Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I.V Nursing Lecture 1 shekhan 2024
I.V Nursing Lecture 1 shekhan 2024
Uploaded by
Collective CompanyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ivf Drug StudyDocument9 pagesIvf Drug StudyRyu Bomi0% (2)
- Amcp Media List 8Document96 pagesAmcp Media List 8api-407904109No ratings yet
- TBE-Pressure Vessel Standard TemplateDocument4 pagesTBE-Pressure Vessel Standard TemplateSiva baalanNo ratings yet
- Como Calcular LiquidosDocument8 pagesComo Calcular Liquidoskaterinavila300No ratings yet
- Intravenous Therapy: Crystalloid and Colloid Solutions: Jassin M. Jouria, MDDocument21 pagesIntravenous Therapy: Crystalloid and Colloid Solutions: Jassin M. Jouria, MDTaniaNo ratings yet
- IV TherapyDocument56 pagesIV TherapyTmz AguilarNo ratings yet
- New Trend IV FluidsDocument9 pagesNew Trend IV FluidsMarfu'ah Mar'ahNo ratings yet
- PHAR635 Parenteral Dosage Forms: Instructors: Dr. Tarek Jenani Dr. Faten HamedDocument29 pagesPHAR635 Parenteral Dosage Forms: Instructors: Dr. Tarek Jenani Dr. Faten HamedundeadrebornNo ratings yet
- Fluid Management For Critically Ill PatientDocument7 pagesFluid Management For Critically Ill PatientNatalindah Jokiem Woecandra T. D.No ratings yet
- 2022 Anesth s1t3 Venous Access and Fluid ManagementDocument6 pages2022 Anesth s1t3 Venous Access and Fluid ManagementMac Vince HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Short Term Effect of Intravenous Fluid Therapy in Paediatric Intensive Care Unit On Serum Electrolytes and Renal Function Tests of ChildrenDocument7 pagesShort Term Effect of Intravenous Fluid Therapy in Paediatric Intensive Care Unit On Serum Electrolytes and Renal Function Tests of ChildrenIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 52389924-IV-therapy NotesDocument57 pages52389924-IV-therapy Notesrye08No ratings yet
- Makalah Can JadiDocument13 pagesMakalah Can JadiTaufiks RohmansNo ratings yet
- IV TherapyDocument10 pagesIV TherapyKate Beatriz ServanoNo ratings yet
- 2019 IV LectureDocument38 pages2019 IV LectureKAUH EducationNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument29 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesLinh Tra100% (1)
- 8.3 IV Fluids, IV Tubing, and Assessment of An IV SystemDocument1 page8.3 IV Fluids, IV Tubing, and Assessment of An IV SystemPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Líquidos NejmDocument11 pagesLíquidos Nejmestudio.slupmNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy in Critically Ill AdultsDocument17 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy in Critically Ill AdultsntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- Update Terapi Cairan Pada: Pasien Covid-19Document43 pagesUpdate Terapi Cairan Pada: Pasien Covid-19Alita Mei RosfyanitaNo ratings yet
- Nutritie Parentala Apa Electroliti Si VitamineDocument7 pagesNutritie Parentala Apa Electroliti Si VitamineGrosu SebastianNo ratings yet
- Principles of Fluid Management 2015 PDFDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Fluid Management 2015 PDFJorge DíazNo ratings yet
- Intravenous TherapyDocument10 pagesIntravenous TherapyS. AmberNo ratings yet
- Abstract IV Fluids Composition and IndicationDocument1 pageAbstract IV Fluids Composition and IndicationThe MindNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Management of Fluids and Electrolytes in ChildrenDocument6 pagesPerioperative Management of Fluids and Electrolytes in ChildrenBetyCamarilloNo ratings yet
- Principles of Fluid Management 2015Document17 pagesPrinciples of Fluid Management 2015MANUELNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Hyponatremia Management: by Craig B. Whitman, Pharm.D., BCPS, BCCCPDocument16 pagesFluid and Hyponatremia Management: by Craig B. Whitman, Pharm.D., BCPS, BCCCPAleksandar Dimovski100% (1)
- Assisting in Ivf InsertionDocument76 pagesAssisting in Ivf Insertionrechelle mae legaspiNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Uid Therapy For Anaesthetists and IntensivistsDocument4 pagesPerioperative Uid Therapy For Anaesthetists and IntensivistsDanitza Pari TiconaNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy TempDocument34 pagesIV Therapy TempJoy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Intravenous Fluids in Acutely Ill Patients: Review ArticleDocument11 pagesMaintenance Intravenous Fluids in Acutely Ill Patients: Review ArticleyoiiiNo ratings yet
- 8.3 IV Fluids, IV Tubing, and Assessment of An IV System: Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient CareDocument12 pages8.3 IV Fluids, IV Tubing, and Assessment of An IV System: Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient Caremelodia gandezaNo ratings yet
- Dwi Arya Jurnal UjianDocument8 pagesDwi Arya Jurnal Ujianwulan nadiaNo ratings yet
- IV SolutionsDocument7 pagesIV SolutionsJeg B. Israel Jr.No ratings yet
- DONE - Activity For Intravenous TherapyDocument6 pagesDONE - Activity For Intravenous TherapyDexie James Ventenilla DizonNo ratings yet
- IJOPP - v5 - I3 - 2012 5Document7 pagesIJOPP - v5 - I3 - 2012 5Ambujesh ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- G SurgeryDocument21 pagesG SurgerySRO oONo ratings yet
- Principles of Fluid ManagementDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Fluid ManagementBrainy-Paykiesaurus LuminirexNo ratings yet
- 4 Fases de La FluidoterapiaDocument8 pages4 Fases de La FluidoterapiaAna Claudia Rodríguez MárquezNo ratings yet
- Obrien2013 PDFDocument11 pagesObrien2013 PDFIrham AbsharNo ratings yet
- ARCS Paediatric IV Fluid GuidelinesDocument16 pagesARCS Paediatric IV Fluid GuidelinesWidyadarya Triyono PutriNo ratings yet
- Infusions and Parenteral Fluids 2000Document4 pagesInfusions and Parenteral Fluids 2000Alexia OwenNo ratings yet
- JVBS FluidtherapyDocument16 pagesJVBS FluidtherapyvetthamilNo ratings yet
- 12 Dentistry L12 Parenteral NutritionDocument13 pages12 Dentistry L12 Parenteral NutritionmyydsamyydsaNo ratings yet
- JAPI Jun 2024 PublicationDocument10 pagesJAPI Jun 2024 Publicationlakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Admixtures: Salvatore J Turco, Pharmd, FashpDocument13 pagesIntravenous Admixtures: Salvatore J Turco, Pharmd, FashpRead WhiteNo ratings yet
- Hiponatremia in The ClinicaDocument19 pagesHiponatremia in The ClinicaHugo GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skills: Intravenous Fluid and Setting Up A DripDocument30 pagesClinical Skills: Intravenous Fluid and Setting Up A DripNabhan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Selection PDFDocument12 pagesIntravenous Fluid Selection PDFVASGJGNo ratings yet
- IV FluidsDocument33 pagesIV Fluidsartmanx112No ratings yet
- Handout 4Document6 pagesHandout 4Judea PagedpedNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid SelectionDocument12 pagesIntravenous Fluid SelectionTracy100% (4)
- Am J Clin Nutr 2016 Maughan 717 23Document7 pagesAm J Clin Nutr 2016 Maughan 717 23sfvsvsNo ratings yet
- INTRAVENOUS THERAPY AND BLOOD TRANSFUSION HandoutDocument21 pagesINTRAVENOUS THERAPY AND BLOOD TRANSFUSION HandoutMicah TuringanNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceFrom EverandFluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Intravenous Therapy Administration: a practical guideFrom EverandIntravenous Therapy Administration: a practical guideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Kidney Disease Management: A Practical Approach for the Non-Specialist Healthcare PractitionerFrom EverandKidney Disease Management: A Practical Approach for the Non-Specialist Healthcare PractitionerNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Disorders and Critically Ill Patients: From Pathophysiology to TreatmentFrom EverandMetabolic Disorders and Critically Ill Patients: From Pathophysiology to TreatmentCarole IchaiNo ratings yet
- ID injection 2023 (1) (1)Document20 pagesID injection 2023 (1) (1)Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation Nursing Lecture 10 Shekhan 2024Document14 pagesOxygenation Nursing Lecture 10 Shekhan 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Health Assesment Nursing lecture 9-Shechan 2024Document43 pagesHealth Assesment Nursing lecture 9-Shechan 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Nursing Lecture 8 Shekhan 2024Document13 pagesNursing Process Nursing Lecture 8 Shekhan 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Nursing lecture 14 Shekhan 2024Document10 pagesBlood Transfusion Nursing lecture 14 Shekhan 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Bowel Elimination 2024Document15 pagesBowel Elimination 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Loss, Grieving, and Death Nursin Lecture 15 Shekhan 2024Document12 pagesLoss, Grieving, and Death Nursin Lecture 15 Shekhan 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- NG Tube 2024Document17 pagesNG Tube 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- You Dippy TwatDocument24 pagesYou Dippy Twatjas3113No ratings yet
- Schedules Under Tamil Nadu Value Added Tax Act, 2006actDocument42 pagesSchedules Under Tamil Nadu Value Added Tax Act, 2006actvickyani1986yahoo.co.inNo ratings yet
- Thesis OfwDocument3 pagesThesis Ofwyazi080% (1)
- Your Habit Body A Better Model of The Unconscious For EveryoneDocument24 pagesYour Habit Body A Better Model of The Unconscious For EveryoneBubi Sutomo100% (1)
- Cara Pemeriksaan Kimia DarahDocument3 pagesCara Pemeriksaan Kimia DarahCut MuannasNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesCase Analysis: ObjectivesJoan BalendrezNo ratings yet
- QuesDocument3 pagesQuesbhanu sharmaNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Two Models of Experimental Periodontitis in RatsDocument8 pagesA Comparison of Two Models of Experimental Periodontitis in RatsRoza NafilahNo ratings yet
- Paramyxovirus and RubellaDocument65 pagesParamyxovirus and RubellaishlionNo ratings yet
- (Cheating Sister) (Cheating Sister)Document12 pages(Cheating Sister) (Cheating Sister)M.hanif RosyidiNo ratings yet
- Resuscitation Trolley Checklist: RrcsuDocument7 pagesResuscitation Trolley Checklist: RrcsuPatrick SimembaNo ratings yet
- Community Program Development and Management in PNPDocument2 pagesCommunity Program Development and Management in PNP21. PLT PAGALILAUAN, EDITHA MNo ratings yet
- 36IJELS 109202041 Pandemic PDFDocument4 pages36IJELS 109202041 Pandemic PDFIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- Jealousy As Good: Bad Behavior and JealousyDocument2 pagesJealousy As Good: Bad Behavior and JealousyInesha FebrinaNo ratings yet
- 110-10, Marsh FunnelDocument2 pages110-10, Marsh FunnelBella NabilaNo ratings yet
- Soal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 9 Semester GanjilDocument6 pagesSoal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 9 Semester GanjilDc Honeybee100% (1)
- Super Its 300h-3009964Document9 pagesSuper Its 300h-3009964Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- Terex Genie Rl4000 Operation Manual d1Document6 pagesTerex Genie Rl4000 Operation Manual d1florine100% (60)
- Risk and Return AnalysisDocument22 pagesRisk and Return AnalysisRanjan Saini100% (1)
- Acute Coronary SyndromesDocument3 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromesbedogdelongeNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0045653519308616 MainDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S0045653519308616 MainBianca Elena AzanfireNo ratings yet
- Little AlbertDocument9 pagesLittle Albert20528055 SHAISTA RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Gout and Othercrystal-Associated ArthropathiesDocument31 pagesGout and Othercrystal-Associated ArthropathiesLia pramitaNo ratings yet
- Sandhya Vandhanam Argya Pradhanam: 1.om Achyuthaya Nama 2.om Ananthaya Nama 3.om Govindaya NamaDocument12 pagesSandhya Vandhanam Argya Pradhanam: 1.om Achyuthaya Nama 2.om Ananthaya Nama 3.om Govindaya Namaindyaone2003No ratings yet
- Soal Uh Tema 6Document5 pagesSoal Uh Tema 6Norma SulistianingsihNo ratings yet
- Harvard Formatting 2018Document9 pagesHarvard Formatting 2018Shariff sebeNo ratings yet
- Diary of An Insurance Seller AllDocument9 pagesDiary of An Insurance Seller AllPriyanka Patel100% (1)
- Chlorine Energy 2520 BalanceDocument4 pagesChlorine Energy 2520 Balancetonzz10No ratings yet
I.V Nursing Lecture 1 shekhan 2024
I.V Nursing Lecture 1 shekhan 2024
Uploaded by
Collective CompanyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
I.V Nursing Lecture 1 shekhan 2024
I.V Nursing Lecture 1 shekhan 2024
Uploaded by
Collective CompanyCopyright:
Available Formats
Ministry of higher education Second Semester/First Class
and scientific research Academic year 2023- 2024
Duhok Polytechnic University
College for Health and Medical
Techniques / Shekhan
Nursing Department
Lecture 1
Intravenous Injection and Infusion
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Learning Outcomes:
After completing this chapter, you will be able to:
1. Discuss the function, distribution, composition, movement, and regulation of fluids
and electrolytes in the body.
2. Describe the regulation of acid–base balance in the body, including the roles of
buffers, the lungs, and the kidneys.
3. Identify factors affecting normal body fluid, electrolyte, and acid–base balance.
4. Discuss risk factors for, and causes and effects of, fluid, electrolyte, and acid
–base imbalances.
5. Collect assessment data related to clients’ fluid, electrolyte, and acid–base balances.
6. Identify examples of nursing diagnoses, outcomes, and interventions for clients with
altered fluid, electrolyte, or acid–base balance.
7. Teach clients measures to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance.
8. Implement measures to correct imbalances of fluids, electrolytes, acids, and
bases, such as enteral or parenteral replacements and blood transfusions
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Intravenous Injection and Infusion
Intravenous Route(I.V.):
Because intravenous (IV) medication enter the client’s
bloodstream directly by way of a vein, they are appropriate
when a rapid effect is required. This route is also appropriate
when medications are too irritating to tissues to be given by other
routes. Intravenous therapy may be used for fluids volume
replacement, to correct electrolyte imbalances, to deliver
medications, and for blood transfusions. The intravenous (IV)
route includes peripheral and central veins. Medication
administered intravenously have an immediate effect, and
consequently it is the most dangerous route for drug
administration. Drugs administered in this manner cannot be
recalled once they have been given.
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
For this reason only selectively qualified nurses are permitted to
administer IV medications.
Despite its inherent risks, there are legitimate reasons for using IV
route . With all IV medication administration. it is very important
to observe client's closely for signs of adverse reactions. Because
the drugs enters the bloodstream directly and acts immediately,
there is no way it can be withdrawn or its action terminated,
therefore the nurse or doctors must take special care to avoid any
errors about the preparation of drug and the calculation of the
dose. Intravenous medication are administered either continuously
or intermittently. Intravenous administration is the route chosen
when :
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
1- A quick response is needed during an emergency.
2- Patients have disorders that affect absorption or metabolism of
drugs like burned patients.
3- Blood levels of drugs need to be maintained at a constant
therapeutic level.
4- It is in the patient’s best interests to avoid discomfort of
repeated intramuscular injection.
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Vein puncture and Intravenous Infusion
Intravenous fluids are solutions that are infused through
a patient's vein. It is necessary to teach nursing personnel how
to perform vein puncture and start intravenous infusions. They
may be used for the following purposes:
1- To maintain or restore fluids balance when oral replacement
is inadequate or impossible .
2- To maintain or replace electrolytes.
3- To administer water – soluble vitamins.
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
4-
To administer drugs.
5-
To replace blood and blood products.
6-
When a very rapid effect is needed.
7-
In sever disturbance of fluids and electrolytes balance.
8-
When the patient is unable to take and retain oral
nourishment.
Fluids for such treatments consist of water with electrolytes,
sugar, or medications added in concentrations that depend on your
need. The rate and quantity of intravenous fluid given depends on
your medical condition, body size, and age
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Types of Fluids
There are two types of I.V. Solutions:
1 – Crystalloid solutions:
Which consist of water and other uniformly dissolved
crystals such as salt and sugar, They are subdivided into:
A – Isotonic Solutions: Which is administer to maintain fluid
balance among patients who may
not be able to eat or drink for a short
period of time.
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
B - Hypotonic Solutions: Which are administer to patient who
have diarrhea or vomits.
C - Hypertonic Solutions: Which are not used very frequently
except for extreme cases in which it
is necessary to reduce cerebral edema
2 - Colloid Solutions:
Which consist of water and molecules of
suspended substances like blood cells and
blood products like albumin. It is used to replace
circulating blood volume (Blood, Blood products,
and solutions known as plasma.
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Fluids used during I.V. infusion:
1- 9% Normal Saline ( also known as NS, 0.9NaCl, or NSS) .
2- Lactated Ringers (also known as LR, Ringers Lactate, or RL).
3- 5% Dextrose in Water (also known as D5 or D5W) .
4- 4.5% Normal Saline (also known as Half Normal Saline,
0.45NaCl).
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Preparing Intravenous Solutions:
Intravenous solutions are most commonly stored in
plastic bags containing 1,000 , 500, 250 , 100,ML of
solutions. Before preparing the solutions the
nurse inspects the container and determine that:
1- The type of solution is same that prescribed by the physician.
2- The solution is clear and transparent.
3- The expiration dates has not elapsed.
4- No leaks are apparent.
5- A separate label is attached identifying the type and amount of
other drugs added to the commercial solutions.
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Complications associated with Intravenous Infusion:
1 - Infection.
2 - Fluid infiltration.
3 - Phlebitis.
4 - Circulatory overload.
5 - Blockage of the infusion.
6 - A dislodged IV catheter
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Nurses can avoid dislodging IV catheter by staying still or being
careful not to pull on the tubing during fluid administration. A
collapsed vein is more likely to occur if you need to have an IV
catheter in place for an extended period of time.
Complications related to the regulation of fluids include giving
too much fluid too rapidly, causing fluid overload. Alternatively,
not enough fluid may be given or it’s released too slowly.
Overload can cause symptoms such as a headache, high blood
pressure, anxiety, and trouble breathing. Some overload can be
tolerated if you’re fairly health. But if you have other health
problems, it can be dangerous.
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Side Effects Of I.V. Infusion
1 - Flushing 2 - Headache 3- Dizziness 4 - Chills
5 - Muscle cramps 6 - Back/joint pain 7 - Fever
8 - Nausea, or vomiting may occur.
Tell doctor or other health care professional right away if any of
these effects occur, persist, or worsen. Pain, redness, and swelling
at the injection site may also occur.
Intravenous fluids (usually shortened to 'IV' fluids)
are liquids given to replace water, sugar and salt that you might
need if you are ill or having an operation, and can't eat or drink as
you would normally.
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
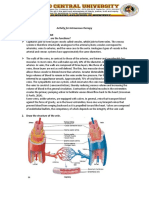
Intravenous cannula (l.V. cannula)
Is a flexible tube which when inserted into the
body is used either to withdraw fluid or insert
medication.
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Factors Influencing The Rate of Flow:
1 - The size of the needle
2 - The height of the bottle
3 - The viscosity of the fluids
-----------------------------------------------
The site for infusion
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Equipment
1-Infusion set consist of the following ( bottle of
solution, air vent drip champer, clamp, tubing,
needle adapter, needle used for adult 18, 19,20,
21, 22 gauge with short bevel (1- 2 ) inch length
2- Alcohol sponge
3- Tourniquet.
4- Adhesive tape and scissors.
5- I.V holder.
6- Arm splint.
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Calculating infusion (drip) rates:
The rate of administration of a continuous or
intermittent infusion may be calculated from the
following equation:
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
IV Cannula Sizes
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Cannula Steps
• Apply the tourniquet
• Re-check the vein
• Clean the patients skin with the alcohol wipe
• Remove the cannula from its packaging and remove the
needle cover ensuring not to touch the needle.
• Insert the needle, bevel upwards at about 30 degrees.
• Advance the rest of the cannula into the vein
• Release the tourniquet
• Remove the needle
• Apply the plaster to the cannula
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Step 1
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Step 2 Step 3
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Step 4 Step 5
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Step 6 Step 7
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
Step 8 Step 9
زانكويا ثوليتةكنيكى يا دهؤك
جامعـة دهــوك التقــنية
Duhok Polytechnic University
You might also like
- Ivf Drug StudyDocument9 pagesIvf Drug StudyRyu Bomi0% (2)
- Amcp Media List 8Document96 pagesAmcp Media List 8api-407904109No ratings yet
- TBE-Pressure Vessel Standard TemplateDocument4 pagesTBE-Pressure Vessel Standard TemplateSiva baalanNo ratings yet
- Como Calcular LiquidosDocument8 pagesComo Calcular Liquidoskaterinavila300No ratings yet
- Intravenous Therapy: Crystalloid and Colloid Solutions: Jassin M. Jouria, MDDocument21 pagesIntravenous Therapy: Crystalloid and Colloid Solutions: Jassin M. Jouria, MDTaniaNo ratings yet
- IV TherapyDocument56 pagesIV TherapyTmz AguilarNo ratings yet
- New Trend IV FluidsDocument9 pagesNew Trend IV FluidsMarfu'ah Mar'ahNo ratings yet
- PHAR635 Parenteral Dosage Forms: Instructors: Dr. Tarek Jenani Dr. Faten HamedDocument29 pagesPHAR635 Parenteral Dosage Forms: Instructors: Dr. Tarek Jenani Dr. Faten HamedundeadrebornNo ratings yet
- Fluid Management For Critically Ill PatientDocument7 pagesFluid Management For Critically Ill PatientNatalindah Jokiem Woecandra T. D.No ratings yet
- 2022 Anesth s1t3 Venous Access and Fluid ManagementDocument6 pages2022 Anesth s1t3 Venous Access and Fluid ManagementMac Vince HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Short Term Effect of Intravenous Fluid Therapy in Paediatric Intensive Care Unit On Serum Electrolytes and Renal Function Tests of ChildrenDocument7 pagesShort Term Effect of Intravenous Fluid Therapy in Paediatric Intensive Care Unit On Serum Electrolytes and Renal Function Tests of ChildrenIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 52389924-IV-therapy NotesDocument57 pages52389924-IV-therapy Notesrye08No ratings yet
- Makalah Can JadiDocument13 pagesMakalah Can JadiTaufiks RohmansNo ratings yet
- IV TherapyDocument10 pagesIV TherapyKate Beatriz ServanoNo ratings yet
- 2019 IV LectureDocument38 pages2019 IV LectureKAUH EducationNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument29 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesLinh Tra100% (1)
- 8.3 IV Fluids, IV Tubing, and Assessment of An IV SystemDocument1 page8.3 IV Fluids, IV Tubing, and Assessment of An IV SystemPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Líquidos NejmDocument11 pagesLíquidos Nejmestudio.slupmNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy in Critically Ill AdultsDocument17 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy in Critically Ill AdultsntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- Update Terapi Cairan Pada: Pasien Covid-19Document43 pagesUpdate Terapi Cairan Pada: Pasien Covid-19Alita Mei RosfyanitaNo ratings yet
- Nutritie Parentala Apa Electroliti Si VitamineDocument7 pagesNutritie Parentala Apa Electroliti Si VitamineGrosu SebastianNo ratings yet
- Principles of Fluid Management 2015 PDFDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Fluid Management 2015 PDFJorge DíazNo ratings yet
- Intravenous TherapyDocument10 pagesIntravenous TherapyS. AmberNo ratings yet
- Abstract IV Fluids Composition and IndicationDocument1 pageAbstract IV Fluids Composition and IndicationThe MindNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Management of Fluids and Electrolytes in ChildrenDocument6 pagesPerioperative Management of Fluids and Electrolytes in ChildrenBetyCamarilloNo ratings yet
- Principles of Fluid Management 2015Document17 pagesPrinciples of Fluid Management 2015MANUELNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Hyponatremia Management: by Craig B. Whitman, Pharm.D., BCPS, BCCCPDocument16 pagesFluid and Hyponatremia Management: by Craig B. Whitman, Pharm.D., BCPS, BCCCPAleksandar Dimovski100% (1)
- Assisting in Ivf InsertionDocument76 pagesAssisting in Ivf Insertionrechelle mae legaspiNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Uid Therapy For Anaesthetists and IntensivistsDocument4 pagesPerioperative Uid Therapy For Anaesthetists and IntensivistsDanitza Pari TiconaNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy TempDocument34 pagesIV Therapy TempJoy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Intravenous Fluids in Acutely Ill Patients: Review ArticleDocument11 pagesMaintenance Intravenous Fluids in Acutely Ill Patients: Review ArticleyoiiiNo ratings yet
- 8.3 IV Fluids, IV Tubing, and Assessment of An IV System: Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient CareDocument12 pages8.3 IV Fluids, IV Tubing, and Assessment of An IV System: Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient Caremelodia gandezaNo ratings yet
- Dwi Arya Jurnal UjianDocument8 pagesDwi Arya Jurnal Ujianwulan nadiaNo ratings yet
- IV SolutionsDocument7 pagesIV SolutionsJeg B. Israel Jr.No ratings yet
- DONE - Activity For Intravenous TherapyDocument6 pagesDONE - Activity For Intravenous TherapyDexie James Ventenilla DizonNo ratings yet
- IJOPP - v5 - I3 - 2012 5Document7 pagesIJOPP - v5 - I3 - 2012 5Ambujesh ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- G SurgeryDocument21 pagesG SurgerySRO oONo ratings yet
- Principles of Fluid ManagementDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Fluid ManagementBrainy-Paykiesaurus LuminirexNo ratings yet
- 4 Fases de La FluidoterapiaDocument8 pages4 Fases de La FluidoterapiaAna Claudia Rodríguez MárquezNo ratings yet
- Obrien2013 PDFDocument11 pagesObrien2013 PDFIrham AbsharNo ratings yet
- ARCS Paediatric IV Fluid GuidelinesDocument16 pagesARCS Paediatric IV Fluid GuidelinesWidyadarya Triyono PutriNo ratings yet
- Infusions and Parenteral Fluids 2000Document4 pagesInfusions and Parenteral Fluids 2000Alexia OwenNo ratings yet
- JVBS FluidtherapyDocument16 pagesJVBS FluidtherapyvetthamilNo ratings yet
- 12 Dentistry L12 Parenteral NutritionDocument13 pages12 Dentistry L12 Parenteral NutritionmyydsamyydsaNo ratings yet
- JAPI Jun 2024 PublicationDocument10 pagesJAPI Jun 2024 Publicationlakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Admixtures: Salvatore J Turco, Pharmd, FashpDocument13 pagesIntravenous Admixtures: Salvatore J Turco, Pharmd, FashpRead WhiteNo ratings yet
- Hiponatremia in The ClinicaDocument19 pagesHiponatremia in The ClinicaHugo GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skills: Intravenous Fluid and Setting Up A DripDocument30 pagesClinical Skills: Intravenous Fluid and Setting Up A DripNabhan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Selection PDFDocument12 pagesIntravenous Fluid Selection PDFVASGJGNo ratings yet
- IV FluidsDocument33 pagesIV Fluidsartmanx112No ratings yet
- Handout 4Document6 pagesHandout 4Judea PagedpedNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid SelectionDocument12 pagesIntravenous Fluid SelectionTracy100% (4)
- Am J Clin Nutr 2016 Maughan 717 23Document7 pagesAm J Clin Nutr 2016 Maughan 717 23sfvsvsNo ratings yet
- INTRAVENOUS THERAPY AND BLOOD TRANSFUSION HandoutDocument21 pagesINTRAVENOUS THERAPY AND BLOOD TRANSFUSION HandoutMicah TuringanNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceFrom EverandFluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Intravenous Therapy Administration: a practical guideFrom EverandIntravenous Therapy Administration: a practical guideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Kidney Disease Management: A Practical Approach for the Non-Specialist Healthcare PractitionerFrom EverandKidney Disease Management: A Practical Approach for the Non-Specialist Healthcare PractitionerNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Disorders and Critically Ill Patients: From Pathophysiology to TreatmentFrom EverandMetabolic Disorders and Critically Ill Patients: From Pathophysiology to TreatmentCarole IchaiNo ratings yet
- ID injection 2023 (1) (1)Document20 pagesID injection 2023 (1) (1)Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation Nursing Lecture 10 Shekhan 2024Document14 pagesOxygenation Nursing Lecture 10 Shekhan 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Health Assesment Nursing lecture 9-Shechan 2024Document43 pagesHealth Assesment Nursing lecture 9-Shechan 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Nursing Lecture 8 Shekhan 2024Document13 pagesNursing Process Nursing Lecture 8 Shekhan 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Nursing lecture 14 Shekhan 2024Document10 pagesBlood Transfusion Nursing lecture 14 Shekhan 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Bowel Elimination 2024Document15 pagesBowel Elimination 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- Loss, Grieving, and Death Nursin Lecture 15 Shekhan 2024Document12 pagesLoss, Grieving, and Death Nursin Lecture 15 Shekhan 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- NG Tube 2024Document17 pagesNG Tube 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- You Dippy TwatDocument24 pagesYou Dippy Twatjas3113No ratings yet
- Schedules Under Tamil Nadu Value Added Tax Act, 2006actDocument42 pagesSchedules Under Tamil Nadu Value Added Tax Act, 2006actvickyani1986yahoo.co.inNo ratings yet
- Thesis OfwDocument3 pagesThesis Ofwyazi080% (1)
- Your Habit Body A Better Model of The Unconscious For EveryoneDocument24 pagesYour Habit Body A Better Model of The Unconscious For EveryoneBubi Sutomo100% (1)
- Cara Pemeriksaan Kimia DarahDocument3 pagesCara Pemeriksaan Kimia DarahCut MuannasNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesCase Analysis: ObjectivesJoan BalendrezNo ratings yet
- QuesDocument3 pagesQuesbhanu sharmaNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Two Models of Experimental Periodontitis in RatsDocument8 pagesA Comparison of Two Models of Experimental Periodontitis in RatsRoza NafilahNo ratings yet
- Paramyxovirus and RubellaDocument65 pagesParamyxovirus and RubellaishlionNo ratings yet
- (Cheating Sister) (Cheating Sister)Document12 pages(Cheating Sister) (Cheating Sister)M.hanif RosyidiNo ratings yet
- Resuscitation Trolley Checklist: RrcsuDocument7 pagesResuscitation Trolley Checklist: RrcsuPatrick SimembaNo ratings yet
- Community Program Development and Management in PNPDocument2 pagesCommunity Program Development and Management in PNP21. PLT PAGALILAUAN, EDITHA MNo ratings yet
- 36IJELS 109202041 Pandemic PDFDocument4 pages36IJELS 109202041 Pandemic PDFIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- Jealousy As Good: Bad Behavior and JealousyDocument2 pagesJealousy As Good: Bad Behavior and JealousyInesha FebrinaNo ratings yet
- 110-10, Marsh FunnelDocument2 pages110-10, Marsh FunnelBella NabilaNo ratings yet
- Soal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 9 Semester GanjilDocument6 pagesSoal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 9 Semester GanjilDc Honeybee100% (1)
- Super Its 300h-3009964Document9 pagesSuper Its 300h-3009964Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- Terex Genie Rl4000 Operation Manual d1Document6 pagesTerex Genie Rl4000 Operation Manual d1florine100% (60)
- Risk and Return AnalysisDocument22 pagesRisk and Return AnalysisRanjan Saini100% (1)
- Acute Coronary SyndromesDocument3 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromesbedogdelongeNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0045653519308616 MainDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S0045653519308616 MainBianca Elena AzanfireNo ratings yet
- Little AlbertDocument9 pagesLittle Albert20528055 SHAISTA RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Gout and Othercrystal-Associated ArthropathiesDocument31 pagesGout and Othercrystal-Associated ArthropathiesLia pramitaNo ratings yet
- Sandhya Vandhanam Argya Pradhanam: 1.om Achyuthaya Nama 2.om Ananthaya Nama 3.om Govindaya NamaDocument12 pagesSandhya Vandhanam Argya Pradhanam: 1.om Achyuthaya Nama 2.om Ananthaya Nama 3.om Govindaya Namaindyaone2003No ratings yet
- Soal Uh Tema 6Document5 pagesSoal Uh Tema 6Norma SulistianingsihNo ratings yet
- Harvard Formatting 2018Document9 pagesHarvard Formatting 2018Shariff sebeNo ratings yet
- Diary of An Insurance Seller AllDocument9 pagesDiary of An Insurance Seller AllPriyanka Patel100% (1)
- Chlorine Energy 2520 BalanceDocument4 pagesChlorine Energy 2520 Balancetonzz10No ratings yet