Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03assessment of Posture
03assessment of Posture
Uploaded by
Xulkanain ZECopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Scoliosis, Kyphosis, LordosisDocument54 pagesScoliosis, Kyphosis, LordosisMj Briones100% (1)
- Assessment of Posture: Prepared By: Floriza P. de Leon, PTRPDocument17 pagesAssessment of Posture: Prepared By: Floriza P. de Leon, PTRPFloriza de Leon100% (1)
- Genu Valgus & Genu VarusDocument51 pagesGenu Valgus & Genu VarusAlfionita WikaNo ratings yet
- Overview Congenital Musculoskeletal DisorderDocument84 pagesOverview Congenital Musculoskeletal DisorderRyan Trian100% (3)
- Exam Study GuideDocument45 pagesExam Study GuideJanae TaylorNo ratings yet
- Low Back Ache: Capt PramodDocument67 pagesLow Back Ache: Capt PramodPramod MahenderNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities MusculoSkeletal SystemDocument116 pagesCongenital Abnormalities MusculoSkeletal SystemVii syilsaNo ratings yet
- Body PositionsDocument22 pagesBody PositionsDaniella AwurumibeNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis Disease OverviewDocument7 pagesScoliosis Disease OverviewReema Akberali nooraniNo ratings yet
- Poc ScoliosisDocument20 pagesPoc ScoliosisSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- KiposisDocument13 pagesKiposisHidaya UlyaaNo ratings yet
- Spine: Phase III Teaching University of EdinburghDocument36 pagesSpine: Phase III Teaching University of Edinburghharutomoyukei6439No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal AssessmentDocument69 pagesMusculoskeletal AssessmentWorku Kifle100% (2)
- Posture and its biomechanics (1)Document42 pagesPosture and its biomechanics (1)chandraakarshitaNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of ScoliosisDocument54 pagesApproach To A Case of ScoliosisJocuri KosoNo ratings yet
- PostureDocument85 pagesPostureDr.Debanjan Mondal (pt)100% (1)
- Benign Hyper Mobility Joint SyndromeDocument35 pagesBenign Hyper Mobility Joint Syndromewawano1No ratings yet
- Orthopath Final ReviewDocument16 pagesOrthopath Final ReviewharrischoeNo ratings yet
- Congenital Hips DislocationDocument6 pagesCongenital Hips DislocationMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument57 pagesMusculoskeletal DisordersjoycechicagoNo ratings yet
- Postural AssessmentDocument64 pagesPostural AssessmentNikks BoradeNo ratings yet
- Share 'DEFORMITIES - PPTX'Document105 pagesShare 'DEFORMITIES - PPTX'Hunaid 1000No ratings yet
- Scoliosis PPT B IngDocument11 pagesScoliosis PPT B IngSyifa Anindya100% (1)
- Back PainDocument9 pagesBack PaindrrselvarajNo ratings yet
- Anomalies of Skeletal System-1Document44 pagesAnomalies of Skeletal System-1Meena Koushal100% (1)
- Biomechanics of SpineDocument41 pagesBiomechanics of SpineMuhammad MustaqeemNo ratings yet
- Work Related Musculoskeletal DISORDERS (Penyakit Muskuloskeletal Terkait Kerja)Document58 pagesWork Related Musculoskeletal DISORDERS (Penyakit Muskuloskeletal Terkait Kerja)Wong RakatNo ratings yet
- Deformities OF The Lower Limb: DR - Tehreem NasirDocument57 pagesDeformities OF The Lower Limb: DR - Tehreem NasirAhmed SaeedNo ratings yet
- Kyphosis, Lordosis, ScoliosisDocument22 pagesKyphosis, Lordosis, ScoliosisTheeya Quigao100% (1)
- Ergo Experiment 2Document15 pagesErgo Experiment 2John Paul Espineli FeranilNo ratings yet
- 2.problem of Shoulder and ElbowDocument98 pages2.problem of Shoulder and ElbowlmaNo ratings yet
- Department of Anatomy:: Physiological and Pathological Curvatures ofDocument24 pagesDepartment of Anatomy:: Physiological and Pathological Curvatures ofShahbaz RainaNo ratings yet
- Spinal StenosisDocument3 pagesSpinal StenosisyamnaarshadNo ratings yet
- 3.pediatric Hip DisordersDocument92 pages3.pediatric Hip DisordersMahmoud Abu Al AmrainNo ratings yet
- Spine Care FinalDocument220 pagesSpine Care FinalmansiagrawalNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment - NPDocument98 pagesOrthopedic Physical Assessment - NPRG VengatramanNo ratings yet
- Perthes Disease: Mohamed Hamood MohamedDocument4 pagesPerthes Disease: Mohamed Hamood MohamedMohamed HamoodNo ratings yet
- Structural DeformitiesDocument10 pagesStructural DeformitiesChriszanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Pediatric OrthopedicsDocument28 pagesPediatric OrthopedicsEdwin OkonNo ratings yet
- Student Ortho OscevDocument17 pagesStudent Ortho OscevMuradNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain: Iowa State University Environmental Health & SafetyDocument20 pagesLow Back Pain: Iowa State University Environmental Health & SafetyA. AkbariNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dislocation: DR Saseendar SDocument55 pagesShoulder Dislocation: DR Saseendar SPankaj VatsaNo ratings yet
- Duchenne Muscular DystrophyDocument32 pagesDuchenne Muscular DystrophyMr.P.Ramesh, Faculty of Physiotherapy, SRUNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Joint AssessmentDocument92 pagesShoulder Joint Assessmentsonali tushamerNo ratings yet
- Lower Extremity DisordersDocument25 pagesLower Extremity DisordersJameson87No ratings yet
- 1 Pediatric Musculoskeletal Disorders-2Document57 pages1 Pediatric Musculoskeletal Disorders-2naeemullahNo ratings yet
- Organ System Muscular Skeletal SystemsDocument7 pagesOrgan System Muscular Skeletal SystemsJehannaMarEnggingAbdurahmanNo ratings yet
- 1 - OrthopaedicsDocument82 pages1 - Orthopaedicsq77gkyhzs4No ratings yet
- Gait and Balance: Sheila Maria G. BatoonDocument32 pagesGait and Balance: Sheila Maria G. BatoonGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Spinal InjuryDocument24 pagesSpinal InjuryFuad Ahmad ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Congenital MalformationDocument27 pagesCongenital Malformationandre kesumaNo ratings yet
- 1400 PediOrtho SouderDocument73 pages1400 PediOrtho SouderAnonymous 43mqs5pElf100% (1)
- Postural AssessmentDocument63 pagesPostural Assessmentdariand100% (1)
- ScoliosisDocument25 pagesScoliosisshanel18100% (1)
- Herniated Nucleus PulposusDocument17 pagesHerniated Nucleus PulposusCharmaine Joyce Fajardo RosquetaNo ratings yet
- Lectures of Orthopedics by DR Abas Hassan Ahmed: Developmental Dysplasia of The Hip (DDH)Document25 pagesLectures of Orthopedics by DR Abas Hassan Ahmed: Developmental Dysplasia of The Hip (DDH)Wizz Háķìm ĻêşòwNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and Lordosis4352Document17 pagesAbnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and Lordosis4352alyyn2045No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to The Posture, Spine Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to The Posture, Spine Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Spinal Stenosis: A Beginner's Quick Start Guide to Managing the Condition Through Diet and Other Lifestyle Remedies, With Sample RecipesFrom EverandSpinal Stenosis: A Beginner's Quick Start Guide to Managing the Condition Through Diet and Other Lifestyle Remedies, With Sample RecipesNo ratings yet
- Conservative Management of A Young Adult With Hip ArthrosisDocument9 pagesConservative Management of A Young Adult With Hip ArthrosisKanika SinhaNo ratings yet
- Mulligan's Mobilisation With Movement A Review of The TenetsDocument21 pagesMulligan's Mobilisation With Movement A Review of The TenetsKanika SinhaNo ratings yet
- Methods For Assessing Leg Length DiscrepancyDocument13 pagesMethods For Assessing Leg Length DiscrepancyKanika SinhaNo ratings yet
- CervicothoracicSpine AssessmentDocument16 pagesCervicothoracicSpine AssessmentKanika SinhaNo ratings yet
03assessment of Posture
03assessment of Posture
Uploaded by
Xulkanain ZEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
03assessment of Posture
03assessment of Posture
Uploaded by
Xulkanain ZECopyright:
Available Formats
Postural development Common spinal deformities Patient history Observation Examination
Correct posture
Position in which
minimum stress is placed on each joint. (Magee)
Faulty posture
Any position that
increases stress on joints
Birth
Entire spine concave forward (flexed) Primary curves x Thoracic spine x Sacrum
Developmental (usually around 3 mos.)
Secondary curves Cervical spine Lumbar spine
Factors affecting posture
Bony contours Laxity of ligamentous structures Fascial & musculotendinous tightness Muscle tonus Pervic angle Joint position & mobility Neurogenic outflow & inflow
Causes of poor posture
Positional factors x Appearance of increased height (social stigma) x Muscle imbalances/contractures x Pain x Respiratory conditions Typically can be managed
conservatively through ther ex & education
Causes of poor posture
Structural factors x Congential anomalies x Developmental problems x Trauma x Disease Not typically easily
managed s sx
Lordosis
Excessive anterior
curvature of the spine Exaggeration of normal curves in the cervical & lumbar spines
Lordosis causes:
Postural deformity Lax muscles (esp. abs) Heavy abdomen Compensatory mechanisms Hip flexion contracture Spondylolisthesis Congential problems Fashion (high heels)
Lordosis
Swayback deformity x Increased pelvic inclination (40) x Typically includes kyphosis
Kyphosis
Excessive posterior
curvature of the spine
x x x x Round back Humpback/gibbus Flat back Dowagers Hump
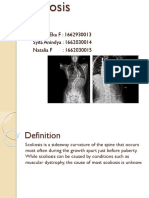
Scoliosis
Nonstructural x Functional x May be related to leg length discrepancy Structural x Lacks normal flexibility x Asymmetric movements
Scoliosis
Ideopathic x Approx. 75-85% of all structural cases are ideopathic x Stretch concave curve x Strengthen convex curve
History of injury? Any previous back or neck pain? Any positions of comfort? Family history? Previous illnesses, surgeries, or severe injuries? Hx of other conditions (connective tissue diseases such as Marfans Syndrome)?
Footwear? Patient age? Growth spurt? In females, related to menarche/menses? In males, related to voice change Deformity progressive or stationary?
Neurologic symptoms? Nature, extent, type, and duration of pain? Exacerbating activities or positions? Difficulty breathing? Dominant hand? Previous treatment? Did it help?
Body type
Ectomorph Mesomorph Endomorph
Anterior view
Head straight on
shoulders Shoulders level Clavicles/AC joints Sternum & ribs Waist angles & arm positions Carrying angles Iliac crests ASIS Patellae Knees Fibular heads
Malleoli level Arches Foot rotation Bowing of bones Diastematomyelia (hairy patches) Pigmented lesions
x Caf au lait spots x neurofibromatosis
You might also like
- Scoliosis, Kyphosis, LordosisDocument54 pagesScoliosis, Kyphosis, LordosisMj Briones100% (1)
- Assessment of Posture: Prepared By: Floriza P. de Leon, PTRPDocument17 pagesAssessment of Posture: Prepared By: Floriza P. de Leon, PTRPFloriza de Leon100% (1)
- Genu Valgus & Genu VarusDocument51 pagesGenu Valgus & Genu VarusAlfionita WikaNo ratings yet
- Overview Congenital Musculoskeletal DisorderDocument84 pagesOverview Congenital Musculoskeletal DisorderRyan Trian100% (3)
- Exam Study GuideDocument45 pagesExam Study GuideJanae TaylorNo ratings yet
- Low Back Ache: Capt PramodDocument67 pagesLow Back Ache: Capt PramodPramod MahenderNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities MusculoSkeletal SystemDocument116 pagesCongenital Abnormalities MusculoSkeletal SystemVii syilsaNo ratings yet
- Body PositionsDocument22 pagesBody PositionsDaniella AwurumibeNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis Disease OverviewDocument7 pagesScoliosis Disease OverviewReema Akberali nooraniNo ratings yet
- Poc ScoliosisDocument20 pagesPoc ScoliosisSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- KiposisDocument13 pagesKiposisHidaya UlyaaNo ratings yet
- Spine: Phase III Teaching University of EdinburghDocument36 pagesSpine: Phase III Teaching University of Edinburghharutomoyukei6439No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal AssessmentDocument69 pagesMusculoskeletal AssessmentWorku Kifle100% (2)
- Posture and its biomechanics (1)Document42 pagesPosture and its biomechanics (1)chandraakarshitaNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of ScoliosisDocument54 pagesApproach To A Case of ScoliosisJocuri KosoNo ratings yet
- PostureDocument85 pagesPostureDr.Debanjan Mondal (pt)100% (1)
- Benign Hyper Mobility Joint SyndromeDocument35 pagesBenign Hyper Mobility Joint Syndromewawano1No ratings yet
- Orthopath Final ReviewDocument16 pagesOrthopath Final ReviewharrischoeNo ratings yet
- Congenital Hips DislocationDocument6 pagesCongenital Hips DislocationMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument57 pagesMusculoskeletal DisordersjoycechicagoNo ratings yet
- Postural AssessmentDocument64 pagesPostural AssessmentNikks BoradeNo ratings yet
- Share 'DEFORMITIES - PPTX'Document105 pagesShare 'DEFORMITIES - PPTX'Hunaid 1000No ratings yet
- Scoliosis PPT B IngDocument11 pagesScoliosis PPT B IngSyifa Anindya100% (1)
- Back PainDocument9 pagesBack PaindrrselvarajNo ratings yet
- Anomalies of Skeletal System-1Document44 pagesAnomalies of Skeletal System-1Meena Koushal100% (1)
- Biomechanics of SpineDocument41 pagesBiomechanics of SpineMuhammad MustaqeemNo ratings yet
- Work Related Musculoskeletal DISORDERS (Penyakit Muskuloskeletal Terkait Kerja)Document58 pagesWork Related Musculoskeletal DISORDERS (Penyakit Muskuloskeletal Terkait Kerja)Wong RakatNo ratings yet
- Deformities OF The Lower Limb: DR - Tehreem NasirDocument57 pagesDeformities OF The Lower Limb: DR - Tehreem NasirAhmed SaeedNo ratings yet
- Kyphosis, Lordosis, ScoliosisDocument22 pagesKyphosis, Lordosis, ScoliosisTheeya Quigao100% (1)
- Ergo Experiment 2Document15 pagesErgo Experiment 2John Paul Espineli FeranilNo ratings yet
- 2.problem of Shoulder and ElbowDocument98 pages2.problem of Shoulder and ElbowlmaNo ratings yet
- Department of Anatomy:: Physiological and Pathological Curvatures ofDocument24 pagesDepartment of Anatomy:: Physiological and Pathological Curvatures ofShahbaz RainaNo ratings yet
- Spinal StenosisDocument3 pagesSpinal StenosisyamnaarshadNo ratings yet
- 3.pediatric Hip DisordersDocument92 pages3.pediatric Hip DisordersMahmoud Abu Al AmrainNo ratings yet
- Spine Care FinalDocument220 pagesSpine Care FinalmansiagrawalNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment - NPDocument98 pagesOrthopedic Physical Assessment - NPRG VengatramanNo ratings yet
- Perthes Disease: Mohamed Hamood MohamedDocument4 pagesPerthes Disease: Mohamed Hamood MohamedMohamed HamoodNo ratings yet
- Structural DeformitiesDocument10 pagesStructural DeformitiesChriszanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Pediatric OrthopedicsDocument28 pagesPediatric OrthopedicsEdwin OkonNo ratings yet
- Student Ortho OscevDocument17 pagesStudent Ortho OscevMuradNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain: Iowa State University Environmental Health & SafetyDocument20 pagesLow Back Pain: Iowa State University Environmental Health & SafetyA. AkbariNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dislocation: DR Saseendar SDocument55 pagesShoulder Dislocation: DR Saseendar SPankaj VatsaNo ratings yet
- Duchenne Muscular DystrophyDocument32 pagesDuchenne Muscular DystrophyMr.P.Ramesh, Faculty of Physiotherapy, SRUNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Joint AssessmentDocument92 pagesShoulder Joint Assessmentsonali tushamerNo ratings yet
- Lower Extremity DisordersDocument25 pagesLower Extremity DisordersJameson87No ratings yet
- 1 Pediatric Musculoskeletal Disorders-2Document57 pages1 Pediatric Musculoskeletal Disorders-2naeemullahNo ratings yet
- Organ System Muscular Skeletal SystemsDocument7 pagesOrgan System Muscular Skeletal SystemsJehannaMarEnggingAbdurahmanNo ratings yet
- 1 - OrthopaedicsDocument82 pages1 - Orthopaedicsq77gkyhzs4No ratings yet
- Gait and Balance: Sheila Maria G. BatoonDocument32 pagesGait and Balance: Sheila Maria G. BatoonGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Spinal InjuryDocument24 pagesSpinal InjuryFuad Ahmad ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Congenital MalformationDocument27 pagesCongenital Malformationandre kesumaNo ratings yet
- 1400 PediOrtho SouderDocument73 pages1400 PediOrtho SouderAnonymous 43mqs5pElf100% (1)
- Postural AssessmentDocument63 pagesPostural Assessmentdariand100% (1)
- ScoliosisDocument25 pagesScoliosisshanel18100% (1)
- Herniated Nucleus PulposusDocument17 pagesHerniated Nucleus PulposusCharmaine Joyce Fajardo RosquetaNo ratings yet
- Lectures of Orthopedics by DR Abas Hassan Ahmed: Developmental Dysplasia of The Hip (DDH)Document25 pagesLectures of Orthopedics by DR Abas Hassan Ahmed: Developmental Dysplasia of The Hip (DDH)Wizz Háķìm ĻêşòwNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and Lordosis4352Document17 pagesAbnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and Lordosis4352alyyn2045No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to The Posture, Spine Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to The Posture, Spine Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Spinal Stenosis: A Beginner's Quick Start Guide to Managing the Condition Through Diet and Other Lifestyle Remedies, With Sample RecipesFrom EverandSpinal Stenosis: A Beginner's Quick Start Guide to Managing the Condition Through Diet and Other Lifestyle Remedies, With Sample RecipesNo ratings yet
- Conservative Management of A Young Adult With Hip ArthrosisDocument9 pagesConservative Management of A Young Adult With Hip ArthrosisKanika SinhaNo ratings yet
- Mulligan's Mobilisation With Movement A Review of The TenetsDocument21 pagesMulligan's Mobilisation With Movement A Review of The TenetsKanika SinhaNo ratings yet
- Methods For Assessing Leg Length DiscrepancyDocument13 pagesMethods For Assessing Leg Length DiscrepancyKanika SinhaNo ratings yet
- CervicothoracicSpine AssessmentDocument16 pagesCervicothoracicSpine AssessmentKanika SinhaNo ratings yet