Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1.aayush inflammation and respiratory
1.aayush inflammation and respiratory
Uploaded by
AAYUSH BAGALECopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Respiratory Infections 1Document62 pagesRespiratory Infections 1Eduardo Valdez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument11 pagesChronic BronchitisNazurah AzmiraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of PneumoniaDocument56 pagesPharmacotherapy of Pneumoniahoneylemon.co100% (1)
- Aggressive PeriodontitisDocument27 pagesAggressive PeriodontitisRanuch TakNo ratings yet
- Avian FluDocument22 pagesAvian FluCici Novelia ManurungNo ratings yet
- Bronkitis and PneumoniaDocument16 pagesBronkitis and PneumoniaRegir KurNo ratings yet
- Presentati ON ON Bronchitis: Presented by K.vani M.SC (N) 1st YearDocument30 pagesPresentati ON ON Bronchitis: Presented by K.vani M.SC (N) 1st Yearvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorder Note BSC 3rd YearDocument41 pagesRespiratory Disorder Note BSC 3rd YearNancyNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Bacteria.: Risk For InfectionDocument5 pagesTuberculosis Bacteria.: Risk For InfectionLag Lag AlbercaNo ratings yet
- respiratory diseaseDocument13 pagesrespiratory diseasesumitk.1919141No ratings yet
- Asthmatic Attack: Miriti M.D Masters of Clinical Medicine Accidents and Emergency Facilitator: DR Simba DR MburuguDocument26 pagesAsthmatic Attack: Miriti M.D Masters of Clinical Medicine Accidents and Emergency Facilitator: DR Simba DR MburuguDennis MiritiNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument20 pagesPneumoniaFeizalNo ratings yet
- Asthama & COPDDocument84 pagesAsthama & COPDAbdullah BhattiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestation:: Medical ManagementDocument5 pagesClinical Manifestation:: Medical ManagementChristina BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Infectious and Inflammatory DisordersDocument84 pagesInfectious and Inflammatory DisordersMariel OracoyNo ratings yet
- PNEUMONIADocument24 pagesPNEUMONIAwheeyycoldandhot55No ratings yet
- CD Part 2 - Communicable Diseases With Pics (1) ConDocument239 pagesCD Part 2 - Communicable Diseases With Pics (1) ConMackoi SalamanesNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia and VAP PreventionDocument35 pagesPneumonia and VAP Preventionhendro harahapNo ratings yet
- Pedia Bronchial Asthma-1Document43 pagesPedia Bronchial Asthma-1MAHEJS HDNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Viruses: Organisms Causing PneumoniaDocument17 pagesRespiratory Viruses: Organisms Causing PneumoniaSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- REQ - PneumoniaDocument6 pagesREQ - PneumoniaAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Infections of The Respiratory System 1Document56 pagesInfections of The Respiratory System 1x8jx8dcsyvNo ratings yet
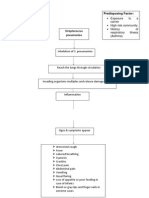
- Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorDocument4 pagesPrecipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorRoxanne Ganayo ClaverNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersDocument93 pagesManagement of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersErica Clerigo Landicho100% (1)
- PneumoniaDocument16 pagesPneumoniamalope mahlatseNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory InfectionDocument71 pagesLower Respiratory Infectionpaulyn ramos100% (1)
- Nursing InterventionsDocument68 pagesNursing Interventionsash aliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 030Document12 pagesChapter 030Carlese GambleNo ratings yet
- Understanding EnteritisDocument28 pagesUnderstanding EnteritisRoshan Shrestha100% (2)
- Asthma: Pio T. Esguerra II, MD, FPCP, FPCCP Pulmonary & Critical Care FEU-NRMF Medical CenterDocument98 pagesAsthma: Pio T. Esguerra II, MD, FPCP, FPCCP Pulmonary & Critical Care FEU-NRMF Medical CenteryayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: What Causes ItDocument4 pagesPneumonia: What Causes ItMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Topic:Influenza: Assigned By:Maam Madiha Presented By:Tahira Ijaz Misbah MumtazDocument25 pagesTopic:Influenza: Assigned By:Maam Madiha Presented By:Tahira Ijaz Misbah MumtazPriya bhattiNo ratings yet
- 3 PneumoniaDocument17 pages3 PneumoniaMohamed Na3eemNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument7 pagesPneumoniapashiem88No ratings yet
- Learning Material RLE NCM 112Document5 pagesLearning Material RLE NCM 112shiro the catNo ratings yet
- Ch. 26. URT DisordersDocument106 pagesCh. 26. URT Disordersمحمد الحواجرةNo ratings yet
- AsmaDocument31 pagesAsmaseptiman zebuaNo ratings yet
- General Medicine Course-Part I&II-3rdyrDocument364 pagesGeneral Medicine Course-Part I&II-3rdyrbiography& lifestyleNo ratings yet
- 3 Bacterial PneumoniaDocument30 pages3 Bacterial PneumoniaAP ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DiseasesDocument11 pagesRespiratory DiseasesMichael Angelo SeñaNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument45 pagesBronchial Asthmamaggykariuki002No ratings yet
- Eman YousifDocument9 pagesEman Yousifsheka mNo ratings yet
- Communicable DisesaseDocument111 pagesCommunicable Disesasebrillaboy266No ratings yet
- Seminar1 1Document71 pagesSeminar1 1Tibebe S. TadesseNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PandemicsDocument5 pagesRespiratory PandemicsJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Cahaya InternasionalDocument9 pagesJurnal Cahaya InternasionalCahaya YusmaniNo ratings yet
- Asthma and COPDDocument28 pagesAsthma and COPDShoaib PatelNo ratings yet
- Adult NursingDocument13 pagesAdult Nursing00060651No ratings yet
- Ward Case PresentationDocument92 pagesWard Case PresentationSuzette Rae TateNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 48 The Child With Alterations in Respiratory FunctionsDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 48 The Child With Alterations in Respiratory Functionselsaqum98No ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory InfectionDocument27 pagesUpper Respiratory Infectionakoeljames8543No ratings yet
- Physiotherapy of Avian RespiratoryDocument3 pagesPhysiotherapy of Avian RespiratoryMichael MekhaNo ratings yet
- Module 12: Infection Control in Health Care Settings: Image Courtesy Of: World Lung FoundationDocument37 pagesModule 12: Infection Control in Health Care Settings: Image Courtesy Of: World Lung FoundationAniruddhaNo ratings yet
- هتاكربو الله ةمحرو مكيلع ملاسلا - We will talk about pneumonia, in the this presentation, we will talk about several point, includingDocument7 pagesهتاكربو الله ةمحرو مكيلع ملاسلا - We will talk about pneumonia, in the this presentation, we will talk about several point, includingFhfj FmfmfmfNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument64 pagesBronchial AsthmaDr. NasrumminallahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29: Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasesDocument5 pagesChapter 29: Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasesjefrocNo ratings yet
- Patho-pharmacology-II Unit 2-B Respiratory System and Diseases Related To This SystemDocument33 pagesPatho-pharmacology-II Unit 2-B Respiratory System and Diseases Related To This SystemYounas BhattiNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument8 pagesAsthmaLankeshwaraNo ratings yet
- BRONCHOPNEUMONIADocument18 pagesBRONCHOPNEUMONIAMANEESH MANINo ratings yet
- 04 Acute Bronchitis and Pneumonia in ChildrenDocument58 pages04 Acute Bronchitis and Pneumonia in ChildrenMi PatelNo ratings yet
- Body condition scoring in cattle newDocument30 pagesBody condition scoring in cattle newAAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- Newcastle-disease [Roll no. 02]Document25 pagesNewcastle-disease [Roll no. 02]AAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- 17.aachal himachal sah YersiniosisDocument14 pages17.aachal himachal sah YersiniosisAAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- 11. bishnuViral ArthritisDocument15 pages11. bishnuViral ArthritisAAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- Mastitis_FinalDocument36 pagesMastitis_FinalAAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- GiardiasisDocument36 pagesGiardiasisAAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- 9. bijay cia roll no.9Document13 pages9. bijay cia roll no.9AAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Principles of Disease and EpidemiologyDocument53 pagesChapter 14: Principles of Disease and EpidemiologyAbhishek Isaac MathewNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2Document3 pagesJurnal 2Farra PattipawaeNo ratings yet
- MCB4211Document11 pagesMCB4211Nadir A IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Tongue DisordersDocument31 pagesTongue DisordersMaphoto Xola0% (1)
- Desain Ruangan Pelayanan TB Di Admisi, Poli (Aziza Ariyani)Document58 pagesDesain Ruangan Pelayanan TB Di Admisi, Poli (Aziza Ariyani)endangsuhandaNo ratings yet
- Review of Osteoimmunology and The Host Response in Endodontic and Periodontal LesionsDocument16 pagesReview of Osteoimmunology and The Host Response in Endodontic and Periodontal LesionsNaeem MoollaNo ratings yet
- CHICKENPOXDocument32 pagesCHICKENPOXCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- ImuDocument28 pagesImuLukmanAnugrahNo ratings yet
- Eczema Patient LeafletDocument4 pagesEczema Patient LeafletAbdul KareemNo ratings yet
- (THT) Allergic Rhinitis For Medical StudentDocument40 pages(THT) Allergic Rhinitis For Medical StudentTheresia Radinda FelimNo ratings yet
- CT Evaluation of Enteritis and ColitisDocument40 pagesCT Evaluation of Enteritis and ColitisOscar NogueraNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration FormDocument2 pagesHealth Declaration Formlouis alvarezNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaSalwiyadiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-Natural History of DiseaseDocument21 pagesLecture 4-Natural History of Diseasehuma0% (1)
- Nutri TherapyDocument2 pagesNutri TherapySamuel DiazNo ratings yet
- South Africa CMV Viral Load Testing May2015Document4 pagesSouth Africa CMV Viral Load Testing May2015EnergadeNo ratings yet
- NipahDocument34 pagesNipahpraisidNo ratings yet
- 2chemical MediatorDocument1 page2chemical MediatorUu UuNo ratings yet
- Radio Broad Script EditedDocument5 pagesRadio Broad Script EditedEasy.No ratings yet
- r142881987 Bastian Octavio Gomez Figueroa CUR142881987Document1 pager142881987 Bastian Octavio Gomez Figueroa CUR142881987BastiánNo ratings yet
- 5.infecciones Micóticas Del Sistema Nervioso CentralDocument13 pages5.infecciones Micóticas Del Sistema Nervioso CentralLiz NuñezNo ratings yet
- Morinda Citrifolia (Noni) in The Treatment of PsoriasisDocument2 pagesMorinda Citrifolia (Noni) in The Treatment of PsoriasisAlexandra VlachouNo ratings yet
- Malarial Pathogenesis: By: Kareem Waleed Hamimy 6 Year Medical Student Kasr Al Ainy - Cairo UniversityDocument20 pagesMalarial Pathogenesis: By: Kareem Waleed Hamimy 6 Year Medical Student Kasr Al Ainy - Cairo UniversityKareem Waleed Ibrahim HamimyNo ratings yet
- Lymphangitis TreatmentDocument2 pagesLymphangitis TreatmentHarista Miranda SalamNo ratings yet
- Clerks ExamDocument4 pagesClerks ExamvannieloveNo ratings yet
- Tugas Uas Writing For General Comunication Kelas BDocument9 pagesTugas Uas Writing For General Comunication Kelas Bhadijah offical43119No ratings yet
- Pre-Test Questionnaire, COVID-19Document1 pagePre-Test Questionnaire, COVID-19Minhazur Rahman SakibNo ratings yet
- AIR DROP EXAMنسختي PDFDocument35 pagesAIR DROP EXAMنسختي PDFYara AlmouallemNo ratings yet
- Appropiate Allergic Testing and The Interpretation - Dr. Deshinta Putri Mulya, SP - PD (K) KAIDocument40 pagesAppropiate Allergic Testing and The Interpretation - Dr. Deshinta Putri Mulya, SP - PD (K) KAIEllenNo ratings yet
1.aayush inflammation and respiratory
1.aayush inflammation and respiratory
Uploaded by
AAYUSH BAGALE0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views17 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views17 pages1.aayush inflammation and respiratory
1.aayush inflammation and respiratory
Uploaded by
AAYUSH BAGALECopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 17
Inflammation and Respiratory
Disease Complex in Poultry
Inflammation and Respiratory Disease
Complex in Poultry
• Inflammation and respiratory diseases in poultry have a significant
impact on the poultry industry.
• These conditions can lead to economic losses, decreased productivity,
and compromised bird welfare.
• Understanding the complex nature of respiratory diseases and the role
of inflammation is essential for effective management and control.
• This presentation aims to provide insights into the causes, mechanisms,
and preventive measures for inflammation and respiratory disease
complex in poultry.
Causes of Inflammation and Respiratory
Disease Complex in Poultry:
• Infectious Agents: Bacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens can cause
respiratory infections in poultry, triggering inflammation.
• Environmental Factors: Poor air quality, high humidity, and
temperature extremes contribute to respiratory diseases and
subsequent inflammation.
• Management Practices: Inadequate biosecurity, overcrowding, and
nutritional imbalances increase the risk of respiratory diseases and
inflammation.
Mechanism of Inflammation in Poultry:
• Inflammation is a natural immune response triggered by pathogens or
injury in poultry.
• Immune cells, such as macrophages, recognize and engulf pathogens or
damaged cells.
• Immune cells release signaling molecules called cytokines to recruit
additional immune cells.
• These immune cells work together to destroy pathogens and clear cellular
debris.
• Inflammatory mediators increase blood flow, causing redness and swelling.
• Increased blood flow brings more immune cells and nutrients to support
the immune response and tissue repair.
• Inflammatory cytokines activate the adaptive immune response, leading to
the production of specific antibodies against pathogens.
Common Respiratory Diseases in Poultry:
• Infectious Bronchitis (IB)
• Newcastle Disease (ND)
• Avian Influenza (AI)
• Infectious Laryngotracheitis (ILT)
These common respiratory diseases can have devastating effects on
poultry health and production. Understanding their etiology and clinical
signs is essential for timely diagnosis and effective management.
Infectious Bronchitis (IB)
Infectious bronchitis is a highly contagious viral respiratory disease that
affects chickens of all ages.
• Etiology:
Infectious bronchitis virus (IBV)
• Clinical Signs:
Respiratory distress, nasal discharge, decreased egg production
Infectious
Bronchitis
(IB)
Newcastle Disease (ND)
Newcastle disease is a viral infection that primarily affects the
respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems of poultry.
• Etiology:
Newcastle disease virus (NDV)
• Clinical Signs:
Respiratory distress, greenish diarrhea, nervous system signs
Newcastle
Disease
(ND)
Avian Influenza (AI)
Avian influenza is a highly contagious viral disease that can cause
severe respiratory illness and high mortality in poultry.
• Etiology:
Influenza viruses (H5N1, H7N9, etc.)
• Clinical Signs:
Respiratory distress, drop in egg production, high mortality rates
Avian
Influenza
(AI)
Infectious Laryngotracheitis (ILT)
Infectious laryngotracheitis is a viral respiratory disease characterized
by inflammation of the larynx and trachea
• Etiology:
Gallid herpesvirus 1 (GaHV-1)
• Clinical Signs:
Respiratory distress, coughing, blood-stained mucus, decreased egg
production
Infectious
Laryngotracheitis
(ILT)
Impact of Inflammation on Respiratory
Health
• Excessive or chronic inflammation can have detrimental effects on
respiratory health in poultry.
• Prolonged inflammation can lead to damage to the respiratory tissues
and structures.
• Inflammatory processes can disrupt the normal functioning of the
respiratory system, including the airways and lung parenchyma.
• Damaged respiratory tissues can impair the exchange of oxygen and
carbon dioxide, compromising the overall respiratory efficiency.
• Inflammation-induced changes in the airways can result in increased
mucus production, airway narrowing, and reduced airflow.
Management and Control Strategies:
• Biosecurity: Implement rigorous measures to prevent disease
introduction and spread.
• Vaccination: Follow appropriate protocols to protect poultry against
respiratory pathogens.
• Ventilation and Environmental Management: Maintain optimal air
quality and environmental conditions.
• Monitoring and Adjustments: Regularly assess and modify strategies
based on disease prevalence and vaccine efficacy.
Treatment and Control Strategies:
• Medication: Administer appropriate medication as directed by a
veterinarian.
• Supportive Care: Provide proper nutrition, hydration, and a stress-free
environment.
• Collaboration with Veterinarians: Seek professional guidance for
accurate diagnosis and effective control strategies.
• Antibiotics, Antiviral Agents, and Immunomodulators: Use judiciously
and according to veterinary guidance.
• Effective control strategies require collaboration, proper medication,
and supportive care.
Conclusion
• Understanding inflammation and respiratory diseases is important for
poultry health.
• Taking proactive measures early on helps reduce the impact of these
diseases.
• Good biosecurity, vaccinations, and proper ventilation are important
prevention methods.
• Timely diagnosis, treatment, and working closely with veterinarians
are key to controlling the diseases.
• By focusing on poultry health, we can maintain productivity and
ensure the well-being of our birds.
You might also like
- Respiratory Infections 1Document62 pagesRespiratory Infections 1Eduardo Valdez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument11 pagesChronic BronchitisNazurah AzmiraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of PneumoniaDocument56 pagesPharmacotherapy of Pneumoniahoneylemon.co100% (1)
- Aggressive PeriodontitisDocument27 pagesAggressive PeriodontitisRanuch TakNo ratings yet
- Avian FluDocument22 pagesAvian FluCici Novelia ManurungNo ratings yet
- Bronkitis and PneumoniaDocument16 pagesBronkitis and PneumoniaRegir KurNo ratings yet
- Presentati ON ON Bronchitis: Presented by K.vani M.SC (N) 1st YearDocument30 pagesPresentati ON ON Bronchitis: Presented by K.vani M.SC (N) 1st Yearvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorder Note BSC 3rd YearDocument41 pagesRespiratory Disorder Note BSC 3rd YearNancyNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Bacteria.: Risk For InfectionDocument5 pagesTuberculosis Bacteria.: Risk For InfectionLag Lag AlbercaNo ratings yet
- respiratory diseaseDocument13 pagesrespiratory diseasesumitk.1919141No ratings yet
- Asthmatic Attack: Miriti M.D Masters of Clinical Medicine Accidents and Emergency Facilitator: DR Simba DR MburuguDocument26 pagesAsthmatic Attack: Miriti M.D Masters of Clinical Medicine Accidents and Emergency Facilitator: DR Simba DR MburuguDennis MiritiNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument20 pagesPneumoniaFeizalNo ratings yet
- Asthama & COPDDocument84 pagesAsthama & COPDAbdullah BhattiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestation:: Medical ManagementDocument5 pagesClinical Manifestation:: Medical ManagementChristina BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Infectious and Inflammatory DisordersDocument84 pagesInfectious and Inflammatory DisordersMariel OracoyNo ratings yet
- PNEUMONIADocument24 pagesPNEUMONIAwheeyycoldandhot55No ratings yet
- CD Part 2 - Communicable Diseases With Pics (1) ConDocument239 pagesCD Part 2 - Communicable Diseases With Pics (1) ConMackoi SalamanesNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia and VAP PreventionDocument35 pagesPneumonia and VAP Preventionhendro harahapNo ratings yet
- Pedia Bronchial Asthma-1Document43 pagesPedia Bronchial Asthma-1MAHEJS HDNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Viruses: Organisms Causing PneumoniaDocument17 pagesRespiratory Viruses: Organisms Causing PneumoniaSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- REQ - PneumoniaDocument6 pagesREQ - PneumoniaAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Infections of The Respiratory System 1Document56 pagesInfections of The Respiratory System 1x8jx8dcsyvNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorDocument4 pagesPrecipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorRoxanne Ganayo ClaverNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersDocument93 pagesManagement of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersErica Clerigo Landicho100% (1)
- PneumoniaDocument16 pagesPneumoniamalope mahlatseNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory InfectionDocument71 pagesLower Respiratory Infectionpaulyn ramos100% (1)
- Nursing InterventionsDocument68 pagesNursing Interventionsash aliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 030Document12 pagesChapter 030Carlese GambleNo ratings yet
- Understanding EnteritisDocument28 pagesUnderstanding EnteritisRoshan Shrestha100% (2)
- Asthma: Pio T. Esguerra II, MD, FPCP, FPCCP Pulmonary & Critical Care FEU-NRMF Medical CenterDocument98 pagesAsthma: Pio T. Esguerra II, MD, FPCP, FPCCP Pulmonary & Critical Care FEU-NRMF Medical CenteryayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: What Causes ItDocument4 pagesPneumonia: What Causes ItMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Topic:Influenza: Assigned By:Maam Madiha Presented By:Tahira Ijaz Misbah MumtazDocument25 pagesTopic:Influenza: Assigned By:Maam Madiha Presented By:Tahira Ijaz Misbah MumtazPriya bhattiNo ratings yet
- 3 PneumoniaDocument17 pages3 PneumoniaMohamed Na3eemNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument7 pagesPneumoniapashiem88No ratings yet
- Learning Material RLE NCM 112Document5 pagesLearning Material RLE NCM 112shiro the catNo ratings yet
- Ch. 26. URT DisordersDocument106 pagesCh. 26. URT Disordersمحمد الحواجرةNo ratings yet
- AsmaDocument31 pagesAsmaseptiman zebuaNo ratings yet
- General Medicine Course-Part I&II-3rdyrDocument364 pagesGeneral Medicine Course-Part I&II-3rdyrbiography& lifestyleNo ratings yet
- 3 Bacterial PneumoniaDocument30 pages3 Bacterial PneumoniaAP ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DiseasesDocument11 pagesRespiratory DiseasesMichael Angelo SeñaNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument45 pagesBronchial Asthmamaggykariuki002No ratings yet
- Eman YousifDocument9 pagesEman Yousifsheka mNo ratings yet
- Communicable DisesaseDocument111 pagesCommunicable Disesasebrillaboy266No ratings yet
- Seminar1 1Document71 pagesSeminar1 1Tibebe S. TadesseNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PandemicsDocument5 pagesRespiratory PandemicsJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Cahaya InternasionalDocument9 pagesJurnal Cahaya InternasionalCahaya YusmaniNo ratings yet
- Asthma and COPDDocument28 pagesAsthma and COPDShoaib PatelNo ratings yet
- Adult NursingDocument13 pagesAdult Nursing00060651No ratings yet
- Ward Case PresentationDocument92 pagesWard Case PresentationSuzette Rae TateNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 48 The Child With Alterations in Respiratory FunctionsDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 48 The Child With Alterations in Respiratory Functionselsaqum98No ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory InfectionDocument27 pagesUpper Respiratory Infectionakoeljames8543No ratings yet
- Physiotherapy of Avian RespiratoryDocument3 pagesPhysiotherapy of Avian RespiratoryMichael MekhaNo ratings yet
- Module 12: Infection Control in Health Care Settings: Image Courtesy Of: World Lung FoundationDocument37 pagesModule 12: Infection Control in Health Care Settings: Image Courtesy Of: World Lung FoundationAniruddhaNo ratings yet
- هتاكربو الله ةمحرو مكيلع ملاسلا - We will talk about pneumonia, in the this presentation, we will talk about several point, includingDocument7 pagesهتاكربو الله ةمحرو مكيلع ملاسلا - We will talk about pneumonia, in the this presentation, we will talk about several point, includingFhfj FmfmfmfNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument64 pagesBronchial AsthmaDr. NasrumminallahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29: Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasesDocument5 pagesChapter 29: Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasesjefrocNo ratings yet
- Patho-pharmacology-II Unit 2-B Respiratory System and Diseases Related To This SystemDocument33 pagesPatho-pharmacology-II Unit 2-B Respiratory System and Diseases Related To This SystemYounas BhattiNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument8 pagesAsthmaLankeshwaraNo ratings yet
- BRONCHOPNEUMONIADocument18 pagesBRONCHOPNEUMONIAMANEESH MANINo ratings yet
- 04 Acute Bronchitis and Pneumonia in ChildrenDocument58 pages04 Acute Bronchitis and Pneumonia in ChildrenMi PatelNo ratings yet
- Body condition scoring in cattle newDocument30 pagesBody condition scoring in cattle newAAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- Newcastle-disease [Roll no. 02]Document25 pagesNewcastle-disease [Roll no. 02]AAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- 17.aachal himachal sah YersiniosisDocument14 pages17.aachal himachal sah YersiniosisAAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- 11. bishnuViral ArthritisDocument15 pages11. bishnuViral ArthritisAAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- Mastitis_FinalDocument36 pagesMastitis_FinalAAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- GiardiasisDocument36 pagesGiardiasisAAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- 9. bijay cia roll no.9Document13 pages9. bijay cia roll no.9AAYUSH BAGALENo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Principles of Disease and EpidemiologyDocument53 pagesChapter 14: Principles of Disease and EpidemiologyAbhishek Isaac MathewNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2Document3 pagesJurnal 2Farra PattipawaeNo ratings yet
- MCB4211Document11 pagesMCB4211Nadir A IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Tongue DisordersDocument31 pagesTongue DisordersMaphoto Xola0% (1)
- Desain Ruangan Pelayanan TB Di Admisi, Poli (Aziza Ariyani)Document58 pagesDesain Ruangan Pelayanan TB Di Admisi, Poli (Aziza Ariyani)endangsuhandaNo ratings yet
- Review of Osteoimmunology and The Host Response in Endodontic and Periodontal LesionsDocument16 pagesReview of Osteoimmunology and The Host Response in Endodontic and Periodontal LesionsNaeem MoollaNo ratings yet
- CHICKENPOXDocument32 pagesCHICKENPOXCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- ImuDocument28 pagesImuLukmanAnugrahNo ratings yet
- Eczema Patient LeafletDocument4 pagesEczema Patient LeafletAbdul KareemNo ratings yet
- (THT) Allergic Rhinitis For Medical StudentDocument40 pages(THT) Allergic Rhinitis For Medical StudentTheresia Radinda FelimNo ratings yet
- CT Evaluation of Enteritis and ColitisDocument40 pagesCT Evaluation of Enteritis and ColitisOscar NogueraNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration FormDocument2 pagesHealth Declaration Formlouis alvarezNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaSalwiyadiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-Natural History of DiseaseDocument21 pagesLecture 4-Natural History of Diseasehuma0% (1)
- Nutri TherapyDocument2 pagesNutri TherapySamuel DiazNo ratings yet
- South Africa CMV Viral Load Testing May2015Document4 pagesSouth Africa CMV Viral Load Testing May2015EnergadeNo ratings yet
- NipahDocument34 pagesNipahpraisidNo ratings yet
- 2chemical MediatorDocument1 page2chemical MediatorUu UuNo ratings yet
- Radio Broad Script EditedDocument5 pagesRadio Broad Script EditedEasy.No ratings yet
- r142881987 Bastian Octavio Gomez Figueroa CUR142881987Document1 pager142881987 Bastian Octavio Gomez Figueroa CUR142881987BastiánNo ratings yet
- 5.infecciones Micóticas Del Sistema Nervioso CentralDocument13 pages5.infecciones Micóticas Del Sistema Nervioso CentralLiz NuñezNo ratings yet
- Morinda Citrifolia (Noni) in The Treatment of PsoriasisDocument2 pagesMorinda Citrifolia (Noni) in The Treatment of PsoriasisAlexandra VlachouNo ratings yet
- Malarial Pathogenesis: By: Kareem Waleed Hamimy 6 Year Medical Student Kasr Al Ainy - Cairo UniversityDocument20 pagesMalarial Pathogenesis: By: Kareem Waleed Hamimy 6 Year Medical Student Kasr Al Ainy - Cairo UniversityKareem Waleed Ibrahim HamimyNo ratings yet
- Lymphangitis TreatmentDocument2 pagesLymphangitis TreatmentHarista Miranda SalamNo ratings yet
- Clerks ExamDocument4 pagesClerks ExamvannieloveNo ratings yet
- Tugas Uas Writing For General Comunication Kelas BDocument9 pagesTugas Uas Writing For General Comunication Kelas Bhadijah offical43119No ratings yet
- Pre-Test Questionnaire, COVID-19Document1 pagePre-Test Questionnaire, COVID-19Minhazur Rahman SakibNo ratings yet
- AIR DROP EXAMنسختي PDFDocument35 pagesAIR DROP EXAMنسختي PDFYara AlmouallemNo ratings yet
- Appropiate Allergic Testing and The Interpretation - Dr. Deshinta Putri Mulya, SP - PD (K) KAIDocument40 pagesAppropiate Allergic Testing and The Interpretation - Dr. Deshinta Putri Mulya, SP - PD (K) KAIEllenNo ratings yet





























































![Newcastle-disease [Roll no. 02]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/751232572/149x198/4a98b97c5f/1721229815?v=1)