Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH03
CH03
Uploaded by
Nelson Chetevik0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views48 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views48 pagesCH03
CH03
Uploaded by
Nelson ChetevikCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 48
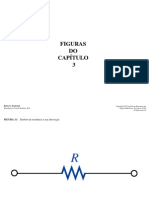
FIGURE 3.1 Resistance symbol and notation.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.2 Factors affecting the resistance of a conductor.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.3 Cases in which R2 > R1. For each case, all remaining parameters that control the resistance level are the same.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.4 Defining the circular mil (CM).
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.5 Verification of Eq. (3.4): ACM = (dmils)2.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.6 Defining the constant ρ (resistivity).
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.7 Example 3.2.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.8 Example 3.3.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.9 Popular wire sizes and some of their areas of application.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.10 Example 3.6.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.11 Defining ρ in ohm-centimeters.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.12 Thin-film resistor (note Fig. 3.22).
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.13 (a) Positive temperature coefficient-conductors; (b) negative temperature coefficient-semiconductors.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.14 Effect of temperature on the resistance of copper.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.15 Rising temperatures of superconductors.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.16 Defining the critical temperature Tc.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.17 Fixed composition resistor.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.18 Fixed composition resistors of different wattage ratings.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.19 Curves showing percentage temporary resistance changes from +20°C values. (Courtesy of Allen-Bradley Co.)
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.20 Fixed resistors. [Parts (a) and (c) courtesy of Ohmite Manufacturing Co. Part (b) courtesy of Philips Components Inc.]
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.21 Miniature fixed resistors. [Part (a) courtesy of Ohmite Manufacturing Co. Parts (b) and (c) courtesy of Dale Electronics,
Inc.]
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.22 Thick-film resistor networks. (Courtesy of Dale Electronics, Inc.)
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.23 Potentiometer: (a) symbol; (b) and (c) rheostat connections; (d) rheostat symbol.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.24 Molded composition-type potentiometer. (Courtesy of Allen-Bradley Co.)
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.25 Terminal resistance of a potentiometer: (a) between outside terminals; (b) among all three terminals.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.26 Potentiometers: (a) 4-mm (≈5/32") trimmer (courtesy of Bourns, Inc.); (b) conductive plastic and cermet element (sourtesy
of Clarostat Mfg. Co.)
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.27 Potentiometer control of voltage levels.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.28 Color coding of fixed molded composition resistor.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.29 Guaranteeing the full range of resistor values for the given tolerance: (a) 20%; (b) 10%.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.30 Werner von Siemens.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.31 Measuring the resistance of a single element.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.32 Checking the continuity of a connection.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.33 Identifying the leads of a multilead cable.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.34 Thermistor: (a) characteristics; (b) symbol.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.35 NTC (negative temperature coefficient) and PTC (positive temperature coefficient) thermistors. (Courtesy of Siemens
Components, Inc.)
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.36 Photoconductive cell: (a) characteristics; (b) symbol.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.37 Photoconductive cells. (Courtesy of EG&G VACTEC, Inc.)
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.38 Varistors available with maximum dc voltage ratings between 18 V and 615 V. (Courtesy of Philips Components, Inc.)
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.39 Electric baseboard: (a) 2-ft section; (b) interior; (c) heating element; (d) nichrome coil.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.40 Dashboard dimmer control in an automobile.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.41 Resistive strain gauge. (© Copyright Omega Engineering, Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduced with the permission of
Omega Engineering, Inc., Stamford, CT 06907.)
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.42 Using Mathcad to perform a basic mathematical operation.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.43 Defining the order of mathematical operations for Mathcad.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.44 Using Mathcad to calculate the resistance of a copper conductor.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.45 Problem 9.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.46 Problem 11.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.47 Problem 16.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
FIGURE 3.48 Problem 22.
Robert L. Boylestad Copyright ©2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Introductory Circuit Analysis, 10ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Imvf Condensing Unit 208V 150213 PDFDocument125 pagesImvf Condensing Unit 208V 150213 PDFAndrés Hernández100% (1)
- Siwes Report CHISOM SAM ORJIDocument41 pagesSiwes Report CHISOM SAM ORJISOMSKI1100% (2)
- Fire Safety Full ReportDocument30 pagesFire Safety Full ReportNoor Asni100% (1)
- Shop ManualDocument217 pagesShop ManualNoval Aveiro100% (2)
- Figuras DO Capítulo 3: Robert L. BoylestadDocument20 pagesFiguras DO Capítulo 3: Robert L. BoylestadFelipe SuzartNo ratings yet
- Figuras DO Capítulo 3: Robert L. BoylestadDocument20 pagesFiguras DO Capítulo 3: Robert L. BoylestadLazaro Marques de Oliveira JuniorNo ratings yet
- CH02Document35 pagesCH02Nelson ChetevikNo ratings yet
- CH01Document6 pagesCH01Nelson ChetevikNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Robert L. Boylestad and Louis NashelskyDocument23 pagesTransistor: Robert L. Boylestad and Louis NashelskyRafael PeluzioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Small Sinal Analysis of FETDocument46 pagesChapter 8 Small Sinal Analysis of FETsakibNo ratings yet
- Bölüm 1 FiguresDocument71 pagesBölüm 1 FiguresMustafaNo ratings yet
- Fig. 2.44 Half-Wave Rectifier.: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 9eDocument160 pagesFig. 2.44 Half-Wave Rectifier.: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 9eLelouch ViNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor, Diode and Power Supplies: Chapter TwoDocument43 pagesSemiconductor, Diode and Power Supplies: Chapter TwoApostrophe Fareez ImprezzaNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 4Document101 pagesCapitulo 4Ricardo CanoNo ratings yet
- 2a Semiconductor Diodes MZMDocument48 pages2a Semiconductor Diodes MZMSyahmi AkmalNo ratings yet
- Figure 12 - 1 JFET Construction.: Robert T. PaynterDocument10 pagesFigure 12 - 1 JFET Construction.: Robert T. Payntermk07 natNo ratings yet
- 10 Amp OP Chap14 Boylestad PDFDocument35 pages10 Amp OP Chap14 Boylestad PDFMarcos PavanNo ratings yet
- CH03Document26 pagesCH03Jay ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Diode Applications-1Document22 pagesChapter2 Diode Applications-1ViricoNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 p3Document16 pagesChapter4 p3mayankardeshanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document27 pagesChapter 9hessa 2001No ratings yet
- B-Stad CH 08Document30 pagesB-Stad CH 08academicopersonalNo ratings yet
- Chap8 PDFDocument39 pagesChap8 PDFOmar Ahmed AbuLeilaNo ratings yet
- BJT OperationsDocument21 pagesBJT Operationsarondaniel ocampoNo ratings yet
- FIGURE 4.1 Georg Simon Ohm.: Robert L. BoylestadDocument36 pagesFIGURE 4.1 Georg Simon Ohm.: Robert L. BoylestadDaniel AlbuquerqueNo ratings yet
- ECE FET Small Signal AnalysisDocument52 pagesECE FET Small Signal AnalysisGmae Fampulme100% (1)
- BJT AC AnalysisDocument44 pagesBJT AC AnalysisSmadi Rana2001No ratings yet
- Chapter2 p1 NITHDocument22 pagesChapter2 p1 NITHPriyanshu GargNo ratings yet
- CH 05 Emisor Comun BJTDocument16 pagesCH 05 Emisor Comun BJTrobertoNo ratings yet
- Grs BebanDocument11 pagesGrs BebanAlan TetraxNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory: Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument26 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory: Bipolar Junction TransistorsKavinesh AnanthanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Diode ApplicationDocument57 pagesModule 3 - Diode ApplicationnaviescarillaNo ratings yet
- Transistors and Applications PDFDocument28 pagesTransistors and Applications PDFLeticia MelloNo ratings yet
- DC Biasing-Bjts: Dr. Talal SkaikDocument16 pagesDC Biasing-Bjts: Dr. Talal Skaikmessage4guruNo ratings yet
- FIGURE 9-1 Basic Class A Amplifier Operation. Output Is Shown 180 Out of Phase With The Input (Inverted)Document51 pagesFIGURE 9-1 Basic Class A Amplifier Operation. Output Is Shown 180 Out of Phase With The Input (Inverted)Komal SharmaNo ratings yet
- RLC Circuits and ResonanceDocument40 pagesRLC Circuits and ResonanceMaryam Dia100% (1)
- Diode Applications: Dr. Talal SkaikDocument22 pagesDiode Applications: Dr. Talal SkaikBenj MendozaNo ratings yet
- Capítulo 7: Electrónica: Teoría de Circuitos y Dispositivos ElectrónicosDocument109 pagesCapítulo 7: Electrónica: Teoría de Circuitos y Dispositivos ElectrónicosGermán GamboaNo ratings yet
- 2 Diode ApplicaDocument34 pages2 Diode Applicaagung rakaNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 p1Document24 pagesChapter4 p1mayankardeshanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document39 pagesChapter 5ah626167No ratings yet
- Electronic Device Lecture3Document57 pagesElectronic Device Lecture3kusumadiahNo ratings yet
- Clase5-6 Transistor BJT PolDocument42 pagesClase5-6 Transistor BJT PolAdrian Alejandro Sarasti AlzateNo ratings yet
- Transistor CharacteristicsDocument25 pagesTransistor Characteristicsmanish100% (1)
- B-Stad CH 03 PDFDocument26 pagesB-Stad CH 03 PDFOzan DokuyucuNo ratings yet
- BJT DC Biasing 4 - p2Document20 pagesBJT DC Biasing 4 - p2FajarNo ratings yet
- Resistance: Publishing As Pearson (Imprint) BoylestadDocument25 pagesResistance: Publishing As Pearson (Imprint) BoylestadislammuddinNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DiodesDocument37 pagesSemiconductor DiodeshasnolNo ratings yet
- 4 - Lecture 3 Electric TechnologyDocument81 pages4 - Lecture 3 Electric Technologymujahidghazali7No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit TheoryDocument27 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theoryyahoc46031No ratings yet
- Chapter4 p2Document19 pagesChapter4 p2mayankardeshanaNo ratings yet
- BJT AC AnalysisDocument22 pagesBJT AC AnalysisDonna OrqueNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory: Field Effect Transistor (FET)Document57 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory: Field Effect Transistor (FET)Rabbi KhanNo ratings yet
- Applied Electronics Ch 1_2Document21 pagesApplied Electronics Ch 1_2robelassefa708No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory Electronic Devices and Circuit TheoryDocument42 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory Electronic Devices and Circuit TheoryEfliana DadiNo ratings yet
- Electronics 1 (1st Exam) CDocument33 pagesElectronics 1 (1st Exam) CcyarakkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document46 pagesChapter 4najlaNo ratings yet
- B Stad - CH - 02 Diode Applications UpdatedDocument36 pagesB Stad - CH - 02 Diode Applications UpdatedJoyce HerreraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document30 pagesChapter 8abd syNo ratings yet
- Diodes and RectifiersDocument62 pagesDiodes and RectifiersAli IqbalNo ratings yet
- Cap 4 ADocument31 pagesCap 4 ADiego SilvaNo ratings yet
- HV Switch Gear - PPT-Rev01Document11 pagesHV Switch Gear - PPT-Rev01Lalit Kumar JainNo ratings yet
- Under-/Over-Voltage Beep For Manual Stabiliser: K. Udhaya KumaranDocument2 pagesUnder-/Over-Voltage Beep For Manual Stabiliser: K. Udhaya KumaranMani BlackyNo ratings yet
- Catalyst Deactivation - Is It Predictable What To Do PDFDocument14 pagesCatalyst Deactivation - Is It Predictable What To Do PDFBamrung SungnoenNo ratings yet
- 750-0006 MarinerOMNIPURESeriesM55 Sept15Document4 pages750-0006 MarinerOMNIPURESeriesM55 Sept15Angel Mauricio Toledo CidNo ratings yet
- CH18 - Planar Kinetics of A Rigid Body Work and Energy - DynamicDocument59 pagesCH18 - Planar Kinetics of A Rigid Body Work and Energy - DynamicRs sniperNo ratings yet
- Splash Protection - SOLASguidelines ChII-2-15.2Document8 pagesSplash Protection - SOLASguidelines ChII-2-15.2Marco Aurélio SchelesNo ratings yet
- Tube Lay Out Gas ExchangerDocument1 pageTube Lay Out Gas ExchangerHudaFiHayyatNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Enthalpy Changes: Basic Principles and Calculations in Chemical EngineeringDocument7 pagesCalculation of Enthalpy Changes: Basic Principles and Calculations in Chemical EngineeringSafa AlniamiNo ratings yet
- ch07 LectureDocument48 pagesch07 LecturehawcNo ratings yet
- Lit 18626 06 75 - 1369Document90 pagesLit 18626 06 75 - 1369andysuomi100% (1)
- Bevis, J. F. and H. J. Jeffery. British Plants Their Biology and Ecology (1920)Document361 pagesBevis, J. F. and H. J. Jeffery. British Plants Their Biology and Ecology (1920)shelfedgeNo ratings yet
- Ariston Genus 23-27-30 MFFI - 27RFFiDocument76 pagesAriston Genus 23-27-30 MFFI - 27RFFipvale23No ratings yet
- Gravitational Waves: Einstein's Legacy: Vinod KumarDocument4 pagesGravitational Waves: Einstein's Legacy: Vinod KumarPrakash HiremathNo ratings yet
- User's Operation and Maintenance Manual For Double-Wheel Motorcycle QJ150T-10Document131 pagesUser's Operation and Maintenance Manual For Double-Wheel Motorcycle QJ150T-10horacio MorlacchiNo ratings yet
- Wood Stove TroubleShooting GuideDocument19 pagesWood Stove TroubleShooting Guideew6082No ratings yet
- Applied ElectronicsDocument110 pagesApplied ElectronicsRahul CP100% (1)
- sm-K1017314E DX210W LowResDocument1,184 pagessm-K1017314E DX210W LowResDavid Apaza Hurtado100% (1)
- LM3370 Dual Synchronous Step-Down DC-DC Converter With Dynamic Voltage Scaling FunctionDocument23 pagesLM3370 Dual Synchronous Step-Down DC-DC Converter With Dynamic Voltage Scaling FunctionHabibulla BavajiNo ratings yet
- CWTUM - Technical Notes - 001Document15 pagesCWTUM - Technical Notes - 001Anonymous xTGQYFrNo ratings yet
- Psoc Course FileDocument14 pagesPsoc Course Filecholleti sriramNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Conversion de UnidadesDocument9 pagesTabla de Conversion de UnidadesMinervaHernandezSalazarNo ratings yet
- CV Saed DababnehDocument12 pagesCV Saed DababnehSaed DababnehNo ratings yet
- Major 317 AccidentsDocument13 pagesMajor 317 AccidentsBamaNo ratings yet
- 17th Scheme 7th Sem PDFDocument12 pages17th Scheme 7th Sem PDFMadan V LNo ratings yet
- 1563519208153-Question Bank (Electrical-Emu Deptt.)Document232 pages1563519208153-Question Bank (Electrical-Emu Deptt.)mfenta153No ratings yet
- Low Voltage 3-Phase Induction Motors Range 0.55kW To 500kW: Australia & New ZealandDocument12 pagesLow Voltage 3-Phase Induction Motors Range 0.55kW To 500kW: Australia & New ZealandwmehmoodNo ratings yet