings yet
- GI A2PLUS U4 Grammar BasicsDocument1 pageGI A2PLUS U4 Grammar BasicsEnglish HouseNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Rvsed Integrated English Ta 2019 - 2020Document11 pagesUnit 2 Rvsed Integrated English Ta 2019 - 2020Aliyyu Sheva KresnandaNo ratings yet
- Course Grammar: Guide Expected Work TimeDocument8 pagesCourse Grammar: Guide Expected Work TimeCamiloLMNo ratings yet
- G6 U4 L4 Grammar-Worksheet-1Document4 pagesG6 U4 L4 Grammar-Worksheet-1Nguyễn Ngọc MaiNo ratings yet
- PORTFOLIO CONTENTS For My RWS StudentsDocument7 pagesPORTFOLIO CONTENTS For My RWS Studentsenglishpublishers498No ratings yet
- Activity 5 Around The CityDocument2 pagesActivity 5 Around The CityAndreitaNo ratings yet
- 01 PPTX EAPPDocument52 pages01 PPTX EAPPdanica.paglinawanNo ratings yet
- 01 PPTX EAPPDocument79 pages01 PPTX EAPPdanica.paglinawanNo ratings yet
- Kids Avanzado 3 EfDocument54 pagesKids Avanzado 3 Efjesus.ochoadelaxNo ratings yet
- English II Unit 2.Document10 pagesEnglish II Unit 2.Eddy RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Working With QUANTIFIERS: Some Lemons Some Tea (Not) Any Onions (Not) Any MilkDocument1 pageWorking With QUANTIFIERS: Some Lemons Some Tea (Not) Any Onions (Not) Any MilkKaren VigoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. English II.Document10 pagesUnit 2. English II.Ivailo ApitzNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 6, QUARTER 1, WEEK 5, DAY 1-5presentation1Document101 pagesENGLISH 6, QUARTER 1, WEEK 5, DAY 1-5presentation1princess nicole lugtuNo ratings yet
- A. Name Five Different Methods of Bible Marking. B. Explain How Each Method Would Be Used. C. List Advantages and Disadvantages of EachDocument7 pagesA. Name Five Different Methods of Bible Marking. B. Explain How Each Method Would Be Used. C. List Advantages and Disadvantages of EachElida Valdez De JoseNo ratings yet
- Dhesserie Andrei G. Paglinawan Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDhesserie Andrei G. Paglinawan Lesson PlanDhesserie PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- On My Plate American English StudentDocument7 pagesOn My Plate American English StudentChan Myae KoNo ratings yet
- Bible Marking HonorDocument20 pagesBible Marking HonorKerry-Ann WilsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Lesson 1 - Getting StartedDocument26 pagesUnit 1 - Lesson 1 - Getting StartedANH NGUYEN THI LANNo ratings yet
- English 10 - Unit 1 - Lesson 1 - Getting StartedDocument30 pagesEnglish 10 - Unit 1 - Lesson 1 - Getting StartedTrường Đặng XuânNo ratings yet
- 1st Demo Lesson Plan EDITEDDocument7 pages1st Demo Lesson Plan EDITEDAte AnjieNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Guía 2Document7 pagesActivity 2 - Guía 2KaterineNo ratings yet
- On Speaking VstepDocument30 pagesOn Speaking VstepQuỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- QuantifiersDocument1 pageQuantifiersFenna YaZzNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - FoodDocument27 pagesWeek 5 - FoodyakovajalahNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - FoodDocument27 pagesWeek 5 - FoodyakovajalahNo ratings yet
- (1201) Subordinators and Transitions to Compare and Contrast (無答案版)Document13 pages(1201) Subordinators and Transitions to Compare and Contrast (無答案版)Abigail B.MoralesNo ratings yet
- "Healthy Eating" Unit 2: Programa de Inglés TransversalDocument12 pages"Healthy Eating" Unit 2: Programa de Inglés TransversalFelipe Flores FrezNo ratings yet
- Places To VisitDocument15 pagesPlaces To Visitedson.8102.morenoNo ratings yet
- 2018 10-12 English Study Kit Final Final FinalDocument179 pages2018 10-12 English Study Kit Final Final FinalRãphã Mtonga100% (1)
- 7activity 5 Around The CityDocument2 pages7activity 5 Around The CityCristian GaleanoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Consumer Society?: ExploreDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Consumer Society?: ExplorePaula VargasNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 InglesDocument2 pagesActivity 5 Inglessindy lorena RubioNo ratings yet
- LESSON EXEMPLAR Contrasting and ComparingDocument5 pagesLESSON EXEMPLAR Contrasting and ComparingRowell GuevaraNo ratings yet
- SPEAKING TEST IELTS Sep-Dec 2020Document18 pagesSPEAKING TEST IELTS Sep-Dec 2020Ian Skitz Jucs100% (1)
- EnglishDocument29 pagesEnglishJong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ano Lectivo 2005/2006: Escola Secundária Padre Benjamim Salgado Prova Escrita de INGLÊS - 11º Ano - Turmas F/GDocument4 pagesAno Lectivo 2005/2006: Escola Secundária Padre Benjamim Salgado Prova Escrita de INGLÊS - 11º Ano - Turmas F/Ganpacheco1No ratings yet
- Misión 24Document25 pagesMisión 24Eugeo KiriyagaNo ratings yet
- Key14thMay 1Document1 pageKey14thMay 1thisthehiNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 1From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ARI - 820-2000 Ice Storage BinsDocument8 pagesARI - 820-2000 Ice Storage BinsHellenHoaNo ratings yet
- FKKTDocument4 pagesFKKTSameehu TVNo ratings yet
- Jurnal DiagnosticDocument21 pagesJurnal DiagnosticLIPTA100% (1)
- Obiee 11g Technical Overview 078853 PDFDocument56 pagesObiee 11g Technical Overview 078853 PDFmithudeepuNo ratings yet
- Data Mining and Credit ScoringDocument8 pagesData Mining and Credit ScoringHaniyaAngelNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument12 pagesElasticity of DemandJohn Eric EstrelladoNo ratings yet
- 1120 Lab Packet Fa 17Document37 pages1120 Lab Packet Fa 17abhishek kumar50% (2)
- Controlling The Solution of Linear Systems - FenicsprojectDocument6 pagesControlling The Solution of Linear Systems - FenicsprojectXu MoranNo ratings yet
- SF Condition - Assessment of Steel StructureDocument5 pagesSF Condition - Assessment of Steel StructureTharach JanesuapasaereeNo ratings yet
- 323-1701-090 r10 1 PDFDocument174 pages323-1701-090 r10 1 PDFbruno_terranova132No ratings yet
- Componentes de Ingles Pregunta 2Document14 pagesComponentes de Ingles Pregunta 2Andres Salazar RoviraNo ratings yet
- HiddenMarkovModels RobertFreyStonyBrook PDFDocument34 pagesHiddenMarkovModels RobertFreyStonyBrook PDFPradeep Srivatsava ManikondaNo ratings yet
- 7.standard Adapter Framework Modules (AF - Modules) PDFDocument5 pages7.standard Adapter Framework Modules (AF - Modules) PDFankaiah_yadavNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Swahili LanguageDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Swahili LanguagePhilemon SundayNo ratings yet
- Grab The Attention of Your Audience With A Creative PresentationDocument8 pagesGrab The Attention of Your Audience With A Creative Presentationandrei2andrei_3No ratings yet
- Site Specific Dance Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSite Specific Dance Lesson Planapi-294432587No ratings yet
- Safety Campaign - Awareness On Permit To Work SystemDocument36 pagesSafety Campaign - Awareness On Permit To Work SystemsivaNo ratings yet
- Lec4.5 Volumes of Solids of RevolutionDocument329 pagesLec4.5 Volumes of Solids of RevolutionNiña Josephine MorenoNo ratings yet
- Paper Dahlen For DummiesDocument13 pagesPaper Dahlen For DummiesRino TabiangNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 PDFDocument2 pagesLab 10 PDFamitmsh1995No ratings yet
- 3D Finite Element Modeling of Precast Wall Panels Connection Under Monotonic LoadingDocument11 pages3D Finite Element Modeling of Precast Wall Panels Connection Under Monotonic Loadingabhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA Interview Questions 1Document14 pagesOracle DBA Interview Questions 1Munib Mohsin33% (3)
- Criteria and An Objective Approach To Selecting Commercial Real-Time Operating Systems Based On Published InformationDocument20 pagesCriteria and An Objective Approach To Selecting Commercial Real-Time Operating Systems Based On Published Informationsuneerav17No ratings yet
- Moisture-Density Relations of Soils Using A 4.54-kg (10-lb.) Rammer and A 457-mm (18-In.) Drop AASHTO T-180-10 (Method D-Modified)Document3 pagesMoisture-Density Relations of Soils Using A 4.54-kg (10-lb.) Rammer and A 457-mm (18-In.) Drop AASHTO T-180-10 (Method D-Modified)Muhammad Irfan Khan100% (1)
- Williamsk Portfolio Educ 6330Document29 pagesWilliamsk Portfolio Educ 6330api-328011965No ratings yet
- Genie Mobile App: User ManualDocument57 pagesGenie Mobile App: User ManualRyan TivisNo ratings yet
- Servo-Motor: Batch 7: Mouli R N Nagaaswin N Naveen K Nilesh Ram Praveen K Nirmal Kumar SDocument27 pagesServo-Motor: Batch 7: Mouli R N Nagaaswin N Naveen K Nilesh Ram Praveen K Nirmal Kumar SThameem AbbasNo ratings yet
- Opentext Documentum Archive Services For Sap: Configuration GuideDocument38 pagesOpentext Documentum Archive Services For Sap: Configuration GuideDoond adminNo ratings yet