Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsLocal complications of maxillofacial area injuries
Local complications of maxillofacial area injuries
Uploaded by
razykontar1Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- TB of BoneDocument18 pagesTB of BoneGarvit batraNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Disease of BonesDocument93 pagesInflammatory Disease of BonesNelson LagatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document32 pagesChapter 10Henderi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Bone II-2Document59 pagesDisorders of Bone II-2Guhan DergNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis of Jaws: Presented By: Anuradha B.D.S Final YearDocument11 pagesOsteomyelitis of Jaws: Presented By: Anuradha B.D.S Final YearGujjar VishalNo ratings yet
- OsteomyelitisDocument29 pagesOsteomyelitistaha saadNo ratings yet
- Periapical DiseasesDocument43 pagesPeriapical DiseasesKHALED WALEEDNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis Oral SurgeryDocument17 pagesOsteomyelitis Oral SurgeryFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Wa0006.Document14 pagesWa0006.mldmddhNo ratings yet
- Classification of Diseases of TMJDocument9 pagesClassification of Diseases of TMJSwati DalmiaNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Bone and Soft Tissue-LectureDocument52 pagesPathology of Bone and Soft Tissue-Lecturejohnwickshopping79No ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis: Oral Pathology 4 Stage DR - Hemn M.Sharif (B.D.S, MSC, O.Medicine) 2-4-2020Document18 pagesOsteomyelitis: Oral Pathology 4 Stage DR - Hemn M.Sharif (B.D.S, MSC, O.Medicine) 2-4-2020محمد عبدالهادي إسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis Oral SurgeryDocument17 pagesOsteomyelitis Oral SurgerySmile GuyNo ratings yet
- Blue Modern Medical - Health PresentationDocument22 pagesBlue Modern Medical - Health Presentationكرم الباريNo ratings yet
- Radio CaseeeeDocument24 pagesRadio CaseeeeAhmed ZarifNo ratings yet
- Complication of ExodontiaDocument54 pagesComplication of ExodontiaHudh HudNo ratings yet
- Chronic OsteomylitisqDocument5 pagesChronic Osteomylitisqdrahmed1028No ratings yet
- Bone Disease 1Document26 pagesBone Disease 1Ari IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Disorder of BoneDocument13 pagesInflammatory Disorder of Bonedentist07801644159No ratings yet
- Pulp and Periapical TissuesDocument2 pagesPulp and Periapical TissuesBhaveshNo ratings yet
- OsteomyelitisDocument15 pagesOsteomyelitis2018B-04Desti RhomaliaNo ratings yet
- Bone Infections For PMDocument31 pagesBone Infections For PM202201666No ratings yet
- OSTEOMYELITISDocument5 pagesOSTEOMYELITISArafat Masud Niloy100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Inflammatory Disorders of Bones and Joints 209Document16 pagesChapter 10 Inflammatory Disorders of Bones and Joints 209saleh nurazhariNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis of The JawsDocument70 pagesOsteomyelitis of The JawsMONIKANo ratings yet
- Complications After AmputationDocument44 pagesComplications After AmputationGulzar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Due To The Sharp Bending of The Vessels in The Metaphysic and Also by The Hematoma Formed After InjuryDocument6 pagesDue To The Sharp Bending of The Vessels in The Metaphysic and Also by The Hematoma Formed After InjuryBashar EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Patho (Osteomyelitis)Document2 pagesPatho (Osteomyelitis)sidaveNo ratings yet
- SMNR - 4... Wound HealingDocument62 pagesSMNR - 4... Wound HealingDrAmar GillNo ratings yet
- Special Lecture 5Document10 pagesSpecial Lecture 5HussainNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis: Dr. Dewi Klarita Furtuna, M.Ked - Klin., SP - MKDocument49 pagesOsteomyelitis: Dr. Dewi Klarita Furtuna, M.Ked - Klin., SP - MKStefNo ratings yet
- Plain X Rays of BonesDocument17 pagesPlain X Rays of BonesEmmanuella NoelNo ratings yet
- OsteomyelitisDocument28 pagesOsteomyelitisZelalem AbrhamNo ratings yet
- Complications of FracturesDocument29 pagesComplications of FracturesAlina Panciuc100% (1)
- Osteitis Deformans Paget's Disease of Bone: Age: Sex: SiteDocument11 pagesOsteitis Deformans Paget's Disease of Bone: Age: Sex: Sitesalma.almontasir89No ratings yet
- Infections of The Bone Dr. Mehzabin AhmedDocument14 pagesInfections of The Bone Dr. Mehzabin AhmednhemieNo ratings yet
- Xray of Bones in OsteomyelitisDocument35 pagesXray of Bones in OsteomyelitisBukola AjokeNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Temporomandibular JointDocument27 pagesDiseases of The Temporomandibular JointJustDen090% (1)
- L25 Inflammatory Joint DiseasesDocument27 pagesL25 Inflammatory Joint Diseases8ht2twrg5fNo ratings yet
- 3 First Treat FractDocument40 pages3 First Treat FractYoussef ElbeharyNo ratings yet
- L2 PathoDocument3 pagesL2 Pathodrahmed1028No ratings yet
- Blue Modern Medical - Health Presentation - 2Document22 pagesBlue Modern Medical - Health Presentation - 2كرم الباريNo ratings yet
- Periodontal PocketDocument48 pagesPeriodontal PocketMaha JabeenNo ratings yet
- Periodontics Bone Loss and Patterns of Bone DestructionDocument10 pagesPeriodontics Bone Loss and Patterns of Bone Destructionsupriya bhartiNo ratings yet
- Radio CaseeeeDocument24 pagesRadio CaseeeeAhmed ZarifNo ratings yet
- 34 OsteomyelitisDocument3 pages34 OsteomyelitisDurga VoraNo ratings yet
- Remota 170426124830Document34 pagesRemota 170426124830Lolo TotoNo ratings yet
- .Document33 pages.3bdullah al3yuniNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Morpho-Pathological Characteristic of Acute, Chronic and Exacherbate Stage of Apical Periodontitis. Positive and Differentiol DiagnosisDocument53 pagesClinical and Morpho-Pathological Characteristic of Acute, Chronic and Exacherbate Stage of Apical Periodontitis. Positive and Differentiol DiagnosisShany SchwarzwaldNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Process Short For StudentsDocument70 pagesInflammatory Process Short For StudentsLiliana Mitu PanfiliiNo ratings yet
- Bone InfectionsDocument22 pagesBone InfectionsOmar MustafaNo ratings yet
- MSK PathologyDocument21 pagesMSK PathologyMFC 2019No ratings yet
- Bones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasDocument34 pagesBones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis of JawsDocument28 pagesOsteomyelitis of JawsGujjar VishalNo ratings yet
- Non Odontogenic InfectionDocument38 pagesNon Odontogenic InfectionMuhamad ArifNo ratings yet
- Arthritis (OA RA)Document50 pagesArthritis (OA RA)sarvinakumaresan1No ratings yet
- 5 Inflammation of Bone NewDocument15 pages5 Inflammation of Bone Newnightfury200313No ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis 130708212636 Phpapp01Document107 pagesOsteomyelitis 130708212636 Phpapp01merikasorNo ratings yet
- 5Document10 pages5razykontar1No ratings yet
- 3Document10 pages3razykontar1No ratings yet
- 2Document10 pages2razykontar1No ratings yet
- 1Document10 pages1razykontar1No ratings yet
- 6266761Document77 pages6266761razykontar1No ratings yet
- Lip&Oral Malignant NeoplasmDocument34 pagesLip&Oral Malignant Neoplasmrazykontar1No ratings yet
- Changes of malar ,arch and bone of noseDocument14 pagesChanges of malar ,arch and bone of noserazykontar1No ratings yet
Local complications of maxillofacial area injuries
Local complications of maxillofacial area injuries
Uploaded by
razykontar10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views9 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views9 pagesLocal complications of maxillofacial area injuries
Local complications of maxillofacial area injuries
Uploaded by
razykontar1Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Local complications of
maxillofacial area injuries
By: Razy Kontar
Local complications :
• Secondary bleeding
• Infectious inflammatory complications
• Traumatic osteomyelitis
• Ankylosis
• Persistent contracture of the masticatory muscles
• Traumatic sinusitis
• Fistula of the salivary glands
• Paresthesia, hyposthesia and hyperesthesia of the skin of the face and
mucosa
Bleeding
1) Intra-tissue
2) External
3) Internal
a) Primary
b) Secondary :Complications such as secondary bleeding may occur 7-15 days
after the injury or at a later date.
Hematoma formation
Haematoma formation post-operatively is usually due to a combination of
inadequate post-operative haemostasis combined with overtight suturing. Its
occurrence leads to the development of considerable swelling of the face and
neck adjacent to the operation site, and the firm swelling is painful and tender on
palpation.
Infectious and inflammatory complications :
soft tissue suppuration
Symptoms :– intense pain;
– peritoneal tissue infiltration and swelling;
– hyperemia of the skin;
– frank fluctuation of the swelling;
– visible discharge of pus;
– fever;
– leukocytosis;
Supporation of bone wound
Suppuration of a bone wound is an inflammatory process, localized only in
the area of the primary lesion of the bone, easily eliminated by draining
the purulent focus. In case of bone wound suppuration, the main sign of
traumatic osteomyelitis is absent — there is no bone necrosis or sequestration.
The duration of this period is 7–10 days.
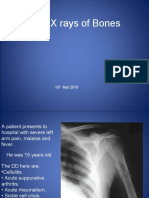
Traumatic osteomyelitis
This is a purulent-necrotic process in the area of jaw damage, which is
accompanied by bone necrosis with the formation of sequesters and bone
Regeneration
1) Acute
2) Subacute
3) Chronic
Ankylosis
This is a persistent reduction of the jaws, caused by the fusion of
the articular surface of the head of the lower jaw with the articular cavity of
the temporal bone.
By the type of forming tissue fibrous and bone ankylosis are distinguished.
Paresthesias , Hypothesias
Paresthesias, hyposthesias and hyperaesthesias of the face skin and oral
mucosa are one of the complications of trauma to the maxillofacial area due to
the case of injuries of the branches of the trigeminal nerve
You might also like
- TB of BoneDocument18 pagesTB of BoneGarvit batraNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Disease of BonesDocument93 pagesInflammatory Disease of BonesNelson LagatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document32 pagesChapter 10Henderi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Bone II-2Document59 pagesDisorders of Bone II-2Guhan DergNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis of Jaws: Presented By: Anuradha B.D.S Final YearDocument11 pagesOsteomyelitis of Jaws: Presented By: Anuradha B.D.S Final YearGujjar VishalNo ratings yet
- OsteomyelitisDocument29 pagesOsteomyelitistaha saadNo ratings yet
- Periapical DiseasesDocument43 pagesPeriapical DiseasesKHALED WALEEDNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis Oral SurgeryDocument17 pagesOsteomyelitis Oral SurgeryFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Wa0006.Document14 pagesWa0006.mldmddhNo ratings yet
- Classification of Diseases of TMJDocument9 pagesClassification of Diseases of TMJSwati DalmiaNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Bone and Soft Tissue-LectureDocument52 pagesPathology of Bone and Soft Tissue-Lecturejohnwickshopping79No ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis: Oral Pathology 4 Stage DR - Hemn M.Sharif (B.D.S, MSC, O.Medicine) 2-4-2020Document18 pagesOsteomyelitis: Oral Pathology 4 Stage DR - Hemn M.Sharif (B.D.S, MSC, O.Medicine) 2-4-2020محمد عبدالهادي إسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis Oral SurgeryDocument17 pagesOsteomyelitis Oral SurgerySmile GuyNo ratings yet
- Blue Modern Medical - Health PresentationDocument22 pagesBlue Modern Medical - Health Presentationكرم الباريNo ratings yet
- Radio CaseeeeDocument24 pagesRadio CaseeeeAhmed ZarifNo ratings yet
- Complication of ExodontiaDocument54 pagesComplication of ExodontiaHudh HudNo ratings yet
- Chronic OsteomylitisqDocument5 pagesChronic Osteomylitisqdrahmed1028No ratings yet
- Bone Disease 1Document26 pagesBone Disease 1Ari IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Disorder of BoneDocument13 pagesInflammatory Disorder of Bonedentist07801644159No ratings yet
- Pulp and Periapical TissuesDocument2 pagesPulp and Periapical TissuesBhaveshNo ratings yet
- OsteomyelitisDocument15 pagesOsteomyelitis2018B-04Desti RhomaliaNo ratings yet
- Bone Infections For PMDocument31 pagesBone Infections For PM202201666No ratings yet
- OSTEOMYELITISDocument5 pagesOSTEOMYELITISArafat Masud Niloy100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Inflammatory Disorders of Bones and Joints 209Document16 pagesChapter 10 Inflammatory Disorders of Bones and Joints 209saleh nurazhariNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis of The JawsDocument70 pagesOsteomyelitis of The JawsMONIKANo ratings yet
- Complications After AmputationDocument44 pagesComplications After AmputationGulzar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Due To The Sharp Bending of The Vessels in The Metaphysic and Also by The Hematoma Formed After InjuryDocument6 pagesDue To The Sharp Bending of The Vessels in The Metaphysic and Also by The Hematoma Formed After InjuryBashar EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Patho (Osteomyelitis)Document2 pagesPatho (Osteomyelitis)sidaveNo ratings yet
- SMNR - 4... Wound HealingDocument62 pagesSMNR - 4... Wound HealingDrAmar GillNo ratings yet
- Special Lecture 5Document10 pagesSpecial Lecture 5HussainNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis: Dr. Dewi Klarita Furtuna, M.Ked - Klin., SP - MKDocument49 pagesOsteomyelitis: Dr. Dewi Klarita Furtuna, M.Ked - Klin., SP - MKStefNo ratings yet
- Plain X Rays of BonesDocument17 pagesPlain X Rays of BonesEmmanuella NoelNo ratings yet
- OsteomyelitisDocument28 pagesOsteomyelitisZelalem AbrhamNo ratings yet
- Complications of FracturesDocument29 pagesComplications of FracturesAlina Panciuc100% (1)
- Osteitis Deformans Paget's Disease of Bone: Age: Sex: SiteDocument11 pagesOsteitis Deformans Paget's Disease of Bone: Age: Sex: Sitesalma.almontasir89No ratings yet
- Infections of The Bone Dr. Mehzabin AhmedDocument14 pagesInfections of The Bone Dr. Mehzabin AhmednhemieNo ratings yet
- Xray of Bones in OsteomyelitisDocument35 pagesXray of Bones in OsteomyelitisBukola AjokeNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Temporomandibular JointDocument27 pagesDiseases of The Temporomandibular JointJustDen090% (1)
- L25 Inflammatory Joint DiseasesDocument27 pagesL25 Inflammatory Joint Diseases8ht2twrg5fNo ratings yet
- 3 First Treat FractDocument40 pages3 First Treat FractYoussef ElbeharyNo ratings yet
- L2 PathoDocument3 pagesL2 Pathodrahmed1028No ratings yet
- Blue Modern Medical - Health Presentation - 2Document22 pagesBlue Modern Medical - Health Presentation - 2كرم الباريNo ratings yet
- Periodontal PocketDocument48 pagesPeriodontal PocketMaha JabeenNo ratings yet
- Periodontics Bone Loss and Patterns of Bone DestructionDocument10 pagesPeriodontics Bone Loss and Patterns of Bone Destructionsupriya bhartiNo ratings yet
- Radio CaseeeeDocument24 pagesRadio CaseeeeAhmed ZarifNo ratings yet
- 34 OsteomyelitisDocument3 pages34 OsteomyelitisDurga VoraNo ratings yet
- Remota 170426124830Document34 pagesRemota 170426124830Lolo TotoNo ratings yet
- .Document33 pages.3bdullah al3yuniNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Morpho-Pathological Characteristic of Acute, Chronic and Exacherbate Stage of Apical Periodontitis. Positive and Differentiol DiagnosisDocument53 pagesClinical and Morpho-Pathological Characteristic of Acute, Chronic and Exacherbate Stage of Apical Periodontitis. Positive and Differentiol DiagnosisShany SchwarzwaldNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Process Short For StudentsDocument70 pagesInflammatory Process Short For StudentsLiliana Mitu PanfiliiNo ratings yet
- Bone InfectionsDocument22 pagesBone InfectionsOmar MustafaNo ratings yet
- MSK PathologyDocument21 pagesMSK PathologyMFC 2019No ratings yet
- Bones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasDocument34 pagesBones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis of JawsDocument28 pagesOsteomyelitis of JawsGujjar VishalNo ratings yet
- Non Odontogenic InfectionDocument38 pagesNon Odontogenic InfectionMuhamad ArifNo ratings yet
- Arthritis (OA RA)Document50 pagesArthritis (OA RA)sarvinakumaresan1No ratings yet
- 5 Inflammation of Bone NewDocument15 pages5 Inflammation of Bone Newnightfury200313No ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis 130708212636 Phpapp01Document107 pagesOsteomyelitis 130708212636 Phpapp01merikasorNo ratings yet
- 5Document10 pages5razykontar1No ratings yet
- 3Document10 pages3razykontar1No ratings yet
- 2Document10 pages2razykontar1No ratings yet
- 1Document10 pages1razykontar1No ratings yet
- 6266761Document77 pages6266761razykontar1No ratings yet
- Lip&Oral Malignant NeoplasmDocument34 pagesLip&Oral Malignant Neoplasmrazykontar1No ratings yet
- Changes of malar ,arch and bone of noseDocument14 pagesChanges of malar ,arch and bone of noserazykontar1No ratings yet