Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Road Map To Total Quality
A Road Map To Total Quality
Uploaded by
M. JokomoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Road Map To Total Quality
A Road Map To Total Quality
Uploaded by
M. JokomoCopyright:
Available Formats
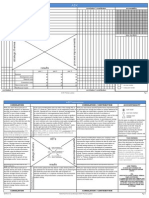
A ROAD MAP TO TOTAL QUALITY
What is Six Sigma
Six Sigma, a process-focused strategy and methodology for business improvement, can be used to improve care processes, eliminate waste, reduce costs, and enhance patient satisfaction. Sigma represents one standard deviation from the average or mean, ranging from three to six; with six being the highest. At Six Sigma, there are only 3.4 parts per million (PPM) defective. (yield = 99.9997%
@ 6sigma level)
Involves the use of statistical tools within a structured methodology.
Six Sigma relies heavily on teams of people working together, not on individual effort. It is customer oriented. A customer being any person, internal or external, who is affected by a process or product change because it is the customer who defines quality. It is supported by an infrastructure of specialists called Master Black Belts, Black Belts, Green Belts and Yellow Belts.
Success depends on:
Highly visible top-down management commitment to the initiatives. A measurement system (metrics) to track the progress. Internal and external benchmarking of the organizations products, services, and processes. Stretch goals to focus on changing the process by which the work gets done Educating all levels of the organization.
Define Measure Analyze
Continuous Improvement Reengineering
Improve
Control
Design
Validate
Control Improve Define Analyze Measure
Define: Define who your customers are, and what their requirements are for your products and services Their expectations. Define your team goals, project boundaries, what you will focus on and what you wont. Define the process you are striving to improve by mapping the process.
Control Improve Define Analyze Measure
Measure: Eliminate guesswork and assumptions about what customers need and expect and how well processes are working. Collect data from many sources to determine speed in responding to customer requests, defect types and how frequently they occur, client feedback on how processes fit their needs, how clients rate us over time, etc. The data collection may suggest Charter revision.
Control Improve Define Analyze Measure
Analyze: Grounded in the context of the customer and competitive environment, analyze is used to organize data and look for process problems and opportunities. This step helps to identify gaps between current and goal performance, prioritize opportunities to improve, identify sources of variation and root causes of problems in the process.
Control Improve Define Analyze Measure Improve: Generate both obvious and creative solutions to fix and prevent problems. Finding creative solutions by correcting root causes requires innovation, technology and discipline.
Control Improve Define Analyze Measure
Control: Insure that the process improvements, once implemented, will hold the gains rather than revert to the same problems again. Various control tools such as statistical process control can be used. Other tools such as procedure documentation helps institutionalize the improvement.
Validate Design Define Analyze Measure
Design: Develop detailed design for new process. Determine and evaluate enabling elements. Create control and testing plan for new design. Use tools such as simulation, benchmarking, DOE, Quality Function Deployment (QFD), FMECA analysis, and cost/benefit analysis.
Validate Design Define Analyze Measure
Validate: Test detailed design with a pilot implementation. If successful, develop and execute a full-scale implementation. Tools in this step include: planning tools, flowcharts/other process management techniques, and work documentation.
Master Black Belts
takes on a leadership role as keeper of the Six Sigma process proven change agent, leader, facilitator, and technical expert in Six Sigma management. advisor to senior executives or business unit managers.
Black Belts
full-time change agent and improvement leader qualified to solve process problems that arise in manufacturing environments
Green Belts
individual who works as a team member for complex projects or as a project leader for simpler projects. Communicate with master black belt, black belt, and process owner throughout all stages of the project. Analyze data through all phases of the project. Train team members in the basic tools and methods through all phases of the project.
Yellow Belts
represent everyone else on the team. staff members, administrators, operations personnel and anyone else who might play a role.
Quality Function Deployment (QFD):
used to understand customer requirements. The QFD identifies customer requirements and rates them on a numerical scale.
The QFD is
The fish-bone diagram helps identify which input variables should be studied further. Cause-and-Effect (C&E) Matrix: The C&E matrix is an extension of the fishbone diagram. Six Sigma teams identify, explore and graphically display all the possible causes related to a problem and search for the root cause.
Fishbone Diagrams: In Six Sigma, all outcomes are the result of specific inputs.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA):
FMEA identifies ways a new product, process or service might fail. This generates scores that enable the team to prioritize things that could go wrong and develop preventative measures.
T-Test: helps Six Sigma teams validate test results using
sample sizes that range from two to 30 data points. Control Charts: Statistical process control, or SPC, relies on statistical techniques to monitor and control the variation in processes. Design of Experiments: When a process is optimized, all inputs are set to deliver the best and most stable output.
You might also like
- Bilal Hyder I170743 20-SEPDocument10 pagesBilal Hyder I170743 20-SEPUbaid0% (1)
- CAPSIM Full Strategy ExcelDocument19 pagesCAPSIM Full Strategy ExcelSiddharth Modi100% (1)
- Li Fung Trading - Case Study SolutionsDocument3 pagesLi Fung Trading - Case Study SolutionsKarthigeyan K Karunakaran100% (2)
- Wadhwani Activity 2Document4 pagesWadhwani Activity 2Emman IsipNo ratings yet
- Basic 7 Tools of Quality: Presentation By: Carla Scardino The Pennsylvania State UniversityDocument37 pagesBasic 7 Tools of Quality: Presentation By: Carla Scardino The Pennsylvania State Universityjitenderbhati07No ratings yet
- Border Control and SecurityDocument4 pagesBorder Control and SecurityUnlimited Gravyyy100% (1)
- Final ExamDocument13 pagesFinal Examjrence100% (1)
- Week 1 Powerpoint SlidesDocument52 pagesWeek 1 Powerpoint SlidesMichel BanvoNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Control PlansDocument2 pagesDynamic Control Plansajitbasrur445No ratings yet
- ANDONDocument8 pagesANDONBftech MumbaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture of Chapter Four Group BehaviourDocument35 pagesLecture of Chapter Four Group BehaviourAwet0% (1)
- Turning PDCA Into A Routine For LearningDocument5 pagesTurning PDCA Into A Routine For LearningjozsefczNo ratings yet
- Bonacorsi Consulting Master DMAIC RoadmapDocument7 pagesBonacorsi Consulting Master DMAIC Roadmapaminos85No ratings yet
- COPQ WorksheetDocument4 pagesCOPQ WorksheetDhinakaranNo ratings yet
- Just in Time System (2) 10000Document24 pagesJust in Time System (2) 10000John GriffiesNo ratings yet
- Training Material For: Easurement Ystem NalysisDocument61 pagesTraining Material For: Easurement Ystem NalysisDotecho Jzo EyNo ratings yet
- Facilitation PowerpointDocument15 pagesFacilitation Powerpointapi-317124737No ratings yet
- Module 3 Matl - Measure PhaseDocument75 pagesModule 3 Matl - Measure PhaseHannah Nicdao TumangNo ratings yet
- The Team Roles: Plant Resource Investigator CoordinatorDocument19 pagesThe Team Roles: Plant Resource Investigator CoordinatorParived BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Thomas A. Little, PH.DDocument110 pagesThomas A. Little, PH.DMiguel PadillaNo ratings yet
- Error-Proofing PDFDocument28 pagesError-Proofing PDFDanang WidoyokoNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Lean Management SystemsDocument26 pagesFacilitating Lean Management SystemsAnand DharunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Workforce FocusDocument47 pagesChapter 3 Workforce FocusRonah Abigail BejocNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Quality Tools and TemplatesDocument2 pagesSix Sigma Quality Tools and Templatesergo22No ratings yet
- BPR MethodologiesDocument29 pagesBPR MethodologiesOsamah S. Alshaya100% (1)
- Session 1 - The Agile Vs Non Agile DivideDocument48 pagesSession 1 - The Agile Vs Non Agile DivideSATHAMRAJU DURGAPRASAD 22810401002No ratings yet
- Meeting Objective Set The Stage Decide What To DoDocument1 pageMeeting Objective Set The Stage Decide What To DoKem RajNo ratings yet
- Story Line For Webinar - LeadershipDocument7 pagesStory Line For Webinar - LeadershipmagrinraphaelNo ratings yet
- Sustaining Success " Yash"Document30 pagesSustaining Success " Yash"Kavya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Basics: Latest ArticlesDocument2 pagesSix Sigma Basics: Latest ArticlesSabbirHasanNo ratings yet
- Team Building StagesDocument5 pagesTeam Building StagesAhmed HadadNo ratings yet
- 10 Days Nos TrainingDocument511 pages10 Days Nos Trainingdayat hidayatNo ratings yet
- Correlation: Is There Any Correlation Between The ACT Score and Students Gpa?Document1 pageCorrelation: Is There Any Correlation Between The ACT Score and Students Gpa?Carlos Oliver MontejanoNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Template Worksheets NCSUDocument35 pagesSix Sigma Template Worksheets NCSUKioshiEvelynSakura50% (2)
- Presented by - Palika CharithaDocument33 pagesPresented by - Palika CharithaPalika CharithaNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Methodology: SeminarDocument23 pagesSix Sigma Methodology: Seminarvishal kumar sinha100% (1)
- Effective Time, Task & Work Planning.: Presented By: Nagham OdehDocument75 pagesEffective Time, Task & Work Planning.: Presented By: Nagham OdehNaggiiNo ratings yet
- Business Process ReengineeringDocument80 pagesBusiness Process Reengineeringlogan wolverineNo ratings yet
- A Bumpy Ride?": Obstacles Can BeDocument1 pageA Bumpy Ride?": Obstacles Can BeSupreet SinghNo ratings yet
- LEANDocument107 pagesLEANMilind KhandaveNo ratings yet
- Looking Into DataDocument117 pagesLooking Into DataKshitij_Batra_9305No ratings yet
- 001 3 Lean+Six+Sigma+Implementation+Manual V9 PDFDocument81 pages001 3 Lean+Six+Sigma+Implementation+Manual V9 PDFJuan Pablo Azcuña C.No ratings yet
- A3 Format From LEIDocument2 pagesA3 Format From LEIterhexNo ratings yet
- 5 MsaDocument81 pages5 MsaVIPIN YADAVNo ratings yet
- Kaizen Blitz Micro 2Document14 pagesKaizen Blitz Micro 2Joven CastilloNo ratings yet
- Assignment NO.2: Abdul Moiz Asim Aziz Aqib Arif Binyameen Aslam Huba RanaDocument12 pagesAssignment NO.2: Abdul Moiz Asim Aziz Aqib Arif Binyameen Aslam Huba RanaRana_hubaNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Proposal (1.1)Document40 pagesSix Sigma Proposal (1.1)Joni Pablo100% (1)
- Statistics Probability Midterm Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesStatistics Probability Midterm Cheat SheetJeff Farmer0% (1)
- 5S WorkshopDocument2 pages5S Workshopnaveenaradhya100% (1)
- Team Work - PPTDocument17 pagesTeam Work - PPTSangita SarkarNo ratings yet
- Green Belt Class NotesDocument11 pagesGreen Belt Class NotesPankaj LodhiNo ratings yet
- Iqa Training Iso 9001-2015Document103 pagesIqa Training Iso 9001-2015ianalleahNo ratings yet
- TQM Versus Six SigmaDocument16 pagesTQM Versus Six Sigmaapi-3751356No ratings yet
- Ownership AccountabilityDocument21 pagesOwnership AccountabilityhrvishalspatilNo ratings yet
- KRA Setting: Deepak BhararaDocument26 pagesKRA Setting: Deepak BhararaDeekhsha KherNo ratings yet
- The Power of Decisions: M. Akbar BhattiDocument21 pagesThe Power of Decisions: M. Akbar BhattiAkbar BhattiNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: By: Mark Joseph G. Villanueva & Mark Anthony Y. RosalesDocument30 pagesDecision Making: By: Mark Joseph G. Villanueva & Mark Anthony Y. RosalesJanice Kimayong100% (1)
- Six Sigma: Process Improvement MethodologyDocument40 pagesSix Sigma: Process Improvement Methodologybabudukku100% (6)
- Capturing 7 Types of WastesDocument2 pagesCapturing 7 Types of WastesNiraj TiwariNo ratings yet
- 6.08 Career Planning and Career DevelopmentDocument33 pages6.08 Career Planning and Career DevelopmentShimanta EasinNo ratings yet
- VARSIGMA - GB - Preparatory Module V1.1 PDFDocument104 pagesVARSIGMA - GB - Preparatory Module V1.1 PDFCharanjeetSinghKhanuja100% (1)
- Reducing Length of Stay Using LeanDocument42 pagesReducing Length of Stay Using LeanAsiimwe D Pius100% (1)
- Business Process Reengineering Using Six Sigma: Abella, Vanessa Balanag, Julie Anne Mojal-Amarillo, Mary Leonite MGT 201Document79 pagesBusiness Process Reengineering Using Six Sigma: Abella, Vanessa Balanag, Julie Anne Mojal-Amarillo, Mary Leonite MGT 201Weng Torres AllonNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management CH 4Document37 pagesStrategic Management CH 4karim kobeissiNo ratings yet
- Taxation Case Digest 3Document9 pagesTaxation Case Digest 3seentherellaaaNo ratings yet
- TEST1 ACC 106 Nov 2017 Solution Part ADocument4 pagesTEST1 ACC 106 Nov 2017 Solution Part AZulaikha JasniNo ratings yet
- CIMA Business Mathematics Fundamentals Past Papers PDFDocument107 pagesCIMA Business Mathematics Fundamentals Past Papers PDFSiphoKhosaNo ratings yet
- VP Sales Business Development in USA Resume Peter BerrioDocument3 pagesVP Sales Business Development in USA Resume Peter BerrioPeterBerrioNo ratings yet
- 2011 Walmart Diversity and Inclusion ADocument20 pages2011 Walmart Diversity and Inclusion ASarah MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Green SEN Environmental Mission StatementDocument7 pagesGreen SEN Environmental Mission StatementAndrés Guillermo García RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Managing The Marketing FunctionDocument9 pagesChapter 11 Managing The Marketing FunctionKristine Santos0% (2)
- Reducido en Inglés. Power Point. SargadelosDocument14 pagesReducido en Inglés. Power Point. SargadelosseniorudcNo ratings yet
- (More) : Vikas VaidDocument3 pages(More) : Vikas VaidMustafa RokeryaNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods William G Zikmund Bizstu - 59de98f81723ddead46a27e1Document33 pagesBusiness Research Methods William G Zikmund Bizstu - 59de98f81723ddead46a27e1Tauhid Ahmed BappyNo ratings yet
- 2 Production: Cbi Market Survey: The Stationery, Office and School Supplies Market in The EuDocument4 pages2 Production: Cbi Market Survey: The Stationery, Office and School Supplies Market in The Euthomas_joseph_18No ratings yet
- Assignment 1: 1. MissionDocument10 pagesAssignment 1: 1. MissionbinhfschoolNo ratings yet
- Company Profile - Elethu Risk ExpandedDocument3 pagesCompany Profile - Elethu Risk Expandedapi-241890029No ratings yet
- Paguio Vs PLDTDocument2 pagesPaguio Vs PLDTAlexandra Nicole Manigos BaringNo ratings yet
- Educational Requirements For CPA Licensure Self-Assessment WorksheetDocument6 pagesEducational Requirements For CPA Licensure Self-Assessment WorksheetMattNo ratings yet
- Smartplant 3D Materials Handling: Taylor D. Cole Vice President, Intergraph Global Metals & Mining IndustryDocument16 pagesSmartplant 3D Materials Handling: Taylor D. Cole Vice President, Intergraph Global Metals & Mining IndustryFlor De Maria SuclupeNo ratings yet
- MTYy MDE3 Y2 Ztcy 1 K YzgzDocument14 pagesMTYy MDE3 Y2 Ztcy 1 K YzgzAway IsNo ratings yet
- June 2018Document244 pagesJune 2018Muhammad HaroonNo ratings yet
- Jetgala Magazine Issue 5Document156 pagesJetgala Magazine Issue 5Jetgala MagazineNo ratings yet
- Recurly Choosing Right Subscription Billing PlatformDocument15 pagesRecurly Choosing Right Subscription Billing PlatformV KeshavdevNo ratings yet
- Invoice: PT - Sitc IndonesiaDocument1 pageInvoice: PT - Sitc IndonesiaMuhammad SyukurNo ratings yet
- Oracle E Business Suite R12 BOM and WIPDocument27 pagesOracle E Business Suite R12 BOM and WIPSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Rural MRKTGDocument52 pagesRural MRKTGSamy7790100% (5)
- Patentes Prof MartinezDocument13 pagesPatentes Prof MartinezMariano TristanNo ratings yet