Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 viewsG3_SENSE-ORGANS-1
G3_SENSE-ORGANS-1
Uploaded by
Love, It's Me JaveCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5835)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- REJURANDocument13 pagesREJURANirwan jun100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: My CoursesDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: My CoursesRcel Balmes100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Healy Resonance ProgramsDocument7 pagesHealy Resonance Programshayley100% (7)
- Chapter 19 Microbial Diseases of The Skin and WoundsDocument8 pagesChapter 19 Microbial Diseases of The Skin and WoundsGRACE MAR CABAHUG100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Facial and Physical Signs of Tissue Salt DeficiencyDocument4 pagesFacial and Physical Signs of Tissue Salt DeficiencyFahad JavedNo ratings yet
- Colorful Illustrative Forms of Energy Science PresentationDocument14 pagesColorful Illustrative Forms of Energy Science PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Colourful Cartoon Science Bodies of Water Quiz Activity PresentationDocument14 pagesColourful Cartoon Science Bodies of Water Quiz Activity PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Teacher Planner for 2024 in Colorful Aesthetic StyleDocument25 pagesTeacher Planner for 2024 in Colorful Aesthetic StyleLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Colorful Illustrative Forms of Energy Science PresentationDocument14 pagesColorful Illustrative Forms of Energy Science PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Colorful Retro Vintage Illustration Animated Medical Technology Education Science PresentationDocument20 pagesColorful Retro Vintage Illustration Animated Medical Technology Education Science PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of AnimalsDocument26 pagesLife Cycle of AnimalsLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Colorful Stickers and Badges Memory Game Fun PresentationDocument17 pagesColorful Stickers and Badges Memory Game Fun PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Blue Green and Purple Illustration Course Syllabus Education PresentationDocument12 pagesBlue Green and Purple Illustration Course Syllabus Education PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- F.-W. Tesch Dr. Agr. (Auth.), P. H. Greenwood D.sc. (Eds.) - The Eel - Biology and Management of Anguillid Eels-Springer Netherlands (1977)Document445 pagesF.-W. Tesch Dr. Agr. (Auth.), P. H. Greenwood D.sc. (Eds.) - The Eel - Biology and Management of Anguillid Eels-Springer Netherlands (1977)deryhermawanNo ratings yet
- Cosmetics Manufacturing Business PlanDocument63 pagesCosmetics Manufacturing Business PlanShihabul Islam ShihabNo ratings yet
- 5 Integumentary SystemDocument67 pages5 Integumentary SystemchelsealivesforeverNo ratings yet
- Hyaluronic Acid by ContiproDocument2 pagesHyaluronic Acid by Contipro61p2bjx5No ratings yet
- Fungal & Parasitic Infestations of The SkinDocument67 pagesFungal & Parasitic Infestations of The SkinGhaith HamdiNo ratings yet
- Clo VateDocument5 pagesClo VateNatalia GomezNo ratings yet
- Review in Peeling ComplicationsDocument8 pagesReview in Peeling ComplicationschipanzeNo ratings yet
- Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocument12 pagesSquamous Cell CarcinomaA. Pathak0% (1)
- Tes Psikotes BUMN - 9 - Bahasa InggrisDocument17 pagesTes Psikotes BUMN - 9 - Bahasa InggrisPrsty 12No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SkinDocument30 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The SkinNancy VargasNo ratings yet
- A Handbook of CosmeticsDocument134 pagesA Handbook of CosmeticsAlifa Syafira Putri76% (25)
- Pigmented Skin LesionsDocument51 pagesPigmented Skin LesionsclikgoNo ratings yet
- Kelebihan Triple StemcellDocument4 pagesKelebihan Triple StemcellMuhammad AffandiNo ratings yet
- Esthetician/paramedical AestheticianDocument2 pagesEsthetician/paramedical Aestheticianapi-121459287No ratings yet
- Iggy - Chapter 26 - Burns - PPDocument34 pagesIggy - Chapter 26 - Burns - PPnicole pilandNo ratings yet
- 2015 - 07094934Document9 pages2015 - 07094934mjimenezgNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Stability Test Cream: No. Nama Produk Tanggal Stabtest 1 Hari 3 Hari 1 MingguDocument3 pagesJadwal Stability Test Cream: No. Nama Produk Tanggal Stabtest 1 Hari 3 Hari 1 MingguAdityaFajhrilFalahNo ratings yet
- Physical InjuriesDocument6 pagesPhysical InjuriesHermay BanarioNo ratings yet
- Immunity (Lecture Notes)Document5 pagesImmunity (Lecture Notes)Anisha NishanthNo ratings yet
- Pricelist SKINTIFIC Jakarta X Beauty II 14 - 17 Dec 2023Document1 pagePricelist SKINTIFIC Jakarta X Beauty II 14 - 17 Dec 2023ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Biology Matters Theory Workbook 1Document196 pagesBiology Matters Theory Workbook 1same faaz100% (1)
- Structure and Function of SkinDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of SkinSarah AndersonNo ratings yet
- English SbaDocument10 pagesEnglish SbakimalaNo ratings yet
- Stock SST 9 Januari 2023Document16 pagesStock SST 9 Januari 2023Rhesa GuttamaNo ratings yet
- CHP 12 - Oral Mucosa-1Document83 pagesCHP 12 - Oral Mucosa-1Areej Fatima100% (2)
G3_SENSE-ORGANS-1
G3_SENSE-ORGANS-1
Uploaded by
Love, It's Me Jave0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views69 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views69 pagesG3_SENSE-ORGANS-1
G3_SENSE-ORGANS-1
Uploaded by
Love, It's Me JaveCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 69
SENSE ORGANS
How do we perceive our surroundings?
SENSE ORGANS
How do we perceive our surroundings?
SENSE ORGANS
How do we perceive our surroundings?
SENSE ORGANS
How do we perceive our surroundings?
SENSE ORGANS
How do we perceive our surroundings?
SENSE ORGANS
WHAT IS A SENSE
• Sense organs are the organs that enable us
ORGAN?
to understand and perceive what is
happening in our surroundings.
• We perceive everything around us
through senses such as sight, hearing,
smell, touch, and taste.
• All of these processes occur with the help
of our sense organs.
Our sense organs
• We have five sense organs.
Eye Skin Nose Tongue Ear
eye
Vision/Sight Sense Organ
• Our eyes are situated in the front
of our head, in two sturdy
sockets.
• With the help of our eyes, we
perceive the color, size, and
movement of the objects around
us.
If we dIdn't have eyes?
• We wouldn't be able to see
the living and non-living
entities around us, our loved
ones, colorful flowers, birds,
and butterflies.
outer layer
• Sclera – the outer layer of
the eye
• Cornea – transparent part
of the coat of the eyeball
Middle layer
• Choroid layer – this layer contains
numerous tiny blood vessels that
nourishes the eye.
• Iris – the colored part of your eye
• Pupil – the small opening in the middle
Middle layer
• Lens - a curved structure in the eye
that that bends light and focuses it for
the retina to help you see images
clearly.
Inner layer
• Retina - receives the light from the lens. It
is made up of rods and cones. The rods let
the eyes sense light while the cones help
identify color.
• Optic nerve - relay messages from your
eyes to your brain to create visual images.
Inner layer
• Retina - receives the light from the
lens. It is made up of rods and
cones. The rods let the eyes sense
light while the cones help identify
color.
• Optic nerve - relay messages
from your eyes to your brain to
create visual images.
Common eye ailments
• Conjunctivitis/sore eyes – it is caused by
bacteria, virus, allergies, or
environmental pollutants such as dust
and smoke. A person with conjunctivitis
has red, swollen, and teary eyes.
• Sty – the eyelid swells and becomes
reddish. It is caused by bacterial
infection.
Common eye defects
• Strabismus –is a disorder in which both eyes
do not line up in the same direction.
Therefore, they do not look at the same object
at the same time. The most common form of
strabismus is known as "crossed eyes.“
• Astimatism – the cornea is shaped more like
a football. This changes the way light enters
the eye and makes objects both near and far
appear blurry.
Common eye defects
• Color blindness – occurs when you are
unable to see colors in a normal way.
• Myopia or nearsightedness – a common
vision condition in which near objects appear
clear, but objects farther away look blurry.
• Hyperopia or farsightedness - is a common
vision condition in which you can see distant
objects clearly, but objects nearby may be
blurry.
Proper care for the eyes
• Proper nutrition – eat food that are rich in
vitamin.
Proper care for the eyes
• Preventing eye damage
Proper care for the eyes
• Good health habits
Proper care for the eyes
• Regular check- up of the eyes
by a doctor
Proper care for the eyes
• First aid treatment
ear
Hearing Sense Organ
• Our ears are our sense
organs for hearing.
• We perceive sounds from
our surroundings through
our ears.
If we dıdn't have ears?
• Speaking is directly related
to hearing.
• If our ears don't hear, we
cannot perceive
conversations.
• Those who are born without
hearing cannot speak.
If we dıdn't have ears?
• Speaking is directly related to hearing.
• If our ears don't hear, we cannot perceive
conversations.
• Those who are born without hearing cannot
speak.
Outer ear
Outer ear
The pinna or Auricle - acts as a funnel that directs the
sound deeper into the ear.
Outer ear
• The ear canal - is a passage way and amplifier for sound waves.
It is a tube that runs from the outer ear to the middle ear. It is
lined with hairs and glands that secrete wax. The wax traps
dusts and bacteria.
Outer ear
• Eardrums - also called the tymphanic membrane, is a thin layer of
tissue that separates the outer ear from the middle ear. The
eardrum vibrates when sound waves hit it. These vibrations move
the bones in the middle ear.
middle ear
• The middle ear contains three
ossicles, which are tiny bones
that transfer the sound from
the eardrum to the inner ear.
• The hammer is attached to the
eardrum; the anvil connects
the hammer to the stirrup; and
the stirrup is connected to the
oval window.
Inner ear
• The cochlea - is a snail - shaped hearing organ. It is made up of
three chambers that spiral around a bony core. The hair cells
inside the cochlea detect sound and send the information through
the cochlear nerve.
Inner ear
• The auditory nerve - or cochlear nerve runs from the
cochlea to the brain stem. It transforms the sound
vibrations into electrical impulses sent to the brain.
Common ear ailments
• Ear infection – an infection of the
middle ear or outer ear. Symptoms
include high fever, abscess, and loss of
hearing. A milky discharge with
unpleasant odor comes out of the ear of
the person with this ailment. He or she
can experience severe pain in the ear.
Common ear ailments
• Ear boil – this is an infection on the outer ear
characterized by infection and swelling. It is
caused by impacted teeth, ear wax, sinusitis,
or prolonged exposure to loud noise.
• Deafness – this is the result of an injury in
the middle and inner ear. When the eardrum
breaks, the person may become partially or
totally deaf. Deafness is the loss of hearing.
Proper care for the ears
1. Clean your outer ear with a clean washcloth.
2. Do not use fingers, hairpins, or toothpicks in removing
earwax.
3. Stay away from exploding firecrackers.
4. When swimming or diving, protect the eardrums by
wearing a cap or using earplugs.
5. When affected by ear diseases, see an otolaryngologist, a
specially trained doctor for ear diseases.
6. Know the first-aid treatment for ear diseases.
Guess the christmas carol game
NOSE
Smell/Olfactory Sense Organ
• The nose is our sense organ for smell.
• We perceive the pleasant and unpleasant
smells in our environment through the
nose.
• We experience the smell of our favorite
foods, roses, and flowers through our
nose.
If we dıdn't have a nose?
• We wouldn't be able to smell
pleasant fragrances, and we
wouldn't be aware of
dangers in our surroundings,
such as unpleasant smells
like smoke.
External part
• Your nose is made up of bone and
cartilage.
• Nostrils – serve as entrance to your nasal-
cavities.
Internal part
• Each nostril has the respiratory
region which is used for breathing
• Olfactory region – which is used
for smelling
• Cilia – small, hair-like structures
lined in the nasal cavities. These
cavities also contain mucous
membranes that secrete a sticky
fluid called mucus
Common nose ailments
• Nosebleed – it is usually caused
by an injury to any part inside the
nose, head injury, high blood
pressure, or weak blood vessels in
the nose.
Propper Care for the nose
1. Cover your nose if you are in a dusty or stinky
place.
2. Keep you nose clean.
3. Avoid blowing your nose hard when you have
colds to prevent nosebleed.
4. Avoid putting any of your fingers or any pointed
object inside your nose.
5. Stay away from smoky areas.
What to do
1.Why is it hard for you to smell
when you have colds?
2.Why can a poultry man
withstand the bad smell of the
chicken manure in the poultry
house?
Tongue
Taste Sense Organ.
• Besinlerin acı, tatlı, ekşi, tuzlu
olup olmadıklarını dilimizle
anlarız.
• Ayrıca dilimiz konuşmamıza da
yardımcı olur.
If we dIdn't have a tongue?
• We perceive if the food is
spoiled through our tongue.
• If our tongue's health is
compromised, we wouldn't be
able to taste the flavors of the
food.
Parts of the tongue and how each works
• Papillae – small projections that covered the surface of the tongue. Within
the papillae are the taste receptors or taste buds.
• People are born with about 10,000 taste buds. A young person like you may
only have at least 5, 000 taste buds – the reason why some food may taste
stronger for you than an adult.
Parts of the tongue and how each works
• Taste buds can distinguish the basic types of tastes: sweet, salty, bitter, and sour.
• The saliva wets and dissolves the food particles. The taste receptors receive the
message and sent it to your brain. Then brain tells you what the taste is.
Parts of the tongue and how
each works
• The sense of taste and sense of smell
are closely associated with each other.
The close association between the two
senses is due to the location of the nose
and the tongue.
Common tongue ailments
• Cracks – these are splits or tears
which can become inflamed and
painful, resulting in ulcers of the
tongue. These can be caused by
biting your tongue. These can be
treated by using oral antiseptic.
Common tongue ailments
• White mouth or oral thrush – this
infection results in white patches on the
tongue that look like cottage cheese.
This white spot could spread to parts
such as the gums, palate, throat and
other parts. It is common among infants
and elderly, especially those who wear
dentures.
Common tongue ailments
• Stomatitis (singaw) – its causes are infection,
biting the tongue, and wearing faulty braces.
Using an oral antiseptic can treat it.
• Sore tongue – is a characterized by inflamed
and irritated taste buds that cause tiny bumps
to form along your tongue. This can be
painful. Tongue soreness may be a symptom
of anemia, diabetes, and other health
condition. This can also be treated by oral
antiseptic.
Proper care of the tongue
• When you brush your teeth, gently brush
your tongue.
• Avoid eating very hot or even very cold
food. it harms your taste buds.
• Eat a balanced diet.
• Use your own toothbrush. Do not borrow
or lend your toothbrush.
SkIn
Touch/Skin Sense Organ.
• The skin is our sense organ for touch.
• Our skin protects our body from
external influences such as impacts and
strikes.
• We perceive the hardness, softness,
coldness, and warmth of the objects
around us through our skin.
If we dIdn't have skın?
• We wouldn't be able to sense
hot and cold temperatures, and
we would be susceptible to
freezing or burning.
• We wouldn't be able to
perform essential functions
such as respiration, and we
wouldn't be able to sweat.
Outer layer
• Epidermis – the outer layer
- The cells in this layer are tough and flat
- The top part of this layer is made up of dead cells. These cells fall of as they
dry up and get flaky. Living cells from the innermost part of the epidermis
replace them.
Inner layer
• Dermis – the inner layer
- It is made up of living cells.
- It has blood vessels, oil glands, and sweat
glands
- Blood vessels: help nourish your skin
- Oil glands: Produce oil to make your skin
shiny and keep it from drying.
- Sweat glands: produce sweat or perspiration to
keep your body cool
Inner layer
• Fatty tissues provide your body with
heat and protect your internal organs.
• The skin has many nerve endings or
receptors located in the dermis. These
nerves ending pick up five skin
sensations – cold, heat, touch, pain,
and pressure. These nerves carry
messages to the brain. Then brain tells
how the object feels.
Work of the skin
• The skin provides a covering for your
body.
• The skin helps the body get rid of
waste materials.
• The skin changes color to prevent sun
damage.
• The skin can feel changes in the
environment
Common skin ailments
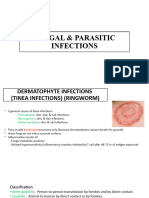
• Scabies (galis)
• Ringworm (buni) and Athlete’s
foot (alipunga)
• Tinea flava (an-an)
• Boil (pigsa)
• Acne
Proper care for the skin
1. Take a bath every day.
2. Washing helps prevent acne by removing the
extra oil.
3. Limiting your exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet
rays is another way of protecting your skin.
4. Eat food rich in vitamins A and B such as fruits
and vegetables.
5. Consult a doctor when you have skin problems.
What’s in the box???
Avtivity time!
Directions: match the cards with the right sense organ.
Stick the sense organs picture cards on the board shown in the
picture.
Directions: use the words given in the box to fill the blanks.
1. Lance can ____________ the movie using with his eyes.
2. Nicole can __________ the food with her tongue.
3. Karen can ___________ with her nose
4. Ronald can _________ the music with his ears.
5. Harrison can _________ the pillow is soft.
Source page
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5835)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- REJURANDocument13 pagesREJURANirwan jun100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: My CoursesDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: My CoursesRcel Balmes100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Healy Resonance ProgramsDocument7 pagesHealy Resonance Programshayley100% (7)
- Chapter 19 Microbial Diseases of The Skin and WoundsDocument8 pagesChapter 19 Microbial Diseases of The Skin and WoundsGRACE MAR CABAHUG100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Facial and Physical Signs of Tissue Salt DeficiencyDocument4 pagesFacial and Physical Signs of Tissue Salt DeficiencyFahad JavedNo ratings yet
- Colorful Illustrative Forms of Energy Science PresentationDocument14 pagesColorful Illustrative Forms of Energy Science PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Colourful Cartoon Science Bodies of Water Quiz Activity PresentationDocument14 pagesColourful Cartoon Science Bodies of Water Quiz Activity PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Teacher Planner for 2024 in Colorful Aesthetic StyleDocument25 pagesTeacher Planner for 2024 in Colorful Aesthetic StyleLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Colorful Illustrative Forms of Energy Science PresentationDocument14 pagesColorful Illustrative Forms of Energy Science PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Colorful Retro Vintage Illustration Animated Medical Technology Education Science PresentationDocument20 pagesColorful Retro Vintage Illustration Animated Medical Technology Education Science PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of AnimalsDocument26 pagesLife Cycle of AnimalsLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Colorful Stickers and Badges Memory Game Fun PresentationDocument17 pagesColorful Stickers and Badges Memory Game Fun PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- Blue Green and Purple Illustration Course Syllabus Education PresentationDocument12 pagesBlue Green and Purple Illustration Course Syllabus Education PresentationLove, It's Me JaveNo ratings yet
- F.-W. Tesch Dr. Agr. (Auth.), P. H. Greenwood D.sc. (Eds.) - The Eel - Biology and Management of Anguillid Eels-Springer Netherlands (1977)Document445 pagesF.-W. Tesch Dr. Agr. (Auth.), P. H. Greenwood D.sc. (Eds.) - The Eel - Biology and Management of Anguillid Eels-Springer Netherlands (1977)deryhermawanNo ratings yet
- Cosmetics Manufacturing Business PlanDocument63 pagesCosmetics Manufacturing Business PlanShihabul Islam ShihabNo ratings yet
- 5 Integumentary SystemDocument67 pages5 Integumentary SystemchelsealivesforeverNo ratings yet
- Hyaluronic Acid by ContiproDocument2 pagesHyaluronic Acid by Contipro61p2bjx5No ratings yet
- Fungal & Parasitic Infestations of The SkinDocument67 pagesFungal & Parasitic Infestations of The SkinGhaith HamdiNo ratings yet
- Clo VateDocument5 pagesClo VateNatalia GomezNo ratings yet
- Review in Peeling ComplicationsDocument8 pagesReview in Peeling ComplicationschipanzeNo ratings yet
- Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocument12 pagesSquamous Cell CarcinomaA. Pathak0% (1)
- Tes Psikotes BUMN - 9 - Bahasa InggrisDocument17 pagesTes Psikotes BUMN - 9 - Bahasa InggrisPrsty 12No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SkinDocument30 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The SkinNancy VargasNo ratings yet
- A Handbook of CosmeticsDocument134 pagesA Handbook of CosmeticsAlifa Syafira Putri76% (25)
- Pigmented Skin LesionsDocument51 pagesPigmented Skin LesionsclikgoNo ratings yet
- Kelebihan Triple StemcellDocument4 pagesKelebihan Triple StemcellMuhammad AffandiNo ratings yet
- Esthetician/paramedical AestheticianDocument2 pagesEsthetician/paramedical Aestheticianapi-121459287No ratings yet
- Iggy - Chapter 26 - Burns - PPDocument34 pagesIggy - Chapter 26 - Burns - PPnicole pilandNo ratings yet
- 2015 - 07094934Document9 pages2015 - 07094934mjimenezgNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Stability Test Cream: No. Nama Produk Tanggal Stabtest 1 Hari 3 Hari 1 MingguDocument3 pagesJadwal Stability Test Cream: No. Nama Produk Tanggal Stabtest 1 Hari 3 Hari 1 MingguAdityaFajhrilFalahNo ratings yet
- Physical InjuriesDocument6 pagesPhysical InjuriesHermay BanarioNo ratings yet
- Immunity (Lecture Notes)Document5 pagesImmunity (Lecture Notes)Anisha NishanthNo ratings yet
- Pricelist SKINTIFIC Jakarta X Beauty II 14 - 17 Dec 2023Document1 pagePricelist SKINTIFIC Jakarta X Beauty II 14 - 17 Dec 2023ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Biology Matters Theory Workbook 1Document196 pagesBiology Matters Theory Workbook 1same faaz100% (1)
- Structure and Function of SkinDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of SkinSarah AndersonNo ratings yet
- English SbaDocument10 pagesEnglish SbakimalaNo ratings yet
- Stock SST 9 Januari 2023Document16 pagesStock SST 9 Januari 2023Rhesa GuttamaNo ratings yet
- CHP 12 - Oral Mucosa-1Document83 pagesCHP 12 - Oral Mucosa-1Areej Fatima100% (2)