Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sampling Distribution Of The Estimator
Sampling Distribution Of The Estimator
Uploaded by
krishnavamsi.madati0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesSampling Distribution Of The Estimator
Sampling Distribution Of The Estimator
Uploaded by
krishnavamsi.madatiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Sampling Distribution Of The
Estimator
In statistics, it is the probability distribution of the given statistic
estimated on the basis of a random sample. It provides a generalized
way to statistical inference.
The estimator is the generalized mathematical parameter to calculate
sample statistics. An estimate is the result of the estimation.
The sampling distribution of estimator depends on the sample size. The
effect of change of the sample size has to be determined. An estimate
has a single numerical value and hence they are called point estimates.
• Since our estimators are statistics (particular functions of random
variables), their distribution can be derived from the joint distribution
of X1 . . . Xn.
• It is called the sampling distribution because it is based on the joint
distribution of the random sample.
• Sampling distributions of estimators depend on sample size, and we
want to know exactly how the distribution changes as we change this
size so that we can make the right trade-offs between cost and
accuracy
There are various estimators like sample mean, sample standard
deviation, proportion, variance, range etc.
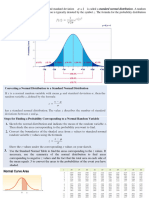
Sampling distribution of the mean: It is the population mean from
which the samples are drawn. For all the sample sizes, it is likely to be
normal if the population distribution is normal.
The population mean is equal to the mean of the sampling
distribution of the mean. Sampling distribution of mean has the
standard deviation, which is as follows:
Where
is the standard deviation of the sampling mean is the
population standard deviation and n is the sample size.
As the size of the sample increases, the spread of the sampling
distribution of the mean decreases. But the mean of the distribution
remains the same and it is not affected by the sample size.
The sampling distribution of the standard deviation is the standard
error of the standard deviation. It is defined as:
here is the sampling distribution of the standard deviation.
It is positively skewed for small n but it approximately becomes
normal for sample sizes greater than 30.
Advantages:
Sampling distribution, a statistical tool, helps calculate the
probability of an event by repeatedly sampling a small
group of subjects rather than sampling an entire
population.
The sampling distribution of a sample statistic is the
distribution of the point estimates based on samples of a
fixed size, n, from a certain population.
It is useful to think of a particular point estimate as being drawn
from a sampling distribution.
You might also like
- Isye 6412A Theoretical Statistics Fall 2019Document2 pagesIsye 6412A Theoretical Statistics Fall 2019Yasin Çagatay GültekinNo ratings yet
- Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) in Excel TutorialDocument8 pagesKernel Density Estimation (KDE) in Excel TutorialNumXL ProNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Inference For Categorical Data PDFDocument48 pagesBayesian Inference For Categorical Data PDFLili CRNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document24 pagesChapter 16Senthil RNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 6 Asymptotic Properties PDFDocument4 pagesLecture Note 6 Asymptotic Properties PDFranjana kashyapNo ratings yet
- A Level Further Mathematics For OCR A Statistics Student Book 1 (AS/A Level) Scheme of WorkDocument21 pagesA Level Further Mathematics For OCR A Statistics Student Book 1 (AS/A Level) Scheme of Workshah kaivanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document5 pagesProblem Set 1Afanti NasruddinNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Management - 2Document14 pagesStatistics For Management - 2Nandhini P Asst.Prof/MBA100% (3)
- Notes RMDocument2 pagesNotes RMAlisNo ratings yet
- Central Limit TheoremDocument3 pagesCentral Limit TheoremMohammad ImthiyazNo ratings yet
- Population - Entire Group of Individuals About Which We Want Information. Sample - Part of The Population From Which We Actually Collect InformationDocument5 pagesPopulation - Entire Group of Individuals About Which We Want Information. Sample - Part of The Population From Which We Actually Collect Informationlauren smithNo ratings yet
- Standard Error: Sampling DistributionDocument5 pagesStandard Error: Sampling DistributionErica YamashitaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology - Chapter 8Document21 pagesResearch Methodology - Chapter 8Muthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv 1. Testing of HypothesisDocument28 pagesUnit-Iv 1. Testing of Hypothesismalleda haneeshNo ratings yet
- Sampling DistributionDocument7 pagesSampling DistributionSunil Kumar Hg HgNo ratings yet
- Super Position TheoremDocument14 pagesSuper Position TheoremEnoch DammuNo ratings yet
- What Is Sampling DistributionDocument1 pageWhat Is Sampling Distributiontemedebere0% (1)
- What Is SamplingDocument18 pagesWhat Is SamplingYvonne Alonzo De BelenNo ratings yet
- Inferential StatisticsDocument38 pagesInferential Statisticszephers2002100% (1)
- Revision SB Chap 8 12 Updated 1Document44 pagesRevision SB Chap 8 12 Updated 1Ngan DinhNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Statistical Inference: Eg: What Is The Average Income of All Stern Students?Document11 pagesSampling and Statistical Inference: Eg: What Is The Average Income of All Stern Students?Ahmad MostafaNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument49 pagesStatisticshazalulger5No ratings yet
- 3.3 Sampling DistributionDocument22 pages3.3 Sampling Distributionyouservezeropurpose113No ratings yet
- Sample DistributionDocument20 pagesSample Distributionhifazat aliNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inference Vs Descriptive Statistics: ConclusionsDocument19 pagesStatistical Inference Vs Descriptive Statistics: ConclusionsMaxence AncelinNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distributions: The Basic Practice of StatisticsDocument14 pagesSampling Distributions: The Basic Practice of StatisticsUsernamefireNo ratings yet
- "Minhaj University Lahore": Inferential StatisticsDocument6 pages"Minhaj University Lahore": Inferential StatisticsMuhammad MadniNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Statistical and ModellingDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Statistical and Modellingkurniajay8No ratings yet
- Confidence Intervals PDFDocument5 pagesConfidence Intervals PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Sampling and EstimationDocument51 pages8.1 Sampling and EstimationNguyễn Thanh NhậtNo ratings yet
- Stat For Fin CH 4 PDFDocument17 pagesStat For Fin CH 4 PDFWonde BiruNo ratings yet
- Sampling MethodsDocument7 pagesSampling MethodsshreebhagyeshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Statistics22100629No ratings yet
- 7 EstimationDocument91 pages7 EstimationTESFAYE YIRSAWNo ratings yet
- Stat Notes IIDocument48 pagesStat Notes IIbuTchaNo ratings yet
- HypothesisDocument11 pagesHypothesissonnetthomasNo ratings yet
- Sampling DistributionDocument29 pagesSampling Distributiondawit tesfaNo ratings yet
- Data Sci LinkedinDocument3 pagesData Sci LinkedinangelNo ratings yet
- DMA 1 ReviewOfProbabilityDocument45 pagesDMA 1 ReviewOfProbability[CO - 174] Shubham MouryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Sampling DistributionDocument35 pagesChapter 5 Sampling DistributionSURIA ATIKA AHMAD ASRINo ratings yet
- Confidence Interval, Standard ErorDocument21 pagesConfidence Interval, Standard ErorRHEY ANNE TEHENGNo ratings yet
- U3-L4 - Sampling DistributionsDocument25 pagesU3-L4 - Sampling DistributionsSudhagar DNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Inferential StatisticsDocument9 pagesBasic Concepts of Inferential Statisticsstatistics-consultation100% (5)
- Statistics Ready ReckonerDocument4 pagesStatistics Ready ReckonerAdarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Sampling DistDocument40 pagesSampling DistSanket SharmaNo ratings yet
- Econometric SDocument37 pagesEconometric Sestheradrian419No ratings yet
- AP Stat Ch17Document110 pagesAP Stat Ch17Ryan Robert AbundoNo ratings yet
- Sampling DistributionDocument19 pagesSampling DistributionUpasana Abhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Standard DeviationDocument22 pagesStandard Deviationdev414No ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document7 pagesLecture 7muendokyalo11No ratings yet
- Stat W7 Q3Document27 pagesStat W7 Q3Puffers The fishNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics - IV (15MAT41) Module-V: SAMPLING THEORY and Stochastic ProcessDocument28 pagesEngineering Mathematics - IV (15MAT41) Module-V: SAMPLING THEORY and Stochastic ProcessKK VC100% (1)
- Introduction To Inferential StatisticsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Inferential StatisticsJuvee TimayNo ratings yet
- Statistics Notes For CLT & Sampling TechniquesDocument11 pagesStatistics Notes For CLT & Sampling Techniqueshatakeabiii07No ratings yet
- Sample SizeDocument6 pagesSample SizeClaudio Garretón VénderNo ratings yet
- The CLT and Sampling DistributionsDocument1 pageThe CLT and Sampling DistributionsDj XperiaNo ratings yet
- Stat 115 - Basic Statistical MethodsDocument6 pagesStat 115 - Basic Statistical MethodsaramafeNo ratings yet
- Week 6. Chapter 7 Introduction To Inferential StatisticsDocument24 pagesWeek 6. Chapter 7 Introduction To Inferential Statisticspramodh kumarNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Descriptive and Inferential StatisticsDocument9 pagesDifference Between Descriptive and Inferential StatisticsKen EncisoNo ratings yet
- 3 - Introduction To Inferential StatisticsDocument32 pages3 - Introduction To Inferential StatisticsVishal ShivhareNo ratings yet
- Statistics - The Big PictureDocument4 pagesStatistics - The Big PicturenaokiNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Sampling DistributionsDocument44 pagesSampling and Sampling Distributionskunal kabraNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument46 pagesSampling and Sampling DistributionMaria Loida Veronica NaborNo ratings yet
- Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Tests For MeansDocument40 pagesConfidence Intervals and Hypothesis Tests For MeansJosh PotashNo ratings yet
- Lect9 Math231Document42 pagesLect9 Math231Qasim RafiNo ratings yet
- Lehmann-Scheffe TheoremDocument15 pagesLehmann-Scheffe TheoremEve Zaiyeh FamorNo ratings yet
- Estimation 1Document13 pagesEstimation 1Kurt PlatonNo ratings yet
- 08 LCD Slide Handout 1Document5 pages08 LCD Slide Handout 1Jana Gabrielle Canonigo0% (1)
- From Alpha To Omega: A Practical Solution To The Pervasive Problem of Internal Consistency EstimationDocument14 pagesFrom Alpha To Omega: A Practical Solution To The Pervasive Problem of Internal Consistency EstimationLuis Angel Hernandez MirandaNo ratings yet
- The Least Squer MethodDocument192 pagesThe Least Squer MethodRR886No ratings yet
- Ridge Regression: Effects of MulticollinearityDocument21 pagesRidge Regression: Effects of MulticollinearitywekwekNo ratings yet
- Slides (Handout) - Caio - Chapter 4 (Wooldridge)Document99 pagesSlides (Handout) - Caio - Chapter 4 (Wooldridge)Maria ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Econometrics, 5 Edition: Chapter 2: Properties of The Regression Coefficients and Hypothesis TestingDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Econometrics, 5 Edition: Chapter 2: Properties of The Regression Coefficients and Hypothesis TestingRamarcha KumarNo ratings yet
- IntroEconmerics AcFn 5031 (q1)Document302 pagesIntroEconmerics AcFn 5031 (q1)yesuneh98No ratings yet
- Regression AnalysisDocument280 pagesRegression AnalysisA.Benhari100% (1)
- Bell Mccaffrey 2002Document16 pagesBell Mccaffrey 2002734500203No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing - Estimation Theory-Kay-2Document2 pagesFundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing - Estimation Theory-Kay-2MjNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics and Probability For Engineers Chapter - 8Document13 pagesApplied Statistics and Probability For Engineers Chapter - 8MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ridge RegressionDocument21 pagesRidge RegressionTiberiu TincaNo ratings yet
- Gloss PDFDocument8 pagesGloss PDFSaadat Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- J. K. Shah Classes Sampling Theory and Theory of EstimationDocument37 pagesJ. K. Shah Classes Sampling Theory and Theory of EstimationGautamNo ratings yet
- Essays On Computational Problems in InsuranceDocument125 pagesEssays On Computational Problems in InsuranceAlmaz GetachewNo ratings yet
- LOVDocument43 pagesLOVMei FadillahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4stats and ProbDocument41 pagesChapter 4stats and ProbSarada SanNo ratings yet
- Nonstationary Panels, Panel Cointegration, and Dynamic Panels PDFDocument337 pagesNonstationary Panels, Panel Cointegration, and Dynamic Panels PDFBhuwanNo ratings yet
- 4 Estimation HandoutDocument2 pages4 Estimation HandoutKaysh QwertyNo ratings yet
- To Pool or Not To Pool: Homogeneous Versus Heterogeneous Estimators Applied To Cigarette DemandDocument10 pagesTo Pool or Not To Pool: Homogeneous Versus Heterogeneous Estimators Applied To Cigarette DemandVeeMeasNo ratings yet
- Hetero PartDocument11 pagesHetero Partaya.said2020No ratings yet