Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer
Uploaded by
pooran singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views12 pagesPPT on Prostate Cancer for Nursing Students
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPPT on Prostate Cancer for Nursing Students
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views12 pagesProstate Cancer
Prostate Cancer
Uploaded by
pooran singhPPT on Prostate Cancer for Nursing Students
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
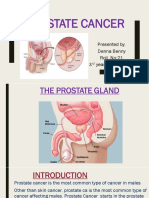
PROSTATE CANCER
MR. POORAN SINGH BHATI
ASSISTANT PROFESSOR
MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING
SMT. D.S.S.N.I
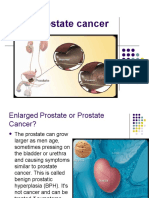
PROSTATE CANCER
PROSTATE CANCER
It is the most common cancer in men other than non-melanoma skin cancer.
The majority (>75%) of cases occur in men over age 65 year.
It is a malignant tumor of the prostate gland.
It is cancer that occurs in a men’s prostate- a small walnut shaped gland that produces the seminal fluid that
nourishes & transport sperm.
It usually grow slowly & initially remains confined to the prostate gland where it may not cause serious harm.
ETIOLOGY & RISK FACTORS-
The exact cause is unknown.
Genetic factors.
Aging above 60 year.
Environmental factors exposure to chemical dye (cigarette smoking, toxins etc.)
High fat intake.
Hormonal influences.
STAGES OF PROSTATE CANCER
Stage-I- Clinically unrecognized.
Stage-Ia- <5% of prostatic tissue neoplastic.
Stage-Ib- >5% of prostatic tissue neoplastic.
Stage-II- Clinically intracapsular.
Stage-IIa- Nodules <2cm & surrounded by palpably normal tissue.
Stage-IIb- Nodules >2cm or multiple nodules.
Stage-III- Clinical extra-capsular.
Stage-IIIa- Minimal extra-capsular.
Stage-IIIb- Large tumors involving seminal vesicles, adjacent structure or both
Stage-IV- Metastatic tissue.
Stage-IVa- Pelvic lymph node metastasis.
Stage-IVb- Distant metastasis to bone, viscera or other soft tissue structure
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
It may cause no sign & symptoms in its early stage.
Prostate cancer that is more advanced may cause S/S such as:-
Trouble urination
Decrease force in the stream of urine.
Blood in the semen (Hematospermia)
Discomfort in the pelvic area.
Erectile dysfunction
Hematuria.
Burning or pain during urination.
A sensation of incomplete emptying of the bladder even after passing urine.
Frequent nocturnal urination.
Abdominal pain.
Urinary retention.
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUTION
History collection
Physical examination
Digital rectal examination hard nodule felt of the prostate.
Trans-rectal ultrasound (TRUS).
Lab test Alkaline & acid phosphate, PSA elevation (Prostate specific antigen) denotes tumor growth.
Trans rectal needle aspiration & biopsy done.
X-ray
Sonography.
CT Scan
MRI done to rule out metastasis.
Normal PSA value- 4ng/ml
MANAGEMENT
1. Radiation therapy
2. Chemotherapy
3. Hormonal therapy
4. Surgical management:-
Laser ablation of prostate
Cryo surgery ablation
Redical prostatectomy- It is surgery to remove the entire prostate gland & surrounding lymph nodes.
Laproscopic prostatectomy- During a laproscopic redical prostatectomy, the doctor perform surgery through
small incision in the abdomen with the assistance of a tiny camera.
Orchiectomy- Removal of your testicles to reduce testosterone level in your body.
Bilateral Orchiectomy.
Biological therapy(Immunotherapy)- It uses your body immune system to fight cancer cells. One type of
biological therapy called Spileucel-T (Provenge) has been developed to treat advanced or recuurent prostate
cancer.
You might also like
- Surgery GNC RN FINAL EXAM QUESITION PAPERDocument149 pagesSurgery GNC RN FINAL EXAM QUESITION PAPERFan Eli100% (7)
- CA Cervix NewDocument54 pagesCA Cervix NewBi PinNo ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument31 pagesProstate CancerDan KennethNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Ca PresentationDocument25 pagesColorectal Ca Presentationapi-399299717No ratings yet
- Manhood Perfectly RestoredDocument54 pagesManhood Perfectly Restoredluckyreads67% (3)
- Prostate CancerDocument39 pagesProstate CancerMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Testicular Cancer Charyl Jane C. Acut Central Mindanao University College of Nursing Theresa Linda Narreto-PinaganDocument4 pagesTesticular Cancer Charyl Jane C. Acut Central Mindanao University College of Nursing Theresa Linda Narreto-PinaganCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary CancersDocument58 pagesGenitourinary CancersAyeNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma of Prostate: Dr. Saadat Hashmi Consultant UrologistDocument48 pagesCarcinoma of Prostate: Dr. Saadat Hashmi Consultant UrologistMuhammad ArsalNo ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument59 pagesProstate CancerJasmin Jacob100% (6)
- PATH DR - Hameed Male Reproductive System Lec 4Document45 pagesPATH DR - Hameed Male Reproductive System Lec 4Cosplay AccountNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument53 pagesCervical Cancerthamizh555No ratings yet
- Symptoms: Definition of Cervical Cancer: Cancer That Forms in Tissues of The Cervix (The Organ Connecting The UterusDocument5 pagesSymptoms: Definition of Cervical Cancer: Cancer That Forms in Tissues of The Cervix (The Organ Connecting The UterusHazel Joy Hokson-DiazNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Cancers by EasterDocument19 pagesReproductive System Cancers by EasterIGA ABRAHAM100% (1)
- 11 Prostate CancerDocument52 pages11 Prostate Cancerclaire yowsNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CA 450918 SHDocument52 pagesOvarian CA 450918 SH180045No ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer: Presented By, Denna Benny Roll. No:21 3 Year B. SC NursingDocument58 pagesProstate Cancer: Presented By, Denna Benny Roll. No:21 3 Year B. SC NursingSamuel LalNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ehsanur Reza Assistant Professor, Surgery MMCDocument45 pagesDr. Ehsanur Reza Assistant Professor, Surgery MMCIshtiaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument9 pagesBreast CancerLilia Tejada AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument10 pagesProstate Canceraji20No ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument7 pagesChapter TwoPrometheus OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer - PPTX 2013Document49 pagesBreast Cancer - PPTX 2013heba1997bshNo ratings yet
- Malignant Ovarian TumourDocument46 pagesMalignant Ovarian Tumourahmed shorshNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument4 pagesCervical CancerMarjorie Mae R. HerreraNo ratings yet
- 9 - Male Reproductive CancersDocument91 pages9 - Male Reproductive CancersAlexa RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer in TripuraDocument13 pagesProstate Cancer in TripuraSnehendu BhowmikNo ratings yet
- What Is Bladder Cancer?Document26 pagesWhat Is Bladder Cancer?Percy Crisia Garcia SazonNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer ReportDocument4 pagesCervical Cancer ReportRose SalviejoNo ratings yet
- Ovarian MalignancyDocument51 pagesOvarian MalignancydeepaNo ratings yet
- Urology Nursing Presentation Emily MarsallDocument37 pagesUrology Nursing Presentation Emily MarsallHerdy Rizky SusetyoNo ratings yet
- Genito Urinary Disorder LectureDocument64 pagesGenito Urinary Disorder LectureIrzan GustantoNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument7 pagesCervical CancerLarisse de LeonNo ratings yet
- Malignant Ovarian TumourDocument42 pagesMalignant Ovarian TumourJones MarinaNo ratings yet
- Testicular Tumors LastDocument41 pagesTesticular Tumors LastMerfat MahyobeNo ratings yet
- Case Study: - Courtney ChaneyDocument29 pagesCase Study: - Courtney Chaneyapi-313356122No ratings yet
- 20.MBBS Pancreatic CancerDocument52 pages20.MBBS Pancreatic Cancermrajah95No ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer: Kepaniteraan Klinik Bagian Obstetri Ginekologi FK Uns / Rsud Dr. Moewardi SurakartaDocument28 pagesCervical Cancer: Kepaniteraan Klinik Bagian Obstetri Ginekologi FK Uns / Rsud Dr. Moewardi SurakartaobsgynNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The UterusDocument5 pagesCancer of The UterusShreyas WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Group Health EducationDocument20 pagesGroup Health EducationBrijesh Yadav100% (1)
- Prostate Cancer: Presented By: Franklin Que, BSN-RNDocument41 pagesProstate Cancer: Presented By: Franklin Que, BSN-RNfrank_1785No ratings yet
- Epithelial ovarian tumors1Document35 pagesEpithelial ovarian tumors1venkatasuyaNo ratings yet
- 16.uterine Disorders (B.m.a)Document35 pages16.uterine Disorders (B.m.a)Jimmy MainaNo ratings yet
- Pra VeenDocument88 pagesPra VeenPraveen PraviiNo ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument5 pagesProstate CancerBrilliant Osai-OyeteNo ratings yet
- Testicular Cancer Is A Disease in Which Cells Become Malignant (Cancerous) inDocument5 pagesTesticular Cancer Is A Disease in Which Cells Become Malignant (Cancerous) inAngel CastroNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer: What You Need To KnowDocument2 pagesProstate Cancer: What You Need To KnowMedlabs - Sehtak Bil DeniaNo ratings yet
- Ovarian and Prostate CancerDocument51 pagesOvarian and Prostate CancerMa. Angelica Alyssa RachoNo ratings yet
- GenitoUrinary CancerDocument5 pagesGenitoUrinary CancerRaman KumarNo ratings yet
- Testicular TumorsDocument42 pagesTesticular TumorsarhamNo ratings yet
- Romero 1Document3 pagesRomero 1rochelleNo ratings yet
- Cancer Cervix: BY Ahmed Magdy ElmohandesDocument34 pagesCancer Cervix: BY Ahmed Magdy ElmohandesAhmed ElmohandesNo ratings yet
- Prostate FinalDocument6 pagesProstate FinalivanaldrichNo ratings yet
- Particular Cancer Power PointDocument101 pagesParticular Cancer Power PointKoRnflakesNo ratings yet
- Bladder CancerDocument18 pagesBladder CancerakochaNo ratings yet
- Prostate GlandDocument14 pagesProstate GlandJake MillerNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The Endometrium FinalDocument3 pagesCancer of The Endometrium FinalJoy KirumbaNo ratings yet
- Cancer of Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesCancer of Reproductive SystemPia SempronNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Surgery in IndiaDocument9 pagesCervical Cancer Surgery in Indiadkumar1986No ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument45 pagesProstate CancerNeethiselvam Devadoss100% (2)
- Group 8 Prostate and Testicular Cancer 1Document27 pagesGroup 8 Prostate and Testicular Cancer 1ShiangNo ratings yet
- 9 Urinary and Male GenitalDocument31 pages9 Urinary and Male GenitalFlavia CatalinaNo ratings yet
- L 3 The Urinary Bladder& UrethraDocument28 pagesL 3 The Urinary Bladder& UrethraAdnan Al-aniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ProstateDocument2 pagesAnatomy ProstateCarl Julienne MasangcayNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostate HyperplasiaDocument6 pagesBenign Prostate HyperplasiaFreddy PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Male and FemaleDocument27 pagesReproductive System - Male and FemaleJerome CameroNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Hyperplasia: Diagnosis and Treatment (1994) Was The Starting Point ForDocument14 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Hyperplasia: Diagnosis and Treatment (1994) Was The Starting Point ForAnemiaHemolyticNo ratings yet
- EN - PIL Omnic TocasDocument7 pagesEN - PIL Omnic Tocasarade43No ratings yet
- Prostate GlandDocument21 pagesProstate GlandNups patilNo ratings yet
- PR TGMDocument24 pagesPR TGMmarinanananaNo ratings yet
- b9 PKM 2 Urinary Retention Dr. Christian Ronald Tanggo Sp.uDocument63 pagesb9 PKM 2 Urinary Retention Dr. Christian Ronald Tanggo Sp.uDaud ParluhutanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Face Reading in Chinese MedicineDocument25 pagesSummary of Face Reading in Chinese MedicineDoña InesNo ratings yet
- Radiological SemioticsDocument24 pagesRadiological Semioticsnikhil gendreNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies of Urinary BladderDocument102 pagesCongenital Anomalies of Urinary Bladdernancy voraNo ratings yet
- Practica Reproducitve Systme and PresentDocument10 pagesPractica Reproducitve Systme and PresentLauris CassoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Problems-IfmDocument16 pagesUrinary Problems-Ifmapi-675909478No ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Bladder Outlet Obstruction (BOO)Document73 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Bladder Outlet Obstruction (BOO)Swe Zin NaingNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Russel Cepriano V151622 MOA Feb 2021Document2 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Russel Cepriano V151622 MOA Feb 2021Yeasa DolleteNo ratings yet
- Large-Glandproliferations Oftheprostate: Kenneth A. IczkowskiDocument26 pagesLarge-Glandproliferations Oftheprostate: Kenneth A. IczkowskiCesart LlerenaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive OrganDocument49 pagesMale Reproductive OrganRannel Violenda Roxas PalomarNo ratings yet
- Effects of Transurethral Resection of Prostate (Turp) On Uroflowmetry Parameters On Patients Having Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument6 pagesEffects of Transurethral Resection of Prostate (Turp) On Uroflowmetry Parameters On Patients Having Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaKamran AfzalNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument31 pagesMale Reproductive SystemnamitaNo ratings yet
- Mo Man2Document38 pagesMo Man2paujosaNo ratings yet
- Blessed Thistle and Blue VervainDocument4 pagesBlessed Thistle and Blue VervainSoror OnyxNo ratings yet
- Answers For Your Prostate 2022 (Part 1) - Best Answers About Prostate 2022Document51 pagesAnswers For Your Prostate 2022 (Part 1) - Best Answers About Prostate 2022MarcoNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Pembimbing: DR Herinto Himawan Sp.UDocument42 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Pembimbing: DR Herinto Himawan Sp.Uilma aulia zahraNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Guideline - American Urological AssociationDocument51 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Guideline - American Urological AssociationPUTRI ANGGRAINI BNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary Radiology ExamDocument9 pagesGenitourinary Radiology ExamNour NoorNo ratings yet
- Testicular TorsionDocument20 pagesTesticular TorsionnurisumirizqiNo ratings yet