Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 viewsWINSEM2023-24_BCHE302L_TH_VL2023240501241_2024-01-24_Reference-Material-I
WINSEM2023-24_BCHE302L_TH_VL2023240501241_2024-01-24_Reference-Material-I
Uploaded by
bala a guy with a gangCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Mass Transfer Tutorial: Distillation Example Problem 2: Mccabe-Thiele MethodDocument11 pagesMass Transfer Tutorial: Distillation Example Problem 2: Mccabe-Thiele MethodTapiwa KapondaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium.2 ExampleDocument14 pagesEquilibrium.2 Examplekindenew50% (2)
- Distillation Aspen HysysDocument66 pagesDistillation Aspen HysysCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios.1-Varios Equipos, Multicomponentes, Sin RX PDFDocument4 pagesEjercicios.1-Varios Equipos, Multicomponentes, Sin RX PDFMafee VelezNo ratings yet
- Problems in Mass TransferDocument3 pagesProblems in Mass TransferAngelica Joyce BenitoNo ratings yet
- Coulson Sample ProblemsDocument13 pagesCoulson Sample ProblemsHayley AñonuevoNo ratings yet
- Problem Set # 2Document5 pagesProblem Set # 2Dharyl Flores0% (2)
- Reviewer 1Document12 pagesReviewer 1Vanessa Denise AguilarNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument11 pagesReviewerApril Joyce RaymundoNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument40 pagesDistillationEbook Download100% (2)
- Deviations and Non Conformances SOP PDFDocument1 pageDeviations and Non Conformances SOP PDFAlinaNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2015-16 CP3149 04-Aug-2015 RM01 Tutorial-1Document2 pagesFALLSEM2015-16 CP3149 04-Aug-2015 RM01 Tutorial-1ShashwatAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 200412Document2 pagesIndividual Assignment 200412Zaidi ZakariaNo ratings yet
- MTO AssignmentDocument4 pagesMTO AssignmentBishal LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Distillation Problem Set PDFDocument1 pageDistillation Problem Set PDFEfraim AbuelNo ratings yet
- Distillation Problem SetDocument1 pageDistillation Problem SetEfraim Abuel100% (1)
- Sheet 8 McCabe ThieleDocument2 pagesSheet 8 McCabe ThieleMohamed Fateem0% (1)
- Assignment Problems Batch I (R.No. 102117001 To 102117011)Document7 pagesAssignment Problems Batch I (R.No. 102117001 To 102117011)Nishanth ChandranNo ratings yet
- CH353 Exercise Problem 6 Batch IIDocument2 pagesCH353 Exercise Problem 6 Batch IISagarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 DistillationDocument6 pagesTutorial 2 Distillationmaheema rimalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Chapter 2 (June - Oct 2013)Document5 pagesTutorial-Chapter 2 (June - Oct 2013)paulineanakmawatNo ratings yet
- Ert 313/4 - Bioseparation Engineering Assignment 1 Date of Submission: 20 Jan 2011Document2 pagesErt 313/4 - Bioseparation Engineering Assignment 1 Date of Submission: 20 Jan 2011Muzammil IqbalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial in MT 2Document3 pagesTutorial in MT 2mohanraj1990No ratings yet
- Che F244 1183 C 2015 2Document4 pagesChe F244 1183 C 2015 2shubhamNo ratings yet
- Distillation TutorialDocument17 pagesDistillation TutorialXin-YiWoon100% (1)
- Distillation (Reviewer)Document3 pagesDistillation (Reviewer)TJ ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Che 246 - Mass Transfer and Unit Operations Tutorial-Chapter 2 (Distillation)Document5 pagesChe 246 - Mass Transfer and Unit Operations Tutorial-Chapter 2 (Distillation)fatien zakariaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2aliNo ratings yet
- #Separation TUT1Document1 page#Separation TUT1ibtihal esamNo ratings yet
- Distillation - Self Study QuestionsDocument8 pagesDistillation - Self Study QuestionsEsther MaidenNo ratings yet
- Distillation Exercises - Set 1Document3 pagesDistillation Exercises - Set 1Fred VoNo ratings yet
- Separo Quiz No. 2Document1 pageSeparo Quiz No. 2Bench GuecoNo ratings yet
- 400L Chemical Engr. Past Questions (2012/2013)Document52 pages400L Chemical Engr. Past Questions (2012/2013)ifiokNo ratings yet
- 2023 SPU260S Tutorial 3 QuestionsDocument6 pages2023 SPU260S Tutorial 3 QuestionsMABUKE NDINAINWI INNOCENTIANo ratings yet
- Diploma Examination, May 2015: (Petroleum Refining Engineering) 110. DistillationDocument2 pagesDiploma Examination, May 2015: (Petroleum Refining Engineering) 110. DistillationgebremichaelNo ratings yet
- MTO Assignment3Document2 pagesMTO Assignment3Krishnaveni RNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 (7332)Document8 pagesAssignment 4 (7332)Musa KaleemNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Set4ansDocument4 pagesChemical Reaction Set4ansffffffNo ratings yet
- BdeM Taller No. 2Document2 pagesBdeM Taller No. 2Luisfer PriceNo ratings yet
- Ayırma İşlemleri SorularDocument9 pagesAyırma İşlemleri SorularElif Yaren Öztürk0% (1)
- Sheet 4 AbsorptionDocument4 pagesSheet 4 AbsorptionMohamed FateemNo ratings yet
- TareaDocument3 pagesTareaAydee GarciaNo ratings yet
- TutrealDocument2 pagesTutrealsaint deanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DistillationDocument3 pagesTutorial DistillationManu Indivare Nundoolall100% (1)
- Assignment On Continuous Distillation - McCabe-Thiele Method (1) - 1442573024785Document5 pagesAssignment On Continuous Distillation - McCabe-Thiele Method (1) - 1442573024785sri pragna0% (1)
- 3A Total Feed of 200 MolDocument2 pages3A Total Feed of 200 Molgebre0% (1)
- Peme1025: Engineering Sciences 1: Mass Balances Tutorial Sheet 1Document4 pagesPeme1025: Engineering Sciences 1: Mass Balances Tutorial Sheet 1Kwasi NuamahNo ratings yet
- Universiti Kuala Lumpur Ccb10702 Material Balances Tutorial 2Document2 pagesUniversiti Kuala Lumpur Ccb10702 Material Balances Tutorial 2Surendra Louis DupuisNo ratings yet
- BdeM Taller No. 2 Una Sola Unidad 2018-VDocument4 pagesBdeM Taller No. 2 Una Sola Unidad 2018-VMarelbis RangelNo ratings yet
- Separation ProcessesDocument3 pagesSeparation ProcessesJoshua SolomonNo ratings yet
- Lectut CHN-102 PDF ReactiveDocument4 pagesLectut CHN-102 PDF ReactiveTanmaysainiNo ratings yet
- NothingDocument2 pagesNothingAniruddh Modi100% (1)
- Separation Processes IDocument3 pagesSeparation Processes IAmesh Chiyogami100% (1)
- Taller Balance Sin RXN QCADocument4 pagesTaller Balance Sin RXN QCAValentina BaldovinosNo ratings yet
- Material Balance SheetDocument4 pagesMaterial Balance Sheetsyed waheed ul hasanNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument6 pagesDistillationanita_shar29No ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Cellulose Nanocrystals: Properties, Production and ApplicationsFrom EverandCellulose Nanocrystals: Properties, Production and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Carbon Nanomaterials for Advanced Energy Systems: Advances in Materials Synthesis and Device ApplicationsFrom EverandCarbon Nanomaterials for Advanced Energy Systems: Advances in Materials Synthesis and Device ApplicationsWen LuNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BCHE207L TH VL2023240100110 2023-04-24 Reference-Material-IDocument103 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BCHE207L TH VL2023240100110 2023-04-24 Reference-Material-Ibala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BCHE301L TH VL2023240100109 2023-05-11 Reference-Material-IDocument93 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BCHE301L TH VL2023240100109 2023-05-11 Reference-Material-Ibala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BCHE301L TH VL2023240100109 2023-05-16 Reference-Material-IIDocument23 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BCHE301L TH VL2023240100109 2023-05-16 Reference-Material-IIbala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material II 26-07-2022 Module12Document6 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material II 26-07-2022 Module12bala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material II 08-08-2022 Module15Document2 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material II 08-08-2022 Module15bala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 Module1 1Document38 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 Module1 1bala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material I 08-08-2022 Module14Document2 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material I 08-08-2022 Module14bala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- Letter From The Domestic Abuse Commissioner To The Prime MinisterDocument2 pagesLetter From The Domestic Abuse Commissioner To The Prime MinisterAmber HenshawNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument32 pagesCapital StructureFebson Lee Mathew100% (1)
- Valeriano 2B Pat-Final-ExamDocument24 pagesValeriano 2B Pat-Final-ExamAira Rowena TalactacNo ratings yet
- CH 5.palepuDocument34 pagesCH 5.palepuRavi OlaNo ratings yet
- Tatum v. Mississippi Department of Corrections Et Al - Document No. 12Document2 pagesTatum v. Mississippi Department of Corrections Et Al - Document No. 12Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Alexander Shevyakin (Александр Шевякин) - Lists of Jews disguised (Списки замаскированных евреев) - 2009Document92 pagesAlexander Shevyakin (Александр Шевякин) - Lists of Jews disguised (Списки замаскированных евреев) - 2009ayazan2006100% (1)
- General Accident: Comprehensive Personal LiabilityDocument1 pageGeneral Accident: Comprehensive Personal LiabilityJun FalconNo ratings yet
- Sexual Harassment TheoryDocument8 pagesSexual Harassment Theorysmithkumar88No ratings yet
- Tic Honey TirumalaDocument2 pagesTic Honey TirumalaVamshi Krishna ArigelaNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets - EDHEC Risk InstituteDocument386 pagesCapital Markets - EDHEC Risk InstituteRicky Rick100% (1)
- Partnership Support: Form For ResidenceDocument8 pagesPartnership Support: Form For ResidenceChrisNo ratings yet
- Amazing Grace Sorpano y PianoDocument4 pagesAmazing Grace Sorpano y PianoRoberto ErazoNo ratings yet
- Sec.21 To 26Document1 pageSec.21 To 26Laguna ProbationNo ratings yet
- Anoushka Mishra Ba - LLB (H) 1841802021 Loc 6thsemDocument30 pagesAnoushka Mishra Ba - LLB (H) 1841802021 Loc 6thsemFlorosia StarshineNo ratings yet
- 1 The Province of North Cotabato Vs GRP, G.R. No. 183591, October 14, 2008Document145 pages1 The Province of North Cotabato Vs GRP, G.R. No. 183591, October 14, 2008Right CydNo ratings yet
- The Unionist February 2014Document8 pagesThe Unionist February 2014novvotikNo ratings yet
- DSCF Press ReleaseDocument2 pagesDSCF Press ReleaseGodwin IwekaNo ratings yet
- 1624 1637Document5 pages1624 1637cris50% (2)
- Plant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible Assets: Accounting Principles, Ninth EditionDocument21 pagesPlant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible Assets: Accounting Principles, Ninth EditionMehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- The Story of Charlie "Two Shoes" TsuiDocument8 pagesThe Story of Charlie "Two Shoes" Tsuisavannahnow.comNo ratings yet
- Fullpapers Jahie514e394812full PDFDocument23 pagesFullpapers Jahie514e394812full PDFMhisna She TwibbyNo ratings yet
- 13-Fisher v. Trinidad G.R. No. L-17518 October 30, 1922Document13 pages13-Fisher v. Trinidad G.R. No. L-17518 October 30, 1922Jopan SJNo ratings yet
- Ervin Leon Edwards LawsuitDocument25 pagesErvin Leon Edwards Lawsuittom clearyNo ratings yet
- Yoma 120905 Oir FinalDocument53 pagesYoma 120905 Oir FinaljwkNo ratings yet
- EXTRAJUDICIAL Settlement of Estate APRONIO CORONADODocument3 pagesEXTRAJUDICIAL Settlement of Estate APRONIO CORONADOFiona FedericoNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument13 pagesElectrostaticssjo0567% (3)
- Social ChangeDocument11 pagesSocial ChangeRupert BautistaNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document3 pagesBook 1Brendan ClancyNo ratings yet
- Accounting Fact SheetDocument1 pageAccounting Fact SheetSergio OlarteNo ratings yet
WINSEM2023-24_BCHE302L_TH_VL2023240501241_2024-01-24_Reference-Material-I
WINSEM2023-24_BCHE302L_TH_VL2023240501241_2024-01-24_Reference-Material-I
Uploaded by
bala a guy with a gang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views7 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views7 pagesWINSEM2023-24_BCHE302L_TH_VL2023240501241_2024-01-24_Reference-Material-I
WINSEM2023-24_BCHE302L_TH_VL2023240501241_2024-01-24_Reference-Material-I
Uploaded by
bala a guy with a gangCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Numericals
• A continuous fractionating column is to be designed to separate 14000 kg/h of a
mixture of 40% benzene and 60% toluene at 1 atm into an overhead product
containing 97% benzene and a bottom product containing 98% toluene. These
percentages are by weight. The feed is available at 293 K (20 °C) and 1 atm. A
reflux ratio of three times the minimum is used.
Determine: (a) The quantities of overhead and bottoms in kmol/h.
(b) The number of real/actual plates required and the optimum position of feed
plate.
• Given :
• Benzene and tolune form an ideal system with a relative volatility of 2.5
• The molal latent heats of benzene and tolune are 30800 and 33300 kJ/kmol
respectively.
• The bubble point of feed at 1 atm is 368 K (95 °C) and its specific heat is 1.85
kJ/(kg.K).
• Overall efficiency of 60% can be assumed.
2.1-Mc cabe thiele
• A rectification column is fed 100kgmol/h of a mixture of 50 mol
% benzene and 50 mol% toluene at 101.32kpa abs pressure.
The feed is a liquid at its boiling point. The distillate is to contain
90mol% benzene and the bottoms 10mol% benzene. The reflux
ratio is 4.5:1
Benzene and toluene form an ideal system with a relative
volatility of 2.5
(i) Calculate the kg mol/h distillate, kg mol/h bottoms
(ii) The number of theoretical trays using McCabe Thiele
method
(iii) Minimum reflux ratio
(iv) Minimum number of theoretical plates at total reflux
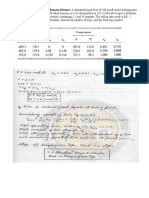
1. A binary mixture of methanol (30% by weight) and ethanol(70% by weight) is to be
separated by fractionation to obtain each of 95% purity by weight. Calculate the
minimum reflux and the number of ideal plates at total reflux if the feed is 30%
vaporised. Also calculate the actual number of plates if a reflux ratio of twice the
minimum is used when the overall plate efficiency is 60%
The system follow raoult's law. The following vapour pressure data are available
Temperatu 64 67 70 73 76 78
re °C
Methanol 760 820 920 1020 1150 1260
mmHg
Ethanol 420 430 470 610 690 760
mmHg
A binary distillation column is operating under the conditions given
below:
Feed rate = 400 kmol/hr
Overhead product rate = 200 kmol/hr
Mole fraction of more volatile component in overhead product = 0.97.
Mole fraction of more volatile component in bottom product = 0.02.
Bottom product rate = 200 kmol/hr
Reflux ratio = 3.5
In the stripping section, it was found that the mole fraction of the volatile
component in the vapour leaving a plate is 0.33 while its mole fraction in
the liquid coming to the same plate is 0.25. Assuming constant molal
counter flow, determine whether the feed is vapour, liquid or partially
vapourized
You might also like
- Mass Transfer Tutorial: Distillation Example Problem 2: Mccabe-Thiele MethodDocument11 pagesMass Transfer Tutorial: Distillation Example Problem 2: Mccabe-Thiele MethodTapiwa KapondaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium.2 ExampleDocument14 pagesEquilibrium.2 Examplekindenew50% (2)
- Distillation Aspen HysysDocument66 pagesDistillation Aspen HysysCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios.1-Varios Equipos, Multicomponentes, Sin RX PDFDocument4 pagesEjercicios.1-Varios Equipos, Multicomponentes, Sin RX PDFMafee VelezNo ratings yet
- Problems in Mass TransferDocument3 pagesProblems in Mass TransferAngelica Joyce BenitoNo ratings yet
- Coulson Sample ProblemsDocument13 pagesCoulson Sample ProblemsHayley AñonuevoNo ratings yet
- Problem Set # 2Document5 pagesProblem Set # 2Dharyl Flores0% (2)
- Reviewer 1Document12 pagesReviewer 1Vanessa Denise AguilarNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument11 pagesReviewerApril Joyce RaymundoNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument40 pagesDistillationEbook Download100% (2)
- Deviations and Non Conformances SOP PDFDocument1 pageDeviations and Non Conformances SOP PDFAlinaNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2015-16 CP3149 04-Aug-2015 RM01 Tutorial-1Document2 pagesFALLSEM2015-16 CP3149 04-Aug-2015 RM01 Tutorial-1ShashwatAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 200412Document2 pagesIndividual Assignment 200412Zaidi ZakariaNo ratings yet
- MTO AssignmentDocument4 pagesMTO AssignmentBishal LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Distillation Problem Set PDFDocument1 pageDistillation Problem Set PDFEfraim AbuelNo ratings yet
- Distillation Problem SetDocument1 pageDistillation Problem SetEfraim Abuel100% (1)
- Sheet 8 McCabe ThieleDocument2 pagesSheet 8 McCabe ThieleMohamed Fateem0% (1)
- Assignment Problems Batch I (R.No. 102117001 To 102117011)Document7 pagesAssignment Problems Batch I (R.No. 102117001 To 102117011)Nishanth ChandranNo ratings yet
- CH353 Exercise Problem 6 Batch IIDocument2 pagesCH353 Exercise Problem 6 Batch IISagarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 DistillationDocument6 pagesTutorial 2 Distillationmaheema rimalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Chapter 2 (June - Oct 2013)Document5 pagesTutorial-Chapter 2 (June - Oct 2013)paulineanakmawatNo ratings yet
- Ert 313/4 - Bioseparation Engineering Assignment 1 Date of Submission: 20 Jan 2011Document2 pagesErt 313/4 - Bioseparation Engineering Assignment 1 Date of Submission: 20 Jan 2011Muzammil IqbalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial in MT 2Document3 pagesTutorial in MT 2mohanraj1990No ratings yet
- Che F244 1183 C 2015 2Document4 pagesChe F244 1183 C 2015 2shubhamNo ratings yet
- Distillation TutorialDocument17 pagesDistillation TutorialXin-YiWoon100% (1)
- Distillation (Reviewer)Document3 pagesDistillation (Reviewer)TJ ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Che 246 - Mass Transfer and Unit Operations Tutorial-Chapter 2 (Distillation)Document5 pagesChe 246 - Mass Transfer and Unit Operations Tutorial-Chapter 2 (Distillation)fatien zakariaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2aliNo ratings yet
- #Separation TUT1Document1 page#Separation TUT1ibtihal esamNo ratings yet
- Distillation - Self Study QuestionsDocument8 pagesDistillation - Self Study QuestionsEsther MaidenNo ratings yet
- Distillation Exercises - Set 1Document3 pagesDistillation Exercises - Set 1Fred VoNo ratings yet
- Separo Quiz No. 2Document1 pageSeparo Quiz No. 2Bench GuecoNo ratings yet
- 400L Chemical Engr. Past Questions (2012/2013)Document52 pages400L Chemical Engr. Past Questions (2012/2013)ifiokNo ratings yet
- 2023 SPU260S Tutorial 3 QuestionsDocument6 pages2023 SPU260S Tutorial 3 QuestionsMABUKE NDINAINWI INNOCENTIANo ratings yet
- Diploma Examination, May 2015: (Petroleum Refining Engineering) 110. DistillationDocument2 pagesDiploma Examination, May 2015: (Petroleum Refining Engineering) 110. DistillationgebremichaelNo ratings yet
- MTO Assignment3Document2 pagesMTO Assignment3Krishnaveni RNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 (7332)Document8 pagesAssignment 4 (7332)Musa KaleemNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Set4ansDocument4 pagesChemical Reaction Set4ansffffffNo ratings yet
- BdeM Taller No. 2Document2 pagesBdeM Taller No. 2Luisfer PriceNo ratings yet
- Ayırma İşlemleri SorularDocument9 pagesAyırma İşlemleri SorularElif Yaren Öztürk0% (1)
- Sheet 4 AbsorptionDocument4 pagesSheet 4 AbsorptionMohamed FateemNo ratings yet
- TareaDocument3 pagesTareaAydee GarciaNo ratings yet
- TutrealDocument2 pagesTutrealsaint deanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DistillationDocument3 pagesTutorial DistillationManu Indivare Nundoolall100% (1)
- Assignment On Continuous Distillation - McCabe-Thiele Method (1) - 1442573024785Document5 pagesAssignment On Continuous Distillation - McCabe-Thiele Method (1) - 1442573024785sri pragna0% (1)
- 3A Total Feed of 200 MolDocument2 pages3A Total Feed of 200 Molgebre0% (1)
- Peme1025: Engineering Sciences 1: Mass Balances Tutorial Sheet 1Document4 pagesPeme1025: Engineering Sciences 1: Mass Balances Tutorial Sheet 1Kwasi NuamahNo ratings yet
- Universiti Kuala Lumpur Ccb10702 Material Balances Tutorial 2Document2 pagesUniversiti Kuala Lumpur Ccb10702 Material Balances Tutorial 2Surendra Louis DupuisNo ratings yet
- BdeM Taller No. 2 Una Sola Unidad 2018-VDocument4 pagesBdeM Taller No. 2 Una Sola Unidad 2018-VMarelbis RangelNo ratings yet
- Separation ProcessesDocument3 pagesSeparation ProcessesJoshua SolomonNo ratings yet
- Lectut CHN-102 PDF ReactiveDocument4 pagesLectut CHN-102 PDF ReactiveTanmaysainiNo ratings yet
- NothingDocument2 pagesNothingAniruddh Modi100% (1)
- Separation Processes IDocument3 pagesSeparation Processes IAmesh Chiyogami100% (1)
- Taller Balance Sin RXN QCADocument4 pagesTaller Balance Sin RXN QCAValentina BaldovinosNo ratings yet
- Material Balance SheetDocument4 pagesMaterial Balance Sheetsyed waheed ul hasanNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument6 pagesDistillationanita_shar29No ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Cellulose Nanocrystals: Properties, Production and ApplicationsFrom EverandCellulose Nanocrystals: Properties, Production and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Carbon Nanomaterials for Advanced Energy Systems: Advances in Materials Synthesis and Device ApplicationsFrom EverandCarbon Nanomaterials for Advanced Energy Systems: Advances in Materials Synthesis and Device ApplicationsWen LuNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BCHE207L TH VL2023240100110 2023-04-24 Reference-Material-IDocument103 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BCHE207L TH VL2023240100110 2023-04-24 Reference-Material-Ibala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BCHE301L TH VL2023240100109 2023-05-11 Reference-Material-IDocument93 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BCHE301L TH VL2023240100109 2023-05-11 Reference-Material-Ibala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BCHE301L TH VL2023240100109 2023-05-16 Reference-Material-IIDocument23 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BCHE301L TH VL2023240100109 2023-05-16 Reference-Material-IIbala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material II 26-07-2022 Module12Document6 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material II 26-07-2022 Module12bala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material II 08-08-2022 Module15Document2 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material II 08-08-2022 Module15bala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 Module1 1Document38 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 Module1 1bala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material I 08-08-2022 Module14Document2 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BMAT201L TH VL2022230102300 Reference Material I 08-08-2022 Module14bala a guy with a gangNo ratings yet
- Letter From The Domestic Abuse Commissioner To The Prime MinisterDocument2 pagesLetter From The Domestic Abuse Commissioner To The Prime MinisterAmber HenshawNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument32 pagesCapital StructureFebson Lee Mathew100% (1)
- Valeriano 2B Pat-Final-ExamDocument24 pagesValeriano 2B Pat-Final-ExamAira Rowena TalactacNo ratings yet
- CH 5.palepuDocument34 pagesCH 5.palepuRavi OlaNo ratings yet
- Tatum v. Mississippi Department of Corrections Et Al - Document No. 12Document2 pagesTatum v. Mississippi Department of Corrections Et Al - Document No. 12Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Alexander Shevyakin (Александр Шевякин) - Lists of Jews disguised (Списки замаскированных евреев) - 2009Document92 pagesAlexander Shevyakin (Александр Шевякин) - Lists of Jews disguised (Списки замаскированных евреев) - 2009ayazan2006100% (1)
- General Accident: Comprehensive Personal LiabilityDocument1 pageGeneral Accident: Comprehensive Personal LiabilityJun FalconNo ratings yet
- Sexual Harassment TheoryDocument8 pagesSexual Harassment Theorysmithkumar88No ratings yet
- Tic Honey TirumalaDocument2 pagesTic Honey TirumalaVamshi Krishna ArigelaNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets - EDHEC Risk InstituteDocument386 pagesCapital Markets - EDHEC Risk InstituteRicky Rick100% (1)
- Partnership Support: Form For ResidenceDocument8 pagesPartnership Support: Form For ResidenceChrisNo ratings yet
- Amazing Grace Sorpano y PianoDocument4 pagesAmazing Grace Sorpano y PianoRoberto ErazoNo ratings yet
- Sec.21 To 26Document1 pageSec.21 To 26Laguna ProbationNo ratings yet
- Anoushka Mishra Ba - LLB (H) 1841802021 Loc 6thsemDocument30 pagesAnoushka Mishra Ba - LLB (H) 1841802021 Loc 6thsemFlorosia StarshineNo ratings yet
- 1 The Province of North Cotabato Vs GRP, G.R. No. 183591, October 14, 2008Document145 pages1 The Province of North Cotabato Vs GRP, G.R. No. 183591, October 14, 2008Right CydNo ratings yet
- The Unionist February 2014Document8 pagesThe Unionist February 2014novvotikNo ratings yet
- DSCF Press ReleaseDocument2 pagesDSCF Press ReleaseGodwin IwekaNo ratings yet
- 1624 1637Document5 pages1624 1637cris50% (2)
- Plant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible Assets: Accounting Principles, Ninth EditionDocument21 pagesPlant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible Assets: Accounting Principles, Ninth EditionMehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- The Story of Charlie "Two Shoes" TsuiDocument8 pagesThe Story of Charlie "Two Shoes" Tsuisavannahnow.comNo ratings yet
- Fullpapers Jahie514e394812full PDFDocument23 pagesFullpapers Jahie514e394812full PDFMhisna She TwibbyNo ratings yet
- 13-Fisher v. Trinidad G.R. No. L-17518 October 30, 1922Document13 pages13-Fisher v. Trinidad G.R. No. L-17518 October 30, 1922Jopan SJNo ratings yet
- Ervin Leon Edwards LawsuitDocument25 pagesErvin Leon Edwards Lawsuittom clearyNo ratings yet
- Yoma 120905 Oir FinalDocument53 pagesYoma 120905 Oir FinaljwkNo ratings yet
- EXTRAJUDICIAL Settlement of Estate APRONIO CORONADODocument3 pagesEXTRAJUDICIAL Settlement of Estate APRONIO CORONADOFiona FedericoNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument13 pagesElectrostaticssjo0567% (3)
- Social ChangeDocument11 pagesSocial ChangeRupert BautistaNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document3 pagesBook 1Brendan ClancyNo ratings yet
- Accounting Fact SheetDocument1 pageAccounting Fact SheetSergio OlarteNo ratings yet