Professional Documents
Culture Documents
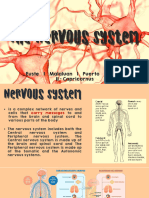
Nervous System
Nervous System
Uploaded by
Rhea Michaela Serrada Flores0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views59 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views59 pagesNervous System
Nervous System
Uploaded by
Rhea Michaela Serrada FloresCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 59
NERVOUS SYSTEM
What is nervous system?
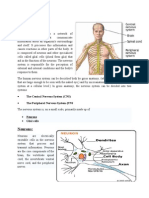
The nervous system is a complex network of
nerves and cells that carry messages to and
from the brain and spinal cord to various parts
of the body.
The nervous system includes both the Central
nervous system and Peripheral nervous
system.
The Central nervous system is made up of the
brain and spinal cord.
The Peripheral nervous system is made up of
the Somatic and the Autonomic nervous
systems.
The central nervous system is divided into two
major parts: the brain and the spinal cord.
The brain
The brain lies within the skull and is shaped
like a mushroom. The brain consists of four
principal parts:
the brain stem
the cerebrum
the cerebellum
the diencephalon
The brain weighs approximately 1.3 to 1.4 kg. It
has nerve cells called the neurons and
supporting cells called the glia.
There are two types of matter in the brain:
grey matter and white matter. Grey matter
receives and stores impulses. Cell bodies of
neurons and neuroglia are in the grey matter.
White matter in the brain carries impulses to
and from grey matter. It consists of the nerve
fibers (axons).
The brain stem
The brain stem is also known as the Medulla
oblongata. It is located between the pons and
the spinal cord and is only about one inch long.
The cerebrum
The cerebrum forms the bulk of the brain and is
supported on the brain stem. The cerebrum is
divided into two hemispheres. Each hemisphere
controls the activities of the side of the body
opposite that hemisphere.
The hemispheres are further divided into four
lobes:
Frontal lobe
Temporal lobes
Parietal lobe
Occipital lobe
The cerebellum
This is located behind and below the cerebrum.
The diencephalon
The diencephalon is also known as the fore
brain stem. It includes the thalamus and
hypothalamus. The thalamus is where sensory
and other impulses go and coalesce.
The hypothalamus is a smaller part of the
diencephalon
Other parts of the brain
Other parts of the brain include the midbrain
and the pons:
the midbrain provides conduction pathways to
and from higher and lower centers
the pons acts as a pathway to higher
structures; it contains conduction pathways
between the medulla and higher brain centers
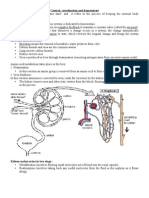
The spinal cord
The spinal cord is along tube like structure
which extends from the brain. The spinal cord
is composed of a series of 31 segments. A pair
of spinal nerves comes out of each segment.
The region of the spinal cord from which a pair
of spinal nerves originates is called the spinal
segment. Both motor and sensory nerves are
located in the spinal cord.
The spinal cord is about 43 cm long in adult
women and 45 cm long in adult men and
weighs about 35-40 grams. It lies within the
vertebral column, the collection of bones (back
bone).
Other parts of the central nervous system
The meninges are three layers or membranes
that cover the brain and the spinal cord. The
outermost layer is the dura mater. The middle
layer is the arachnoid, and the innermost layer
is the pia mater. The meninges offer protection
to the brain and the spinal cord by acting as a
barrier against bacteria and other
microorganisms.
The Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) circulates
around the brain and spinal cord. It protects
and nourishes the brain and spinal cord.
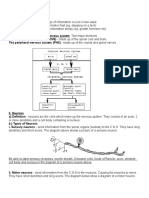
Neurons
The neuron is the basic unit in the nervous
system. It is a specialized conductor cell that
receives and transmits electrochemical nerve
impulses. A typical neuron has a cell body and
long arms that conduct impulses from one
body part to another body part.
There are three different parts of the neuron:
the cell body
dendrites
axon
Cell body of a neuron
The cell body is like any other cell with a
nucleus or control center.
Dendrites
The cell body has several highly branched,
thick extensions that appear like cables and are
called dendrites. The exception is a sensory
neuron that has a single, long dendrite instead
of many dendrites. Motor neurons have
multiple thick dendrites. The dendrite's
function is to carry a nerve impulse into the cell
body.
Axon
An axon is a long, thin process that carries
impulses away from the cell body to another
neuron or tissue. There is usually only one
axon per neuron.
Myelin Sheath
The neuron is covered with the Myelin Sheath
or Schwann Cells. These are white segmented
covering around axons and dendrites of many
peripheral neurons. The covering is continuous
along the axons or dendrites except at the point
of termination and at the nodes of Ranvier.
The neurilemma is the layer of Schwann cells
with a nucleus. Its function is to allow
damaged nerves to regenerate. Nerves in the
brain and spinal cord do not have a
neurilemma and, therefore cannot recover
when damaged.
Types of neuron
Neurons in the body can be classified according to
structure and function. According to structure neurons
may be multipolar neurons, bipolar neurons, and
unipolar neurons:
Multipolar neurons have one axon and several dendrites.
These are common in the brain and spinal cord
Bipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite. These
are seen in the retina of the eye, the inner ear, and the
olfactory (smell) area.
Unipolar neurons have one process extending from the
cell body. The one process divides with one part acting as
an axon and the other part functioning as dendrite. These
are seen in the spinal cord.
What Is the Peripheral Nervous System?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the
division of the nervous system containing all
the nerves that lie outside of the
central nervous system (CNS). The primary
role of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the
organs, limbs and skin. These nerves extend
from the central nervous system to the
outermost areas of the body.
The nerves that make up the
peripheral nervous system are actually the
axons or bundles of axons from neuron cells.
The Peripheral nervous system
The Peripheral nervous system is made up of
two parts:
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
The somatic system is the part of the peripheral
nervous system responsible for carrying
sensory and motor information to and from
the central nervous system. The somatic
nervous system derives its name from the
Greek word soma, which means "body." The
somatic system is responsible for transmitting
sensory information as well as for voluntary
movement.
This system contains two major types of
neurons: sensory neurons (or afferent neurons)
that carry information from the nerves to the
central nervous system, and motor neurons (or
efferent neurons) that carry information from
the brain and spinal cord to muscle fibers
throughout the body.
The somatic nervous system consists of
peripheral nerve fibers that pick up sensory
information or sensations from the peripheral
or distant organs (those away from the brain
like limbs) and carry them to the central
nervous system.
These also consist of motor nerve fibers that
come out of the brain and take the messages for
movement and necessary action to the skeletal
muscles. For example, on touching a hot object
the sensory nerves carry information about the
heat to the brain, which in turn, via the motor
nerves, tells the muscles of the hand to
withdraw it immediately.
The whole process takes less than a second to
happen. The cell body of the neuron that
carries the information often lies within the
brain or spinal cord and projects directly to a
skeletal muscle.
Autonomic Nervous System
Another part of the nervous system is the
Autonomic Nervous System. It has three parts:
the sympathetic nervous system
the parasympathetic nervous system
the enteric nervous system
This nervous system controls the nerves of the
inner organs of the body on which humans
have no conscious control. This includes the
heartbeat, digestion, breathing (except
conscious breathing) etc.
The nerves of the autonomic nervous system
enervate the smooth involuntary muscles of the
(internal organs) and glands and cause them to
function and secrete their enzymes etc.
The Enteric nervous system is the third part of
the autonomic nervous system. The enteric
nervous system is a complex network of nerve
fibers that innervate the organs within the
abdomen like the gastrointestinal tract,
pancreas, gall bladder etc. It contains nearly
100 million nerves.
Neurons in the peripheral nervous system
The smallest worker in the nervous system is
the neuron. For each of the chain of impulses
there is one preganglionic neuron, or one
before the cell body or ganglion, that is like a
central controlling body for numerous neurons
going out peripherally.
The preganglionic neuron is located in either
the brain or the spinal cord. In the autonomic
nervous system this preganglionic neuron
projects to an autonomic ganglion. The
postganglionic neuron then projects to the
target organ.
In the somatic nervous system there is only one
neuron between the central nervous system
and the target organ while the autonomic
nervous system uses two neurons.
You might also like
- Afifi AK, Functional Neuroanatomy. 2005 (Book)Document873 pagesAfifi AK, Functional Neuroanatomy. 2005 (Book)Eguzki Izukaitz NogueraNo ratings yet
- Nervou S System:: NeuronsDocument16 pagesNervou S System:: NeuronsFizzah100% (4)
- HISTOLOGY Nervous System LAB 6 Lab NotesDocument5 pagesHISTOLOGY Nervous System LAB 6 Lab NotesRNStudent1No ratings yet
- The Central Nervous System (CNS)Document8 pagesThe Central Nervous System (CNS)reineNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System Is A Complex Network of Nerves and Cells That Carry Messages To and From TheDocument18 pagesThe Nervous System Is A Complex Network of Nerves and Cells That Carry Messages To and From TheJanineLingayoCasilenNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesNervous SystemYalu EinahpetsNo ratings yet
- What Is The Nervous System?Document6 pagesWhat Is The Nervous System?Dee Olivar CamaongayNo ratings yet
- Updated Central and Peripheral Nervous System TestDocument8 pagesUpdated Central and Peripheral Nervous System TestScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument46 pagesNervous SystemIponla KarlChristianNo ratings yet
- Neurobehavior System: 1. Ratna Ensa Novitra 2. Asri Setiyaningrum 3. Nuzullia Kusuma AnggiaDocument8 pagesNeurobehavior System: 1. Ratna Ensa Novitra 2. Asri Setiyaningrum 3. Nuzullia Kusuma AnggiaAsri Saranghae SmashNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Summary NotesDocument9 pagesNervous System - Summary NotesHarshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Nervous System PDFDocument11 pagesIntroduction To The Nervous System PDFEmanuel DragomirescuNo ratings yet
- Structure of Brain Nervous System-20-04-2020Document3 pagesStructure of Brain Nervous System-20-04-2020Jethalal GadaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Dr. Hendy Wijaya, M. BiomedDocument26 pagesNervous System: Dr. Hendy Wijaya, M. BiomedWndy 0903No ratings yet
- Science Sofie 10 3 RevDocument11 pagesScience Sofie 10 3 Revjinxtapperhat07No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemJavi OceansoulNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Overview: FunctionDocument11 pagesNervous System - Overview: FunctionAadil JuttNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesNervous SystemxoxogeloNo ratings yet
- Reading 7 The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesReading 7 The Nervous Systemlephuongvy1406No ratings yet
- 4.2 Nervious Tissues.pptxDocument36 pages4.2 Nervious Tissues.pptxZaara RashéidNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesThe Nervous Systemvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System Is The BodyDocument18 pagesThe Nervous System Is The Bodyvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Biological Basis of Behavior, Structure of Neurons and Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Biological Basis of Behavior, Structure of Neurons and Nervous SystemAliaNo ratings yet
- Human Regulatory SystemDocument23 pagesHuman Regulatory SystemNina WirdiyanaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesThe Nervous SystemMegha DevanpalliNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS_SYSTEMDocument4 pagesNERVOUS_SYSTEMgqqd57v89vNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemalanNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions Nervoys SDocument3 pagesCoordinated Functions Nervoys SGwency Ross Alvarez (Gwen)No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument31 pagesThe Nervous SystemceneveNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Nervous SystemUmair BasheerNo ratings yet
- Ervous Ystem: Structural ClassificationDocument95 pagesErvous Ystem: Structural ClassificationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- 1. Introduction of Anatomynervous System (1)Document75 pages1. Introduction of Anatomynervous System (1)Aldood Al NatarNo ratings yet
- Nscelec4-Week 15Document23 pagesNscelec4-Week 15Jeune Kristine OngNo ratings yet
- 9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMDocument24 pages9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterDocument25 pagesNervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterRegin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Nervous System, Neuronal Communication and Organization of BrainDocument17 pagesNervous System, Neuronal Communication and Organization of BrainPriyamvada VermaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System TTCDocument24 pagesNervous System TTCelber campos valdesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument26 pagesNervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (3)
- The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesThe Nervous SystemAltheaNo ratings yet
- CH 7 The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCH 7 The Nervous Systemapi-267543553No ratings yet
- Nervous TissuesDocument13 pagesNervous TissuesSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument23 pagesModule 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorRoxie May Theresse AbagatnanNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument43 pagesControl and CoordinationDukhi InsaanNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Sensory Neurological SystemDocument35 pagesAssessing The Sensory Neurological SystemSusan Maglaqui100% (1)
- Lect 12Document70 pagesLect 12fatima shahNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Control System of The BodyDocument31 pagesWelcome To The Control System of The BodypadiosNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDocument7 pages1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemSumaira Noreen100% (1)
- Control, Coordination and Human BrainDocument8 pagesControl, Coordination and Human BrainSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Week 2Document6 pagesNeuroscience Week 2Naima AhmadNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System RECORDINGSDocument52 pagesThe Nervous System RECORDINGSKathy Angeli Bel-idaNo ratings yet
- 4-The Nervous SystémDocument6 pages4-The Nervous SystémEma FröhlichováNo ratings yet
- (Lecture - 4) Neuropsychology of Human BehaviorDocument58 pages(Lecture - 4) Neuropsychology of Human BehaviorN. W. FlannelNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument17 pagesHuman BrainAkbota KuanishkyzyNo ratings yet
- LP 1.2 in PhysioBio PsychologyDocument11 pagesLP 1.2 in PhysioBio PsychologyWayne GodioNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 LecNotesDocument49 pagesUnit 1 LecNotesAnn NguyenNo ratings yet
- How Your Brain WorksDocument7 pagesHow Your Brain WorksMRITZNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 (Nervous System)Document14 pagesUNIT 4 (Nervous System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous System: BrainDocument12 pagesThe Central Nervous System: BrainsheinelleNo ratings yet
- Bio Paper KetigaDocument14 pagesBio Paper KetigaElsa NandaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Nervous System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Nervous System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve Problems: Anne M.B. MosconyDocument40 pagesPeripheral Nerve Problems: Anne M.B. MosconyAkbar GazaliNo ratings yet
- 6BI05 June 2011Document24 pages6BI05 June 2011areyouthere92No ratings yet
- NeuronsDocument32 pagesNeuronsDesadaNo ratings yet
- WORKSHOP No 2Document25 pagesWORKSHOP No 2Jose QuintoNo ratings yet
- Chapt 39Document7 pagesChapt 39Hakesh PratikNo ratings yet
- Organization of NSDocument20 pagesOrganization of NSnadine azmyNo ratings yet
- U6 - Sensory Organs and Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesU6 - Sensory Organs and Nervous Systempovad44811No ratings yet
- Memory Game Problem:: Temporal LobeDocument4 pagesMemory Game Problem:: Temporal LobeDherick RaleighNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue - UpdatedDocument129 pagesNervous Tissue - UpdatedPojangNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Nervous SystemPractice Test and KeyDocument13 pagesCH 8 Nervous SystemPractice Test and KeyvpcpharmdNo ratings yet
- Advanced Anatomy Questions PDFDocument63 pagesAdvanced Anatomy Questions PDFJoanne BlancoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4 - Body's Control SystemDocument7 pagesWorksheet 4 - Body's Control SystemPatricio IsaranNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Upper Limb and Lower Limb Choice Reaction TimeDocument12 pagesDifferences Between Upper Limb and Lower Limb Choice Reaction TimeKurt VogelNo ratings yet
- Neuroplasticity - Chap 6Document3 pagesNeuroplasticity - Chap 6Althea YabutNo ratings yet
- Bs Psych Qualifying ExamDocument61 pagesBs Psych Qualifying ExamicaNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Peripheral Nerve DisordersDocument288 pagesBasic Principles of Peripheral Nerve DisordersJosé Ramírez100% (1)
- GBSDocument33 pagesGBSbungadielaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Neuropathies in Clinical PracticeDocument398 pagesPeripheral Neuropathies in Clinical PracticeIka Gultom100% (1)
- StructuralDocument13 pagesStructuralClaudia Pérez LuisNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissuesDocument33 pagesNervous TissuesElyzza Wye AlbaoNo ratings yet
- 8A The Nervous System and Neurones 8A CheckpointDocument8 pages8A The Nervous System and Neurones 8A CheckpointsalmaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System NotesDocument8 pagesNervous System NotesGina ChunNo ratings yet
- Notes For HomeostasisDocument21 pagesNotes For Homeostasisfreednemon83% (6)
- Schwann CellsDocument7 pagesSchwann CellsVictor Manuel Granada AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Biology Textbook Part 1 English Medium - Kerala STD 10Document72 pagesBiology Textbook Part 1 English Medium - Kerala STD 10Sreelakshmi PMNo ratings yet
- Genetics For PediatriciansDocument321 pagesGenetics For PediatriciansHemali AdvaniNo ratings yet
- NEET Mein JEET-2022: Neural Control and Coordination - Practice Test-17Document4 pagesNEET Mein JEET-2022: Neural Control and Coordination - Practice Test-17Amit kumarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Peripheral Nerve Injury A Brief ReviewDocument7 pagesPathophysiology of Peripheral Nerve Injury A Brief ReviewChristopher Alexander ToroNo ratings yet