Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Sensors: Level I
Introduction To Sensors: Level I
Uploaded by
Julie SoosaiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Sensors: Level I
Introduction To Sensors: Level I
Uploaded by
Julie SoosaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Training Series: Level I
Introduction to Sensors
Level I
Training Series: Level I
Course Topics
Sensors Definition Sensor Building Blocks
Electrical Interface
Tell me about it:
Sensing Technology
I see it:
Housings
Looks are everything:
Level I
Sensor Basics
Level II
Products and Applications
Level III
Advance Problem Solving
Training Series: Level I
Sensor Definitions
What are we talking about ?
Sensor Definitions
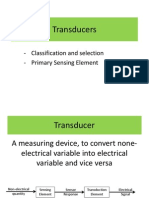
What is a Sensor?
Used in Industrial Automation:
Electrical device capable of identifying change within an automated process.
Sometimes
Sensor = Switch
Sensor Definitions
Sensor Uses
Sensors in our world
Automatic opening doors Grocery check-out conveyer shut-off Safety sensors on garage doors
Sensors in Manufacturing
Part position verification Counting products Liquid level control Quality control inspection Personal safety systems
Sensor Definitions
Sensor Building Blocks
The three major components:
The sensing side
Front-end
The electrical side
Back-end
Housing
Sensor Definitions
Building Block Concept
most any
Sensing technology
most any
Housing
most any
Electrical interface
Sensor Definitions
The Building Blocks
Front-end - Sensing
Five technology choices:
Inductive Optical Capacitive Magnetic Mechanical
Selection base on: Application
Sensor Definitions
The Building Blocks
Back-end Electrical
Options:
Electrical voltage
AC/DC DC
Output type
Discrete (on-off, like a switch) Analog
Selection base on: Control System
Sensor Definitions
The Building Blocks
The Sensors Housings
Material Options:
Metal (nickel-plated brass) Stainless steel Aluminum Plastic
Shape (mounting style):
Tubular Block
Selection base on: Environment
Sensor Definitions
The Building Blocks
and the real world
Housing
Environment
Training Series: Level I
Electrical Interface
The Back-end
Electrical Interface
Electrical Interface
Divided into 2 areas:
Operating voltage
Power
Output signal type
Signal
Electrical Interface
Output Signal Types
Discrete
ON or OFF YES or NO
Analog
Speed control Position information
MIN
MAX
Signal
Electrical Interface
Operating Voltage
Direct Current (DC) Alternating Current (AC)
Current flows in only ONE direction Safe, easy-to-handle power source Current changes direction 60 times a second Readily available
Power
Electrical Interface
Basic Electrical Principals
What is electricity?
Flow (current) or potential flow (voltage) of electrons
Interesting fact:
Electron flow is similar to water flow We will use this analogy during our class
Electrical Interface
Basic Series Circuit
Using Water Analogy:
Potential Flowing
Water Valve Hydro motor Water Tank
Electrical Interface
Basic Series Circuit
Electronics:
Potential Flowing
Switch Battery
+ Electric Motor
Basic ON or OFF operation
Electrical Interface
A discrete Sensor is a Switch
Sensing Side
Electronics
Electronics
Front-end
Power Wires
Switch
Electrical Interface
Basic Sensor Circuit
Sensors with relay output
Electronics
Unlike a switch, sensors require power to operate
+ -
Electrical Interface
Types of discrete electrical outputs
Sensors of today use Solid-State outputs, not mechanical relays
Today Yesterday
PNP, 3-wire NPN, 3-wire AC/DC, 2-wire
Relay
Electrical Interface
The NPN & PNP output
Functions similar to a switch,
But current only flows in one direction
PNP Transistor Mechanical Switch
Electrical Interface
The Different Transistors
What direction do you want current to flow?
NPN
Also called Sinking
PNP
Also called Sourcing
Electrical Interface
PNP, 3-wire
Standard diagram form
As shown in our catalog
The Sensor
1 4 3
Connector Pins The Load
+ Load PNP Output -
Electrical Interface
PNP, 3-wire
Watching the current flow
Sensors Power Output Signal
1 4 3 Load
+ PNP Output -
Electrical Interface
NPN, 3-wire
Watching the current flow
Sensors Power Output Signal
1 4 3 Load
+ NPN Output -
Electrical Interface
The 2-wire AC/DC output
Functions similar to a switch,
But with a small leak
Triac Sensors Power
Supply from leakage current
Output Signal
1 3
Load
~ ~
Electrical Interface
Quick Reference:
wiring PNP & NPN
NPN PNP
Sensor is PNP
+ Load -
Positive
Negative
Electrical Interface
If given a choice, which discrete sensor type should I choose?
1st CHOICE
1 4 3 Load +
PNP or NPN, 3-wire - Fewer interface problems - Largest selection - Lowest unit costs
AC/DC, 2-wire - Many interface issues - Smaller selection - Susceptible to noise
2nd CHOICE
1 3 Load ~ ~
Electrical Interface
Normally Open (NO) vs. Normally Closed (NC)
Is it on (closed)?
Identifies the non-active state (target not present) of the sensor Is it off (open)?
Normally Open
Electronics
+ -
Electrical Interface
Normally Open (NO) vs. Normally Closed (NC)
Is it on (closed)?
Identifies the non-active state (target not present) of the sensor Is it off (open)?
Normally Closed
Electronics
+ -
Electrical Interface
Analog Outputs
Unlike a discrete output with two defined states, analog signals have an infinite number of states.
Discrete
Voltage On
Off
Time
Analog
Voltage
Max
Min
Time
Electrical Interface
Analog Uses
To provide absolute measurement or position information
Measurement
Position
Electrical Interface
Analog Applications!
What can you do with measurement information? Measure thickness Spool diameter Rotational position Position feedback Liquid level Measure tool wear Sort parts Null out machine wear Determine part Null out thermal orientation expansion Measure vibration Verify die position Measure straightness Verify bend radius Hydraulic or pneumatic Part profiling cylinder position Stack height
Expanding possibilities
Electrical Interface
Analog Data
We know analog information provides:
Measurement information Position information
What devices use analog information?
Panel meters
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 10
Control systems
Measurement
Electrical Interface
Analog Information
The many forms for representing measurement or position information
10 10 5
Voltage
0 20 -10 20 -5
Current
0 4
Digital Pulse
Electrical Interface
Analog Voltage
Information contained in varying voltage
Maximum Voltage Half Voltage
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 10
Measurement
Water Analogy
Volt Meter
Electrical Interface
Analog Current
Information contained in varying Current
Maximum Current Half Current
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 10
Measurement
Water Analogy
Current Meter
Electrical Interface
Digital Pulse
Information contained in digital pulse timing
Measurement range
Maximum measurement Minimum measurement Half way
Pulse Width
1 0.00 50.00 00.00
Meter
Measurement range
Start/Stop
Electrical Interface
Electrical Interface REVIEW
Operating voltage: Sensor Power
DC: Safest AC: Most available
Power
Output signal types
Signal Discrete
PNP, 3-wire NPN, 3-wire AC/DC 2-wire
Analog
Voltage Current Digital pulse
Training Series: Level I
Sensing Technologies
Sensing Technologies
Sensing Technologies
Non- Contact
No physical contact with target Preferred method for sensing end products
Contact
Contact with target Simplest method available
Sensing Technologies
Contact Sensing
Mechanical switch
Contact with plunger opens electrical contacts
Sensing Technologies
Non-Contact
Popular sensing technologies
Inductive Sensors
Metal targets
Optical Sensors
Target capable of reflecting or blocking light
Capacitive Sensors
Liquids/solids
Magnetic Field Sensors
Magnets
Sensing Technologies
Inductive
When voltage is applied, an electromagnetic field is generated and extends out the face of the sensor. When metal enters the sensing zone, an eddy current is induced in the metal.
The change in eddy current is detected and the sensors output is energized.
Sensing Technologies
Inductive
Two basic Sensing types
Flush mount
Shorter range Sensor can be buried in metal
Non-flush mount
Longer range Sensor can NOT be buried in metal
Sensing Technologies
Optical
Regardless of the operating mode, all optical sensors share the same operating principle:
Operation
Emits a light beam then detects or measures changes in received light. Light emitter
Visible red Laser Infrared
Light receiver
Sensing Technologies
Optical
Optical sensors offer three main sensing modes
Thru-beam Retroreflective Diffuse
Note: There are other sensing modes available, but they are covered in other courses.
Sensing Technologies
Optical: Thru-Beam
Separate emitter and receiver Beam-break operation
Target blocks beam
Emitter
Receiver
Great for long range and dirty environments
Sensing Technologies
Optical: Retroreflective
Emitter and receiver in one unit Requires a reflector Beam-break operation
Target block light beam
Reflector Emitter
Provides good range in well defined area
Sensing Technologies
Optical: Diffuse
Emitter and receiver in one unit Convenient stand-alone design Beam-make operation
Light reflects off target
Target
Simple point and shoot operation
Sensing Technologies
Capacitive
Detects target based on density Electrostatic field established Target detected when field properties change
Target
Simple point and shoot operation
Sensing Technologies
Magnetic
Detects magnetic field Magnetic field can travel through aluminum Used extensively with pneumatic cylinders
Magnet
Sees through aluminum
S N
Sensing Technologies
Sensing Technologies
Head-to-Head
Mechanical: Popular, simple
Inductive: Rugged, cost-effective Optical, Thru-beam: Long range Optical, Retro: Mid range Optical, Diffuse: Short range Capacitive: Liquid & bulk targets Magnetic: Pneumatic cylinders
Training Series: Level I
Housings
Physical looks
Housings
Housing Function
Protection from environment Mounting provisions Electrical connection
Housings
Protection from environment
Multiple degrees of protection liquids
IP65: Protects against water mist IP67: Protects against temporary immersion IP68: Protects against continuous immersion
Multiple level of physical abuse
Metal housing Plastic housing
Housings
Mounting Provisions
Depends on shape of housing
Tubular
Popular for short range sensors Range adjustments made by moving sensor in and out
Block
Popular for optical sensors Easy to align horizontally and vertically
Housings
Easy mounting and range adjustment
Inductive Sensor Capacitive
Tubular Housings
Optical Sensor
Magnetic
Housings
Block Housings
Provides Inductive Sensor thru-holes for mounting bolts Allows for easy beam alignment
Optical Sensor
BOS-SR2
Housings
Combination Housings
Combination Inductive Sensor of tubular and block housings
Optical Sensor
Housings
Application Specific Shapes
Magnetic
Inductive Sensor
Hydraulic Cylinder
Ring Sensor
Valve Position
Clamp Position
Optical Sensor
Slot Sensors
Pneumatic Cylinders
Windows
Fiber-optics
Housings
Electrical Connection
Cable Out version
Economical: no additional cable to purchase Difficult to replace sensor
Connector version
Cost: must purchase mating cable Much easier to replace sensor
Housings
Cable Connection Options
Cable Lengths
Standard lengths: 2m, 3m & 5m
Jacket Material
PVC: Standard, low cost jacketing PuFlex: For flexing applications
Housings
Connector Options
Industry standard connector sizes:
Micro (M12)
Most popular, mid-size Available in 3, 4, 5 and 8 pins
Nano (M8)
Smallest size Available in 3 and 4 pins
Mini
Largest size Available in 3 and 4 pins
Housings
Sensor Housings REVIEW
Protection from environment
IP65, IP67, IP68
Mounting provisions
Tubular, Block, Combination, Application specific shapes
Electrical connection
Cable out and connectors
Sensors Definitions
Sensor Fundamentals
Questions & Answers
Housing Environment
Training Series: Level I
Sensor Basics
You might also like
- ASHRAE Laboratory Design Guide Second EdDocument330 pagesASHRAE Laboratory Design Guide Second EdMarco Antonio Camacho Tezanos Pinto100% (2)
- A2 UNIT 5 Everyday English Teacher's NotesDocument1 pageA2 UNIT 5 Everyday English Teacher's NotesCarolinaNo ratings yet
- PLC Input and Output DevicesDocument10 pagesPLC Input and Output Devicesletz277100% (4)
- 07-Intro To SensorsDocument27 pages07-Intro To SensorsRemo Rubian EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Senosrs KBSDocument37 pagesSenosrs KBSMurugadas HarnanNo ratings yet
- Sensors and ActuatorsDocument109 pagesSensors and ActuatorsDr-Amit Kumar Singh100% (2)
- IE 3371:automatic Control Systems: Chapter 2:sensors and TransducersDocument54 pagesIE 3371:automatic Control Systems: Chapter 2:sensors and Transducersفيصل aNo ratings yet
- Describe How To Use Electronic Instruments For ComponentDocument72 pagesDescribe How To Use Electronic Instruments For ComponentKobby BrineNo ratings yet
- WS 1020Document44 pagesWS 1020Sunil Sree NathNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Course Lab WorkbookDocument103 pagesBasic Electronics Course Lab WorkbookApril ShowersNo ratings yet
- 3 - Sensor and ActuatorsDocument31 pages3 - Sensor and Actuatorsmehulprajapati1661No ratings yet
- Merged DocDocument5 pagesMerged Docabd elwahab tawfikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sensors and Actuators: S. Senthil RajaDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Sensors and Actuators: S. Senthil RajassrgmanNo ratings yet
- Sensors: A.K.A. Interfacing To The Real WorldDocument21 pagesSensors: A.K.A. Interfacing To The Real WorldSAMHITHA DNo ratings yet
- Different Instruments 2018Document99 pagesDifferent Instruments 2018harshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Diagnosis Technique - BRDocument32 pagesChapter 4 Diagnosis Technique - BRSadrina MahamudNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Electronics1Document38 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Electronics1jeniferNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical EngineeringDocument100 pagesBasics of Electrical Engineeringdeep voraNo ratings yet
- Intro 32Document252 pagesIntro 32ANTONo ratings yet
- 01 Sensors PDFDocument68 pages01 Sensors PDFNimsiri AbhayasingheNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document13 pagesTask 1Eng MohamedNo ratings yet
- Sensors and TransducersDocument118 pagesSensors and TransducersDhaval Patel100% (1)
- Instrumentation: Submitted By-Debaraj Kakati ECE-12/16 DuietDocument27 pagesInstrumentation: Submitted By-Debaraj Kakati ECE-12/16 DuietRajNo ratings yet
- C8: Sensor and Sensor TechnologyDocument72 pagesC8: Sensor and Sensor TechnologyOladokun Sulaiman Olanrewaju100% (4)
- Different Instruments 2019Document99 pagesDifferent Instruments 2019AnjaliNo ratings yet
- Types of CRO:-: What Is A CRO?Document10 pagesTypes of CRO:-: What Is A CRO?Eng MohamedNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Data Acquisition: Radar GunDocument91 pagesSensors and Data Acquisition: Radar GunBurak Bildirici100% (1)
- Sensors Dan ActuatorDocument21 pagesSensors Dan ActuatorMarsius SihombingNo ratings yet
- Rolling Mill AutomationDocument23 pagesRolling Mill AutomationMohamed AlkharashyNo ratings yet
- 09EC309 Sagar HapaniDocument14 pages09EC309 Sagar HapaniSagar HapaniNo ratings yet
- Signal Processing and SensorsDocument51 pagesSignal Processing and SensorsKassimNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital InterfacingDocument71 pagesAnalog and Digital InterfacingSook Sabuy100% (2)
- 3 Sensors and TransducersDocument139 pages3 Sensors and TransducersZoroNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Sensors 1 - 2021-22Document55 pagesWeek 7 Sensors 1 - 2021-22KrisNo ratings yet
- Final Report 2020Document26 pagesFinal Report 2020Siva BadrinathNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - 2022 - FinalDocument67 pagesLecture 3 - 2022 - FinalFrancis LubangoNo ratings yet
- PLC Level 1Document46 pagesPLC Level 1Mohamed MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Practical ElectronicsDocument107 pagesPractical ElectronicsSaeed Ali Shahani100% (2)
- Lect 1a Introduction To Electronic InstrumentationDocument38 pagesLect 1a Introduction To Electronic InstrumentationEzzadin AbdowahabNo ratings yet
- Testing DeviceDocument13 pagesTesting Devicehabtemariam mollaNo ratings yet
- Ews Exp 4Document49 pagesEws Exp 4Ojas GokhaleNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Controls For Fluid Power CircuitsDocument69 pagesBasic Electrical Controls For Fluid Power Circuitsloveincyber3No ratings yet
- 3 Sensors and TransducersDocument99 pages3 Sensors and TransducersSon Athena100% (2)
- For More Visit WWW - Ktunotes.in: Sensor TechnologyDocument21 pagesFor More Visit WWW - Ktunotes.in: Sensor TechnologyVISHAL MUKUNDANNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 Title History of Electronics: Student: Prof: Talangan, Trinidad Engr. Norlan SantosDocument8 pagesAssignment No. 1 Title History of Electronics: Student: Prof: Talangan, Trinidad Engr. Norlan SantosTrinidad TalanganNo ratings yet
- Cảm Biến Điện Áp (Bản Sơ)Document11 pagesCảm Biến Điện Áp (Bản Sơ)Du DinhNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Slide NoteDocument35 pagesWeek 10 Slide NoteJunsyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 1 Sensor and TransducersDocument48 pagesChapter 3 Part 1 Sensor and TransducersFikadu Eshetu100% (1)
- Sensors and TransducersDocument79 pagesSensors and TransducersMohdQasim0% (1)
- Workshop Training Manual COURSE: WS1020: Central Workshop Indian Institute of Technology Madras CHENNAI - 600036, INDIADocument44 pagesWorkshop Training Manual COURSE: WS1020: Central Workshop Indian Institute of Technology Madras CHENNAI - 600036, INDIAhariharanhemanthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2 SensorDocument33 pagesChapter 2 2 Sensorlamvantrongphuc.2021No ratings yet
- Keca, Kevi, Keva en 2003.05.20Document8 pagesKeca, Kevi, Keva en 2003.05.20Mahyar MashayekhiNo ratings yet
- Scientech 2311: Scope of LearningDocument4 pagesScientech 2311: Scope of LearningarielfoxtoolsNo ratings yet
- Data Acquisition: Reference Book Jovitha Jerome, "Virtual Instrumentation and LABVIEW", PHI LearningDocument40 pagesData Acquisition: Reference Book Jovitha Jerome, "Virtual Instrumentation and LABVIEW", PHI LearningpankajNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument126 pagesBasic ElectronicsFarazNo ratings yet
- Multimeter Parts and FunctionsDocument3 pagesMultimeter Parts and FunctionsDavid Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Basra Engineering technical collage رDocument5 pagesBasra Engineering technical collage رزينب عبد الناصر عاتي عبدالله الموحيNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1afif fizerNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Topic 1: Sensor, Actuator, Detector, TransmitterDocument10 pagesWeek 5 Topic 1: Sensor, Actuator, Detector, TransmitternatzenNo ratings yet
- Stem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles V11From EverandStem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles V11No ratings yet
- Stem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V11From EverandStem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V11No ratings yet
- Student Enrolment Information (From Table 4.1) : N-Sanctioned Intake of The ProgramDocument31 pagesStudent Enrolment Information (From Table 4.1) : N-Sanctioned Intake of The Programbhagwat uchaleNo ratings yet
- Development of A Hybrid - Untitled BorrachaDocument7 pagesDevelopment of A Hybrid - Untitled BorrachaPV Minox-ClubNo ratings yet
- Modelling Football Penalty KicksDocument12 pagesModelling Football Penalty Kicksleilasoboh0No ratings yet
- Filter Backwash Recycling Rule Recycle Notification FormDocument3 pagesFilter Backwash Recycling Rule Recycle Notification FormMuhammadUsmanNo ratings yet
- Fall 2022 Digital CatalogDocument27 pagesFall 2022 Digital CatalogThe ExperimentNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Guide by John Dolan PDFDocument28 pagesTroubleshooting Guide by John Dolan PDFVenkatesh AllaNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Strength of Ships - An Introduction - TheNavalArchDocument24 pagesLongitudinal Strength of Ships - An Introduction - TheNavalArchfarazali2919No ratings yet
- 221-227 Jett1403026Document7 pages221-227 Jett1403026Jared VallesNo ratings yet
- Linear KinematicsDocument39 pagesLinear KinematicsSteven LongNo ratings yet
- The Portrait of A Lady: Khushwant SinghDocument8 pagesThe Portrait of A Lady: Khushwant SinghRK RishteyNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping Procedures: Why Should We Pay Attention To Housekeeping at Work?Document4 pagesHousekeeping Procedures: Why Should We Pay Attention To Housekeeping at Work?Selva KumarNo ratings yet
- QMB Fishbone DiagramDocument3 pagesQMB Fishbone DiagramElaine MacalandaNo ratings yet
- Teacher Coaching and Development ProcessDocument7 pagesTeacher Coaching and Development Processapi-563613616No ratings yet
- Week.2 Foundation To Business Strategy: Introduction: What Is Strategy?Document10 pagesWeek.2 Foundation To Business Strategy: Introduction: What Is Strategy?Shmail MohmmedNo ratings yet
- Control Commissioning: SeriesDocument52 pagesControl Commissioning: SeriesHeiner Hidalgo100% (2)
- Henri Fayol Would Have A Workplace Where Managers Would Plan, Organize, CommandDocument2 pagesHenri Fayol Would Have A Workplace Where Managers Would Plan, Organize, CommandĐặng Như Ý100% (1)
- Centricast Piping System 1 14 Inch Fittings and Accessories CatalogDocument20 pagesCentricast Piping System 1 14 Inch Fittings and Accessories CatalogOlmer Romero MendezNo ratings yet
- Hastie, R. (2001) .Document33 pagesHastie, R. (2001) .David Alejandro Alvarez MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Wire Race Bearings As Roller Bearings: Light Bearings For InnovationDocument8 pagesWire Race Bearings As Roller Bearings: Light Bearings For Innovationkizzie1No ratings yet
- Schrödinger's Cat Is A Thought ExperimentDocument10 pagesSchrödinger's Cat Is A Thought ExperimentirayoNo ratings yet
- Hurdle Concept by SKKDocument12 pagesHurdle Concept by SKKDipendra PoudelNo ratings yet
- Chap 05Document5 pagesChap 05Asif Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Agents in AIDocument41 pagesIntelligent Agents in AIrwt91848No ratings yet
- Geotech ReportDocument43 pagesGeotech ReportShahab Ali0% (1)
- How To Use A CompassDocument7 pagesHow To Use A Compasskenneth mayao100% (1)
- Rational Equation, Inequality and FunctionDocument5 pagesRational Equation, Inequality and FunctionMichaelle BunaoNo ratings yet
- Timeline MineDocument1 pageTimeline MineJane Angela FerrerNo ratings yet
- QRISDocument5 pagesQRISistdajemaandNo ratings yet