Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12th Reproduction in Humans
12th Reproduction in Humans
Uploaded by
STARK PRIME GAMING0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views58 pages12th reproduction in human by Juber Ansari.
Maharashtra, India.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document12th reproduction in human by Juber Ansari.
Maharashtra, India.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views58 pages12th Reproduction in Humans
12th Reproduction in Humans
Uploaded by
STARK PRIME GAMING12th reproduction in human by Juber Ansari.
Maharashtra, India.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 58
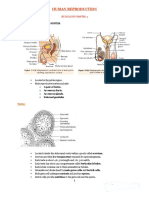
Human Reproduction
Male & Female Reproductive
System
-By Juber Ansari
Introduction
• Humans are sexually reproducing and
viviparous
• Reproductive Events:
– Gametogenesis
– Insemination
– Fertilisation
– Implantation
– Gestation
– Parturition
The Male Reproductive System
• Located in pelvis region
• Includes:
– A pair of testes
– Accessory ducts
– Glands
– & external genitalia
The Male Reproductive System
The Male Reproductive System
The Male Reproductive System
• Testes:
– Situated outside abdominal cavity
– Within a pouch called ‘scrotum’
– It helps to maintain low temperature (2-2.5OC
lower than body temp necessary for
spermatogenesis)
– Oval in shape, 4-5cm in length & 2-3 cm in
width
– Having 250 compartments called ‘testicular
lobules’.
The Male Reproductive System
Testes
The Male Reproductive System
Testes
• Each lobules has 1-3 highly coiled
seminiferous tubules
• Sperms are produced in these lobules
• Each Seminiferous tubules has 2 types of
cells in it
– Male germ cells (spermatogonia)
• Undergo meiotic division to form sperm
– Sertoli cells
• Provide nutrition to the germ cells
Testes
Testes
• The region outside seminiferous tubules
called ‘Interstitial Spaces’
• It contains Interstitial Cells or Leydig
Cells
• Leydig cells synthesize testicular
hormones called ‘Androgens’
• Other immunologically competent cells are
also present
Sectional View of Seminiferous
Tubules
Male Sex Accessory Ducts
• It includes:
– Rete testes
– Vasa efferentia
• Seminiferous tubules open into this through rete
testes
– Epididymis
• Located posterior to each testes
• Vas efferentia opens into this
• Leads to vas deferens that ascends to abdomen &
loops over the urinary bladder
– Vas deferens
The Male Reproductive System
Male Sex Accessory Ducts
• Bladder receives ducts from seminal
vesicle & opens into urethra as the
ejaculatory ducts
• These ducts store & transport sperm from
testes to outside through urethra
• Urethra originates from bladder &
extends through penis to its external
opening called ‘urethral meatus’
The Male Reproductive System
Male Sex Accessory Glands
• It includes:
– Paired seminal vesicles
– A prostate gland
– & paired bulbourethral glands
• Secretion of these glands constitute the
seminal plasma which is rich in fructose,
calcium & certain enzymes
• These secretions also helps in lubrication
of the penis
The Male Reproductive System
The Penis
• It’s the male external genitalia
• Made of special tissues that helps in
erection to facilitate insemination
• Enlarged end of penis called ‘glans penis’ is
covered by loose fold of skin called
‘foreskin’
The Male Reproductive System
The Female Reproductive System
• Includes:
– A pair of ovaries
– A pair of oviducts (fallopian tube)
– Uterus
– Cervix
– Vagina
– External genitalia
– A pair of mammary gland (support the process
of pregnancy, birth and child care
Female System
The Female Reproductive System
• Located in Pelvic region
• Ovaries are primary female sex organs
• Produces female gamete ‘Ovum’ & several
steroid hormones (ovarian hormones)
• Located one on each side of lower
abdomen
• 2-4 cm length each
• Connected to pelvic wall & uterus by
ligaments
Section of Female Pelvis
Female System
The Female Reproductive System
• Each ovary is covered by thin epithelium
which encloses ‘ovarian stroma’
• Stroma has 2 zones
– A peripheral cortex
– & an inner medulla
• Female accessory ducts includes:
– Oviducts
– Uterus
– Vagina
Ovary
The Oviducts
• Fallopian tube is 10-12 cm in length &
extends from ovary to uterus
• ‘Infundibulum’ is closer to ovaries
• It posses finger like projections called
fimbriae which helps in collection of ovum
after ovulation
• Infundibulum then leads to ‘ampulla’
• Isthmus is last part which joins to uterus
Female System
The Uterus
• Single & also called ‘womb’
• Shaped like inverted pear
• Supported by ligaments attached to pelvic
• Opens into vagina through narrow ‘Cervix’
• Cavity of cervix called ‘Cervical Canal’
which forms ‘Birth Canal’ with vagina
• Uterus has 3 layers of tissue
– Perimetrium (external thin)
– Myometrium (middle thick smooth muscles)
– Endometrium (inner glandular)
The Uterus
• Endometrium undergo cyclic changes
during menstrual cycle
• Myometrium exhibit strong contraction
during delivery of baby
Female External Genitalia
• It includes:
– Mons pubis (cushion of fatty tissues covered
by skin & pubic hair
– Labia majora (fleshy folds of tissue
surrounding vaginal opening)
– Labia minora (paired folds of tissue under
majora)
– Hymen (covers opening of vagina) &
– Clitoris (tiny finger like structure/ female
penis)
Female External Genitalia
Mammary Gland
• It’s the characteristics feature of
mammals
• Paired structures (breasts) contains
glandular tissues & fats
• These tissues are divided into 15-20
mammary lobes containing clusters of cells
called ‘alveoli’
• These cells secrets milk which is stored in
cavities (lumens) of alveoli
Mammary Gland
Mammary Gland
• Alveoli opens into mammary tubules
• Tubules opens into mammary duct
• Several mammary duct joins to form
mammary ampulla
• Mammary ampulla is connected to
‘Lectiferous duct’ through which milk is
sucked out
Mammary Gland
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
PYQ
OU
K Y
A N
T H
You might also like
- Work Book Pregnancy YogaDocument15 pagesWork Book Pregnancy Yogasheela100% (1)
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemGLATIAN MEMERNo ratings yet
- Safe Environment ContractDocument37 pagesSafe Environment Contractdipanjang panjanginNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesThe Reproductive SystemKem Marian MauricioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Human Reproduction - STUDY RATEDocument14 pagesChapter 3 - Human Reproduction - STUDY RATEsriharshitha darapuNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesBiology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemRYLE IBANEZNo ratings yet
- Basic Steps in Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesBasic Steps in Human ReproductionMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: 3.1: Male Reproductive SystemDocument27 pagesHuman Reproduction: 3.1: Male Reproductive SystemAvik BhaumikNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument81 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Male Reproductive SystemMj BrionesNo ratings yet
- HumanreproductionpptDocument59 pagesHumanreproductionpptsugi sivamNo ratings yet
- G5 Science Week 11Document30 pagesG5 Science Week 11Park Vincent PrinceNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesScience 10 - Reproductive SystemHanabi Scarlet ShadowNo ratings yet
- Department of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsDocument69 pagesDepartment of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsBiju MylachalNo ratings yet
- 8reproductive SystemDocument31 pages8reproductive SystemViola ChepletingNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Class 12 NotesDocument21 pagesHuman Reproduction Class 12 NotesTamanna NayakNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument43 pagesHuman Reproductive Systembabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- 3 2 Human Reproductive SystemDocument38 pages3 2 Human Reproductive SystemMarcStep De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- L6 - Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocument60 pagesL6 - Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemJIA YUET NGNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction (Edustudy Point)Document10 pagesHuman Reproduction (Edustudy Point)Vishal UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Male and FemaleDocument61 pagesReproductive System Male and FemaleAsad KHAN100% (1)
- male reproDocument19 pagesmale reprorambhujawanthakurNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument31 pages1 Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductionjose mari chanNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Function: Physiology Department Medical School, University of Methodist IndonesiaDocument21 pagesReproductive Function: Physiology Department Medical School, University of Methodist IndonesiaAlex Syaputra SihalohoNo ratings yet
- Rhsi, LSDocument56 pagesRhsi, LSMary AkellaNo ratings yet
- 1.female Reproductive SystemDocument52 pages1.female Reproductive SystemKhairul HananNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System AutosavedDocument49 pagesThe Female Reproductive System AutosavedVenice izza Venancio100% (1)
- Female-Reproductive-System With LinkDocument26 pagesFemale-Reproductive-System With LinkSteven LiwagNo ratings yet
- Reproductivesystem 170324071445Document64 pagesReproductivesystem 170324071445Trishna GoswamiNo ratings yet
- 5a. Male & Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument119 pages5a. Male & Female Reproductive AnatomyvictorNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction CH-03, Bio, Class-XiiDocument69 pagesHuman Reproduction CH-03, Bio, Class-Xiisumitdhakad543No ratings yet
- 02 Overview of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument30 pages02 Overview of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemsOsman Saidu SesayNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson 1 G5 1Document31 pagesScience Lesson 1 G5 1Sarah JumalonNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: Presented by Parmar Zenith F.Y.M.sc (N) GineraDocument59 pagesFemale Reproductive System: Presented by Parmar Zenith F.Y.M.sc (N) Ginerazenith parmarNo ratings yet
- 1a. Reproductive OrgansDocument60 pages1a. Reproductive OrgansJerrald Meyer L. BayaniNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper Rizal PlumaDocument33 pagesReaction Paper Rizal PlumaJazzd Sy Gregorio0% (1)
- 24 Lecture PPT - Reproductive SystemDocument47 pages24 Lecture PPT - Reproductive Systemjohnjay3110100% (2)
- Cabdi QaadirDocument16 pagesCabdi QaadirJeesteeye Cr7No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction School NotesDocument18 pagesHuman Reproduction School Notessamkaushik318No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemsaranya amuNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument49 pagesReproductive SystemAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ppDocument18 pagesReproductive System ppphillaremedyNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesSexual Reproductive Systemred JimNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesThe Male Reproductive Systemwenfei1026No ratings yet
- Human Male Reproductive SystemDocument45 pagesHuman Male Reproductive Systemcyber secNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System - 1Document62 pagesFemale Reproductive System - 1Reendelle JamiatreNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument94 pagesHuman ReproductionDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document19 pagesThe Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1lourd nabNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument96 pagesHuman Reproductionsanya razaNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 1Document19 pagesThe Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 1valjulene monteNo ratings yet
- Oleza Cannery S. Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesOleza Cannery S. Reproductive SystemCannery OlezaNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument11 pagesHuman ReproductionAdesh BhullarNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System-1Document46 pagesReproductive System-1fhz4t6cnw8No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemamielle azamingNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive OrgansDocument29 pagesAnatomy of Female Reproductive OrgansThrecia RotaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument21 pagesReproductive SystemAshley RañesesNo ratings yet
- 2 Reproductive and Sexual Health 1Document100 pages2 Reproductive and Sexual Health 1Shien Sheena Mae FuaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System BSNDocument23 pagesFemale Reproductive System BSNtintinNo ratings yet
- MF009 6B Human Reproduction System James LDocument26 pagesMF009 6B Human Reproduction System James LPikuNo ratings yet
- FRO Copy-1Document108 pagesFRO Copy-1Mahir RathodNo ratings yet
- ReproDocument80 pagesReprocream o100% (1)
- G PsumatDocument22 pagesG PsumattimworkmakesthedreamworkNo ratings yet
- Initation of Insulin - Final 2023Document27 pagesInitation of Insulin - Final 2023DEWI RIZKI AGUSTINANo ratings yet
- Maret 2018 26-50Document10 pagesMaret 2018 26-50daniel_alexander_susenoNo ratings yet
- Zikora: A Short Story: English Academy ReviewDocument6 pagesZikora: A Short Story: English Academy ReviewOkpara NnazimNo ratings yet
- Percentages For MRCOG1Document3 pagesPercentages For MRCOG1jmoNo ratings yet
- Dogon Mentral HutsDocument12 pagesDogon Mentral Hutscj.email4all5645No ratings yet
- Statement of Values and EthicsDocument3 pagesStatement of Values and EthicsjuliNo ratings yet
- Glubitor OdDocument7 pagesGlubitor OdSerenaNo ratings yet
- USPSTF A and B Recommendations - US Preventive Services Task ForceDocument2 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendations - US Preventive Services Task ForcelamaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Postpartum Hemorrhage - UpToDateDocument48 pagesOverview of Postpartum Hemorrhage - UpToDatewendy100% (1)
- Policy Brief - Maternity LeaveDocument21 pagesPolicy Brief - Maternity Leavebya*boNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics and Social Responsibility (1 Quarter: Week 6)Document6 pagesBusiness Ethics and Social Responsibility (1 Quarter: Week 6)marissa casareno almuete100% (1)
- 2023 Obstetrics1 Part5Document1 page2023 Obstetrics1 Part510 B: Bravo, OliveNo ratings yet
- OB 2.01 High Risk Pregnancy - Prenatal Assessment PDFDocument10 pagesOB 2.01 High Risk Pregnancy - Prenatal Assessment PDFRaquel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Perineal MassageDocument2 pagesAntenatal Perineal MassageFarid NurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- GE Elect 3 Module 13 14 MangiboaDocument8 pagesGE Elect 3 Module 13 14 MangiboaMary Loiesyl Camara Ubay-ubayNo ratings yet
- Consenso Francês 2022Document20 pagesConsenso Francês 2022larissa fernandesNo ratings yet
- Weebly Teaching Plan Childbirth PreparationDocument1 pageWeebly Teaching Plan Childbirth Preparationapi-272566401No ratings yet
- Learner: Lord Mvoula: Test Name Completion Date Score Timespent ResultDocument3 pagesLearner: Lord Mvoula: Test Name Completion Date Score Timespent ResultLord M.No ratings yet
- Preoperative & Postoperative EvaluationDocument61 pagesPreoperative & Postoperative EvaluationSonntagsschule St. Antonius Kloster in KröffelbachNo ratings yet
- VersionDocument2 pagesVersionLiji GeorgeNo ratings yet
- HysterectomyDocument131 pagesHysterectomy8690402592No ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Intrapartum Nursing AssessmentDocument4 pagesChapter 18 Intrapartum Nursing AssessmentMary LowryNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading PRE-CLINICALDocument12 pagesJournal Reading PRE-CLINICALShyenNo ratings yet
- Cin and Cervical CancerDocument7 pagesCin and Cervical CancerChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Abortion Care Thrombose ProfylaxeDocument22 pagesAbortion Care Thrombose ProfylaxeambiebieNo ratings yet
- Girlhood, G. (2020)Document49 pagesGirlhood, G. (2020)chindypermataNo ratings yet
- Andariki Ayurvedam - DRDocument3 pagesAndariki Ayurvedam - DRmurugangdNo ratings yet
- CHN1 Lec Session #16 Sas..Document5 pagesCHN1 Lec Session #16 Sas..Glendie Dela CernaNo ratings yet