Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Managing Labor Using The Partograph
Managing Labor Using The Partograph
Uploaded by
Ajit M Prasad PrasadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Managing Labor Using The Partograph
Managing Labor Using The Partograph
Uploaded by
Ajit M Prasad PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
Managing Labor Using the Partograph
The Partograph
Assessment of fetal well being Assessment of maternal well being Assessment of progress of labor
Using the Partograph
Measuring Fetal Well Being During Labor
Fetal heart rates and pattern Degree of molding, caput Color of amniotic fluid
Using the Partograph
Measuring Maternal Well Being During Labor
Pulse, temperature, blood pressure, respiration Urine output, ketones, protein
Using the Partograph
Measuring Progress of Labor
Cervical dilatation Descent of presenting part Contractions Duration Frequency Alert and action lines
Using the Partograph
Using the Partograph
Patient information: Name, gravida, para, hospital number, date and time of admission, and time of ruptured membranes Fetal heart rate: Record every half hour Amniotic fluid: Record the color at every vaginal examination: I: membranes intact C: membranes ruptured, clear fluid M: meconium-stained fluid B: blood-stained fluid
Using the Partograph
Using the Partograph (continued)
Molding: 1: sutures apposed 2: sutures overlapped but reducible 3: sutures overlapped and not reducible Cervical dilatation: Assess at every vaginal examination, mark with cross (X) Alert line: Line starts at 4 cm of cervical dilatation to the point of expected full dilatation at the rate of 1 cm per hour Action line: Parallel and 4 hours to the right of the alert line
Using the Partograph
Using the Partograph (continued)
Descent assessed by abdominal palpation: Part of head (divided into 5 parts) palpable above the symphysis pubis; recorded as a circle (O) at every vaginal examination. At 0/5, the sinciput (S) is at the level of the symphysis pubis
Using the Partograph
Using the Partograph (continued)
Hours: Time elapsed since onset of active phase of labor (observed or extrapolated) Time: Record actual time Contractions: Chart every half hour; palpate the number of contractions in 10 minutes and their duration in seconds Less than 20 seconds: Between 20 and 40 seconds: More than 40 seconds: Oxytocin: Record amount per volume IV fluids in drops/min. every 30 min. when used Drugs given: Record any additional drugs given
Using the Partograph
Using the Partograph (continued)
Temperature: Record every 2 hours Pulse: Record every 30 minutes and mark with a dot () Blood pressure: Record every 4 hours and mark with arrows Protein, acetone and volume: Record every time urine is passed
Using the Partograph
10
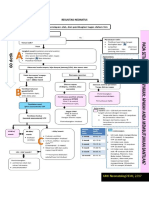
The Modified WHO Partograph (Figure C-10)
Using the Partograph
11
Sample Partograph for Normal Labor (Figure C-11)
Using the Partograph
12
Partograph Showing Prolonged Active Phase of Labor (Figure S-6)
Using the Partograph
13
Partograph Showing Obstructed Labor (Figure S-7)
Using the Partograph
14
Partograph Showing Inadequate Uterine Contractions Corrected with Oxytocin (Figure S-8)
Using the Partograph
15
You might also like
- Day 1 Mission NEETPGDocument142 pagesDay 1 Mission NEETPGKalyan SagarNo ratings yet
- The PartographDocument45 pagesThe PartographKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- PARTOGRAPHDocument9 pagesPARTOGRAPHطاہر محمودNo ratings yet
- Abortion SeminarDocument16 pagesAbortion SeminarAjit M Prasad Prasad100% (2)
- PARTOGRAPH GRP III JomelieDocument6 pagesPARTOGRAPH GRP III JomelieTRISHA NERINo ratings yet
- Technical Series 2 Using PartographDocument5 pagesTechnical Series 2 Using PartographsaryindrianyNo ratings yet
- ParthograghyDocument20 pagesParthograghymameekasim75No ratings yet
- Maintaining The New Partogram: Prepared By: KMIU Ranasinghe & HKDK NadeeshaniDocument27 pagesMaintaining The New Partogram: Prepared By: KMIU Ranasinghe & HKDK Nadeeshanifei cuaNo ratings yet
- 6 PartographDocument50 pages6 PartographEdelyn Arguelles100% (1)
- PARTOGRAPH ModuleDocument11 pagesPARTOGRAPH ModuleWynjoy NebresNo ratings yet
- Week 9 PartographDocument8 pagesWeek 9 PartographRose MendozaNo ratings yet
- PartographDocument11 pagesPartographLakshmi RjNo ratings yet
- WNHS OG Labour-Partogram PDFDocument8 pagesWNHS OG Labour-Partogram PDFAsma ChaudaryNo ratings yet
- Obstructed Labour and The Partogram: EsmoeDocument89 pagesObstructed Labour and The Partogram: EsmoeLana LocoNo ratings yet
- PARTOGRAMDocument17 pagesPARTOGRAMKrutthivaasa PriyaNo ratings yet
- Par To GraphDocument4 pagesPar To GraphAnna QuinioNo ratings yet
- P ArtographDocument87 pagesP ArtographDevuchandana RNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument4 pagesDefinitionJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- P ArtographDocument4 pagesP Artographwar0wolf0No ratings yet
- Case 1Document3 pagesCase 1Akanksha RawatNo ratings yet
- Partograph EditedDocument54 pagesPartograph EditedNathaniel PulidoNo ratings yet
- Part 4: Maternal Condition: ST, ND RDDocument4 pagesPart 4: Maternal Condition: ST, ND RDshova rokaNo ratings yet
- P ArtographDocument40 pagesP ArtographE=MC2No ratings yet
- 6 PartographDocument50 pages6 PartographRUSTOM JAKENo ratings yet
- Partograph 1) DefinitionDocument4 pagesPartograph 1) Definitionshova rokaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal WellbeingDocument24 pagesAssessment of Fetal WellbeingMukesh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Clinical Course and Management of First and SecondDocument66 pagesClinical Course and Management of First and SecondEkawali Sharma100% (1)
- PartographDocument6 pagesPartographalyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- 5.2 Monitoring Labour and Delivery - MSF Medical GuidelinesDocument6 pages5.2 Monitoring Labour and Delivery - MSF Medical GuidelinesClara StevenNo ratings yet
- Resusitasi NeonatusDocument7 pagesResusitasi NeonatusIqbal Miftahul HudaNo ratings yet
- Partograph-Presentation-SBA TrainingDocument11 pagesPartograph-Presentation-SBA TrainingPradeep Verma0% (1)
- Partograph - LectureDocument53 pagesPartograph - Lecturepaula dacaymat100% (1)
- Gynecology All 2Document71 pagesGynecology All 2Hikufe JesayaNo ratings yet
- Uses of PartographDocument6 pagesUses of PartographApril Joy RutaquioNo ratings yet
- Online CPD: Monitoring Labour Using A PartographDocument28 pagesOnline CPD: Monitoring Labour Using A PartographElvisNo ratings yet
- Partograph: DR Ban Hadi F.I.C.O.G. 2018Document35 pagesPartograph: DR Ban Hadi F.I.C.O.G. 2018Ammar AlnajjarNo ratings yet
- WHO PartographDocument23 pagesWHO PartographZabrina Tan CuaNo ratings yet
- Partograph 3Document49 pagesPartograph 3Geeta BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI) : PMID: 3306497Document1 pageAmniotic Fluid Index (AFI) : PMID: 3306497FadhilaKPNo ratings yet
- Practical Examination of Obs Block 2020Document11 pagesPractical Examination of Obs Block 2020Female calmNo ratings yet
- Partograph HandoutsDocument5 pagesPartograph HandoutsJozarine Chelsea LopezNo ratings yet
- The PartographDocument44 pagesThe PartographMs. Jia Mae CasimoNo ratings yet
- CH16 Fetal Assessment TestsDocument22 pagesCH16 Fetal Assessment TestschibimakuNo ratings yet
- Labour and Delivery Care Module: 4. Using The PartographDocument1 pageLabour and Delivery Care Module: 4. Using The PartographJerikaDolorPadilloPatricioNo ratings yet
- Partograph NextDocument50 pagesPartograph NextPrag GK Subedi0% (1)
- P ArtographDocument7 pagesP ArtographMali KanuNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery Room (CP 102)Document9 pagesLabor and Delivery Room (CP 102)pinpindalgoNo ratings yet
- P ArtographDocument34 pagesP ArtographFelaih Binasoy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Partograph PlatformDocument14 pagesPartograph PlatformGreggy Francisco LaraNo ratings yet
- Coass in Charge: Fara/Vicia/Yanti/ Eva/Tryas/Desi Supervisor: Dr. Mulyo Hadi Sungkono, SP - OG (K)Document15 pagesCoass in Charge: Fara/Vicia/Yanti/ Eva/Tryas/Desi Supervisor: Dr. Mulyo Hadi Sungkono, SP - OG (K)Tryas YulithaNo ratings yet
- Case Study FIXDocument66 pagesCase Study FIXPatrick Kelvian100% (1)
- Case Analysis - Pregnant With AsthmaDocument1 pageCase Analysis - Pregnant With AsthmaJanine mae MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Cne Wad Tingkat 3: Siti Shazwani Binti Zulkaflee RN Ba. Health Sciences (Honor) Nursing, USMDocument30 pagesCne Wad Tingkat 3: Siti Shazwani Binti Zulkaflee RN Ba. Health Sciences (Honor) Nursing, USMWanie Kaflee100% (1)
- Partograph Preparation and UseDocument48 pagesPartograph Preparation and Useannyeong_123100% (1)
- Must Know About PartographDocument14 pagesMust Know About PartographJonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- Partograph and EfmDocument65 pagesPartograph and EfmMichelle FactoNo ratings yet
- Postpartal HemorrhageDocument9 pagesPostpartal HemorrhageJkimNo ratings yet
- P ArtographDocument17 pagesP ArtographPrincess RoseNo ratings yet
- Objective Structured Clinical Examination On PartographDocument58 pagesObjective Structured Clinical Examination On PartographMd AliNo ratings yet
- Ectopic and Abortion NCPDocument6 pagesEctopic and Abortion NCPElizabeth Quiñones100% (1)
- Clinical Teaching Birth InjuriesDocument15 pagesClinical Teaching Birth InjuriesAjit M Prasad PrasadNo ratings yet
- Placental SeparationDocument4 pagesPlacental SeparationAjit M Prasad Prasad100% (1)
- Clinical Teaching 4PEUPERAL SEPSISDocument5 pagesClinical Teaching 4PEUPERAL SEPSISAjit M Prasad Prasad100% (1)
- Maternal and Child Health Questions W/ RationaleDocument15 pagesMaternal and Child Health Questions W/ RationaleMaicah ShaneNo ratings yet
- Clinical Study of Postpartum Eclampsia: Dr. S. K. Rath, Dr. Swati AgrawalDocument3 pagesClinical Study of Postpartum Eclampsia: Dr. S. K. Rath, Dr. Swati AgrawalSulabh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care & Management NewDocument21 pagesAntenatal Care & Management NewPabhat Kumar100% (3)
- DR - Novan-Preterm Birth Awam 2Document31 pagesDR - Novan-Preterm Birth Awam 2Mamik ShofiaNo ratings yet
- #12 - NCM 109 (Rle) - TransesDocument4 pages#12 - NCM 109 (Rle) - TransesJaimie BanaagNo ratings yet
- MCN PartographDocument2 pagesMCN PartographAlec Anon100% (1)
- (Augmentation) Medical and SurgicalDocument17 pages(Augmentation) Medical and SurgicalNadiya RashidNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesUmbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureHesti hasanNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and Evaluation of Skilled BirDocument10 pagesMonitoring and Evaluation of Skilled BirNuredin MohemmedNo ratings yet
- NICU QI Project To Decrease Neonatal Death2015Document24 pagesNICU QI Project To Decrease Neonatal Death2015Elias TewabeNo ratings yet
- Sec. 3C - 1 - OB Questions (Answer Key) - BrendaDocument20 pagesSec. 3C - 1 - OB Questions (Answer Key) - Brendacididok84No ratings yet
- CIMS Fact Sheet - Problems and Hazards of Induction of LaborDocument4 pagesCIMS Fact Sheet - Problems and Hazards of Induction of Labordavidcockrell_txNo ratings yet
- Transverse and Oblique LieDocument7 pagesTransverse and Oblique Liekirtyy20No ratings yet
- What Is Teenage PregnancyDocument1 pageWhat Is Teenage PregnancyCjay Hernandez100% (1)
- Anaphy & Pathophy (Hyperemesis)Document6 pagesAnaphy & Pathophy (Hyperemesis)Irish EspinosaNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Administration of Multiple Micronutrient Supplement Mms Tablets On Hemoglobin Levels of Pregnant Women in Pare Pare City Indonesia 63da4575d4ed0Document8 pagesThe Effectiveness of Administration of Multiple Micronutrient Supplement Mms Tablets On Hemoglobin Levels of Pregnant Women in Pare Pare City Indonesia 63da4575d4ed0Nurul khaeraniNo ratings yet
- Partograph and EfmDocument65 pagesPartograph and EfmMichelle FactoNo ratings yet
- Form SibalaDocument2 pagesForm Sibalamacky sympranoNo ratings yet
- Female Foeticide in IndiaDocument1 pageFemale Foeticide in IndiaSubhash BajajNo ratings yet
- Abnormal LaborDocument29 pagesAbnormal LaborHooda PrinceNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Care During The Third Stage of LaborDocument2 pagesPhysiology and Care During The Third Stage of LaborJeffrey KauvaNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anemia Infographics by SlidesgoDocument63 pagesSickle Cell Anemia Infographics by SlidesgoshanggariNo ratings yet
- Councelling and History TakingDocument5 pagesCouncelling and History TakingbashingarNo ratings yet
- THESIS CHN LBWDocument25 pagesTHESIS CHN LBWJessica Merilyn100% (1)
- MPDSR Training Workbook 17.10.30Document29 pagesMPDSR Training Workbook 17.10.30Ebsa MohammedNo ratings yet
- 10 Kuliah Amniotic FluidDocument20 pages10 Kuliah Amniotic FluidAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- Ob Set A and B QuesDocument17 pagesOb Set A and B QuesBok Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Bahan Tugas Tokolitik Ulfadiya Putri 1Document25 pagesBahan Tugas Tokolitik Ulfadiya Putri 1hopa shopNo ratings yet
- 34 121 1 PBDocument8 pages34 121 1 PBdaud edowaiNo ratings yet
- Breech Presentation and DeliveryDocument7 pagesBreech Presentation and DeliverySteven Herbert0% (1)