Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsTransmission Media
Transmission Media
Uploaded by
Akshat Pal 7 Diamond 3Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Unit 2Document23 pagesUnit 2snehatumaskarNo ratings yet
- Wired/Guided Media: Chapter No: 2 Transmission Media Transmission MediaDocument18 pagesWired/Guided Media: Chapter No: 2 Transmission Media Transmission MediaWidimongar JarqueNo ratings yet
- Physical LayerDocument19 pagesPhysical LayerRekha V RNo ratings yet
- DC-Lec-21 (Guided Media)Document56 pagesDC-Lec-21 (Guided Media)Farman AfridiNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 1Document25 pagesMod 2 1HaripriyaNo ratings yet
- UNIT II (Transmission Media)Document59 pagesUNIT II (Transmission Media)Sarthak kadamNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument43 pagesTransmission MediaTech SmartNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument53 pagesTransmission MediaKeyur MahantNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line TheoryDocument84 pagesTransmission Line TheoryTivoj Porras100% (2)
- Transmission Media 1Document2 pagesTransmission Media 1Amit TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Atom Is Comprised ofDocument74 pagesThe Atom Is Comprised ofVladimir OleynikovNo ratings yet
- Nepal Telecom Exam Preparation: (Level 7)Document43 pagesNepal Telecom Exam Preparation: (Level 7)Dipak Kumar NidhiNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument33 pagesTransmission MediaAshish ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media: Introduction To Telecommunications by GokhaleDocument52 pagesTransmission Media: Introduction To Telecommunications by GokhaleVivencio Pascual JrNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Transmission MediaDocument76 pages1.8 Transmission Media19epci002 Akhil SNo ratings yet
- CN Module 2Document44 pagesCN Module 2Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- Lec 7Document29 pagesLec 7Waqas ChNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument17 pagesPresentationPreet RamgarhiaNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument32 pagesTransmission MedianseatonNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument49 pagesTransmission MediaSheba ParimalaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledJohn Matthew Taule OboNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Transmission Media Network Devices1Document27 pagesUnit 3 Transmission Media Network Devices1Amruta ShingoteNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument37 pagesTransmission MediaAbhishek singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two - Transmission MediaDocument29 pagesChapter Two - Transmission MediaMahametNo ratings yet
- ITC3303 - Lecture 4Document26 pagesITC3303 - Lecture 4AhmadNo ratings yet
- DC - Module IIDocument19 pagesDC - Module IIveenadivyakishNo ratings yet
- 02.transmission MediaDocument32 pages02.transmission Mediaksav yadavNo ratings yet
- Unit1-Part B Physical Layer: Guided Media, Unguided MediaDocument33 pagesUnit1-Part B Physical Layer: Guided Media, Unguided MediaAkhila VeerabommalaNo ratings yet
- Guided Transmission MediaDocument23 pagesGuided Transmission MediaJoy PalNo ratings yet
- Final Trans MediaDocument47 pagesFinal Trans MediaGohar HussainNo ratings yet
- DC Module3 - Transmission MediaDocument35 pagesDC Module3 - Transmission MediaMayank RajNo ratings yet
- Wired Transmission Media1.3.1Document27 pagesWired Transmission Media1.3.1Gaurav kambojNo ratings yet
- Jumba Tranms LineDocument27 pagesJumba Tranms LineMisango EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- CNPracticle 2Document15 pagesCNPracticle 2lipin85350No ratings yet
- Power Cable: Distribution, Sizing and MergingDocument59 pagesPower Cable: Distribution, Sizing and MergingM.AbbasNo ratings yet
- Transmission Medium and Physical LayerDocument13 pagesTransmission Medium and Physical Layerchaa2014No ratings yet
- MCWC DarshanDocument108 pagesMCWC DarshanDeepakPradhan100% (1)
- Computer Networks Lecture 4Document55 pagesComputer Networks Lecture 4Super SpecialNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Data Transmission & MediaDocument69 pagesLecture 3 Data Transmission & MediaListon KiwoliNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument32 pagesTransmission MediaAshu KumarNo ratings yet
- DC Module 2Document18 pagesDC Module 2Simal JaanNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer and Its Design Issues Chapter-3Document10 pagesPhysical Layer and Its Design Issues Chapter-3Amir SilwalNo ratings yet
- 3 MediaDocument50 pages3 MediaSami AhmedNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument6 pagesTransmission Mediamahar.nomi1039No ratings yet
- Transmission Medium Guided Transmission Media Wireless TransmissionDocument24 pagesTransmission Medium Guided Transmission Media Wireless TransmissionumeshNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media: by Prof. Salman Naseer AdilDocument48 pagesTransmission Media: by Prof. Salman Naseer AdilHafiz Ahmad ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- ComunicationDocument56 pagesComunicationSuhaila ctNo ratings yet
- DCC Unit2Document76 pagesDCC Unit2Omkar mahamuniNo ratings yet
- 04 TransmissionmediaDocument38 pages04 Transmissionmedia22520101No ratings yet
- Transmission Media PPT FinalDocument36 pagesTransmission Media PPT FinalRanjana PriyaNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument58 pagesTransmission MediaVISHNU SHANKAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Transmission MediaDocument43 pages1.3 Transmission MediaDiimu AfarNo ratings yet
- DCC Unit 2Document39 pagesDCC Unit 2Raj DebadwarNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media - 1Document40 pagesTransmission Media - 1SayeeKumar MadheshNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Transmission Media and Switching (Total Marks-14)Document38 pagesUnit 2: Transmission Media and Switching (Total Marks-14)shubhamNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument39 pagesTransmission Mediachabdulmanan8953No ratings yet
- CN - Module 2-Subsection 1 and 2-2Document43 pagesCN - Module 2-Subsection 1 and 2-2Siddhant YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document66 pagesUnit 2dhruv shahNo ratings yet
- Ambo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceDocument27 pagesAmbo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceNoel GirmaNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
Transmission Media
Transmission Media
Uploaded by
Akshat Pal 7 Diamond 30 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesTransmission Media
Transmission Media
Uploaded by
Akshat Pal 7 Diamond 3Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
Transmission Media
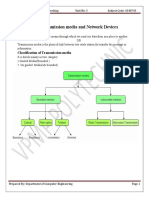
What is Transmission Media ?
• Transmission is a pathway that carries the information from sender to
receiver.
• We use different types cables and waves to transmit data.
• Data is transmitted normally through electrical or electromagnetic
signals
Fibre-Optic- Twisted-Pair-
cable Coaxial Cable
Cable
Wired
Media
Transmission
Transmission Media
Twisted Pair Cable
• A twisted pair cable consists of two conductors.
• Basically copper based.
• With it's own plastic insulation.
Twisted Pair Description
• Provide protection against cross talk or interference (noise).
• One wire use to carry signals to the receiver.
• Second wire used as a ground reference.
• For twisting, after receiving the signals remains same.
• Therefore number of twists per unit length, determines the quality of
cable.
Twisted pair
Advantages:
1st Cheap
2nd Easy to work with
Disadvantages:
1st Low data rate
2nd Short range
Co-axial Cable
• Co-axial cable carries signals of higher frequency ranges the twisted
pair cable.
• Inner conductor is a solid wire.
• Outer conductor serves as a shield against noise and a second conductor.
Coaxial Cable
Advantages:
1st Easy to wire.
2nd Easy to expand.
3rd Moderate level of Electro Magnetic Interference.
Disadvantages:
1st Single cable failure can take down an entire network.
2nd Cost of installation of a coaxial cable is high due to it’s thickness and
stiffness.
3rd Cost of maintenance is also high.
Fibre optic cable
• A Fibre Optic Cable is made up of glass or plastic and transmit
signals in the form of light.
• Nature of light:
• Light travels in a straight line.
• If light goes from one substance to another then the ray of light
changes its direction.
Thank You
Made by - Akshat Pal
Class - 8th Diamond
Roll no - 02
You might also like
- Unit 2Document23 pagesUnit 2snehatumaskarNo ratings yet
- Wired/Guided Media: Chapter No: 2 Transmission Media Transmission MediaDocument18 pagesWired/Guided Media: Chapter No: 2 Transmission Media Transmission MediaWidimongar JarqueNo ratings yet
- Physical LayerDocument19 pagesPhysical LayerRekha V RNo ratings yet
- DC-Lec-21 (Guided Media)Document56 pagesDC-Lec-21 (Guided Media)Farman AfridiNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 1Document25 pagesMod 2 1HaripriyaNo ratings yet
- UNIT II (Transmission Media)Document59 pagesUNIT II (Transmission Media)Sarthak kadamNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument43 pagesTransmission MediaTech SmartNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument53 pagesTransmission MediaKeyur MahantNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line TheoryDocument84 pagesTransmission Line TheoryTivoj Porras100% (2)
- Transmission Media 1Document2 pagesTransmission Media 1Amit TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Atom Is Comprised ofDocument74 pagesThe Atom Is Comprised ofVladimir OleynikovNo ratings yet
- Nepal Telecom Exam Preparation: (Level 7)Document43 pagesNepal Telecom Exam Preparation: (Level 7)Dipak Kumar NidhiNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument33 pagesTransmission MediaAshish ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media: Introduction To Telecommunications by GokhaleDocument52 pagesTransmission Media: Introduction To Telecommunications by GokhaleVivencio Pascual JrNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Transmission MediaDocument76 pages1.8 Transmission Media19epci002 Akhil SNo ratings yet
- CN Module 2Document44 pagesCN Module 2Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- Lec 7Document29 pagesLec 7Waqas ChNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument17 pagesPresentationPreet RamgarhiaNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument32 pagesTransmission MedianseatonNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument49 pagesTransmission MediaSheba ParimalaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledJohn Matthew Taule OboNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Transmission Media Network Devices1Document27 pagesUnit 3 Transmission Media Network Devices1Amruta ShingoteNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument37 pagesTransmission MediaAbhishek singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two - Transmission MediaDocument29 pagesChapter Two - Transmission MediaMahametNo ratings yet
- ITC3303 - Lecture 4Document26 pagesITC3303 - Lecture 4AhmadNo ratings yet
- DC - Module IIDocument19 pagesDC - Module IIveenadivyakishNo ratings yet
- 02.transmission MediaDocument32 pages02.transmission Mediaksav yadavNo ratings yet
- Unit1-Part B Physical Layer: Guided Media, Unguided MediaDocument33 pagesUnit1-Part B Physical Layer: Guided Media, Unguided MediaAkhila VeerabommalaNo ratings yet
- Guided Transmission MediaDocument23 pagesGuided Transmission MediaJoy PalNo ratings yet
- Final Trans MediaDocument47 pagesFinal Trans MediaGohar HussainNo ratings yet
- DC Module3 - Transmission MediaDocument35 pagesDC Module3 - Transmission MediaMayank RajNo ratings yet
- Wired Transmission Media1.3.1Document27 pagesWired Transmission Media1.3.1Gaurav kambojNo ratings yet
- Jumba Tranms LineDocument27 pagesJumba Tranms LineMisango EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- CNPracticle 2Document15 pagesCNPracticle 2lipin85350No ratings yet
- Power Cable: Distribution, Sizing and MergingDocument59 pagesPower Cable: Distribution, Sizing and MergingM.AbbasNo ratings yet
- Transmission Medium and Physical LayerDocument13 pagesTransmission Medium and Physical Layerchaa2014No ratings yet
- MCWC DarshanDocument108 pagesMCWC DarshanDeepakPradhan100% (1)
- Computer Networks Lecture 4Document55 pagesComputer Networks Lecture 4Super SpecialNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Data Transmission & MediaDocument69 pagesLecture 3 Data Transmission & MediaListon KiwoliNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument32 pagesTransmission MediaAshu KumarNo ratings yet
- DC Module 2Document18 pagesDC Module 2Simal JaanNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer and Its Design Issues Chapter-3Document10 pagesPhysical Layer and Its Design Issues Chapter-3Amir SilwalNo ratings yet
- 3 MediaDocument50 pages3 MediaSami AhmedNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument6 pagesTransmission Mediamahar.nomi1039No ratings yet
- Transmission Medium Guided Transmission Media Wireless TransmissionDocument24 pagesTransmission Medium Guided Transmission Media Wireless TransmissionumeshNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media: by Prof. Salman Naseer AdilDocument48 pagesTransmission Media: by Prof. Salman Naseer AdilHafiz Ahmad ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- ComunicationDocument56 pagesComunicationSuhaila ctNo ratings yet
- DCC Unit2Document76 pagesDCC Unit2Omkar mahamuniNo ratings yet
- 04 TransmissionmediaDocument38 pages04 Transmissionmedia22520101No ratings yet
- Transmission Media PPT FinalDocument36 pagesTransmission Media PPT FinalRanjana PriyaNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument58 pagesTransmission MediaVISHNU SHANKAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Transmission MediaDocument43 pages1.3 Transmission MediaDiimu AfarNo ratings yet
- DCC Unit 2Document39 pagesDCC Unit 2Raj DebadwarNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media - 1Document40 pagesTransmission Media - 1SayeeKumar MadheshNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Transmission Media and Switching (Total Marks-14)Document38 pagesUnit 2: Transmission Media and Switching (Total Marks-14)shubhamNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument39 pagesTransmission Mediachabdulmanan8953No ratings yet
- CN - Module 2-Subsection 1 and 2-2Document43 pagesCN - Module 2-Subsection 1 and 2-2Siddhant YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document66 pagesUnit 2dhruv shahNo ratings yet
- Ambo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceDocument27 pagesAmbo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceNoel GirmaNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet